For the first time in its history, in 2023, Uber became profitable, with nearly $1.9 billion in net profits. Indeed on net revenues of over $37 billion, Uber posted a net profit of $1.88 billion, compared with a net loss of $9.14 billion in 2022. In 2021, Uber posted a lower net loss ($496 million), primarily thanks to the business divestitures of various assets. Throughout its history, on an annual basis, Uber has never made a profit except for 2023, when it finally reached profitability, thanks to a shifted focus toward operational efficiency.

Understanding Uber’s financials
Over the years, Uber has created a whole new market, starting from its mobility/ride-sharing platform.

The Uber Business Model set the stage for the food delivery industry.
Indeed, as the pandemic hit, Uber’s business model also entered the delivery business with Uber Eats.

As of 2023, Uber is confirmed to be a behemoth in the mobility industry, spanning anywhere from ride-sharing to food delivery, and freight delivery.

Uber collects a fee on each transaction through its platform as a platform business model.
The fee or take rate might vary based on geography, supply, and demand, but also the ability of Uber to have consolidated market shares.

Indeed, as of 2023, take rates are higher in the ride-sharing industry, where Uber has a more consolidated, dominating position.
Whereas, in the delivery business, where competition is intense, and Uber hasn’t yet consolidated market dominance, its take rates are slightly lower.
As the financial crisis hit the world in 2022, Uber had to further re-focus its business units, thus performing various divestitures.
However, the company is still highly unprofitable.
Yet, the good news is if we look at the Uber Eats segment, this might be getting profitable (if we look at EBITDA).

And the same applies to the Uber Freight segment, which might have broken even by 2023.

Visual Stories Related To the Uber Business Model





In 2022, Uber mobility took 27% of each booking on the platform. At the same time, Uber Eats took 20% of each booking on the delivery platform. The take rate varies according to demand and supply but also market dynamics. In short, in periods of increased competition, the service might charge lower take rates to keep up with it. In 2022, Uber pushed on efficiency, thus raising its take rates, to move toward profitability.
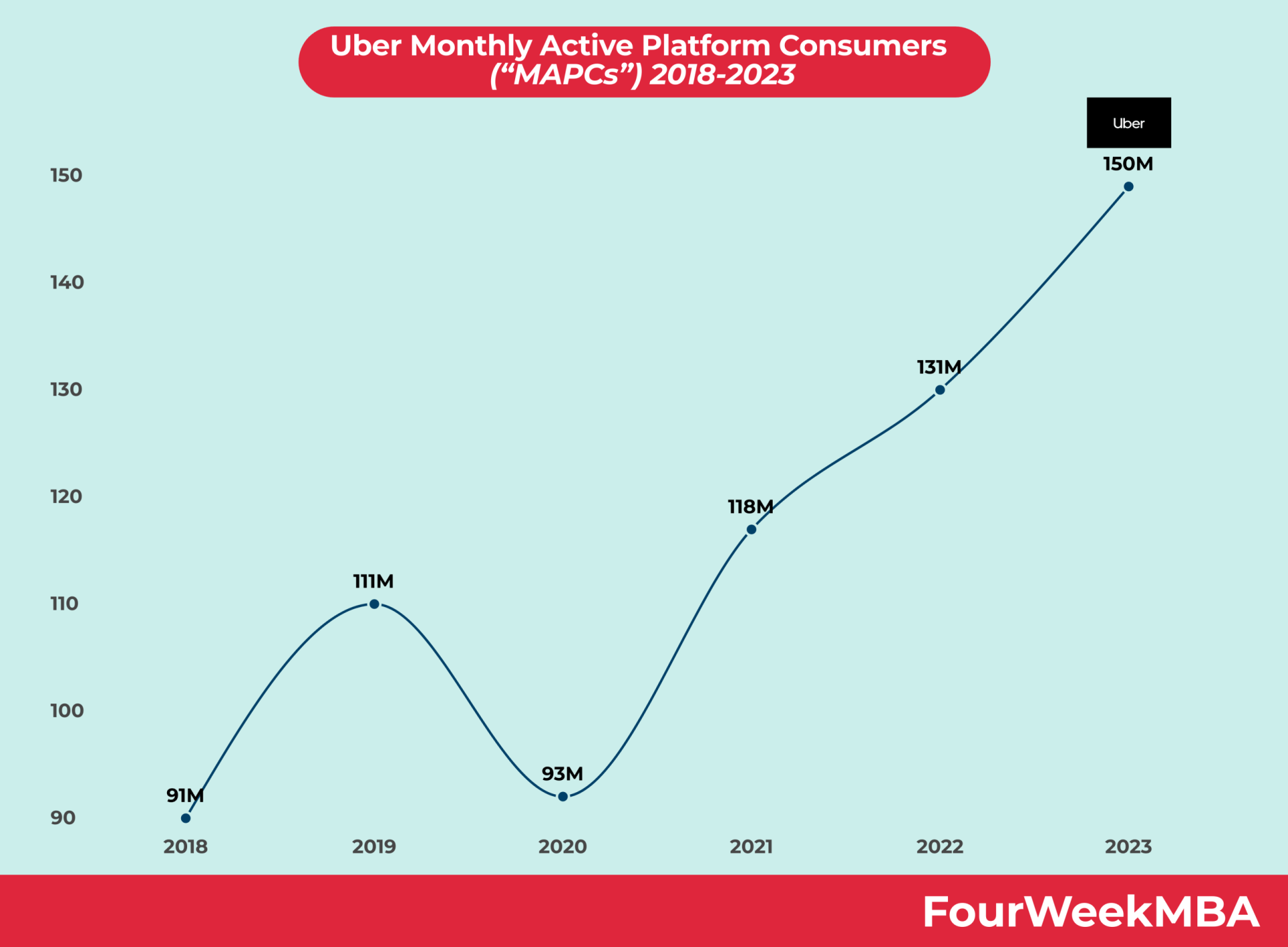
Uber Platform Users