Uber Eats is a three-sided marketplace connecting a driver, a restaurant owner, and a customer with the Uber Eats platform at the center. The three-sided marketplace moves around three players: Restaurants pay commission on the orders to Uber Eats; Customers pay small delivery charges and, at times, cancellation fees; Drivers earn through making reliable deliveries on time. Uber Eats generated $12.2B billion in revenues in 2023, representing almost 33% of Uber’s total revenues.

Uber Business Model Short Description
We describe the Uber Eats business model via the VTDF framework developed by FourWeekMBA.
| Uber Eats Business Model | Description |
| Value Model: Flexible Delivery/Last-Mile Provider. |
The ambition of Uber Eats is to become the go-to last-mile delivery platform. It started with food delivery but aspires to become the go-to place for last-mile delivery.
|
| Technological Model: Three-Sided Network Effects. |
Uber Eats enjoys complex three-sided network dynamics between eaters, restaurants, and drivers. The underlying platform gives riders and drivers additional options (food delivery beyond car-sharing rides). Plugging in restaurants and food partners makes the network more valuable, as an entrepreneurial ecosystem is created on top of Uber Eats business model.
|
| Distribution Model: Branding/Growth Hacking, Deal Making, Lobbying. |
Like Uber, Uber Eats’ distribution leverages a solid brand and infrastructure built over the years and a “lobbying playbook” to connect with local and national policymakers to stabilize the service worldwide.
|
| Financial Model: Platform’s Tax. |
Uber Eats consists of a platform that, by connecting three leading players (eaters, drivers, and restaurants) collects. As a result, a tax for each booking on top of the platform + commissions from restaurants and eaters.
|
Uber Eats Business Model Today

During the pandemic, the delivery platform became a key driver for overall Uber’s growth. In 2021, the delivery platform saw a 114% growth rate!
Yet, by 2022, the delivery business has become a key component of Uber’s business model.
And yet, as things got back to normal and travel restrictions were removed, Uber’s core (mobility) platform returned to become the company’s leading segment.

The delivery platform, though, passed the gross bookings compared to the mobility platform throughout the pandemic.
The delivery platform was instrumental to Uber during the pandemic’s travel restrictions.
Aad, in a way, showed that Uber could use the network effects from the core platform (mobility) to successfully revamp new business segments, like delivery.
Thus, where the pandemic negatively impacted the mobility platform, the delivery was boosted by it.
This two-headed approach helped Uber successfully pass these years. And as of 2022, the mobility platform is back on track, again the company’s core segment.

However, and this is a crucial point to remark on, Uber is no longer just a ride-sharing platform; it’s a three-head company spanning three segments: mobility, delivery, and freight!
Uber Eats Background Story
Uber – The world’s largest ride-share company took an interesting turn in 2014 when it gave birth to “Uber Eats,” called initially Uber Fresh.
Getting food delivered from your favorite local restaurants became as easy as requesting a ride!
Fast forward to today, Uber is heavily investing in the Uber Eats model. The food delivery business is growing fast and gaining momentum around the world.
- Why is Uber building the world’s largest food delivery platform?
- Is it valuable for Uber to turn its drivers into a reliable delivery fleet?
In this post, you’ll learn why Uber is betting big on the Uber Eats business model, its value proposition, operational components, and what it means for the future of Uber.
Related: How Does Uber Make Money? Uber Business Model In A Nutshell
A 3-sided Marketplace Business
Uber Eats is a three-sided marketplace connecting a driver, a restaurant owner and a customer with Uber Eats platform at the center.
- Restaurants pay commission on the orders to Uber Eats.
- Customers pay the small delivery charges and at times, cancellation fee.
- Drivers earn through making reliable deliveries on time.
Source: eng.uber.com
A six-point value proposition
- Blazing fast delivery: Uber Eats promises to deliver within 30 minutes in most of the cities where they are currently operational. It works on the principle that “We don’t want your food traveling halfway across town.”
- No minimum order concept: The customers can order their favorite snack instead of a full meal. The standard delivery fee ensures that all orders are fulfilled irrespective of the order value.
- Existing customer base: Probably, the most valuable asset of all. They already have millions of active Uber users across the globe who can be potential Uber Eats users.
- Better utilization of Uber’s resources: They already have cars/drivers on the road and an effective system to manage it. The inclusion of Uber Eats will only help to increase the utilization across Uber’s different verticals. For example, a cabbie who just finished a trip may handle a food delivery order right afterward.
- A top class algorithm: The algorithm developed by Uber does a great job in neatly organizing the prime factors in online food delivery system. i.e., order management, order allocation and order dispatch.
- The global presence: How hard it would be for them to leverage Uber’s global dominance to scale the business of Uber Eats? Not that hard! While they may face local competitors in every market they penetrate, a competitor with such a global stronghold would be hard to beat!
How ‘Uber Eats’ Makes Money
The chart below completely describes the revenue flow in the Uber Eats ecosystem:
- Standard Delivery Fee OR Convenience Fee: Uber Eats charges a flat delivery fee from its customers irrespective of the order value. The charges vary from $1 to $5 depending on the market they are operating in.
- Recurring Revenue Share from Restaurant Partners: Uber Eats takes a cut of 15% to 40% on every order that is fulfilled from the Restaurant partners. Uber Eats decides the percentage of the commission depending on the age and maturity of the market.
- Marketing & Advertising Fee from Restaurant Partners: Uber Eats is helping their restaurant partners attract more customers and reach a larger customer base by offering customer-facing brand campaigns, relatable social posts and email marketing to Uber’s rider base.
How much Uber Eats pay for their delivery partners or drivers?
The delivery partner’s fee is mainly divided into three segments which are pickup fee, delivery fee and per mile fee also referred to as mileage fee.
The exact figures of these charges vary from region to region. A customer can tip the delivery partners if they want to and 100% of this tip would be allocated to the delivery partner only.
Uber Eats’ Cost-Saving Factors
You’ve heard the saying “Every Penny Saved is Every Penny Earned”? Uber Eats, with its unique three-sided marketplace business model, is both cost-effective and efficient than its competitors.
- Lesser Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) and Shared Marketing Expenses: The current marketing and advertising expense incurred by Uber Eats is comparatively less since it’s getting most of its users through cross-promotion on the Uber App.
- Shared Network of Drivers & Riders: The drivers and riders on Uber double up to work as the delivery fleet, which eases the pain of setting up a delivery network from scratch.
- Savings on Logistics Costs: A well-defined unit economics helps in saving big on the logistics cost as multiple food orders on the same route can be delivered in a single delivery run.
Uber Eats’ Unit Economics
YOU ordered an apple-pie from XYZ restaurant that is priced at $50 Order Value + $5 Delivery Charges. The order will be delivered by ME at your door and ME is currently 3 miles away from your location.
Approximately, this is how the unit economics should reflect:
- Amount paid by YOU: $50 + $5 = $55
- Amount received by XYZ restaurant: $50 – (30% commission on order) = $35
- Delivery Charges: Pickup Fee + Delivery Fee + Per Mile Charges = $4 + $2 + ($2 x 3) = $12
- Net Revenue for Uber Eats = ($55 – $35) – $12 = $8
The Future of Uber Eats
Launched as a last-mile delivery initiative in 2014, Uber Eats, during the pandemic, has pivoted to become a key segment within Uber’s business model, contributing to 44% of the company’s revenue by 2022.
Uber has been doing a great job in innovating and captivating new markets with its exceptional approach.
How should we look at Uber’s presence in this space in a crowded market that is already crowded with online food ordering and delivery platforms?
Is food delivery the real endgame, or are we witnessing the time-honored “sustaining innovation” curve leading to Uber Everything? Only time will tell!
Uber Eats, an advertising business?

One of the most interesting points to make here, in the Uber Eats business model analysis, is that in 2022, Uber launched a new advertising platform segment.
The interesting take here is that Uber Eats proved exceptionally well suited for this sort of revenue stream, as merchants on top of the platform (mostly restaurants) are looking for additional visibility on Uber Eats to boost their orders and widen their customer base.
Indeed, by 2022, Uber generated $500 million in advertising, mainly from Uber Eats sponsored listings!
Key Highlights
- Introduction:
- Uber Eats: A three-sided marketplace connecting drivers, restaurant owners, and customers for food delivery.
- Founded in 2014 as an extension of Uber’s services.
- Value Proposition:
- Flexible Delivery/Last-Mile Provider: Aims to become the go-to last-mile delivery platform for a variety of products beyond food.
- Technological Model:
- Three-Sided Network Effects: Complex dynamics between eaters, restaurants, and drivers create a valuable ecosystem.
- Leveraging Uber’s existing infrastructure and brand.
- Distribution Model:
- Branding/Growth Hacking, Deal Making, Lobbying: Utilizes strong brand presence, lobbying efforts, and partnerships.
- Financial Model:
- Platform’s Tax: Collects revenue through various sources, including delivery fees, commission from restaurants, and advertising.
- Revenue Generation:
- Standard Delivery Fee/Convenience Fee:
- Charges flat delivery fee ($1 to $5) irrespective of order value.
- Recurring Revenue Share from Restaurant Partners:
- Takes 15% to 40% commission on orders from restaurant partners.
- Marketing & Advertising Fee from Restaurant Partners:
- Delivery Partners’ Earnings:
- Earnings from pickup fee, delivery fee, and mileage fee.
- Customers can also tip delivery partners.
- Standard Delivery Fee/Convenience Fee:
- Cost-Saving Factors:
- Lesser Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) through cross-promotion.
- Shared network of drivers and riders for deliveries.
- Savings on logistics costs due to efficient unit economics.
- Future Direction:
- Uber Eats as a key segment within Uber’s business model.
- Potential expansion beyond food delivery, contributing to 44% of Uber’s revenue by 2022.
- Advertising Business Segment:
- Uber Eats launched an advertising segment, generating $500 million in revenue in 2022.
- Sponsored listings provide visibility for restaurants and brands, complementing the platform’s services.
- Key Points:
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Value Proposition | Uber Eats offers the following value propositions for its customers: – Convenience: Providing fast and convenient food delivery services. – Diverse Selection: Offering a wide variety of cuisines and restaurants. – Transparent Pricing: Clear and transparent pricing with delivery fees. – Tracking and Updates: Real-time order tracking and status updates. – Payment Options: Multiple payment methods, including cashless transactions. – Promotions and Discounts: Regular promotions and discounts for cost savings. |
| Core Products/Services | Core products and services provided by Uber Eats include: – Food Delivery Platform: An app and website for customers to browse menus and place orders. – Delivery Fleet: A network of delivery drivers and couriers. – Restaurant Partnerships: Collaborations with restaurants and eateries. – Payment Gateway: Secure payment processing for orders. – Customer Support: Assistance for order inquiries and issues. – Rating and Reviews: Customer feedback and restaurant ratings. – Promotions and Rewards: Offering promotions and rewards to customers. |
| Customer Segments | Uber Eats targets various customer segments: – Consumers: Individuals and families seeking food delivery services. – Restaurants: Partnering with various restaurants and eateries. – Delivery Partners: Independent contractors providing delivery services. – Corporate Customers: Providing catering services to businesses and offices. – Food Entrepreneurs: Offering an option for new food businesses to reach a wider audience. – Event Planners: Catering services for events and gatherings. |
| Revenue Streams | Uber Eats generates revenue through several revenue streams: – Delivery Fees: Charges for delivering orders to customers. – Service Fees: Commissions from restaurants for facilitating orders. – Promotional Fees: Fees from restaurants for running promotions and discounts. – Advertising: Earnings from advertising and featured listings for restaurants. – Subscription Services: Revenue from premium subscription services like Eats Pass. – Delivery Partner Fees: Earnings from delivery partner sign-up and service fees. – Licensing: Licensing agreements with restaurants for their inclusion on the platform. |
| Distribution Strategy | The distribution strategy for Uber Eats focuses on speed and efficiency: – Mobile App and Website: Providing a user-friendly platform for customers to place orders. – Delivery Fleet: Employing a network of delivery drivers and couriers for timely order fulfillment. – Restaurant Partnerships: Collaborating with restaurants to offer their menus on the platform. – Payment Gateway: Ensuring secure and seamless payment processing. – Customer Support: Offering responsive customer support for order-related inquiries and issues. – Rating and Reviews: Encouraging customer feedback and restaurant ratings for quality control. – Marketing and Promotions: Running marketing campaigns and promotions to attract and retain customers. |
Visual Stories Related To the Uber Business Model





In 2022, Uber mobility took 27% of each booking on the platform. At the same time, Uber Eats took 20% of each booking on the delivery platform. The take rate varies according to demand and supply but also market dynamics. In short, in periods of increased competition, the service might charge lower take rates to keep up with it. In 2022, Uber pushed on efficiency, thus raising its take rates, to move toward profitability.
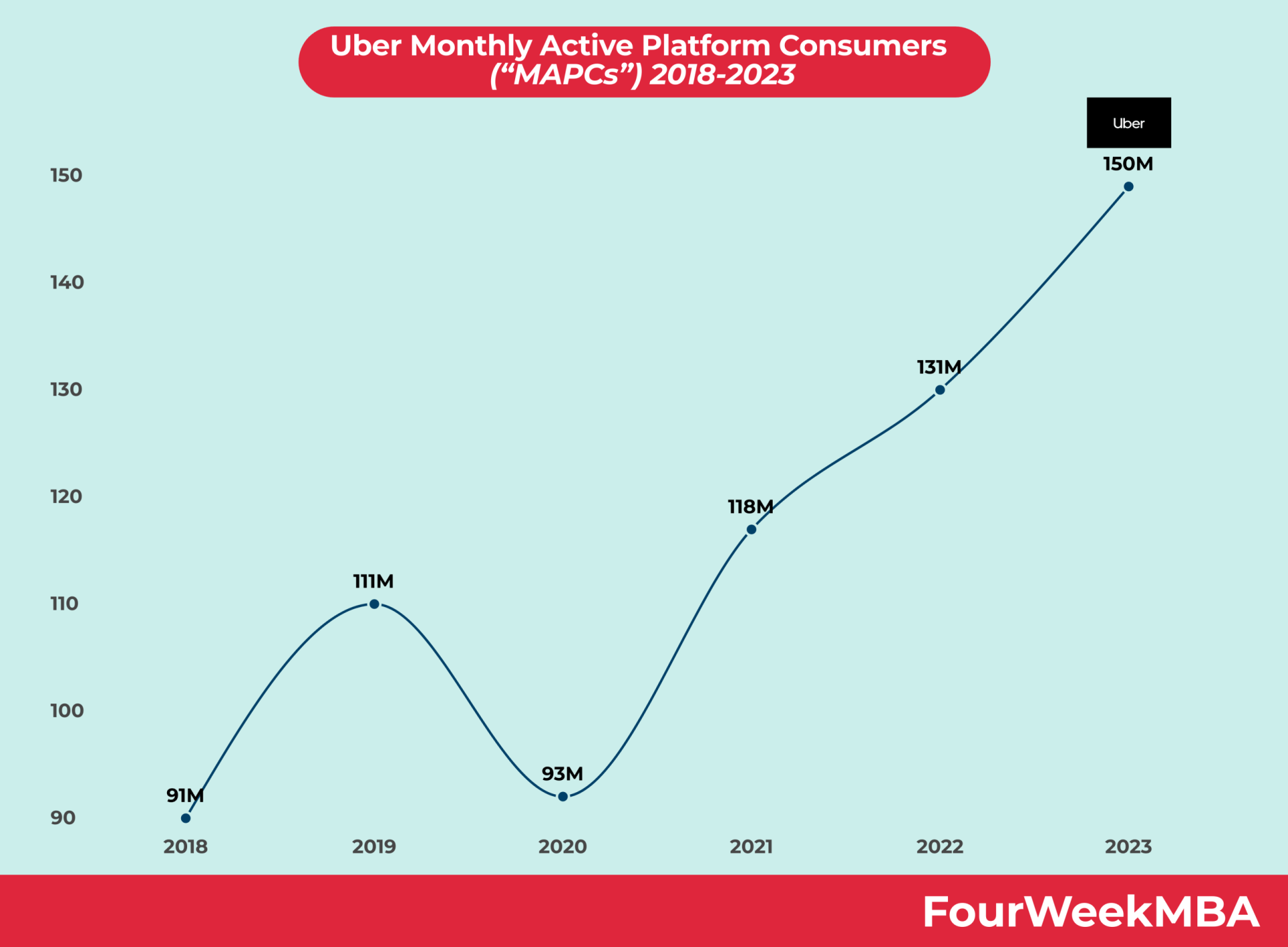
Uber Platform Users











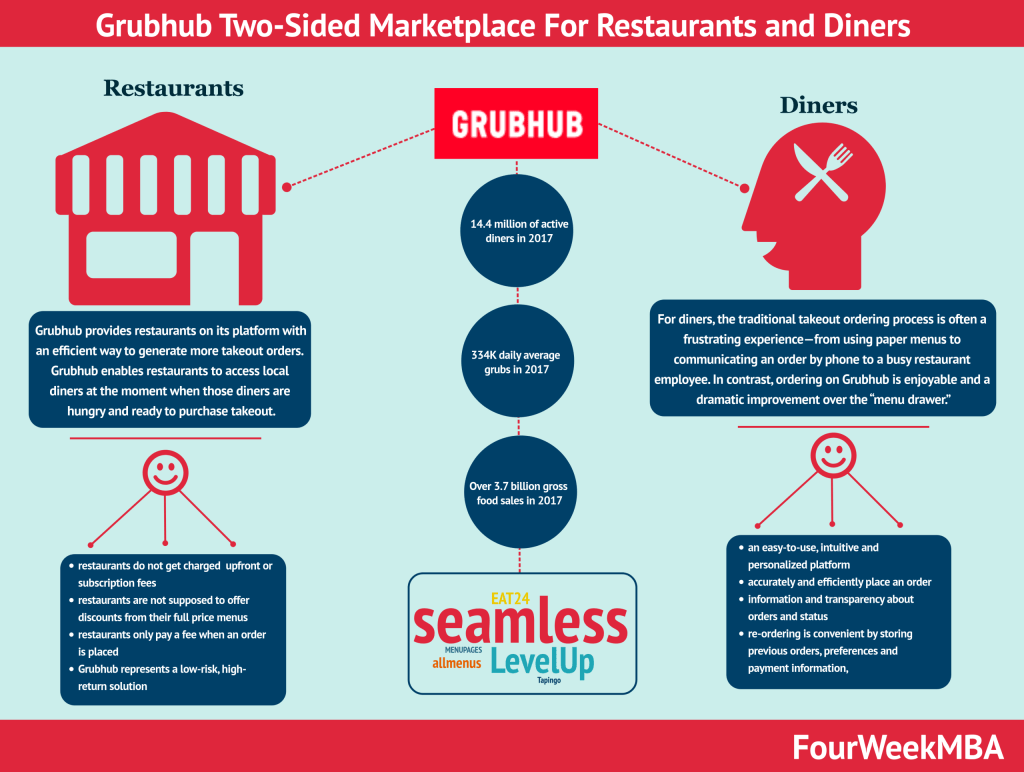


What type of business model is Uber Eats?
Uber Eats is a three-sided marketplace connecting drivers, restaurant owners, and customers. Drivers can leverage the existing Uber platform to perform additional gigs and earn extra income on top of Uber. Restaurant owners can amplify their local service reach by quickly setting up food delivery operations, thus gaining more customers. And customers can leverage the smoothness Uber platform to have food comfortably delivered to their homes.
Is Uber Eats a profitable business?
The company reported that Uber Eats was profitable during the 2021 Q3, as per its earning calls. As of 2021, this makes Uber Eats the only profitable segment of the company. Indeed, as of 2020, Uber reported net losses were over $6.7 billion.
How does Uber Eats make their money?
As a three-sided platform, the company makes money by charging fees on top of the transactions that go through the platform. More precisely, Uber Eats charges standard or convenience delivery fees ($1-5 depending on the market). It also cuts the restaurant owners’ revenues (anywhere between 15-40% of every order depending on the market). And it collects marketing and advertising fees from restaurant partners.











