Among the most recognized car manufacturers, Tesla is valued more than the combined market capitalization of GM and Ford. The company’s direct distribution is a strength. The key when it comes to Tesla is about understanding the size of the market the company is creating, which combines EVs, autonomous driving, energy storage and distribution, and real-time insurance.
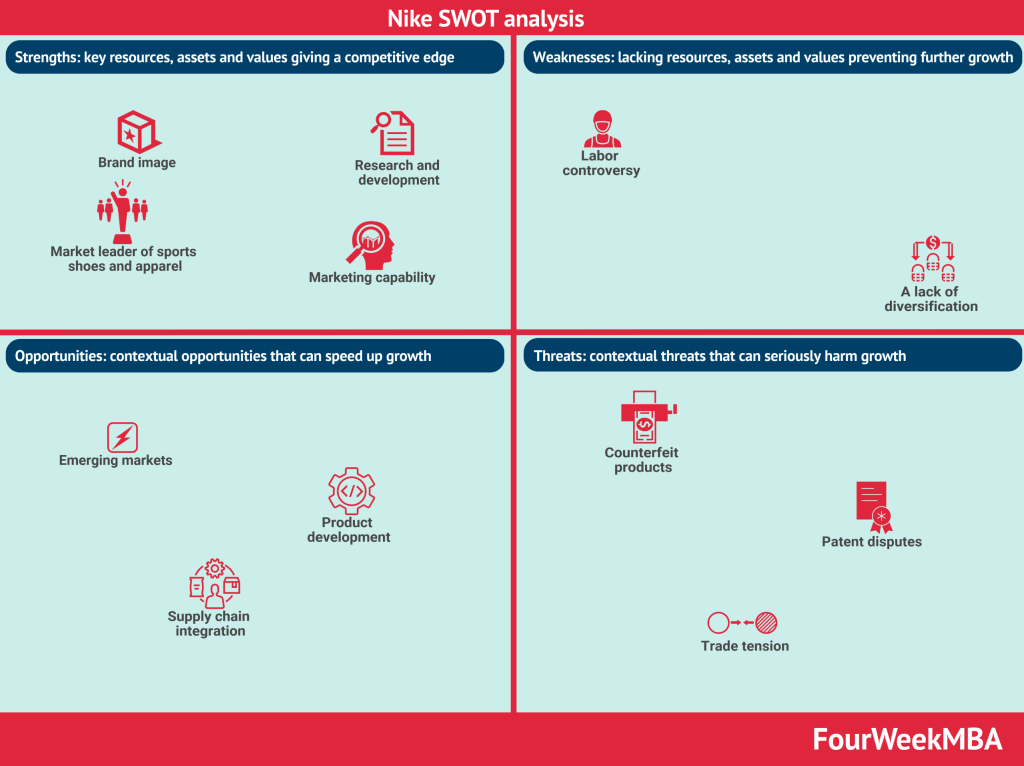
Tesla’s strengths

- Strong brand: Tesla has been able in the last decade to become among the most recognized brand, also thanks to its rockstar CEO, Elon Musk. A single tweet from Elon Musk is worth more than a hundred press releases from major publications. And that helped.
- Direct distribution: Tesla benefits from a direct distribution model, where the cars are primarily sold in its store or online, and thus Tesla is able to cut the middlemen, thus still able to offer the car at an attractive price (at least the Model 3).
- Manufacturing: Tesla has been investing massive resources in building up its own manufacturing facilities, which will be the company’s most important assets for years to come.
Tesla’s weaknesses

- Single-sourced supply chain: while the company still sources most of the components from multiple suppliers, there are still certain, important components that are single-sources. This is in part normal in the car manufacturing space. Yet Tesla tries to prevent the risk of being without the proper stock to assemble the cars by piling stocks of components that are single-sources.
Tesla’s threats
- Competition from leading brands: while Tesla is a recognized brand, it’s still a small player in a niche (electric cars) in the automotive industry. This makes Tesla easily attacked by dominating existing brands.
- Still low electrical vehicle adoption: Tesla is surfing the growth of the electric car industry growth. If that becomes an industry larger than the current automotive industry, then Tesla will be well-positioned for that. However, if that doesn’t happen Tesla won’t be of as much value. And while the company can control part of this process, another part cannot be controlled.
- Delays or other complications in the design, manufacture, launch, and production: if Tesla fails in its go-to-market strategy this can result in big, substantial losses. Therefore, the company will need to make sure to be able to reach its targets in terms of manufacturing and also in developing the proper capability for its manufacturing facilities.
Tesla’s opportunities

Tesla has become among the most recognized car manufacturers. Although, players like GM and Ford delivered more than 2mln cars, compared to Tesla’s over 367K vehicles. Yet Tesla is valued three times more than the combined market capitalization of GM and Ford as the market sees the potential of a market that might become much bigger than the current one.
This huge market potential is reflected in Tesla’s valuation, and the company able to develop new products categories in the space can become a “price setter” where its products will be so differentiated that the company might enjoy good margins for a long time!
Is Tesla a car company?
When Apple launched the iPhone, that indeed was a phone, but it was way more than that, it was a portable computer with Internet access.
The iPhone not only captured the largest market shares of the phone industry, but it also expanded the whole market.
Making the mobile phone market size increase exponentially. And Apple, as of 2022, still takes advantage of this market.

Tesla has borrowed Apple’s playbook to build a business model, starting with cars, but it goes way beyond that.
Is Tesla a car company?
It is, yet, just like the phone industry has been completely reshaped with the iPhone. The car industry is getting completely reshaped with the Tesla EVs.
In fact, Tesla is a car company, a self-driving company, an AI company, a storage and energy distribution company, and more.
This is on the basis of what I like to call market expansion theory.

In short, just like in the 2010s, you could be called a mobile phone company if you just produced the hardware.
Today, the smartphone industry combines hardware, software, and the marketplace.
Therefore, going forward, when we’ll talk about the car industry, we’ll mean something completely different compared to what we think of today, and much much larger.
In fact, EVs combined with self-driving and AI will exponentially grow the size of what, today, we call the car industry.
Just like, in the previous decade what we called the mobile phone industry turned into the smartphone industry.
Key Highlights:
Strengths:
- Vertically integrated operations from manufacturing to distribution.
- Strong brand recognition and leadership of Elon Musk.
- Direct distribution model allows cost savings and control over pricing.
Weaknesses:
- High reliance on automotive sales for revenue.
- Some components single-sourced, posing supply chain risk.
Opportunities:
- Potential for market expansion due to growth in EVs, autonomous driving, energy storage, and real-time insurance.
- Tesla’s brand and innovative products could establish it as a dominant player in new industries.
Threats:
- Competition from established automotive brands.
- Uncertainty in EV market growth and adoption rates.
- Risk of delays or complications in production and manufacturing processes.
Key Takeaways:
- Tesla’s vertically integrated approach and innovative products differentiate it in the automotive industry.
- The company’s potential extends beyond traditional car manufacturing into various interconnected industries.
- Market expansion theory suggests that Tesla’s influence could reshape the concept of the car industry, similar to how smartphones transformed the mobile phone industry.
Read next: Tesla Business Model
Read more: What Is A SWOT Analysis
Related to Tesla


















Read Also: Tesla Business Model, Elon Musk Companies, Who Owns Tesla, Transitional Business Models, Tesla Competitors.
Read Also: Who Is Elon Musk? The Elon Musk’s Story, How Does Elon Musk Make Money, Elon Musk Companies, Bill Gates Companies, Jeff Bezos Companies, Warren Buffett Companies.
How did Tesla use a transitional business model to thrive?
More resources:
- Apple Business Model
- Amazon SWOT Analysis
- Business Models
- Digital Business Models Map
- Business Strategy
- Marketing Strategy
SWOT Analysis Case Studies
















Read Next: SWOT Analysis, Personal SWOT Analysis.









