- Food delivery as a service began in Ancient Rome, with the first online food order reputed to have been facilitated by Pizza Hut in 1994. Today, the online food delivery industry is vast and innovative, driven largely by millennial consumer expectations around quality and convenience.
- In North America, DoorDash enjoys market dominance with approximately 57% market share. Uber Eats and Grubhub are also significant players in North American, with the former leveraging its ride-sharing success to increase awareness and popularity of online food delivery.
- Two companies with a more unique product offering are Instacart and Postmates. Instacart is a grocery delivery and pick-up service utilizing personal shoppers, while Postmates is an on-demand goods delivery service similarly utilizing couriers to deliver almost any type of item in metro areas.
Origin Story
In the food delivery business model companies leverage technology to build platforms that enable users to have the food delivered at home.
This business model usually is set up as a platform and multi-sided marketplace, where the food delivery company makes money by charging commissions to the restaurant and to the customer.
The history of food delivery stretches back further than many realize, with the ancient Romans delivering takeaway meals in clay pots to keep them warm.
The first online food order was accepted by Pizza Hut in 1994, one of the relatively few businesses at the time to utilize a revolutionary food ordering platform. Today, the online food delivery industry is vast, innovative, and no longer confined to fast-food restaurants. Much of the growth in the industry has been driven by millennial and other time-poor consumers desiring convenient yet high-quality food delivery.
Consumers can now order virtually any cuisine they desire from countless participating restaurants. How food is ordered is also rapidly changing. Food orders are now placed through social media, smartwatches, cars, and television screens. What’s more, food delivery is no longer the exclusive domain of traditional vehicles, with robots and drones now playing an important role.
Forbes estimates the online food delivery industry will be worth $200 billion by 2025. With that said, let’s take a look at some of the companies vying for a lucrative slice of this market.
Uber Eats



Uber Eats is an online food ordering and delivery platform launched by Uber in 2014.
Though it was not the first company to offer online food delivery, the growth of its ridesharing service and the sharing economy more generally resulted in food delivery companies receiving more attention.
Uber Eats uses machine learning to suggest specific cuisines and restaurants to consumers based on their order history and other contextual information. Restaurant managers using the platform also get access to data enabling them to refine their food quality and delivery strategy to increase user satisfaction.
Now operating in more than 32 countries, Uber Eats utilizes car, scooter, bike, and foot transport to courier meals to consumers.

Grubhub
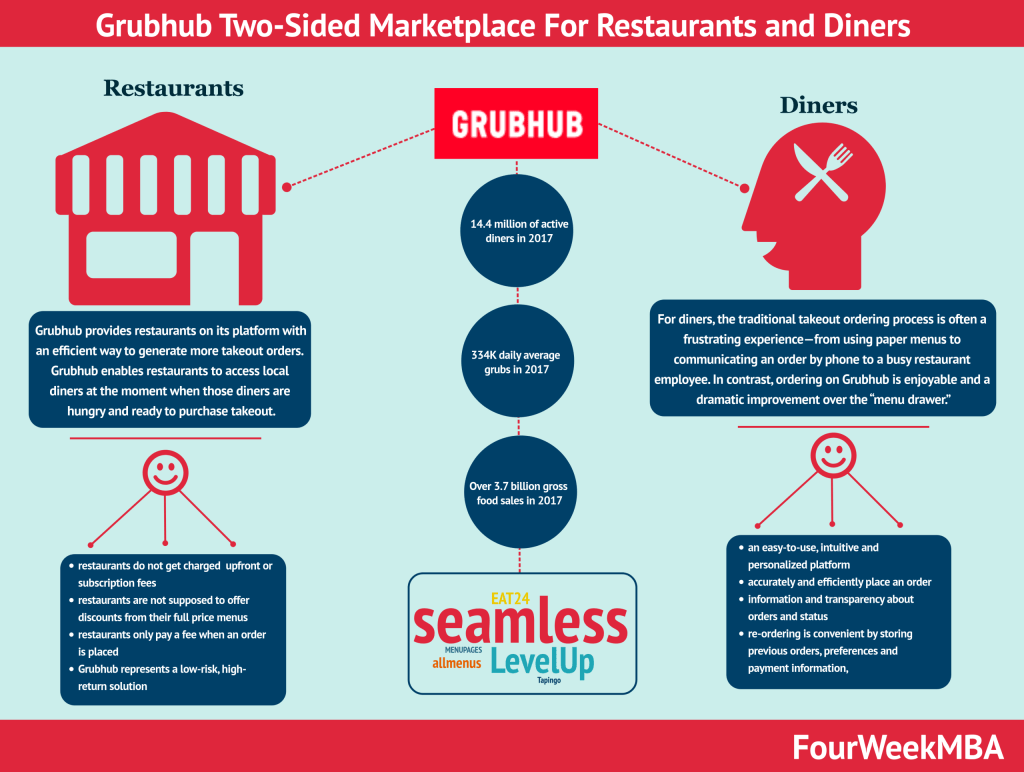
Grubhub is a Chicago-based company founded in 2004 by Matt Maloney and Mike Evans, with the service initially created to provide an alternative to paper menus. Some consider Grubhub to be the first modern food delivery company as most define them today.
In 2011, Grubhub merged with Seamless, an even earlier iteration of online food delivery launched in 1999. Around the same time Uber Eats was launched, Grubhub had been in operation for a decade and was starting to offer delivery to restaurants without a delivery service.
In June 2021, leading online food delivery marketplace Just Eat Takeaway acquired Grubhub for $7.3 billion. The acquisition created the largest online food delivery company outside of China.
DoorDash

DoorDash was founded by Stanford University students Tony Xu, Stanley Tang, Andy Fang, and Evan Moore in January 2013.
The company is known for its technology and innovation, opening its first ghost kitchens in 2019 and becoming one of the first to offer contactless delivery during the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic.
DoorDash also partnered with Starship Technologies to offer robot-assisted deliveries, with the technology being used to make contactless delivery to frontline healthcare workers in the United Kingdom.
DoorDash and its various subsidiaries are the market leader in the United States, capturing approximately 57% of meal delivery sales during July 2021.
Instacart

Instacart is another American food delivery service founded in 2012 by Apoorva Mehta, Max Mullen, and Brandon Leonardo. The company has a focus on grocery delivery and pick-up, with orders assembled for the customer by a personal shopper.
Instacart works with supermarket chains and also local grocers, servicing around 40,000 stores across 5,500 cities in North America.
While the company offers the largest such service in the United States, it suffered from chronic inventory shortages as a result of increased demand during the pandemic in 2020. Instacart is also besieged by a growing cohort of competitors, with CEO Mehta now focused on warding off Amazon in particular in his quest to digitize the grocery retail sector.
Postmates

Postmates is a food delivery service founded in 2011 by Bastian Lehman, Sam Street, and Sean Plaice. The company has an on-demand goods delivery platform enabling consumers in metropolitan areas to get almost anything delivered to their doors for a small fee.
For this reason, Postmates is often referred to as the Uber of food delivery. Comparisons between the two companies have also been drawn because Postmates couriers get order notifications on their smartphones. The company then uses GPS to match demand and supply in the shortest, most convenient way.
Postmates was acquired in July 2020 by Uber for $2.65 billion in an all-stock deal.
Examples of Food Delivery Companies:
- Uber Eats:
- Uber Eats is a three-sided marketplace connecting drivers, restaurant owners, and customers.
- It generates revenue through commissions from restaurants and delivery charges from customers.
- Utilizes machine learning for personalized food recommendations.
- Offers food delivery through various transportation methods, including cars, scooters, bikes, and foot couriers.
- Grubhub:
- Founded in 2004, Grubhub initially aimed to provide an alternative to paper menus.
- Merged with Seamless in 2011 and was later acquired by Just Eat Takeaway in 2021.
- Considered one of the pioneers of modern food delivery.
- Offers a wide range of food delivery options beyond fast food.
- DoorDash:
- Employs a platform business model that enables restaurants to set up delivery operations.
- Generates revenue through delivery fees, memberships, and restaurant advertising.
- Known for innovation, including ghost kitchens and contactless delivery.
- Market leader in the United States with approximately 57% of meal delivery sales.
- Instacart:
- Focuses on grocery delivery and pick-up services.
- Collaborates with supermarket chains and local grocers.
- Charges service fees, membership fees, and runs performance advertising.
- Faced inventory shortages during the 2020 pandemic but remains a major player in grocery delivery.
- Postmates:
- Founded in 2011 as a last-mile delivery service platform.
- Offers on-demand goods delivery in metropolitan areas.
- Generates revenue through various fees, including commission, delivery, service, cart, and cancellation fees.
- Known as the “Uber of food delivery” and was acquired by Uber in 2020 for $2.65 billion.
Key Highlights of the Food Delivery Business Model:
- Historical Roots: Food delivery dates back to Ancient Rome, with the first online food order accepted by Pizza Hut in 1994.
- Market Growth: Forbes estimates the online food delivery industry to be worth $200 billion by 2025.
- Consumer Evolution: Millennial and time-poor consumers have driven the demand for convenient and high-quality food delivery.
- Diverse Ordering Channels: Orders are now placed through various channels, including social media, smartwatches, cars, and TVs.
- Delivery Innovation: The industry has witnessed innovations such as robot-assisted deliveries and drone deliveries.
- Market Dominance: DoorDash holds a 57% market share in North America, with Uber Eats and Grubhub also significant players.
- Unique Players: Instacart focuses on grocery delivery with personal shoppers, while Postmates offers on-demand goods delivery in metro areas.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: Just Eat Takeaway acquired Grubhub, and Uber acquired Postmates in multi-billion dollar deals.
| Aspect | Description | Advantages | Drawbacks | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Restaurant Delivery | This model involves restaurants offering their own delivery services to customers. Restaurants hire their own delivery drivers or use in-house resources to fulfill orders placed directly through their websites or phone calls. | – Restaurants have more control over the delivery process. – Opportunities for branding and customer engagement. – Potential cost savings by avoiding third-party delivery fees. – Ability to offer exclusive menu items and promotions. | – Requires significant investment in staff and logistics. – Limited reach compared to third-party delivery platforms. – Restaurants may face challenges in managing delivery operations efficiently. – May miss out on the customer base of third-party delivery apps. | Pizza Hut, Domino’s, Subway |
| Aggregator Model | Aggregator platforms act as intermediaries between restaurants and customers. They offer websites and mobile apps that allow users to browse menus, place orders, and track deliveries from multiple restaurants in one place. | – Variety of restaurant options for users. – Convenience and ease of ordering from multiple restaurants. – Restaurants can access a broader customer base. – Marketing and promotion opportunities through aggregator platforms. | – Restaurants pay commissions to aggregators for each order. – Limited control over the delivery process and customer data. – Competition among restaurants on aggregator platforms. – Aggregator apps may prioritize certain restaurants over others. | Uber Eats, DoorDash, Grubhub |
| Delivery-Only Kitchens | Also known as ghost kitchens or cloud kitchens, these facilities are dedicated to preparing food for delivery and takeout orders. They often house multiple virtual restaurant brands operating from the same kitchen space. | – Lower overhead costs compared to traditional restaurants. – Ability to experiment with multiple virtual restaurant concepts. – Focused on delivery and takeout, catering to changing consumer preferences. – Access to data and analytics for optimizing menus and operations. | – Limited opportunities for dine-in or in-person experiences. – Challenges in managing multiple virtual brands efficiently. – Requires investment in kitchen facilities and delivery infrastructure. – Dependence on third-party delivery platforms for reaching customers. | Kitchen United, CloudKitchens |
| Meal Kit Delivery | Meal kit companies deliver pre-portioned ingredients and recipes to customers, allowing them to cook restaurant-quality meals at home. Customers subscribe to meal kit services and receive weekly or monthly deliveries. | – Convenience of cooking at home without grocery shopping. – Variety of meal options and dietary preferences. – Reduced food waste with pre-portioned ingredients. – Opportunity to discover new recipes and cooking techniques. | – Subscription-based model requires ongoing customer retention efforts. – Packaging and shipping logistics can be complex and costly. – Competition in the crowded meal kit industry. – Sourcing high-quality and fresh ingredients can be a challenge. | Blue Apron, HelloFresh, Sun Basket |
| Grocery Delivery | Grocery delivery services enable customers to order groceries online and have them delivered to their doorstep. These services are offered by both traditional grocery stores and online-only retailers specializing in grocery products. | – Convenience of online grocery shopping and home delivery. – Access to a wide range of grocery items and brands. – Scheduled deliveries to accommodate customers’ routines. – Opportunity for subscription-based models and loyalty programs. | – Highly competitive market with thin profit margins. – Challenges in ensuring the freshness and quality of perishable items. – Reliance on efficient logistics and last-mile delivery capabilities. – Need for partnerships or in-house supply chain management. | Instacart, Amazon Fresh, Walmart Grocery |
Read Next: Uber Eats Business Model, GrubHub Business Model, DoorDash Business Model, Instacart Business Model, Postmates Business Model.
Main Free Guides:









