Uber’s pricing strategy revolves around dynamic pricing, using surge pricing to match real-time demand. They employ various pricing strategies such as surge pricing during peak hours, differentiated pricing based on service levels, and promotional incentives to attract and retain customers. The strategy aims to optimize revenue, manage demand, and address challenges posed by regulatory constraints and customer perception.
| Pricing Strategy | Description | Example | Implications | Integration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Pricing (Surge Pricing) | Uber uses dynamic pricing to adjust fares in real-time based on supply and demand. Prices increase during high-demand periods, such as rush hours or bad weather. | During a rainstorm, Uber fares may increase significantly to incentivize more drivers to become available and meet increased rider demand. | – Maximizes revenue during peak periods. – Encourages driver availability in high-demand areas. – May lead to price sensitivity and rider dissatisfaction. | Dynamic pricing is integral to Uber’s strategy, allowing it to balance supply and demand effectively. It aligns with the upfront pricing feature to provide transparency and enables flexibility in pricing based on real-time conditions. |
| Ride Types and Tiers | Uber offers various ride types and service tiers, each with different pricing structures. These tiers range from economy to premium and include options like UberX, Uber Black, and UberPool. | Uber Black offers premium vehicles and professional drivers at a higher price point compared to UberX, which features standard vehicles and drivers. | – Attracts a wide range of customer segments. – Offers price flexibility and customization. – Ensures accessibility with various service options. | Ride types and tiers are core to Uber’s strategy, catering to diverse rider preferences and budgets. They integrate with dynamic pricing and upfront pricing, allowing riders to choose the service that aligns with their needs and expectations. |
| Upfront Pricing | Uber introduced upfront pricing, where riders are shown the estimated fare before booking a ride. This feature provides transparency and eliminates fare uncertainty. | Riders can see the total cost of their trip, including any surge pricing, before confirming the ride. | – Enhances transparency and rider trust. – Reduces uncertainty and surprises related to fares. – Encourages more bookings. | Upfront pricing aligns with Uber’s commitment to transparency and customer satisfaction, reducing the chances of fare disputes and promoting trust between riders and the platform. It complements other pricing strategies, ensuring a seamless booking experience. |
| Promotions and Discounts | Uber frequently runs promotions and offers discounts to riders to encourage usage and compete with rival ride-sharing services. Promotions may include discounted rides or free rides for first-time users. | New riders often receive a promo code for a discounted or free first ride with Uber. | – Attracts new users and retains existing ones. – Boosts rider loyalty and engagement. – Mitigates price sensitivity. | Promotions and discounts are integrated into Uber’s strategy, allowing it to compete effectively in the ride-sharing market and incentivize riders to use the platform. They complement upfront pricing and loyalty programs, enhancing the overall customer experience. |
| Subscription Services | Uber offers subscription services like Uber Pass and Uber Eats Pass, providing subscribers with benefits like discounted fares and free delivery on Uber Eats orders. | Uber Pass subscribers pay a monthly fee for discounted rides and other perks, making it more cost-effective for frequent riders. | – Encourages rider loyalty and recurring revenue. – Increases ridership frequency. – Provides cost savings for frequent users. | Subscription services are an integral part of Uber’s strategy, offering riders additional value and encouraging them to use the platform regularly. They integrate with upfront pricing, ensuring that subscribers receive transparent and discounted fares. |
| Loyalty Programs | Uber Rewards is a loyalty program that rewards frequent riders with points for every dollar spent on eligible services. Points can be redeemed for benefits like Uber Cash or priority support. | Frequent Uber riders can accumulate points and enjoy various benefits, such as discounts or faster customer support response times. | – Fosters rider loyalty and engagement. – Encourages repeat usage and spending. – Enhances the overall rider experience. | Loyalty programs complement Uber’s strategy by rewarding and retaining frequent riders, increasing customer retention, and aligning with subscription services and promotions to create a more comprehensive and rewarding experience for users. |
| Geographic Pricing | Uber may adjust pricing based on geographic location, with higher prices in areas of high demand or during special events. Pricing can vary significantly between cities and regions. | Fares in a major metropolitan area during a peak event, like a concert or sports game, may be higher than in less populated areas. | – Maximizes revenue in high-demand areas. – Reflects regional variations in supply and demand. – Provides flexibility for pricing strategies. | Geographic pricing allows Uber to adapt to local market conditions and maximize revenue. It integrates with dynamic pricing, enabling the platform to respond to real-time demand fluctuations in specific geographic regions. |
| Price Transparency | Uber aims to provide transparency in pricing by detailing the fare breakdown for riders. The breakdown includes the base fare, distance traveled, time spent in the ride, and any additional fees. | Riders can review the fare details in the app after completing a trip to understand how the total cost was calculated. | – Enhances rider trust and confidence. – Reduces disputes related to fares. – Provides clarity on pricing components. | Price transparency aligns with Uber’s commitment to providing riders with a clear understanding of their trip costs. It complements upfront pricing and ensures that riders have full visibility into how their fares are calculated. |
| Business and Corporate Pricing | Uber for Business offers customized pricing and billing solutions for corporate clients and organizations, allowing for centralized billing and expense management. | Companies can negotiate pricing agreements with Uber for their employees’ business travel needs, streamlining expenses and transportation logistics. | – Targets the corporate and business travel market. – Simplifies expense management for organizations. – Provides tailored pricing solutions. | Business and corporate pricing integrates with Uber’s strategy by expanding its customer base to include corporate clients. It aligns with the ride types and tiers strategy, allowing businesses to choose the service that suits their employees’ needs. |
| Accessibility Pricing | Uber offers affordable options for riders with accessibility needs, such as UberAssist and UberWAV (Wheelchair Accessible Vehicles), with pricing that reflects the specific services provided. | Riders with mobility challenges can choose accessible ride options at prices that consider the specialized features and support required. | – Addresses the needs of riders with disabilities. – Ensures fair and inclusive pricing. – Provides accessible transportation options. | Accessibility pricing is integrated into Uber’s strategy, reflecting the platform’s commitment to inclusivity and accessibility. It aligns with ride types and tiers, ensuring that riders with diverse needs can access suitable services at reasonable prices. |
Definition and Overview
- Uber Pricing Strategy: Uber, a global ridesharing and transportation company, employs dynamic pricing, often referred to as “surge pricing” or “price surges.” This pricing strategy involves adjusting fares in real-time based on supply and demand dynamics in a particular geographic area.
- Dynamic pricing aims to balance the number of available drivers with the number of ride requests to ensure efficient and reliable service, especially during peak demand periods or special events.
Key Concepts and Components
- Real-Time Adjustments: Uber’s pricing algorithm continuously analyzes data to make fare adjustments in real-time. Factors such as time of day, location, weather conditions, traffic congestion, and local events influence pricing.
- Upfront Pricing: Uber introduced “Upfront Pricing,” which provides passengers with an estimated fare before they request a ride. This transparency allows riders to know the approximate cost of their trip in advance, even during surge pricing periods.
- Multiplier System: Surge pricing is often implemented using a multiplier system. For example, a 2x surge means that the fare will be double the usual rate, while a 3x surge triples it.
- Heat Maps: Uber provides drivers with heat maps that show areas with high demand. Drivers can use this information to position themselves strategically to take advantage of surge pricing.
The Uber Pricing Process
- Demand Analysis: Uber’s algorithm constantly collects data on ride requests, driver availability, and external factors like traffic conditions and events.
- Surge Trigger: When demand in a particular area exceeds the supply of available drivers, the algorithm triggers surge pricing.
- Multiplier Calculation: Surge pricing multipliers are calculated based on the extent of demand and the available supply of drivers in the area.
- Passenger Notification: Passengers are notified of surge pricing and the corresponding multiplier before confirming their ride request.
- Supply Attraction: Surge pricing aims to attract more drivers to high-demand areas by offering them higher earnings potential, thereby increasing the supply of available rides.
Benefits and Applications
- Balancing Supply and Demand: Uber’s dynamic pricing helps match the number of available drivers with passenger demand, ensuring that riders can access rides when they need them, even during peak times.
- Driver Incentives: Surge pricing incentivizes drivers to make themselves available in areas with high demand, resulting in shorter wait times for passengers.
- Price Transparency: Upfront pricing provides transparency to passengers, allowing them to make informed decisions about whether to accept the fare during surge periods.
Challenges and Considerations
- Perception of Unfairness: Surge pricing has faced criticism for being perceived as unfair, especially during emergencies or unexpected high-demand situations.
- Competition: Ridesharing companies, like Lyft, also use dynamic pricing, and competition can influence pricing strategies.
- Regulatory Concerns: Some regions and governments have implemented regulations or restrictions on surge pricing to protect consumers from excessive fares.
Key Highlights
- Dynamic Pricing Focus: Uber’s pricing strategy is centered around dynamic pricing, utilizing surge pricing based on real-time demand and supply.
- Competitor Analysis: The company analyzes competitor pricing and market positioning to stay competitive.
- Customer Segmentation: Uber considers different customer segments and their price sensitivity.
- Cost-Effective Operations: Pricing decisions incorporate operational costs and profitability.
- Surge Pricing: Uber employs surge pricing during peak hours and high-demand periods.
- Differentiated Pricing: Various pricing options are offered for different service levels.
- Promotional Incentives: Promotions and discounts attract and retain customers.
- Revenue Optimization: Pricing is optimized to achieve increased revenue and profitability.
- Demand Balancing: Dynamic pricing helps manage demand and supply effectively.
- Customer Attraction: Competitive and flexible pricing options attract and retain customers.
- Regulatory Challenges: Uber navigates various pricing regulations in different markets.
- Transparent Pricing: Ensuring customers perceive pricing as fair and transparent is crucial.
- Competition Management: Uber addresses competitor reactions to pricing changes.
- Economic Adaptation: Pricing strategies are adjusted to economic conditions and fluctuations.
Visual Stories Related To Uber Business Model





In 2022, Uber mobility took 27% of each booking on the platform. At the same time, Uber Eats took 20% of each booking on the delivery platform. The take rate varies according to demand and supply but also market dynamics. In short, in periods of increased competition, the service might charge lower take rates to keep up with it. In 2022, Uber pushed on efficiency, thus raising its take rates, to move toward profitability.
Uber Platform Users
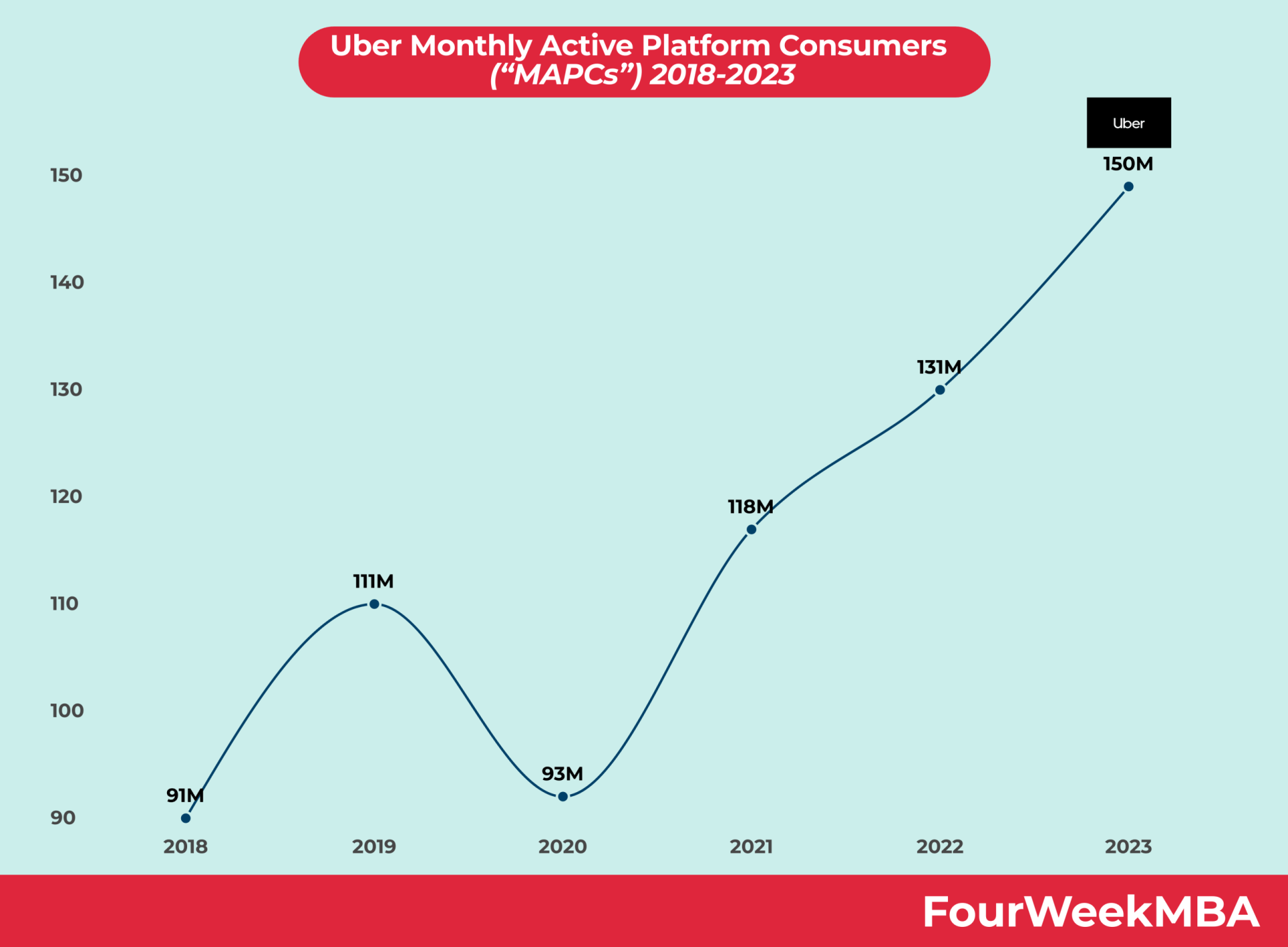











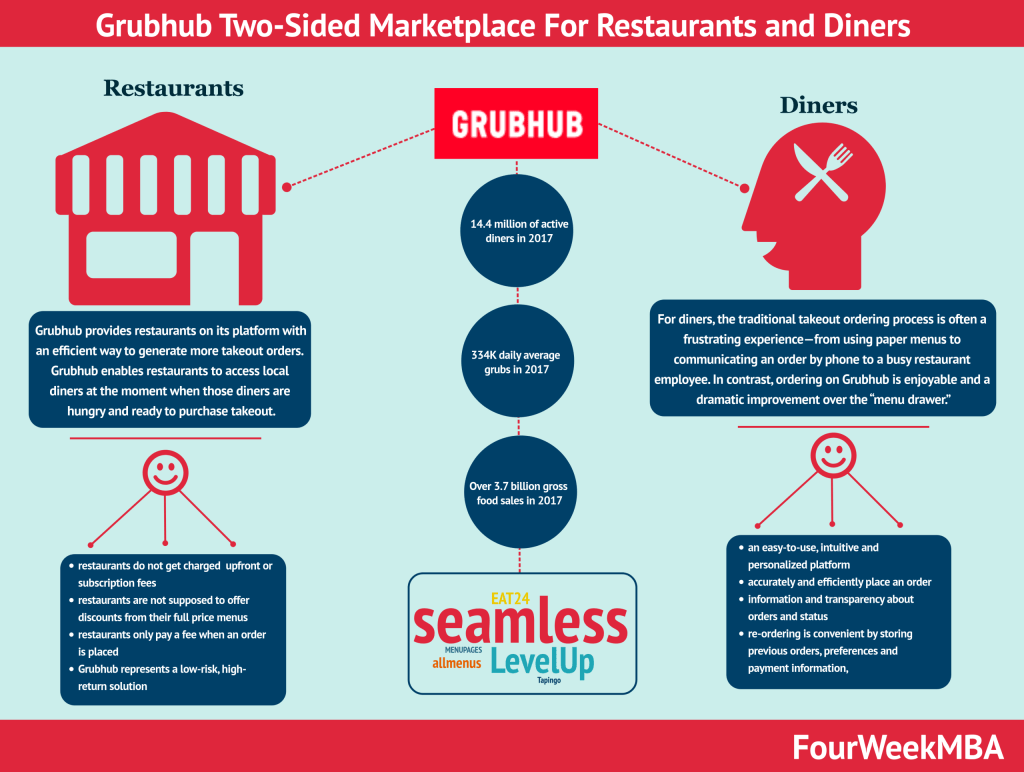

Pricing Related Visual Resources










Read Next: Pricing Strategy.
Connected Business Concepts










Business resources:
- Successful Types of Business Models You Need to Know
- The Complete Guide To Business Development
- Business Strategy: Definition, Examples, And Case Studies
- What Is Market Segmentation? the Ultimate Guide to Market Segmentation
- Marketing Strategy: Definition, Types, And Examples
- Marketing vs. Sales:
- How To Write A Mission Statement
- What is Growth Hacking?
- Growth Hacking Canvas
Handpicked popular case studies from the site:








