Slack follows a freemium model, offering a free version, and users can convert into paying customers if they want more usage or advanced functionalities. Slack combines the free model with a direct sales force to acquire enterprise customers with yearly recurring revenue of over 100K. Those customers were 575 in 2019, and they accounted for 40% of its revenues. In 2021 in a $27.7 billion deal, Slack was acquired by Salesforce. By early 2023, Slack had generated $1.5 billion in yearly revenue.
| Business Model Element | Analysis | Implications | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Value Proposition | Slack’s value proposition centers on: – Team Collaboration: Facilitates real-time communication and collaboration among teams and colleagues. – Channel-Based Organization: Organizes conversations into channels for clarity and efficiency. – Integrations: Offers integration with numerous third-party tools and services to streamline work. – Search Functionality: Provides robust search capabilities to find and retrieve information quickly. – User-Friendly Interface: Offers an intuitive and user-friendly platform for seamless communication. Slack empowers organizations to enhance teamwork, streamline communication, and boost productivity. | Supports real-time collaboration among teams and colleagues. Improves communication clarity and efficiency with channel-based organization. Enhances productivity through integrations with external tools and services. Enables quick access to information with powerful search functionality. Appeals to users with an intuitive and user-friendly interface. Attracts businesses seeking efficient team communication and collaboration solutions. | – Real-time team collaboration. – Channel-based communication. – Integration with third-party tools. – Robust search capabilities. – User-friendly interface. – Attracting businesses seeking efficient collaboration solutions. |
| Customer Segments | Slack serves diverse customer segments, including: 1. Businesses: Small, medium-sized, and large enterprises looking for efficient communication and collaboration solutions. 2. Remote Teams: Companies with remote or distributed teams seeking effective virtual communication tools. 3. Developers: Development teams using Slack for project management and coordination. 4. Educational Institutions: Schools and universities using Slack for remote learning and administration. Slack caters to a wide range of organizations and teams with communication and collaboration needs. | Targets businesses of all sizes seeking efficient communication tools. Offers solutions for remote teams and virtual work environments. Supports developers and project management teams with collaboration tools. Provides services to educational institutions for remote learning and administrative communication. Customizes offerings to address various customer segments. | – Targeting businesses of all sizes. – Providing solutions for remote teams. – Supporting developers and project management. – Offering services to educational institutions. – Customizing offerings for diverse customer needs. |
| Distribution Strategy | Slack’s distribution strategy includes several channels: – Direct Sales: Employs a direct sales team to engage with and sell to enterprise customers. – Freemium Model: Offers a freemium model allowing users to access basic features for free and upgrade for premium features. – Online Platform: Provides an online platform for users to sign up, create teams, and access Slack. – Partnerships: Collaborates with third-party app developers to expand its ecosystem. – Enterprise Sales: Engages in enterprise-level sales for larger organizations. Slack’s distribution channels aim to reach a broad user base, from small teams to large enterprises. | Engages with enterprise customers through a direct sales team. Attracts users with a freemium model that lowers barriers to entry. Provides an accessible online platform for users to create teams and access Slack. Collaborates with app developers to extend its ecosystem and capabilities. Captures larger enterprise clients through specialized sales efforts. Ensures a diverse user base through multiple distribution channels. | – Engaging with enterprise customers through direct sales. – Attracting users with a freemium model. – Providing an accessible online platform. – Collaborating with app developers. – Capturing larger enterprise clients through specialized sales. – Ensuring a diverse user base through various channels. |
| Revenue Streams | Slack generates revenue through the following sources: 1. Subscription Fees: Charges organizations for premium plans with enhanced features and capabilities. 2. Enterprise Sales: Earns revenue from large enterprise customers with specialized needs and services. 3. Slack Connect: Offers additional features and services for inter-organizational communication. 4. App Directory: Takes a percentage of sales made by third-party app developers on the Slack App Directory. 5. Slack Fund: Invests in startups and companies that develop applications for the Slack ecosystem. Diversifies income sources across subscriptions, enterprise sales, partnerships, and investments. | Relies on subscription fees, enterprise sales, Slack Connect, app directory revenue share, and investments. Offers tiered pricing to cater to different business sizes and requirements. Captures larger enterprises with specialized services. Encourages the use of third-party apps through the Slack App Directory. Supports ecosystem growth by investing in startups and developers. Diversifies revenue streams to maintain financial stability. | – Revenue from subscription fees. – Earnings from large enterprise clients. – Additional features and services through Slack Connect. – Share of sales from third-party app developers. – Investments in startups and developers. – Diversifying income sources within the Slack ecosystem. |
| Marketing Strategy | Slack’s marketing strategy comprises these elements: – Content Marketing: Publishes educational content, blog articles, and resources to engage users. – Community Building: Fosters a sense of community among users through forums and events. – Partnerships: Collaborates with third-party app developers to enhance its ecosystem. – Direct Sales: Engages with enterprise customers through direct sales efforts. – Freemium Model: Attracts users with a free version and encourages them to upgrade for premium features. Slack prioritizes content marketing, community building, and partnerships to foster growth and user engagement. | Utilizes content marketing to engage and educate users. Nurtures a community spirit among users through forums and events. Collaborates with app developers to expand its ecosystem. Engages in direct sales efforts to capture enterprise clients. Leverages a freemium model to attract and convert users to premium plans. Prioritizes user engagement and education in its marketing efforts. | – Content marketing to engage and educate users. – Fostering a sense of community among users. – Collaborating with app developers for ecosystem expansion. – Engaging with enterprise customers through direct sales. – Utilizing a freemium model for user acquisition. – Prioritizing user engagement and education. |
| Organization Structure | Slack operates with a functional organizational structure: – Leadership Team: Led by the CEO and top executives responsible for strategic direction. – Engineering and Product Development: Focuses on platform development and feature enhancements. – Sales and Marketing: Drives sales, user acquisition, and marketing efforts. – Customer Success: Ensures customer satisfaction and support. – Partnerships and Ecosystem: Collaborates with third-party developers and app creators. Slack’s structure emphasizes functional specialization and efficiency. | Employs a functional structure with clear divisions for efficient operations. Prioritizes platform development, sales, marketing, and customer support. Collaborates with app developers to expand the ecosystem. Supports strategic direction and decision-making from top executives. Ensures efficiency and specialization in various functional areas. | – Functional structure with clear divisions. – Prioritizing platform development and user support. – Collaborating with app developers for ecosystem growth. – Supporting strategic direction from top executives. – Ensuring efficiency and specialization. |
| Competitive Advantage | Slack’s competitive advantage stems from: – User-Centric Approach: Prioritizes user needs and experience, leading to strong user satisfaction. – Ecosystem Growth: Expands its ecosystem through third-party app integrations and partnerships. – Collaboration Features: Offers effective collaboration features like channels and integrations. – Accessibility: Provides accessibility through a freemium model and an easy-to-use platform. – Enterprise Focus: Captures larger enterprise clients with specialized services. Slack stands out as a user-centric and collaboration-focused communication platform. | Derives a competitive advantage from: – A user-centric approach leading to high satisfaction. – Expanding its ecosystem through integrations and partnerships. – Effective collaboration features and accessibility. – A freemium model that lowers barriers to entry. – Specialized services for enterprise clients. Stands out as a user-centric and collaboration-focused platform in the market. | – User-centric approach and high satisfaction. – Expanding the ecosystem through integrations. – Effective collaboration features and accessibility. – A freemium model for user acquisition. – Specialized services for larger enterprises. – Standing out as a collaboration-focused platform. |
Slack background story
Stewart Butterfield is a serial entrepreneur and co-founder of the photo-sharing website Flickr.
He went through the founding of several companies, in particular, when he founded Glitch (an online game).
When he was running Tiny Spek, which comprised a set of companies, Butterfield and his team needed a communication system to handle the teams within his organizations.
That tool was developed in-house, and it eventually became Slack.
When Slack launched back in 2013, more and more companies signed up until its growth kept compounding. Where did this opportunity come from?
The timing was right!
Butterfield said in an interview for CNET:
“In the last 15 years, the Microsoft hegemony and Office and Windows worship has broken down, and as a result, we’ve gotten a lot of new and, in most cases, better tools…But that means information is scattered across a bunch of different tools and there’s no one search tool that you can go through to search across all of this.”
From that stage, Slack kept inviting larger and larger groups of companies.
Breaking down Slack vision and mission
Our vision is a world where organizational agility is easy to achieve, regardless of an organization’s size
Therefore, the challenge for Slack is to organize more prominent and larger groups of people within organizations.
Indeed, Slack has been using its enterprise customer base more aggressively in recent years.
Our mission is to make people’s working lives simpler, more pleasant and more productive
Slack’s value proposition and mission start from its willingness to reduce fragmentation within tools used by organizations.
One of the critical elements of Slack is integrating with other apps and tools to bring this information together.

How does Slack make money? Slack Freemium subscription model

It generates revenue primarily from paid subscriptions.
Those subscriptions are paid monthly or annually, based on the number of users a company has on Slack.
Slack offers four subscription plans:
- Free,
- Standard,
- Plus,
- And Enterprise Grid.

Source: Slack Financial Prospectus
The Free, Standard, and Plus subscription plans consist of a single workspace or a basic Slack environment configured for each team.
Slack leverages a freemium model that makes it easy for small organizations to try and understand the value of the product.
Once those organizations are “locked-in,” Slack offers additional capabilities (unlimited integrations, shared channels, guest accounts) that drive the free users to become paying customers.
The Enterprise Grid package, instead, is made for larger organizations with – at times – tens of thousands of users.
As Slack points out in its financial prospectus, this requires a product with enhanced functionality, flexibility, administrative control, and security at scale.
Enterprise Grid also allows paid customers to:
- Create and manage an unlimited set of connected workspaces and channels;
- Search across multiple workspaces, making it easy for workers and administrators to tap into their organization’s collective knowledge at scale;
- Access centralized controls to ensure a company’s data remains secure, giving administrators a single point of visibility to provision and manage Slack; and
- Integrate with third-party e-Discovery and data loss prevention tools to help meet security and compliance requirements.

Source: Slack’s website
Slack sales and marketing strategy dissected
Slack combines a self-service go-to-market approach to attract non-paying users. At the same time, it uses direct sales efforts to grow the paid users within larger organizations.
Therefore the sales process usually follows this flywheel model:
- The Slack free version easily attracts a large number of users
- Self-service users become leads for salespeople
- Salespeople convert free users into paying customers, usually within larger enterprises.
- These larger enterprises that join in create organic awareness of Slack inside and outside of their organizations
- Slack keeps investing in its product, and customer experience
- It also employs after-sales customer success representatives, which makes it easy to trigger referral customers
By looking at the company financials, Slack has invested substantially in sales and marketing efforts. Indeed, the company spent almost 99% of its revenues in 2017 on Sales and Marketing activities.
This number stabilized at 63.5% in 2018 and 58% in 2019.
Thus, the freemium business model of Slack still needs some fine-tuning to find the right balance between growth and profitability.
In fact, as of 2019, the company still reported net losses during its IPO.
Currently, though, Slack is pushing on sales and marketing activities to sustain its momentum and growth.
Among the marketing strategies and tactics Slack adopts to drive initial awareness and adoption, there is the Slack website through which users are driven frictionlessly through the free plan.
In short, Slack is acquiring users at high speed without creating a high-touch sales experience. Instead, it relies on its low-touch, frictionless process to increase active users.
Therefore, the Slack product team focuses on organic growth and adoption at that stage.
Once the pipeline is ready, the sales team and the overall organization instead, focus on two key metrics:
- Free-to-paid conversion
- And the net dollar retention rate
When acquiring paid clients for larger accounts, the sales team uses a high-touch sales approach, which complements the self-service approach.
The sales team targets C-suite executives and leaders of a specific business unit.
Therefore, that also includes resources for direct sales such as:
- Field sales force,
- Solution engineers
- Demand generation campaigns
- Webinars
- Analyst relations
- C-suite events
- Partnership marketing and co-marketing
- Annual user conference
Who are Slack’s paid customers?
Organizations on Slack are of all sizes:
- Individual entrepreneurs,
- Freelancers,
- Emerging small businesses,
- Multi-national corporations.
They work across a wide range of industries. According to the Slack 2018 Survey, more than half of its users are in non-technical roles.
As of January 31, 2019, Slack reported more than 600,000 organizations with three or more users, broken down as it follows:
- 88,000 Paid Customers, including more than 65 companies in the Fortune 100
- and more than 500,000 organizations on Slack Free subscription plan.
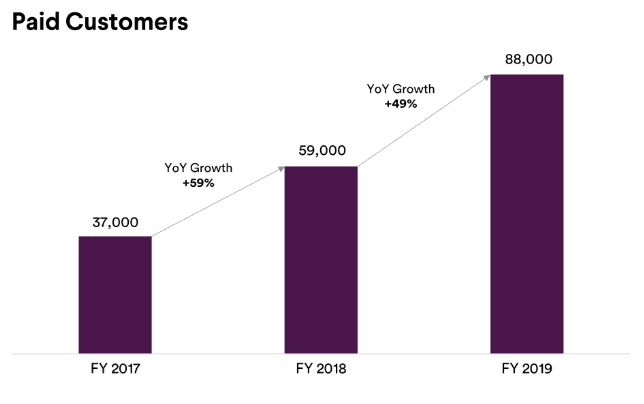
Source: Slack Financial Prospectus
Who’s the customer that really matters to Slack?
Slack also tracks another kind of customer, the one who has a higher ARR, compared to regular paying customers.
This cohort is made of companies with an ARR (annual recurring revenue) higher than $100K.
That is used as a key indicator for the growth of the business. In 2017, 2018, and 2019, those represented approximately 22%, 32%, and 40%.

Source: Slack Financial Prospectus
Slack functionalities and product

Source: Slack Financial Prospectus
Slack key functionalities can be broken down in:
- Messaging and Channels:The channel is the fundamental unit of Slack. Indeed, through the channels people are organized to collaborate on specific tasks, to share information, and get work done. Channels are organized by project, topic, team, or based on the organizational structure and situation. Channels can be public, thus accessible to anyone in the Slack organization. Or private, so that they are available only to certain people within the organization. Messaging happens through the channels.
- Integrations: Integrations help companies to gather information from other applications. Integrations with software like Salesforce help salespeople be more productive. Advanced use cases can help design custom workflows, to perform tasks and actions in Slack. For instance, by integrating Slack with the invoicing system reports and digests can be pulled up from Slack.
- Shared Channels: Shared channels connect Slack workspaces of different organizations. Shared channels can be public or invite-only.
- Search: Everything in Slack, is searchable, so that information within those channels can be retrieved easily.
Is Slack blitzscaling?

It’s interesting to notice how Slack almost quadrupled its revenues from 2017 to 2019. However, it also doubled its expenses. Thus, Slack seems to be in a blitzscaling phase, where it prioritizes speed and growth over anything else. As of 2019, the company is still running at net losses.
Usually, companies blitzscale because they want to quickly gain market shares, and be in a position of dominance. Or they do it to defend their business.
In 2018, Microsoft announced the free version of its Microsoft Teams. Apparently, the move from Microsoft tried to keep up if not dominate the space, thus, take over Slack.
Salesforce acquisition of Slack
In a $27.7 billion deal in 2021, Salesforce acquired Slack.

While Slack is still managed as an independent product, Salesforce is integrating that more and more into its business model.

Key facts and statistics from the Slack business model
- Of the over 500K free users, 88K are paid accounts.
- Within the paid accounts, there is the category of businesses that make over $100K per year in recurring revenues. Those were 575 in 2019, and they represented 40% of its revenues.
- Slack spent almost 99% of its revenues in 2017 for Sales and Marketing activities. This number stabilized to 63.5% in 2018 and 58% by 2019.
- Slack follows a freemium model pattern which quickly brings in free users, which then get funneled within Slack direct sales effort to turn them in paying customers
- Slack primary value proposition starts from fragmentation among tools used by organizations to handle their internal communication workflows
Business Model Explorers
Related Visual Stories






Salesforce Revenue Per Employee













