- SpaceX is a space transportation service and manufacturer of space rockets and other transport vehicles. It was founded by Elon Musk in 2002.
- SpaceX makes money by charging both governmental and commercial customers to send goods into space. These goods include ISS supplies and infrastructure, but also people and satellites for various purposes.
- SpaceX is also in the process of creating its Starlink network, designed to give every citizen access to fast and affordable internet.
| Business Model Element | Analysis | Implications | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Value Proposition | SpaceX’s value proposition is based on several key factors: – Affordable Space Access: SpaceX aims to reduce the cost of space travel, making it more accessible. – Reusable Rockets: The company designs reusable rockets to drive down launch costs. – Mars Colonization: SpaceX envisions making life multi-planetary by colonizing Mars. – Commercial Satellite Deployment: Offers satellite deployment services to private companies. SpaceX’s value proposition is centered on innovation, affordability, and space exploration. | Provides affordable and reliable access to space for a variety of missions. Pioneers the use of reusable rockets to drive down costs. Attracts visionaries and enthusiasts interested in Mars colonization. Offers satellite deployment services to commercial clients. Appeals to customers seeking innovative and cost-effective space solutions. | – Reducing the cost of space travel. – Designing reusable rockets for cost-efficiency. – Pursuing Mars colonization for the future. – Providing satellite deployment services. – Attracting a diverse range of customers with varied interests. |
| Customer Segments | SpaceX serves multiple customer segments, including: 1. Government Agencies: Provides launch services for government satellites and missions. 2. Commercial Companies: Offers satellite deployment and cargo delivery to the International Space Station (ISS). 3. Astronomical and Scientific Organizations: Supports space exploration and research missions. 4. Private Individuals: Enthusiasts interested in space travel and Mars colonization. SpaceX caters to a wide range of clients across the aerospace and space exploration industries. | Addresses the needs of government agencies for satellite launches. Provides commercial companies with cost-effective satellite deployment. Supports astronomical and scientific organizations in research missions. Attracts private individuals interested in space exploration and the possibility of traveling to Mars. Customizes services for diverse customer segments. | – Meeting the launch needs of government agencies. – Offering cost-effective satellite deployment for commercial clients. – Supporting research missions for scientific organizations. – Attracting individuals interested in space exploration. – Customizing services for various aerospace customers. |
| Distribution Strategy | SpaceX’s distribution strategy includes several key components: – Launch Facilities: Utilizes launch facilities worldwide for space missions. – Rocket Delivery: Safely delivers payloads to orbit and the ISS. – Collaboration with Clients: Works closely with clients to meet their specific mission requirements. – Web Presence: Provides information and updates on SpaceX’s website and social media. SpaceX ensures safe and efficient mission delivery, maintains client relationships, and communicates through online channels. | Utilizes launch facilities worldwide for mission deployment. Safely delivers payloads to various orbits and the ISS. Collaborates with clients to meet mission requirements. Maintains a strong online presence for communication and updates. Prioritizes safety and efficient mission execution. | – Leveraging launch facilities globally for missions. – Ensuring safe and reliable payload delivery. – Collaborating closely with clients on mission specifics. – Maintaining an online presence for communication. – Prioritizing safety and mission efficiency. |
| Revenue Streams | SpaceX generates revenue from various sources: 1. Launch Services: Earns income by launching satellites and cargo missions. 2. Commercial Satellite Deployment: Provides satellite deployment services for private companies. 3. ISS Resupply Missions: Contracts with NASA for cargo delivery to the ISS. 4. Starlink: Deploys a satellite internet constellation for global internet access. SpaceX diversifies income through a mix of launch services, satellite deployment, ISS resupply missions, and satellite internet services. | Relies on revenue from launch services for satellite and cargo missions. Offers satellite deployment to commercial clients for additional income. Contracts with NASA for cargo delivery to the ISS. Expands revenue potential through the Starlink satellite internet constellation. Diversifies income streams for financial stability. | – Earnings from satellite and cargo launch services. – Generating revenue from satellite deployment. – Contracting with NASA for ISS cargo missions. – Expanding revenue potential through Starlink internet services. – Diversifying income sources for financial stability. |
| Marketing Strategy | SpaceX’s marketing strategy focuses on the following elements: – Mission Success: Emphasizes successful space missions and achievements. – Public Engagement: Engages the public through live mission broadcasts. – Educational Initiatives: Promotes STEM education and space exploration. – Collaboration Announcements: Announces partnerships and contracts with organizations. SpaceX highlights mission success, engages the public, supports education, and shares collaborative efforts to build trust and enthusiasm for space exploration. | Showcases mission successes and breakthroughs to build trust. Engages the public through live mission broadcasts and updates. Supports STEM education to foster interest in space. Announces partnerships and collaborations to showcase industry leadership. Prioritizes transparency and public engagement in marketing efforts. | – Highlighting successful space missions and achievements. – Engaging the public through live mission broadcasts. – Promoting STEM education and space exploration. – Announcing partnerships and industry collaborations. – Prioritizing transparency and public engagement in marketing. |
| Organization Structure | SpaceX’s organizational structure includes: – Leadership Team: Led by Elon Musk, responsible for overall strategy. – Engineering and Development: Manages rocket design and technology development. – Launch Operations: Oversees mission planning and execution. – Business Development: Explores new opportunities and partnerships. – Customer Support: Ensures client satisfaction and mission success. SpaceX’s structure emphasizes innovation, engineering, efficient operations, and customer satisfaction. | Led by visionary Elon Musk, focusing on innovative space solutions. Prioritizes engineering and technology development for rocket design. Manages efficient mission planning and execution. Explores new business opportunities and partnerships. Ensures customer satisfaction and mission success through support. Supports SpaceX’s strategic direction and growth. | – Led by visionary Elon Musk for innovative solutions. – Focusing on engineering and rocket technology. – Efficiently planning and executing space missions. – Exploring new business opportunities and partnerships. – Ensuring customer satisfaction and mission success. – Supporting strategic growth and direction. |
| Competitive Advantage | SpaceX’s competitive advantage is derived from: – Reusable Rockets: Leads in rocket reusability to reduce launch costs. – Visionary Leadership: Led by Elon Musk, a visionary entrepreneur. – Commercial Contracts: Secures contracts from NASA and private companies. – Mars Colonization Ambition: Envisions making life multi-planetary. – Industry Innovation: Continuously innovates in rocket technology and space exploration. SpaceX stands out as an industry leader with reusable rockets, visionary leadership, a strong client base, Mars colonization plans, and a commitment to innovation. | Derives a competitive advantage from pioneering rocket reusability. Benefits from visionary leadership under Elon Musk. Secures contracts from NASA and private companies for mission diversity. Stands out with ambitious plans for Mars colonization. Maintains a commitment to innovation in rocket technology and space exploration. | – Pioneering rocket reusability for cost-effectiveness. – Benefiting from visionary leadership under Elon Musk. – Securing contracts from NASA and private companies. – Pursuing ambitious plans for Mars colonization. – Committing to continuous innovation in rocket technology and space exploration. – Staying ahead as an industry leader. |
SpaceX Origin Story
SpaceX, formally known as Space Exploration Technologies Corp., is an aerospace manufacturer and space transportation service founded by Elon Musk in 2002.
The company was created to reinvigorate public interest and investment in space exploration.
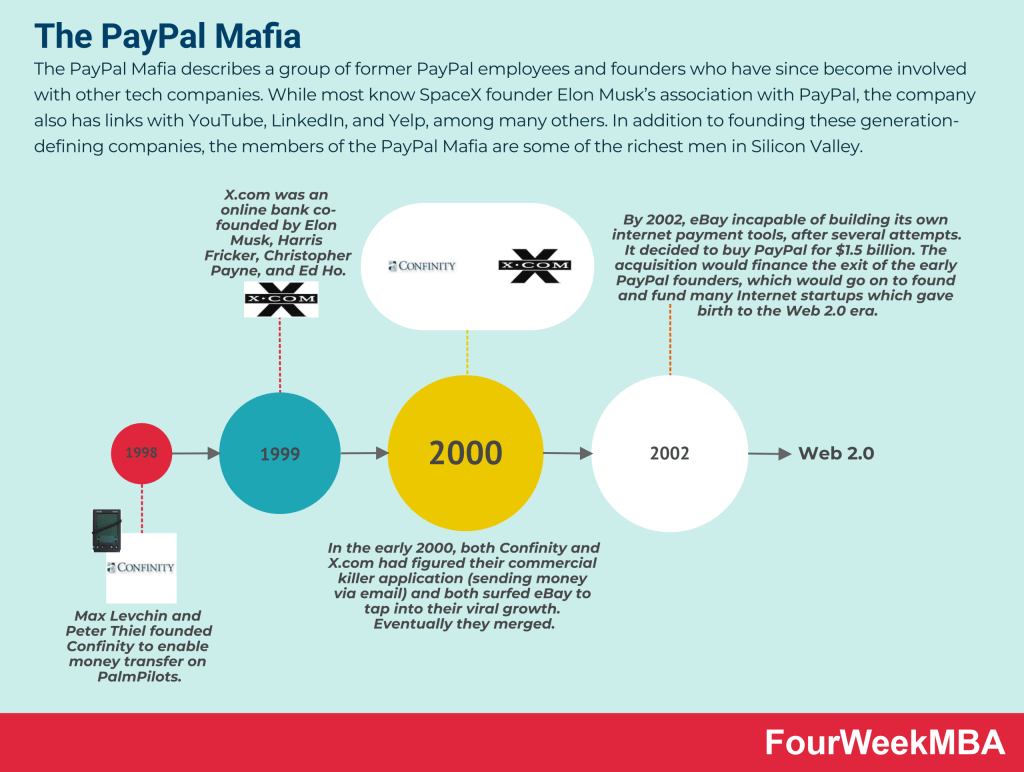
Musk sold his stake in PayPal in 2001 for $200 million, but rather than retire to a tropical island; he started work on establishing a human presence on another planet.
This initiative, with accessible internet and sustainable transportation, comprises three areas Musk deems crucial to humanity’s long-term survival.
Mars Oasis project
Since NASA had no interest in a manned Mars mission, Musk created the Mars Oasis project, where a greenhouse with seeds embedded in a nutrient gel would be landed on the red planet.
In essence, the project would send important data to Earth about the viability of transporting (and sustaining) life on another world.
Musk had to solve two major problems before he could realize his vision. For one, he needed to work out how to sustain plant life in hypobaric environments.
He also needed to develop a cost-effective solution for sending the lander into space.
The cheapest launch vehicles in the USA at the time were around $65 million, and with two extra missions planned in case the first failed, Musk found that the cost of the rockets alone would consume his budget.
Musk then made three failed trips to Russia after attempting to buy intercontinental ballistic missiles for around $10 million each.
While he was ultimately rebuffed and not taken seriously by the sellers, Musk used his experience as inspiration to start a company and build the components himself.
He saw this as a viable solution since the cost of raw materials comprised just 3% of the total price of a rocket.
Employing a combination of vertical integration and cheaper, modular, off-the-shelf componentry, SpaceX could cut the price of a launch by a factor of ten and enjoy a 70% gross margin in the process.
Falcon 1 and Dragon
Rocket engineer Tom Mueller joined SpaceX soon after the company was founded and worked for around two years to develop the first Falcon 1 rocket.
Musk contributed a third of his fortune toward the project despite many believing it was not a worthwhile endeavor. By 2005, the company had amassed some 150 employees.
SpaceX planned to launch Falcon 1 for the first time in November 2003 but suffered numerous setbacks over the next few years.
Getting the rocket into orbit proved to be a steep learning curve for SpaceX.
Thanks to setbacks caused by fuel leaks and collisions, the company took four attempts before a successful launch.
The first occurred on September 28, 2008, with another in July 2009.
Musk would later comment that Falcon 1 was the smallest useful orbital rocket that could be produced, with larger and more complex launch vehicles potentially bankrupt the company if they failed.
Accompanying the rocket was the Dragon spacecraft, named after the 1960s folk song Puff, The Magic Dragon by the group Peter, Paul, and Mary.
Musk said he chose the name Dragon in response to the critics who believed his mission was impossible.
Today, SpaceX has an impressive list of achievements.
It has become the first privately-owned company to launch, orbit, and recover a spacecraft.
SpaceX was also the first company to send a spacecraft to the International Space Station (ISS) and re-use an orbital rocket.
After an injection of $250 million from Korean investors in August 2022, the company is worth around $127 billion.
SpaceX has managed to secure $2 billion in investment capital in 2022 alone because of its visionary ideas and leadership.
SpaceX revenue generation
SpaceX is essentially a delivery service. If an organization wants to send goods to the ISS or launch a satellite into orbit, the company uses its fleet of vehicles, including the Dragon, Falcon Heavy, and Falcon 9.
As successful as SpaceX has been, it should be noted that it competes with several other companies for space delivery services.
These include Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Northrop-Grumman.
With all that said, let’s look at some specific SpaceX revenue streams.
Governmental supply contracts
SpaceX has won several NASA contracts to resupply the International Space Station.
The most recent contract involves $2.9 billion in funding to build a spacecraft to send astronauts to the moon.
The company has also worked with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), launching a satellite in 2012 to monitor global sea levels and oceanic circulation.
The cost of this launch was approximately $82 million.
Similar contracts for the Air Force saw the launch of a GPS satellite in 2015. In 2020, SpaceX won a contract to provide 40% of all U.S. military launch requirements.
In more recent years, SpaceX has made more money from commercial service deliveries. Each delivery using the Falcon 9 rocket is advertised at $62 million.
Starlink
Starlink is a satellite network designed to give every citizen on Earth high-speed internet access.
Although the project is in its infancy, SpaceX has secured government contracts to bring high-speed internet to rural U.S customers.
Finance services firm Morgan Stanley estimate that the service will be offered for $50/month, giving SpaceX $24 billion in annual free cash flow by 2040.
Other sources of SpaceX revenue
Civilian spaceflight
On September 15, 2021, the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft became the first crewed orbital mission without professional astronauts.
The mission, named Inspiration4, was piloted by confessed space geek and billionaire Jared Isaacman who only had around 6,000 hours of experience piloting various aircraft.
Inspiraton4 was powered by the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, and the company also ran a six-month training program for Isaacman and the three other crew members.
While considering his options in the planning stage of the mission, Isaacman noted in an interview that “there was no question it was going to be SpaceX. They’re leading the path.”
Indeed, SpaceX already had a proven track record in transporting astronauts to the International Space Station.
The company made an undisclosed amount of money for facilitating the Crew Dragon mission. However, USA Today estimates that the deal would have been worth somewhere in the tens of millions of dollars.
More to the point, the first successful mission without professional astronauts paves the way for an additional source of company revenue.
There are likely to be further missions in the future as SpaceX continues to work toward commercial spaceflight, with Elon Musk stating that these missions help SpaceX “bring the costs down and make space accessible for all.”
Rideshare program
SpaceX also offers the so-called “Smallsat” rideshare program to give companies with modest payloads affordable access to space.
Prices for this service start at $1 million for a 200 kg (440 lbs) payload delivered to sun-synchronous orbit (SSO), with rates also available for mid-inclination low Earth orbit (LEO), geostationary transfer orbit (GTO), and trans-lunar injection (TLI).
SSO missions depart approximately every four months with more frequent mid-inclination launches.
Additional mass for any mission is charged at $5,000 per kilogram.
If the client payload is delayed for whatever reason, SpaceX also charges a 10% fee to reschedule the launch to a later date.
Since the program was launched in 2017, SpaceX has noted the logistical difficulties of being a small satellite aggregator.
In an interview with Space News magazine in 2019, the vice president of commercial sales Tom Ochinero quipped that trying to get several customers ready at the same time was akin to herding cats.
Ochinero also mentioned that individual launches would go ahead even if the Falcon 9 rockets were not carrying the maximum payload.
In 2021, SpaceX transported 231 small satellites into orbit across two flights in January and June, with clients including telecommunications company Kepler Communications and Earth-imaging business Planet Labs.
A deal was also struck with Varda Space Industries to launch its space factory aboard a mission slated for Q1 2023.
The company hopes to establish the world’s first commercial industrial park at scale, manufacturing items such as fiber optic cables and life-saving pharmaceuticals to take advantage of the zero-gravity, vacuum environment of space.
How much is SpaceX worth today?
SpaceX officially entered the hectocorn list, with a staggering valuation of $137 billion, by January 2023.
Indeed, SpaceX closed a round in January for $750 million, which valued the company at $137 billion, led by investors such as a16z (Andreessen Horowitz).
Early SpaceX investors included Founders Fund, Sequoia, Gigafund, and others.
Read Also: Tesla Business Model, Elon Musk Companies, Who Owns Tesla, Transitional Business Models, Tesla Competitors.
Related To SpaceX






Main Free Guides:


![The History of SpaceX With Eric Berger [FourWeekMBA Podcast] history-of-spacex](https://i0.wp.com/fourweekmba.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/history-of-spacex-150x150.png?resize=150%2C150&ssl=1)






