A tech business model is made of four main components: value model (value propositions, mission, vision), technological model (R&D management), distribution model (sales and marketing organizational structure), and financial model (revenue modeling, cost structure, profitability and cash generation/management). Those elements coming together can serve as the basis to build a solid tech business model.
Learn How To Use This And Many More Frameworks In Business Engineering

VTDF Business Model Template

Keep reading, if you want to understand how to use the framework.
Value model
In the value model we want to answer three core questions:
Vision: What’s the long-term hard problem you’re solving?
Mission: How do you get closer to achieve this hard problem in the short-term?
Value Proposition: What use cases do we prioritize, as they are in target with our customers’ needs?
It usually all starts by a value model which comprises:
- An opportunity: the size of the opportunity will be determined by whether the market exists, it’s still building up, and its growth potential. From the opportunity, it’s possible to evaluate the potential market size (usually tech companies look at TAM).
- A problem to be solved: a problem can be practical, or it can go beyond that. Companies like Nike and Coca-Cola focus most of their efforts on-demand generation. This also applies to tech business models. Before the iPhone people didn’t know they needed a smartphone in the first place.
- A set of value propositions: from the above a company will develop a core value proposition. As it will scale it will be able to satisfy a set of value propositions, which is the glue that keeps together customers and the company.
- Mission and vision: as the company builds up its various models, it also develops its own core beliefs, which are comprised in its mission and vision.
Value propositions

Mission and vision

Technological model And R&D Management
Continuous Innovation: How do we handle engineering resources to sustain continuous innovation for business model expansion?
Breakthrough Innovation: How do we handle engineering resources to promote breakthrough innovation for business model reinvention?
The technological model is the enhancer of the product, and it helps merge together the value proposition with the distribution model. When engineering is done right, it helps bridge the gap between what customers still miss, the product and the way the product is distributed.
The technological model will help satisfy the need of larger and larger portion of the market. From early adopters, to potentially laggards. This will determine the ability of the company to scale up.

In the technological model, the way R&D is managed to produce continuous innovation (to sustain the linear growth of the business) and breakthrough innovation (to enable long-term success of the business) is critical.
Distribution Model
Marketing & Sales: How do we communicate and sell the product to the right audience?
Product Engineering: How do we enable built-in features that help us distribute the product?
Partnerships: Who do we partner with to expand our audience?
Deal Making: What deals do we close that help us get to our audience?

The distribution model helps to bring the product in the hands of customers. The company can leverage on engineering, marketing, sales or all of them, to make the product in fit with the market, via its distribution. That is why, based on what problems the product solves and for whom, it will have an organizational structure more skewed toward engineering and marketing, or engineering and sales, or perhaps a mix of the three. Other things like partnerships and deal making are also part of the distribution model.
Financial model
Revenue Generation: How does the company make money?
Cost Structure: How does the company spend money to make money? (cost of sales)
Profitability: Is the company profitable?
Cash Management & Generation: Is the company cash positive?

The financial model is what enables the company to keep generating enough cash to sustain its operations, not only in the short-term, but also toward R&D and innovation. And it is made of several components:
- Revenue model.
- Cost structure.
- Profitability.
- And cash generation and management.
Revenue model

Cost structure

Profitability
From how the company generates revenues and its cost structure, profitability will be determined. When the revenue model isn’t yet efficient enough to cover up or sustain the cost structure in the long-term, there is when we have a lack of profitability. At the same time, it might happen that a company is profitable but it lacks cash, given its overall financial model. Or it might happen that a company has no profits, or very tight margins and yet it generates a continuous stream of cash.
That is why it’s critical to look at the next element.
Cash generation and management

Profitability doesn’t tell us the whole story. We need to look at cash management. A company like Amazon have been running at very tight profit margins for years, and yet generating massive amounts of cash, invested back in its operations. A company like Netflix has been generating good profit margins, but running with a cash negative model.
This isn’t good or bad in absolute, but it gives us an understanding of the company’s financial mode. Perhaps, Netflix, with a negative cash flow model, it has been investing substantial cash in the development of original shows, which are both critical to generate revenue and also essential to its brand’s strategy. Thus, revenue generation, distribution, and marketing come together here.
Key takeaways
According to the VTDF framework a tech business model can be broken down in four sub-models:
- Value model (value propositions, mission, vision), to answer questions, such as:
Vision: What’s the long-term hard problem you’re solving?
Mission: How do you get closer to achieve this hard problem in the short-term?
Value Proposition: What use cases do we prioritize, as they are in target with our customers’ needs?
- Technological model (R&D management), to answer questions such as:
Continuous Innovation: How do we handle engineering resources to sustain continuous innovation for business model expansion?
Breakthrough Innovation: How do we handle engineering resources to promote breakthrough innovation for business model reinvention?
- Distribution model (sales and marketing organizational structure), to answer questions such as:
Marketing & Sales: How do we communicate and sell the product to the right audience?
Product Engineering: How do we enable built-in features that help us distribute the product?
Partnerships: Who do we partner with to expand our audience?
Deal Making: What deals do we close that help us get to our audience?
- Financial model (revenue modeling, cost structure, profitability and cash generation/management), to answer questions such as:
Revenue Generation: How does the company make money?
Cost Structure: How does the company spend money to make money? (cost of sales)
Profitability: Is the company profitable?
Cash Management & Generation: Is the company cash positive?
From the balance and mixture of those four elements a viable business model is built.
Key Highlights
- Definition: The VTDF framework offers a structured approach to building a tech business model by breaking it down into four key sub-models: Value model, Technological model, Distribution model, and Financial model.
- Value Model:
- Vision: Addressing the long-term hard problem the business aims to solve.
- Mission: Outlining short-term strategies to achieve the long-term goal.
- Value Proposition: Prioritizing use cases that align with customers’ needs.
- The value model focuses on understanding the opportunity, identifying problems to solve, and defining core value propositions.
- Technological Model and R&D Management:
- Continuous Innovation: Managing engineering resources for sustainable continuous innovation.
- Breakthrough Innovation: Allocating resources for promoting breakthrough innovation to reinvent the business model.
- The technological model enhances the product, aligns value propositions, and helps scale the product’s reach based on customer adoption stages.
- Distribution Model:
- Marketing & Sales: Communicating and selling the product effectively to the target audience.
- Product Engineering: Enabling built-in features that facilitate product distribution.
- Partnerships: Identifying partners to expand the product’s audience.
- Deal Making: Closing strategic deals to reach the target audience.
- The distribution model ensures the product reaches customers by leveraging engineering, marketing, sales, partnerships, and deal-making strategies.
- Financial Model:
- Revenue Generation: Defining how the company generates revenue.
- Cost Structure: Determining how expenses are incurred to generate revenue (cost of sales).
- Profitability: Evaluating whether the company is generating profits.
- Cash Management & Generation: Assessing the company’s cash position and cash generation capability.
- The financial model sustains operations, fuels innovation, and maintains long-term viability through revenue modeling, cost structure management, profitability analysis, and cash flow generation.
- Interplay of Elements:
- A successful tech business model is built by integrating these four sub-models.
- The value model sets the foundation by addressing the problem, opportunity, and core value propositions.
- The technological model enhances the product and aligns it with customer adoption stages.
- The distribution model ensures the product reaches the right audience through marketing, sales, partnerships, and deals.
- The financial model supports the entire operation by generating revenue, managing costs, ensuring profitability, and maintaining cash flow.
Examples Of VTDF Framework Applied


Other Business Models Where The VTDF Framework Has Been Used
- Affirm Business Model
- Airbnb Business Model
- Amazon Business Model
- Asana Business Model
- Google Business Model
- Snowflake Business Model
- Sumo Logic Business Model
- Unity Software Business Model
Additional Tools & Frameworks Developed By FourWeekMBA
FourWeekMBA Definition Of Business Model

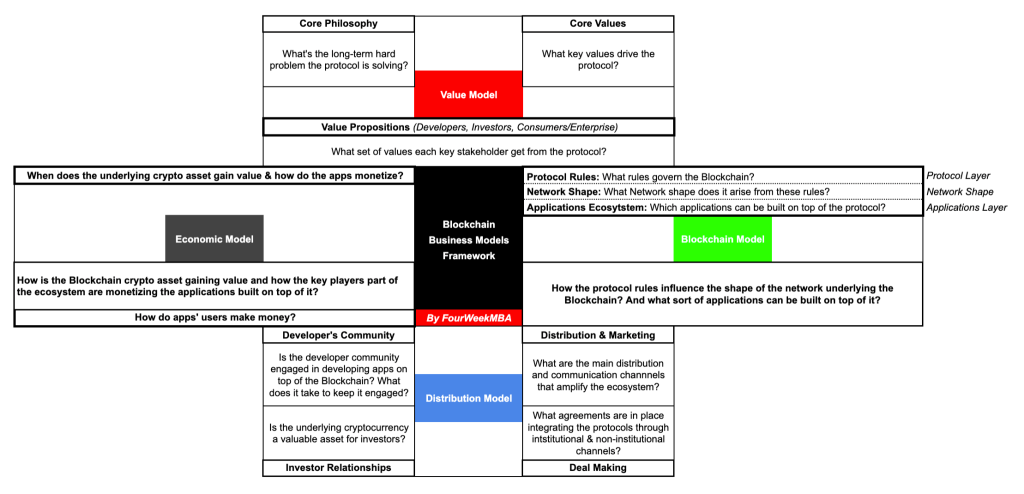
Blockchain Business Models Framework

Transitional Business Models

Market Expansion Theory

Business Scaling Theory

Digital Transformation

Business Engineering

Read next:
- Value Proposition
- Distribution Channels
- How To Write A Mission Statement
- Revenue Models
- Financial Structure
- Profitability
- Cash Flow
Related business resources:









