Strategic analysis is a process to understand the organization’s environment and competitive landscape to formulate informed business decisions, to plan for the organizational structure and long-term direction. Strategic planning is also useful to experiment with business model design and assess the fit with the long-term vision of the business.
| Strategic Analysis | Description | Analysis | Implications | Applications | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Overview | Strategic Analysis is a comprehensive process of examining an organization’s internal and external environments to formulate informed strategic decisions. | – Evaluate internal and external factors affecting the organization. – Identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT). | – Provides a holistic view of the organization’s position and potential. – Guides strategic planning and decision-making. | – Developing a new business strategy for growth and market expansion. – Assessing the competitive landscape in an industry. – Analyzing the internal capabilities of an organization before a merger. | Conducting a SWOT analysis to determine an organization’s competitive position. Assessing market trends and consumer preferences for product development. |
| 2. Internal Analysis | Internal Analysis assesses the organization’s internal factors, including strengths and weaknesses, to understand its capabilities and limitations. | – Identify and evaluate the organization’s internal strengths and weaknesses, such as resources, processes, and skills. – Assess internal performance and capabilities. | – Highlights areas where the organization excels and can gain a competitive edge. – Identifies internal limitations that may hinder progress. | – Assessing internal processes for efficiency improvements. – Identifying core competencies that can lead to competitive advantages. – Evaluating employee skills and training needs. | Recognizing a company’s strong financial position and efficient supply chain as internal strengths. Identifying a lack of innovation and outdated technology as internal weaknesses. |
| 3. External Analysis | External Analysis examines factors in the organization’s external environment, including opportunities and threats, to assess the impact on strategic decisions. | – Identify and evaluate external opportunities and threats, such as market trends, competition, regulatory changes, and economic conditions. – Assess market dynamics. | – Enables the organization to capitalize on favorable external conditions and navigate potential threats. – Helps anticipate and adapt to changes in the external landscape. | – Analyzing market trends to identify growth opportunities. – Assessing competitive forces and market entry barriers. – Monitoring changes in regulations affecting the industry. | Recognizing a growing demand for sustainable products as an external opportunity. Identifying increased competition and market saturation as external threats. |
| 4. SWOT Analysis | SWOT Analysis combines internal and external assessments to create a matrix highlighting an organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. | – Create a SWOT matrix that aligns internal strengths and weaknesses with external opportunities and threats. – Identify strategic implications based on the matrix. | – Provides a clear visual representation of the organization’s strategic position. – Guides strategy development by aligning internal capabilities with external factors. | – Developing strategies that leverage strengths to exploit opportunities. – Addressing weaknesses to mitigate potential threats. – Identifying strategies to capitalize on strengths while managing threats. | Developing a SWOT matrix that shows the organization’s strong brand reputation (S), limited digital presence (W), emerging market opportunities (O), and increasing competition (T). |
| 5. Competitive Analysis | Competitive Analysis focuses on evaluating competitors’ strengths, weaknesses, strategies, and market positioning to gain a competitive advantage. | – Identify key competitors in the industry. – Analyze competitors’ strategies, market share, strengths, and weaknesses. – Assess competitive threats and opportunities. | – Provides insights into the competitive landscape and opportunities for differentiation. – Helps identify potential areas for competitive advantage. | – Benchmarking against competitors to identify areas for improvement. – Analyzing competitor pricing strategies and market share trends. – Identifying gaps in the market where competitors are underserving customers. | Assessing a competitor’s strong distribution network and innovative product offerings. Recognizing a competitor’s limited online presence and customer service challenges. |
| 6. Scenario Analysis | Scenario Analysis involves creating multiple future scenarios based on different variables and assessing the implications of each scenario on strategic decisions. | – Develop alternative future scenarios considering various economic, market, and industry conditions. – Assess the impact of each scenario on the organization’s strategy. | – Helps prepare the organization for different possible futures. – Allows for more informed and adaptive decision-making. | – Scenario planning for business continuity in the face of economic uncertainties. – Evaluating the impact of changing market dynamics on strategic initiatives. – Assessing the potential consequences of regulatory changes. | Preparing for a scenario where there is a sudden economic recession (Scenario A) or a scenario with sustained economic growth (Scenario B). |
| 7. Strategic Planning | Strategic Planning is the process of formulating and implementing strategies based on the findings of the analysis, aligning the organization’s goals and actions. | – Develop a comprehensive strategic plan that incorporates the insights from the analysis. – Define clear objectives, strategies, and action steps. – Allocate resources effectively. | – Ensures that organizational goals and actions are aligned with identified strengths and opportunities. – Guides resource allocation for maximum impact. | – Creating a multi-year strategic plan for organizational growth. – Developing departmental strategies to achieve specific objectives. – Allocating budget and resources based on strategic priorities. | Developing a strategic plan that focuses on leveraging internal strengths to exploit external opportunities. Setting clear objectives to improve market share and innovation capabilities. |
Strategic analysis thinking tools
For the sake of this article, we’ll look at a set of business thinking tools which you can use to assess both the internal positioning, strategy and if it fits with long-term vision and to assess external, competitive forces.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas aims to provide a keen understanding of your business model to provide strategic insights about your customers, product/service, and financial structure;
so that you can make better business decisions.
Blitzscaling canvas
In this article, I’ll focus on the Blitzscaling business model canvas. This is a model based on the concept of Blitzscaling.
That is a particular process of massive growth under uncertainty, and that prioritizes speed over efficiency. It focuses on market domination to create a first-scaler advantage in a scenario of uncertainty.
Pretotyping

Pretotyping is a mixture of the words “pretend” and “prototype,” and it is a methodology used to validate business ideas to improve the chances of building a product or service that people want.
The pretotyping methodology comes from Alberto Savoia’s work summarized in the book “The Right It: Why So Many Ideas Fail and How to Make Sure Yours Succeed.”
This framework is a mixture of the words “pretend” and “prototype,” and it helps to answer such questions (about the product or service to build) as: Would I use it? How, how often, and when would I use it? Would other people buy it? How much would they be willing to pay for it? How, how often, and when would they use it?
Value innovation and blue ocean strategy

A blue ocean is a strategy where the boundaries of existing markets are redefined, and new uncontested markets are created.
At its core, there is value innovation, for which uncontested markets are created, where competition is made irrelevant. And the cost-value trade-off is broken.
Thus, companies following a blue ocean strategy offer much more value at a lower cost for the end customers.
Growth hacking process

Growth hacking is a process of rapid experimentation, coupled with the understanding of the whole funnel, where marketing, product, data analysis, and engineering work together to achieve rapid growth.
The growth hacking process goes through four key stages of analyzing, ideating, prioritizing, and testing.
Pirate metrics

Venture capitalist, Dave McClure, coined the acronym AARRR which is a simplified model that enables to understand what metrics and channels to look at. At each stage for the users’ path toward becoming customers and referrers of a brand.
Engines of growth

In the Lean Startup, Eric Ries defined the engine of growth as “the mechanism that startups use to achieve sustainable growth.”
He described sustainable growth as following a simple rule, “new customers come from the actions of past customers.”
The three engines of growth are the sticky engine, the viral engine, and the paid engine. Each of those can be measured and tracked by a few key metrics, and it helps plan your strategic moves.
RTVN model

The RTVN model is a straightforward framework that can help you design a business model when you’re at the very early stage of figuring out what you need to make it succeed.
Sales cycle

A sales cycle is the process that your company takes to sell your services and products.
In simple words, it’s a series of steps that your sales reps need to go through with prospects that lead up to a closed sale.
Planning ahead of time the steps your sales team needs to take to close a big contract can help you grow the revenues for your business.
Comparable analysis

A comparable company analysis is a process that enables the identification of similar organizations to be used as a comparison to understand the business and financial performance of the target company.
To find comparables, you can look at two key profiles: the business and economic profile. From the comparable company analysis, it is possible to understand the competitive landscape of the target organization.
Porter’s five forces

Porter’s Five Forces is a model that helps organizations to gain a better understanding of their industries and competition.
It was published for the first time by Professor Michael Porter in his book “Competitive Strategy” in the 1980s.
The model breaks down industries and markets by analyzing them through five forces which you can use to have a first assessment of the market you’re in.
Aida model

AIDA stands for attention, interest, desire, and action. This is a model which is used in marketing to describe the potential journey a customer might go through, before purchasing a product or service. Variation of the AIDA model is the CAB model and the AIDCAS model.
PESTEL analysis

The PESTEL analysis is a framework that can help marketers assess whether macro-economic factors are affecting an organization.
This is a critical step that helps organizations identify potential threats and weaknesses. That can be used in other frameworks such as SWOT or to gain a broader and better understanding of the overall marketing environment.
Technology adoption curve

The technology adoption curve is a model which goes through five stages. Each of those stages (innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, and laggard) has a specific psychographic that makes that group of people ready to adopt a tech product.
This simple concept can help you define the right target for your business strategy.
Business model essence

A Business Model Essence, according to FourWeekMBA, is a way to find the critical characteristics of any business to have a clear understanding of that business in a few sentences.
That can be used to analyze existing businesses. Or to draft your Business Model and keep a strategic and execution focus on the key elements to be implemented in the short-medium term.
FourWeekMBA business model framework

An effective business model has to focus on two dimensions: the people dimension and the financial dimension. The people dimension will allow you to build a product or service that is 10X better than existing ones and a solid brand.
The financial dimension will help you develop proper distribution channels by identifying the people that are willing to pay for your product or service and make it financially sustainable in the long run.
TAM, SAM, and SOM

Understanding your TAM, SAM and SOM can help you navigate the market you’re in and to have a laser focus on the market you can reach with your product and service.
Brand Building

Value Proposition Design

Product-Market Fit

Freemium Decision Model

Organizational Design And Structures

Speed-Reversibility Matrix

Minimum Viable Product

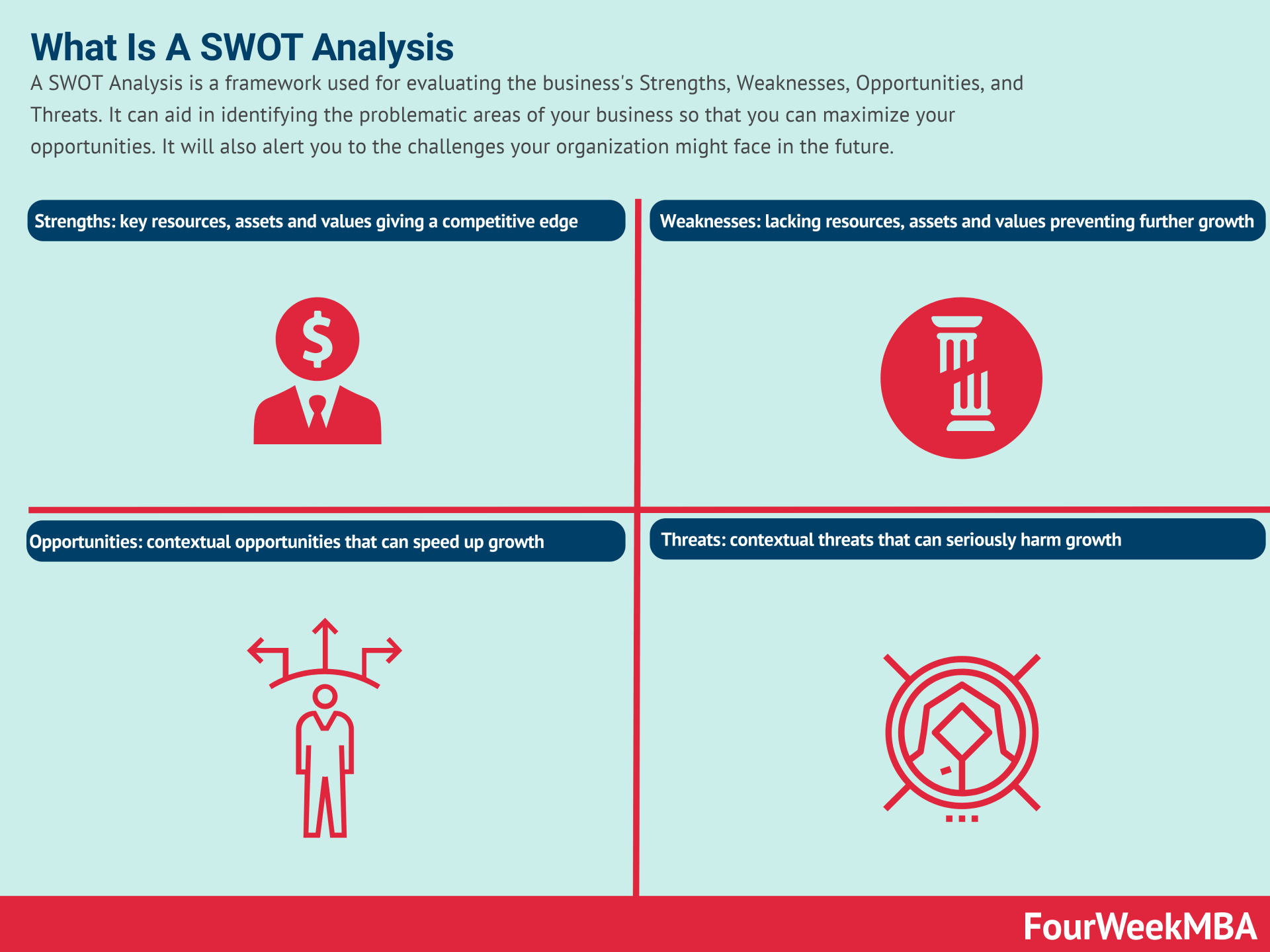
SWOT Analysis
Revenue Modeling

Business Experimentation

Business Analysis

Key Highlights
- Strategic Analysis and Planning:
- Strategic analysis is the process of understanding an organization’s environment and competitive landscape to make informed business decisions.
- Strategic planning involves structuring the organization, long-term direction, and experimenting with business model design.
- Business Model Canvas:
- Provides insights into customers, products/services, and financial structure.
- Aids in making better business decisions by understanding the business model.
- Blitzscaling Canvas:
- Based on the concept of Blitzscaling, a process of rapid growth under uncertainty.
- Prioritizes speed over efficiency and focuses on market domination.
- Pretotyping:
- Combines “pretend” and “prototype” to validate business ideas.
- Helps understand potential customer usage, preferences, and willingness to pay.
- Value Innovation and Blue Ocean Strategy:
- Redefines existing market boundaries and creates uncontested markets.
- Focuses on value innovation and breaking the cost-value trade-off.
- Growth Hacking Process:
- Pirate Metrics:
- AARRR framework for tracking user journey stages.
- Helps identify metrics and channels for customer acquisition and retention.
- Engines of Growth:
- Mechanisms startups use to achieve sustainable growth.
- Sticky, viral, and paid engines are the key types.
- RTVN Model:
- Framework for designing an early-stage business model.
- Sales Cycle:
- Steps taken to sell products or services.
- Helps plan sales team strategies for closing deals.
- Comparable Analysis:
- Identifies similar companies for comparison.
- Understands business and financial performance of target company.
- Porter’s Five Forces:
- Analyzes industry and competition through five forces.
- Helps gain a better understanding of market dynamics.
- AIDA Model:
- Attention, Interest, Desire, and Action model in marketing.
- Describes customer journey before purchasing.
- PESTEL Analysis:
- Assesses macro-economic factors affecting organizations.
- Identifies potential threats and weaknesses.
- Technology Adoption Curve:
- Divides customers into stages for tech product adoption.
- Helps define target audience for business strategy.
- Business Model Essence:
- Identifies critical characteristics of a business in a few sentences.
- Aids in analysis and strategic focus.
- FourWeekMBA Business Model Framework:
- Focus on people and financial dimensions for a successful business model.
- TAM, SAM, and SOM:
- Understanding Total Addressable Market, Serviceable Addressable Market, and Share of Market.
- Brand Building, Value Proposition Design, Product-Market Fit:
- Key concepts for building a recognizable brand and aligning with customers.
- Minimum Viable Product, SWOT Analysis, Revenue Modeling:
- Concepts for efficient product development, analysis, and revenue planning.
| Concept Name | Description | When to Use | Advantages | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Business Model Canvas | The Business Model Canvas is a visual tool that provides a comprehensive view of a business model. It helps in understanding key components such as customers, value proposition, channels, and revenue streams. It aids in making strategic decisions by identifying strengths and weaknesses. | When organizations need to analyze and improve their business model, identify areas for innovation, or communicate their business model effectively to stakeholders. | Provides a structured and visual representation of the business model, fosters strategic thinking, and assists in identifying areas for improvement. | May oversimplify complex business models, and the effectiveness depends on the quality of data and analysis. |
| Blitzscaling Canvas | The Blitzscaling Canvas is a model designed for businesses focused on rapid growth under uncertainty. It emphasizes speed over efficiency and aims for market domination. It helps in prioritizing key aspects of blitzscaling strategy and aligning efforts for rapid growth. | When organizations pursue aggressive growth strategies in highly competitive and uncertain markets, and prioritize speed to capture market share quickly. | Offers a framework for strategic planning in high-growth, competitive environments, and emphasizes the importance of speed and market domination. | May not be suitable for all businesses, as it prioritizes speed over efficiency and may involve higher risks. Requires careful consideration of market dynamics and competition. |
| Pretotyping | Pretotyping is a methodology to validate business ideas by creating simplified, low-cost versions of products or services. It helps in understanding customer preferences and demand before investing in full-scale development. It focuses on answering critical questions about the product or service. | When organizations want to reduce the risk of building products or services that do not meet customer needs or preferences, validate ideas quickly, and make informed decisions about development. | Enables cost-effective validation of ideas, provides insights into customer preferences, and helps in making data-driven decisions before significant investments. | The effectiveness of pretotyping depends on the accuracy of assumptions and may not cover all aspects of product development or market dynamics. |
| Value Innovation and Blue Ocean Strategy | Blue Ocean Strategy involves creating new, uncontested markets by delivering superior value at lower costs. It focuses on breaking the cost-value trade-off and making competition irrelevant. It is used when organizations seek to redefine market boundaries and create new market space. | When organizations want to pursue growth by offering innovative products or services that create uncontested markets, reduce competition, and provide superior value to customers. | Can lead to the creation of new markets and reduced competition, offering unique value propositions to customers. It encourages innovative thinking and differentiation. | Requires innovative thinking and may involve significant changes to existing business models. Implementation can be challenging, and market acceptance may vary. |
| Growth Hacking Process | Growth hacking is a process of rapid experimentation and iterative testing to achieve rapid growth. It involves cross-functional collaboration between marketing, product development, data analysis, and engineering teams to optimize the entire customer acquisition funnel. | When organizations aim to achieve rapid and sustainable growth, optimize customer acquisition, and improve conversion rates by using data-driven experimentation and collaboration across teams. | Accelerates growth by optimizing the entire customer acquisition funnel, encourages data-driven decision-making, and fosters cross-functional collaboration. | Requires access to data and resources for experimentation, and success depends on the effectiveness of experimentation and collaboration across teams. |
| Pirate Metrics | Pirate Metrics, represented by the acronym AARRR (Acquisition, Activation, Retention, Referral, Revenue), provide a simplified model for tracking and analyzing user behavior through various stages of the customer journey. It helps organizations focus on key metrics for growth. | When organizations want to track and analyze user behavior at different stages of the customer journey, improve user acquisition, activation, retention, referrals, and revenue generation by focusing on key metrics. | Simplifies tracking and analysis of user behavior, provides a structured framework for growth metrics, and helps in identifying areas for improvement in the customer journey. | May not cover all aspects of customer behavior and may require customization based on specific business models and objectives. |
| Engines of Growth | The Engines of Growth framework, as defined in the Lean Startup, identifies three mechanisms for achieving sustainable growth: the sticky engine, viral engine, and paid engine. It helps in measuring and tracking key metrics associated with each engine and planning growth strategies accordingly. | When organizations want to understand and measure the mechanisms that drive sustainable growth, whether through user retention, viral marketing, or paid acquisition channels, and plan their growth strategies accordingly. | Provides a clear framework for identifying and measuring different engines of growth, allowing organizations to focus on the most effective strategies for their specific context. | Requires accurate measurement and tracking of key metrics associated with each engine of growth. The effectiveness of each engine may vary based on the business model and target audience. |
| RTVN Model | The RTVN Model is a straightforward framework for designing a business model. It helps in identifying the key elements required for business success, particularly in the early stages. It focuses on defining the right target audience, value proposition, and necessary resources. | When organizations are at the early stage of defining their business model and need a simple framework to identify the critical elements required for success, including the target audience, value proposition, and resources. | Offers a simple and structured approach to business model design, particularly useful for startups and early-stage businesses. Helps in defining the fundamental components needed for business success. | May not cover all aspects of business modeling and strategy, and it may need to be complemented with more detailed analysis as the business evolves. |
| Sales Cycle | A sales cycle is the process that a company follows to sell its products or services. It involves a series of steps and interactions between sales representatives and prospects, leading to the closing of a sale. Planning the sales cycle helps in growing business revenues by improving sales effectiveness. | When organizations want to improve sales effectiveness, enhance revenue generation, and provide a structured approach for sales representatives to engage with prospects and close deals. | Provides a structured approach to sales activities, improves sales team efficiency, and ensures a systematic process for converting prospects into customers. | May vary based on the complexity of the sales process and the type of products or services offered. Effectiveness depends on sales team training and execution. |
| Comparable Analysis | Comparable Company Analysis is a process used to identify and analyze similar organizations that can be used as benchmarks for understanding the business and financial performance of a target company. It helps in assessing the competitive landscape and valuation. | When organizations need to assess the financial and competitive position of a target company, perform valuation analysis, or gain insights into industry dynamics by comparing the target company with similar organizations. | Provides valuable insights into the target company’s financial performance, competitive positioning, and industry benchmarks. Supports informed decision-making in mergers, acquisitions, and investments. | Requires access to relevant financial and market data and may involve challenges in finding truly comparable companies in certain industries or market conditions. |
| Porter’s Five Forces | Porter’s Five Forces is a model that analyzes the competitive forces within an industry to assess its attractiveness and profitability. It examines the bargaining power of suppliers, buyers, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and competitive rivalry. It helps organizations understand industry dynamics. | When organizations want to gain a better understanding of their industry’s competitive forces, assess market attractiveness, and make strategic decisions based on industry dynamics and competitive positioning. | Provides a structured framework for industry analysis and helps organizations identify competitive advantages and potential threats. Supports strategic planning and decision-making by assessing market dynamics. | May require extensive research and data collection to assess each of the five forces accurately. The model’s effectiveness may vary depending on the industry and market conditions. |
| AIDA Model | The AIDA Model (Attention, Interest, Desire, Action) is a marketing model that describes the stages a customer goes through before making a purchase decision. It helps organizations understand and optimize the customer journey by focusing on attention, interest, desire, and action. | When organizations want to understand the customer’s decision-making process, improve marketing effectiveness, and optimize the customer journey by tailoring messaging and strategies to different stages of the AIDA model. | Provides a structured framework for understanding and optimizing the customer journey, aligns marketing efforts with customer behavior, and improves messaging and conversion strategies. | May not capture all aspects of the customer decision-making process and may require adaptation to specific industries or target audiences. The effectiveness depends on the relevance of the AIDA model to the business context. |
| PESTEL Analysis | PESTEL Analysis is a framework used to assess the macroeconomic factors affecting an organization. It examines Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors. It helps organizations identify potential threats and opportunities in the external environment. | When organizations need to evaluate the impact of external factors on their business, identify potential threats and opportunities, and make informed strategic decisions based on a comprehensive analysis of the macroeconomic environment. | Offers a systematic approach to analyzing external factors, enhances strategic planning by considering a broad range of influences, and helps organizations adapt to changing market conditions. | May require extensive data collection and analysis, and the relevance of specific factors may vary across industries and regions. External factors can change rapidly, requiring ongoing monitoring and adaptation. |
| Technology Adoption Curve | The Technology Adoption Curve classifies users into five stages: innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, and laggards. Each stage represents a psychographic profile of users willing to adopt technology products. It helps in targeting the right audience for tech products. | When organizations want to identify the target audience for technology products, plan marketing strategies, and understand the psychographic characteristics of users at different stages of technology adoption. | Provides a simple framework for targeting the right audience, tailoring marketing efforts, and understanding the adoption patterns of technology products. Helps in aligning product strategies with user preferences. | The adoption curve may not apply universally to all technology products, and user behavior can vary based on product type and context. It may require additional research to validate the adoption stages for specific products. |
| Business Model Essence | Business Model Essence, according to FourWeekMBA, is a concise description that captures the critical characteristics of any business in a few sentences. It helps analyze existing businesses or draft business models with a focus on key elements for short to medium-term execution. | When organizations want a concise and clear understanding of the critical characteristics of a business, whether for analysis of existing businesses or for creating a strategic focus on key elements for short to medium-term execution. | Provides a simple and focused description of the essential components of a business, facilitating clear communication and strategic alignment. Helps in prioritizing key elements for execution. | May oversimplify complex business models, and its effectiveness depends on the accuracy of the essence in capturing critical characteristics. It may not cover all nuances of the business model. |
| FourWeekMBA Business Model Framework | The FourWeekMBA Business Model Framework emphasizes two dimensions: the people dimension and the financial dimension. It highlights the importance of creating a product or service that is significantly better than existing offerings and ensuring financial sustainability through effective distribution channels. | When organizations want to develop a comprehensive business model that focuses on delivering superior value to customers, building a strong brand, and achieving financial sustainability through targeted distribution channels. | Emphasizes the dual importance of creating a superior product and achieving financial sustainability. Provides a holistic view of business modeling by considering both people and financial aspects. Helps in strategic planning and execution. | May require careful consideration of brand-building and distribution strategies to ensure success. Effectiveness depends on the ability to deliver a product or service that is significantly better than existing offerings. |
Connected Analysis Frameworks
Failure Mode And Effects Analysis



































Related Strategy Concepts: Go-To-Market Strategy, Marketing Strategy, Business Models, Tech Business Models, Jobs-To-Be Done, Design Thinking, Lean Startup Canvas, Value Chain, Value Proposition Canvas, Balanced Scorecard, Business Model Canvas, SWOT Analysis, Growth Hacking, Bundling, Unbundling, Bootstrapping, Venture Capital, Porter’s Five Forces, Porter’s Generic Strategies, Porter’s Five Forces, PESTEL Analysis, SWOT, Porter’s Diamond Model, Ansoff, Technology Adoption Curve, TOWS, SOAR, Balanced Scorecard, OKR, Agile Methodology, Value Proposition, VTDF Framework, BCG Matrix, GE McKinsey Matrix, Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model.
Main Guides:









