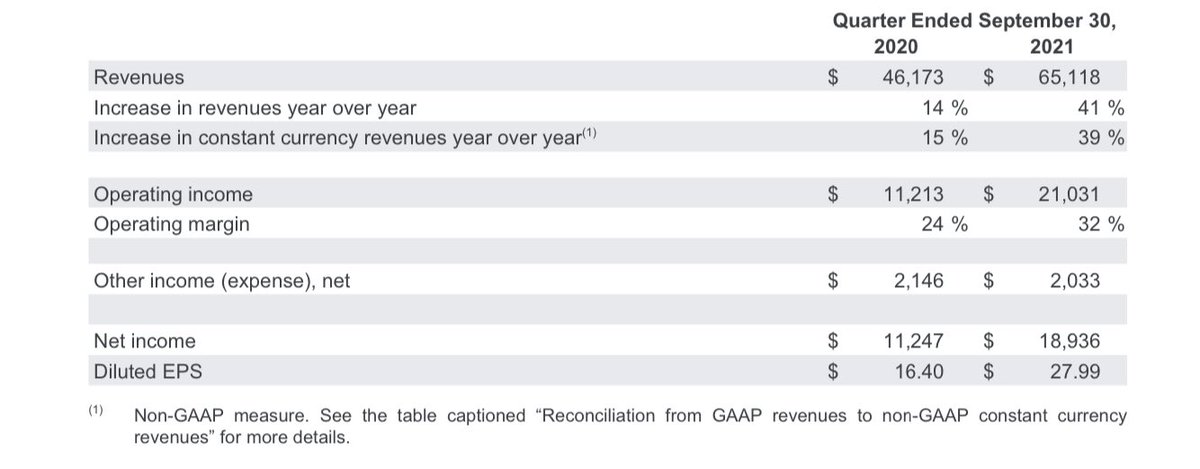
| Company Advertising Segment | 2023 |
| Alphabet (Google, YouTube) | $237.85B |
| Meta (Facebook, Instagram) | $131.95B |

While Google and Facebook rely on advertising as the primary source of revenue, they are two completely different business models.
Both are attention-based or attention merchants, yet there are many key differences.

In which ways Google and Facebook are different?
Advertising: Google is search-based, whereas Facebook is feed-based
In short, on Google, you get advertising based on searches that users input into it.
Compared to the feed, search is a pull mechanism, where Google needs to interpret the intent behind the users’ search to serve ads properly.
On the other hand, for Facebook, the ad machine works by pushing relevant ads to users in their feeds.
It’s important to highlight that also Google has changed a lot in the last few years. And today, in many cases (like Google Discover, and YouTube), also Google’s advertising is more similar to that of Facebook.
Vertical Integration: whereas Google is vertically integrated, owning the whole data supply chain, Facebook is not
In fact, Google has successfully built over the years its supply chain, starting from the operating system (Android), browser (Chrome), and tools (Google search and others) to power up the whole ecosystem.
In addition to that, Google now has also a successful line of hardware products, its Pixel phones, which represent a further step in controlling the supply chain of data.
In fact, by having its smartphones in the hands of millions of people, Google can enhance the distribution of its products and speed up the testing of new products.
On the contrary, Facebook has never built a successful smartphone or hardware for consumers.
This is quite limiting and the reason why Facebook has been pushing toward the Metaverse, with the hope of building a valuable device for VR.
That only happened in part with the acquisition of Oculus, which as of now, though, is more of a gaming console than else.
Cost Structure: Google shares revenues, Facebook does not
In fact, even though most of Google’s revenues come from its properties, Google also has a network for publishers (AdSense) that shares revenues with them.
In addition, YouTube, part of Google’s family of products, also has a mechanism of revenue sharing with creators, which enabled a whole ecosystem to thrive and become stronger and stronger over the years.
This wasn’t true for Facebook, which enjoyed wider margins than Google over the years, as it didn’t share revenues with its creators; over time, this went against the company.
In the current scenario, where a competitor offers more opportunities to creators to monetize their content, many might flock to an alternative platform.
Read Next: Google Business Model, Google Subsidiaries, What Happened To Google Glass?, What happened to Google Plus?, How does Google Maps make money?, Who Owns Google?, How Does YouTube Make Money?, History of Youtube, How Do YouTubers Make Money?
Related Visual Stories












Facebook Organizational Structure












Google Traffic Acquisition Costs










Main Free Guides:
- Business Models
- Business Competition
- Business Strategy
- Business Development
- Digital Business Models
- Distribution Channels
- Marketing Strategy
- Organizational Structure
- Platform Business Models
- Revenue Models
- Tech Business Models
- Blockchain Business Models Framework
Read next:


![How Does Facebook [Meta] Make Money? Facebook Business Model Analysis 2024 facebook-business-model](https://i0.wp.com/fourweekmba.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/facebook-business-model.png?resize=150%2C113&ssl=1)