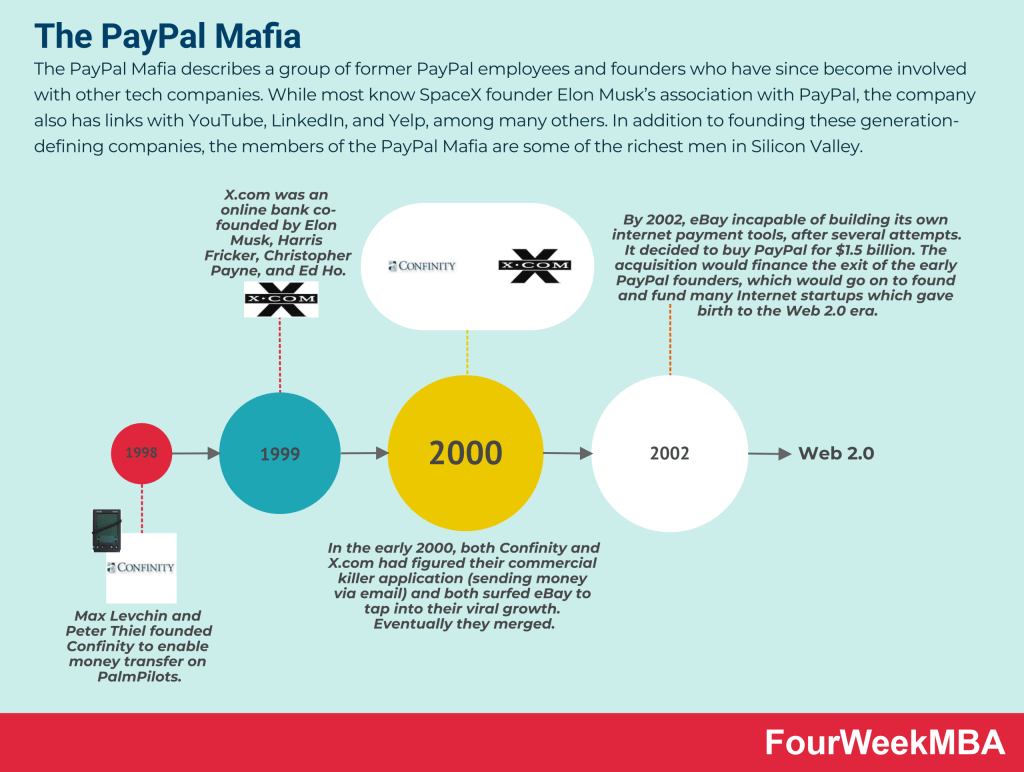
PayPal was first founded in 1998; it was called Confinity (among its founders was Peter Thiel); later, it merged with X.com, its major competitor, founded by Elon Musk (which would become known for other companies like Tesla and SpaceX). From this merger, PayPal was born. In 2002, PayPal was bought by eBay for $1.5 billion. eBay spun off PayPal in 2015, which would be listed as an independent entity. Today, PayPal owns brands like Braintree, Venmo, Xoom, and iZettle. Today, PayPal is mostly owned by institutional investors like The Vanguard Group (8.4%) and Blackrock (6.7%)
| Aspect | Description | Analysis | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Products and Services | PayPal is a digital payments platform that offers a range of financial services. Its core offerings include online payment processing, money transfers, and digital wallet services. PayPal also provides solutions for businesses, including payment processing, invoicing, and merchant services. Additionally, the company has expanded into peer-to-peer payments, online shopping protection, and cryptocurrency services. | PayPal’s primary products and services center around facilitating online payments, money transfers, and digital wallet capabilities. These services cater to both individuals and businesses, enabling secure and convenient financial transactions. PayPal has diversified its offerings with business solutions, peer-to-peer payments (Venmo), online shopping protection (PayPal Buyer Protection), and cryptocurrency services (buying, selling, and holding cryptocurrencies). | Online payment processing, money transfers, digital wallet services, business solutions (e.g., payment processing, invoicing, merchant services), peer-to-peer payments (e.g., Venmo), online shopping protection (e.g., PayPal Buyer Protection), cryptocurrency services (e.g., buying, selling, and holding cryptocurrencies). |
| Revenue Streams | PayPal generates revenue through various channels, primarily transaction fees from online payments and money transfers. The company charges fees to businesses for using its payment processing and merchant services. Additionally, PayPal earns interest income from customer balances held in digital wallets and generates revenue from currency conversion fees. | Revenue sources encompass transaction fees from online payments and money transfers, fees charged to businesses for payment processing and merchant services, interest income from customer balances in digital wallets, and currency conversion fees. Diverse revenue streams contribute to PayPal’s financial stability. | Revenue from transaction fees (e.g., online payments, money transfers), fees for payment processing and merchant services, interest income from customer balances in digital wallets, currency conversion fees. |
| Customer Segments | PayPal serves a broad customer base, including individual consumers, online shoppers, freelancers, small businesses, e-commerce platforms, and larger enterprises. The company’s services cater to various industries and sectors, offering secure and convenient payment solutions. PayPal aims to empower users with digital financial tools. | PayPal’s customer segments encompass individual consumers seeking secure online payments, online shoppers making purchases from e-commerce websites, freelancers receiving payments for services, small businesses utilizing payment processing and merchant services, e-commerce platforms facilitating transactions, and larger enterprises with diverse payment needs. The company’s services target various industries and sectors, providing secure and convenient payment solutions. PayPal’s mission is to empower individuals and businesses with digital financial tools. | Individual consumers (e.g., online shoppers, freelancers), online shoppers making purchases, freelancers receiving payments for services, small businesses utilizing payment processing and merchant services, e-commerce platforms facilitating transactions, larger enterprises with diverse payment needs, PayPal’s mission to empower individuals and businesses with digital financial tools. |
| Distribution Channels | PayPal primarily distributes its services through its website and mobile app, where users can create accounts, link bank accounts or credit cards, and make transactions. The platform is accessible on various devices, including smartphones and computers. PayPal also partners with online merchants to offer its payment services as a checkout option during online shopping. | Distribution channels focus on PayPal’s website and mobile app, enabling users to create accounts, link their financial instruments, and conduct transactions. Accessibility extends to various devices, including smartphones and computers. The company collaborates with online merchants to integrate PayPal as a payment option during the checkout process, making it convenient for users to pay for goods and services. | Distribution through PayPal’s website and mobile app for account management and transactions, accessibility on smartphones and computers, partnerships with online merchants to offer PayPal as a payment option during online shopping checkout. |
| Key Partnerships | PayPal collaborates with various partners to enhance its offerings. These partnerships include online merchants and e-commerce platforms that integrate PayPal as a payment option, banks and financial institutions to facilitate money transfers, payment processors for transaction processing, and technology companies for innovations and integrations. Additionally, PayPal has formed partnerships in the cryptocurrency space to enable cryptocurrency transactions. | Collaborations with online merchants and e-commerce platforms enhance user convenience by offering PayPal as a payment option. Partnerships with banks and financial institutions facilitate money transfers and provide access to customer accounts. Payment processor partnerships enable secure transaction processing. Collaborations with technology companies foster innovations and integrations to enhance PayPal’s services. Partnerships in the cryptocurrency space enable users to buy, sell, and hold cryptocurrencies through the platform. | Collaborations with online merchants and e-commerce platforms for convenient payment options, partnerships with banks and financial institutions for money transfers and account access, collaborations with payment processors for secure transaction processing, partnerships with technology companies for innovations and integrations, collaborations in the cryptocurrency space for cryptocurrency transactions. |
| Key Resources | PayPal’s key resources include its digital payments platform, a vast user base, a network of online merchants and businesses, partnerships with banks and financial institutions, payment processing technology, a mobile app and website infrastructure, customer accounts and balances, a strong brand identity associated with security and trust, and technological capabilities for innovations. | The digital payments platform forms the core resource, enabling secure and convenient financial transactions. A vast user base contributes to the platform’s network effect. Partnerships with online merchants and businesses enrich the ecosystem. Collaborations with banks and financial institutions facilitate money transfers. Payment processing technology ensures secure and efficient transactions. The mobile app and website infrastructure support user access and transactions. Customer accounts and balances provide liquidity. A strong brand identity fosters trust and loyalty. Technological capabilities drive innovations and enhancements. | Digital payments platform for secure and convenient transactions, vast user base contributing to the network effect, partnerships with online merchants and businesses enriching the ecosystem, collaborations with banks and financial institutions for money transfers, payment processing technology ensuring secure and efficient transactions, mobile app and website infrastructure supporting user access and transactions, customer accounts and balances providing liquidity, strong brand identity associated with security and trust, technological capabilities for innovations and enhancements. |
| Cost Structure | PayPal incurs costs related to payment processing, transaction fees, customer support and dispute resolution, marketing and advertising expenses to attract and retain users, employee salaries and benefits for a diverse workforce, technology infrastructure maintenance, research and development (R&D) for platform enhancements and innovations, and potential compliance and regulatory costs. | Costs related to payment processing include transaction fees and expenses associated with the movement of funds. Customer support and dispute resolution expenses are essential for maintaining user satisfaction. Marketing and advertising efforts are crucial for user acquisition and retention. Employee salaries and benefits cover various roles, including customer support, software development, and operations. Technology infrastructure maintenance ensures platform reliability. R&D investments drive platform enhancements and innovations. Compliance and regulatory costs may arise to meet financial industry requirements. | Costs related to payment processing (e.g., transaction fees), customer support and dispute resolution expenses, marketing and advertising expenses for user acquisition and retention, employee salaries and benefits (e.g., customer support, software development, operations), technology infrastructure maintenance for platform reliability, research and development (R&D) investments for platform enhancements and innovations, potential compliance and regulatory costs to meet industry requirements. |
| Competitive Advantage | PayPal’s competitive advantage lies in its user-friendly digital payments platform, a vast and engaged user base, a network effect that attracts both individual consumers and businesses, a strong brand identity associated with security and trust, partnerships with online merchants and banks for convenience and accessibility, payment processing technology that ensures secure and efficient transactions, and continuous innovation | A user-friendly digital payments platform ensures accessibility and ease of use. A vast and engaged user base contributes to the network effect, attracting both consumers and businesses. A strong brand identity fosters trust and loyalty among users. Partnerships with online merchants and banks enhance convenience and accessibility. Payment processing technology ensures secure and efficient transactions. Continuous innovation in financial services keeps PayPal competitive and adaptable to evolving market trends. The platform’s diverse offerings cater to various financial needs, positioning it as a prominent player in the digital payments industry. | User-friendly digital payments platform for accessibility and ease of use, vast and engaged user base contributing to the network effect, strong brand identity fostering trust and loyalty, partnerships with online merchants and banks for convenience and accessibility, payment processing technology ensuring secure and efficient transactions, continuous innovation in financial services for adaptability to market trends, diverse offerings catering to various financial needs, positioning PayPal as a prominent player in the digital payments industry. |
PayPal major shareholders
Today PayPal has become an empire in the fintech space.



The spin-off from eBay

As announced at the time:
In the distribution, eBay Inc. stockholders will receive one share of PayPal common stock for each share of eBay Inc. common stock held as of the close of business on July 8, 2015, the record date for the distribution. Subject to the satisfaction of the conditions to the distribution, the distribution of PayPal common stock is expected to occur on July 17, 2015. PayPal will not issue fractional shares of its common stock in the distribution. Immediately following the distribution, PayPal will be an independent, publicly traded company and will be listed on the NASDAQ Stock Market under the ticker “PYPL.” eBay will continue to trade on the NASDAQ Stock Market under the ticker “EBAY.”

Interestingly, over time, PayPal was born as a side feature within eBay, and after it, was purchased by eBay, PayPal became more valuable than eBay.
In September 2022, PayPal had a market cap of over $100 billion, whereas eBay had a market cap of over $20 billion.

This is PayPal’s board of directors in 2022:


Below is the compensation mix as per PayPal’s financials:

History of PayPal
The story of PayPal is so interesting for a few reasons that we can summarize below.
The story of PayPal has so many events that seem improbable.
Two startups (Confinity and X.com) were two startups operating in the internet payment industry. Yet, while they were neighbors, they also recognized how different was each other’s vision.
Confinity had started to build a valuable company by looking at a narrow application (enabling payments through the PalmPilot).
X.com wanted to be a financial institution.
Those two companies not only had a fundamentally different visions.
They also had different philosophies regarding the underlying technological infrastructure they had developed (X.com leveraged the Microsoft stack, whereas Confinity leveraged Linux, an open-source software).
Eventually, those two companies ended up merging to become one, PayPal.
While both companies had some grandiose visions, the market also turned out in a direction none had foreseen.
Enabling email payments which were supposed to be a “side feature,” became the killer commercial application for both companies.
They also figured that their tools had become extremely relevant on eBay. This triggered an irreversible journey. Where both startups understood the path to growth, leveraged on virality to get there, and eventually decided to merge to tackle the market.
During this process, a new business playbook has been developed.
Today we give for granted, but it didn’t exist at the time.
This playbook comprised concepts like:
And entire business disciplines are based on growth marketing, network effects, and more.
That is why PayPal’s history is so instrumental to the commercial Internet.
The founding members of PayPal would go on to build many other valuable companies and found the next wave of the Internet, what we now call Web 2.0 or Web2.
- Jawed Karim (Youniversity Ventures)
- Jeremy Stoppelman (founded Yelp with Russel Simmons)
- Andrew McCormack (partner at venture capital firm Valar Ventures)
- Premal Shah (non-profit organization Kiva)
- Luke Nosek (Founders Firm)
- Ken Howery (VP at Clarium Capital)
- David Sacks (produced “Thank You for Smoking”)
- Peter Thiel (created hedge fund Clarium Capital and The Founders Firm)
- Keith Rabois (held senior positions at LinkedIn, Slide)
- Reid Hoffman (LinkedIn)
- Max Levchin (Slide. Google bought it for $182 million in 2010)
- Roelof Botha (Sequoia Capital)
- Russel Simmons (Yelp)
- Elon Musk (Tesla, SpaceX)
Key Highlights
- Foundation and Merger: Founded in 1998 as Confinity, later merged with X.com to become PayPal.
- Acquisition by eBay: Acquired by eBay in 2002 for $1.5 billion, integrated into eBay’s marketplace.
- Spin-off from eBay: eBay spun off PayPal in 2015, making it an independent entity.
- Top Institutional Investors: Top institutional investors like The Vanguard Group and BlackRock own significant portions of PayPal’s stocks.
- Key Individual Shareholders: Key individual shareholders include Daniel Schulman, John Rainey, and Mark Britto.
- Revenue Sources: Revenue generated through customer transactions on the Payments Platform and value-added services.
- Financial Performance: In 2022, PayPal recorded over $27.5 billion in revenues and $2.4 billion in net profits.
- Merger and Growth: Merger of Confinity, focused on PalmPilot payments, and X.com, aspiring to be a financial institution.
- Killer Application: Email payments became the killer application, driving PayPal’s growth.
- Pioneering Strategies: PayPal’s history introduced key strategies like freemium, agile development, blitzscaling, and viral growth.
- Growth Concepts: Pioneered concepts for growth marketing and network effects.
- Founders’ Success: PayPal’s founders, including Peter Thiel, Elon Musk, Reid Hoffman, and Max Levchin, went on to build other successful ventures.
- Startupland: Contributed to the growth of companies like Yelp, LinkedIn, Slide, Kiva, and SpaceX.
Related to PayPal








PayPal Transactions Per Active Users

Read More: How Does TD Ameritrade Make Money, How Does Dave Make Money, How Does Webull Make Money, How Does Betterment Make Money, How Does Wealthfront Make Money, How Does M1 Finance Make Money, How Does Mint Make Money, How Does NerdWallet Make Money, How Does Acorns Make Money, How Does SoFi Make Money, How Does Stash Make Money, How Does Robinhood Make Money, How Does E-Trade Make Money, How Does Coinbase Make Money, How Does Affirm Make Money, Fintech Companies And Their Business Models.
List of FinTech Business Models




Braintree



















Read Next: Fintech Business Models, IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, Enterprise AI Business Model, Cloud Business Models.
Read Next: Affirm Business Model, Chime Business Model, Coinbase Business Model, Klarna Business Model, Paypal Business Model, Stripe Business Model, Robinhood Business Model.
Main Free Guides:






![The History of PayPal with Jimmy Soni [FourWeekMBA Podcast] history-of-paypal](https://i0.wp.com/fourweekmba.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/history-of-paypal-150x150.png?resize=150%2C150&ssl=1)


