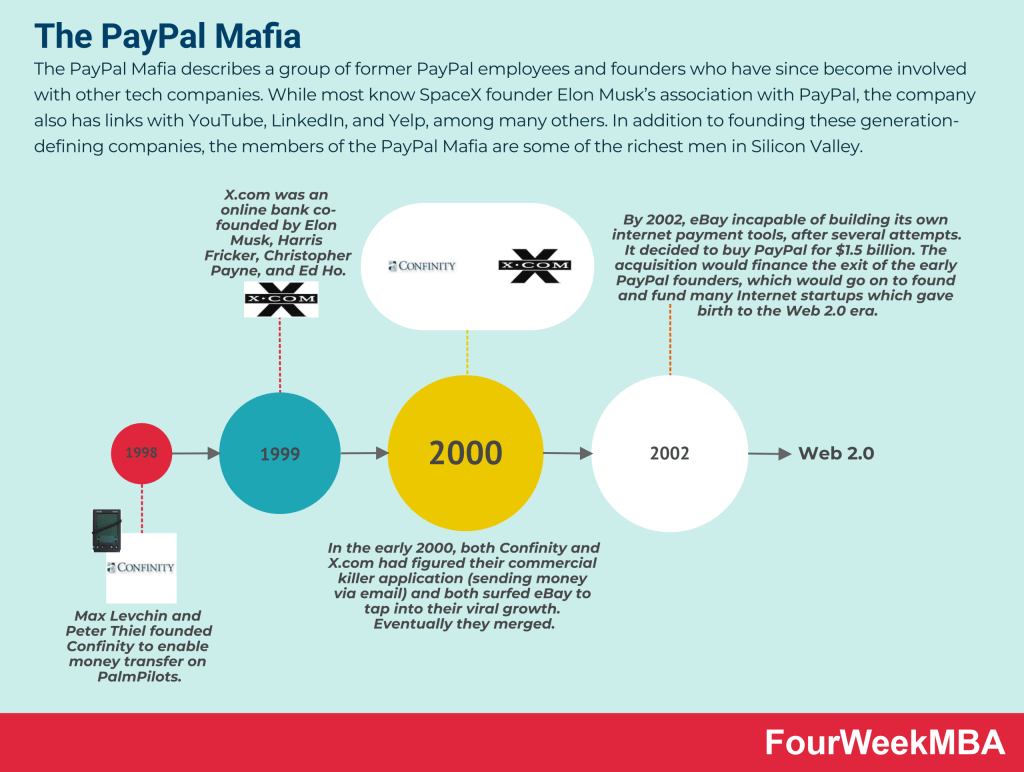
The PayPal Mafia describes a group of former PayPal employees and founders who have since become involved with other tech companies. While most know SpaceX founder Elon Musk’s association with PayPal, the company also has links with YouTube, LinkedIn, and Yelp, among many others. In addition to founding these generation-defining companies, the members of the PayPal Mafia are some of the richest men in Silicon Valley.
Elon Musk


Peter Thiel
Often referred to as the “Don” of the PayPal Mafia, Peter Thiel is one of the original co-founders of PayPal.
Thiel earned $55 million from his 3.7% stake in PayPal after it was sold to eBay, after which he created the hedge fund Clarium Capital and became the first outside investor in fledging Facebook.
His original $500,000 investment would now be worth approximately $9 billion, though the billionaire reduced his holdings by 81% in 2020.
Thiel is also the co-founder of Palantir Technologies, a software and data integration company with clients in the United States Government, military, intelligence, and police.
Jawed Karim
At PayPal, Karim was responsible for implementing the company’s real-time anti-fraud system.
Once his tenure ended, Karim founded YouTube with former PayPal colleagues Steve Chen and Chad Hurley.
Karim continued to act as an advisor while studying computer science at Stanford University.
Once YouTube was acquired by Google, Karim sold his shares which at the time were worth $64 million.
In 2008, Karim founded Youniversity Ventures with early PayPal investors Kevin Hartz and Keith Rabols. The company helps students and graduates develop viable business ideas.
Jeremy Stoppelman
Jeremy Stoppelman had a very early role at PayPal, joining the company as an engineer while it was still known as X.com. He eventually attained the title of Vice President of Engineering.
Stoppelman was another member of the PayPal Mafia to benefit from the eBay acquisition – at least indirectly.
He founded the online review site Yelp with former colleague Russel Simmons after contracting the flu and experiencing difficulty finding a good doctor.
Reid Hoffman
Hoffman joined PayPal as its COO in 2000, handling all external communications. At the time of the eBay acquisition in 2002, he was executive vice president.
Shortly thereafter, Hoffman co-founded LinkedIn – one of the first business-oriented online social networks.
LinkedIn was then acquired by Microsoft in June 2016 for $26.2 billion, with Hoffman taking a seat on the board.

In more recent years, Hoffman has been involved with philanthropic projects.
He currently serves on the boards of the microlending service Kiva and the social change organization Do Something.
Hoffman is also associated with Endeavor Global, which identifies and supports entrepreneurs in emerging markets.
Reid Hoffman is the author of Blitzscaling.

David O. Sacks
David Sacks joined PayPal in 1999 from the management consultancy firm McKinsey & Company.
As COO before the appointment of Hoffman, Sacks was responsible for project management, design, sales and marketing, customer service, fraud operations, and human resources functions.
During his tenure, he grew PayPal revenue to 240 million per year, introduced business accounts, and expanded the platform into multiple currencies and over 80 countries.
Sacks has arguably the most diverse resume of any PayPal Mafia member. In 2005, he produced and financed the satirical comedy Thank You for Smoking.
The following year, he founded the genealogy website Geni.com and Yammer, a social network and productivity tool for internal corporate communication.
Angel investment in technology companies is also a passion for Sacks, having been involved in the industry for two decades.
Some of his investments include Airbnb, Eventbrite, Opendoor, Postmates, Scribd, Slack, and Uber.
Max Levchin
Maksymilian Rafailovych “Max” Levchin is a businessman and software engineer of Ukrainian descent.
Levchin, who was born in Kyiv in 1975, emigrated to the United States in 1991 and settled in Chicago. Levin is also the founder of the fintech company Affirm and VC firm HVF.
Levchin’s story is one of the most interesting within the PayPal Mafia as he would be the co-founder of Confinity, which would later merge with X of Elon Musk to form PayPal.
Levchin was among the A Team within PayPal which steered the direction of the company, together with Musk and Thiel.
He would later found Affirm, of which he’s the CEO.
Dave McClure
David McClure is an angel investor, entrepreneur, and another member of the PayPal mafia.
Born in Morgantown, West Virginia, McClure graduated from Johns Hopkins University with a Bachelor of Science in Mathematical Engineering in 1988.
While the exact circumstances are unclear, McClure found his way to PayPal in 2001 and served as its director of marketing until 2004.
Today, he is best known for devising PayPal’s developer network program which enables third parties to extend the platform’s functionality.
Dave McClure popularized the concept of the AARRR Funnel and pirate metrics!
Luke Nosek
Lukasz “Luke” Nosek is a Polish-American entrepreneur who, like Max Levchin, studied computer science at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign.
How did he become affiliated with PayPal?
Nosek left Netscape in 1998 and became involved in the creation of PayPal with university friends Thiel and Levchin.
Initially, Nosek oversaw PayPal’s marketing strategy and managed to add 1 million users to the platform within six months of launch.
He was also responsible for the popular “Instant Transfer” functionality and the platform’s bonus program.
Keith Rabois
Keith Rabois is an American entrepreneur, investor, and lawyer who is best known for his involvement in companies such as PayPal, Lyft, Airbnb, LinkedIn, Slide, Xoom, Yelp, and Square.
Rabois is currently a general partner at Founders Fund which, as we explained earlier, was established by fellow PayPal mafia members Peter Thiel, Luke Nosek, and Ken Howery.
Scott Banister
Scott Banister was an early advisor and board member at PayPal who is today a start-up founder and angel investor.
Banister is perhaps best known as the inventor of paid search advertising and the associated keyword auction.
Banister was identified as a member of the PayPal Mafia by David Gelles as an investor in the earliest version of the platform.
Banister is also the founder of IronPort Systems, a seller of products to protect enterprises from cyber threats.
When Cisco purchased IronPort in 2007 for $830 million, Banister moved into angel investing among other pursuits and has been compared to Peter Thiel for his prolific activity and success in the industry.
Ken Howery
Ken Howery is an American entrepreneur who was part of the founding team at PayPal. Between 1998 and 2002, Howery served as the company’s CFO.
After it was acquired by eBay, he briefly served that company as its Director of Corporate Development.
In 2004, Howery was reunited with fellow PayPal co-founder Peter Thiel at Clarium Capital.
Howery co-founded the Founders Fund with various other PayPal mafia members in 2005. The San Francisco-based VC firm has around $11 billion in capital under management with investments such as SpaceX, Palantir, Stripe, Anduril, Facebook, and Airbnb.
Eric Jackson
Eric M. Jackson worked in senior roles in marketing at PayPal between 1999 and 2003.
He ran the company’s first campaign to eBay customers in 2000 and developed a way to upsell customers with free accounts to a paid option.
Post-PayPal, Jackson founded the media firm World Ahead Media and made it profitable after just three years before it was acquired in 2008.
In 2010, he co-founded Caplinked with Christopher Grey – a company that provides a safe and fast cloud-based platform for various transactions such as mergers and acquisitions, real estate deals, and capital raises.
A decade later, Jackson co-founded TransitNet which claims to be building the world’s first crypto title registry.
Premal Shah
Premal Shah is an American entrepreneur of Indian descent. According to his LinkedIn profile, Shah spent just over six years at PayPal as one of the company’s first product managers.
In October 2005, Shah also founded the microfinance non-profit Kiva with Jessica Jackley. The Kiva community has now funded over $1.6 billion in loans for underprivileged entrepreneurs.
In addition to his role at Kiva, Shah is also the president of Branch International.
The company is similar to Kiva in that it seeks to scale app-based microfinance across India and Africa. He is also the co-founder and chair of an initiative to accelerate sustainable energy adoption in the aforementioned areas.
The initiative, which Shah describes as the “Kiva for climate”, can be accessed at Renewables.org.
Russel Simmons
Russel Simmons started at PayPal in January 1999 as its first engineer and worked on the team that built the first PayPal system from scratch.
His work primarily involved software-related aspects such as security, availability, internationalization, scalability, availability, codebase management, technology decisions, and engineer mentoring.
Simmons also co-founded the review site Yelp with Jeremy Stoppelman in 2004. In May 2011, he founded the education start-up Learnirvana.
The company’s first product, Lentil, is a way for students to break from traditional educational models and learn by exploring the subjects of their curiosity.
Yishan Wong
Yishan Wong is a technology entrepreneur and investor. He is best known for his role as the CEO of the social news website Reddit from 2012 to 2014.
Before his stint at Reddit, Wong was an executive at Facebook where he worked on various projects such as crowd translation.
Wong joined PayPal in 2001 and held the role of Senior Engineering Manager, Application Services until November 2005.
At the company, Wong primarily worked on payments, internationalization, and technical infrastructure.
Jack Selby
Jack Selby is a tech entrepreneur and investor who is also known for his philanthropic work in the fields of education and social justice.
Selby was one of the co-founders of PayPal and served as the company’s Vice President of Risk Management.
As a result, he was part of the team that developed many of the platform’s fraud detection and prevention processes.
After PayPal was sold to eBay, Selby founded Clarium Capital Management with fellow PayPal mafia member Peter Thiel. He also helped manage Thiel Capital for a time.
In addition to investments in companies like SpaceX and Affirm, Selby has used his PayPal windfall to produce independent films via the company High Frequency Entertainment.
Andrew McCormack
Andrew McCormack is an American entrepreneur who joined PayPal in July 2001.
According to his LinkedIn profile, McCormack served as then-CEO Peter Thiel’s assistant with respect to corporate development and management functions.
McCormack also handled much of PayPal’s IPO road show and developed a lobbying strategy to counteract regulatory issues impacting the platform.
Like Selby, he left PayPal soon after it was acquired to start Clarium Capital Management with Peter Thiel.
He also founded the Sprezzatura Restaurant Group in 2003 before spending time on special projects at Thiel Capital.
Later, he became a founding partner of Valar Ventures – a VC fund that invests in tech start-ups outside of Silicon Valley. Investments include Xero, TransferWise (Wise), BlockFi, and Octane.
Jared Kopf
Jared Kopf is a tech entrepreneur and investor.
He is the co-founder and CEO of AdRoll (now NextRoll), an eCommerce growth platform that helps businesses target and retarget customers across multiple channels such as social media, email, and display advertising.
Kopf likely replaced McCormack as Assistant to the CEO at PayPal after the latter left the company in 2002.
Kopf was only in the role for five months but worked with members of the senior management team on projects in corporate development, strategic planning, financial planning, and investor relations.
Roelof Botha
Roelof Botha is a South African company director, venture capitalist, and actuary.
Botha joined PayPal in 2000 as director of corporate development and later played a pivotal role in navigating the company through its IPO.
Botha was named PayPal CFO in 2001 and was offered a similar position at eBay after it acquired the company.
However, he turned it down to join Sequoia Capital in 2003. Botha has overseen numerous successful investments since that time, including Instagram, Square, and YouTube.
In April 2022, Botha was named Sequoia’s Senior Steward of its global brand and operations.
Over the years, he has also sat on the boards of numerous companies such as Tumblr, Xoom, Eventbrite, Evernote, Block, and Unity Technologies.
Key takeaways
- The PayPal Mafia describes a group of former PayPal employees and founders who have since become involved with other tech companies. Elon Musk is perhaps the most well-known member.
- Peter Thiel is one of the original co-founders of PayPal and is often referred to as the “Don” of the PayPal mafia. Jawed Karim, responsible for implementing PayPal’s fraud protection system, later founded YouTube with colleagues Steve Chen and Chad Hurley.
- Former COO Reid Hoffman left PayPal after the eBay acquisition to found LinkedIn. David O. Sacks, also a former COO, has produced a movie and founded a corporate social network since his time at PayPal. Sacks is also a passionate angel investor.
Read Also: Zero to One, Blitzscaling.
Read More: How Does TD Ameritrade Make Money, How Does Dave Make Money, How Does Webull Make Money, How Does Betterment Make Money, How Does Wealthfront Make Money, How Does M1 Finance Make Money, How Does Mint Make Money, How Does NerdWallet Make Money, How Does Acorns Make Money, How Does SoFi Make Money, How Does Stash Make Money, How Does Robinhood Make Money, How Does E-Trade Make Money, How Does Coinbase Make Money, How Does Affirm Make Money, Fintech Companies And Their Business Models.
Is Elon Musk part of the PayPal Mafia?
Elon Musk is one of PayPal’s members. Indeed, Elon Musk founded X.com, which eventually would merge with Confinity to create PayPal.
Who is the richest of the PayPal Mafia?
Elon Musk is the wealthiest of PayPal’s members, with a net worth, which in 2022 ranged between $180-230 billion. Elon Musk owns Tesla, SpaceX, Twitter, The Boring Company, and Neuralink.
Why is it called PayPal Mafia?
The founding team of PayPal created many companies that defined Silicon Valley after the 2000s. Companies like Tesla, SpaceX, LinkedIn, YouTube, Palantir, and many others came from PayPal’s founding team. That is how they got the title of “PayPal Mafia.”
Why did PayPal remove Elon?
In an internal war in the year 2000, as Elon Musk flew to enjoy his honeymoon, he was ousted as the company’s CEO from the team who led the coupe (Levchin and Sachs primarily, as they wanted to bring back Peter Thiel as CEO of the company). Eventually, as Musk was on his plane back to California, he could not fight back and got ousted as CEO. Musk, with the money from PayPal, exists, as it got sold to eBay, founded SpaceX, and invested in Tesla in the very early days.
Related to PayPal








PayPal Transactions Per Active Users

Read More: How Does TD Ameritrade Make Money, How Does Dave Make Money, How Does Webull Make Money, How Does Betterment Make Money, How Does Wealthfront Make Money, How Does M1 Finance Make Money, How Does Mint Make Money, How Does NerdWallet Make Money, How Does Acorns Make Money, How Does SoFi Make Money, How Does Stash Make Money, How Does Robinhood Make Money, How Does E-Trade Make Money, How Does Coinbase Make Money, How Does Affirm Make Money, Fintech Companies And Their Business Models.
List of FinTech Business Models




Braintree



















Read Next: Fintech Business Models, IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, Enterprise AI Business Model, Cloud Business Models.
Read Next: Affirm Business Model, Chime Business Model, Coinbase Business Model, Klarna Business Model, Paypal Business Model, Stripe Business Model, Robinhood Business Model.
Main Free Guides:









