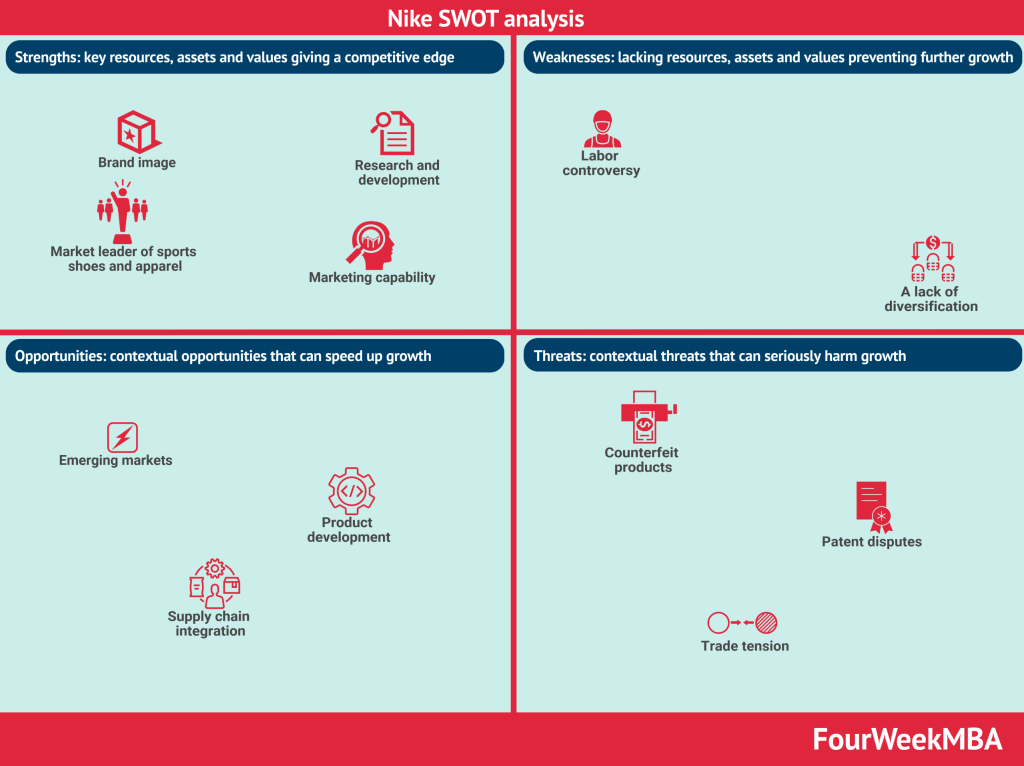
The Knight family owns Nike. Indeed, the top individual shareholder is Travis A. Knight, son of Philip Knight, co-founder of Nike, with a 7% stake in Class A stocks and a 2.4% stake in Class B stocks. On the other hand, the Knight family also controls the company tightly through their Trusts and an LLC called Swoosh (the Nike logo’s shape is a “swoosh”). Through individual shares, Swoosh LLC, and Travis Knight’s irrevocable trust, the Knight family controls over 97% of Class A and 21% of Class B stocks.
| Aspect | Description | Analysis | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Products and Services | Nike is a global sportswear and athletic footwear brand. The company offers a wide range of athletic apparel, footwear, equipment, and accessories for various sports and activities. Nike also provides digital fitness and training apps, including the Nike Training Club (NTC) and Nike Run Club (NRC). | Nike’s core offerings include athletic apparel and footwear, targeting athletes and sports enthusiasts. The brand is known for its innovative product designs and technology. Digital fitness apps enhance customer engagement and loyalty. | Nike athletic shoes (e.g., Nike Air Max), sportswear (e.g., Nike Dri-FIT), equipment (e.g., basketballs), digital fitness and training apps (e.g., Nike Training Club), accessories (e.g., Nike socks). |
| Revenue Streams | Nike generates revenue primarily through the sale of athletic footwear and apparel. Income also comes from equipment sales, accessories, and licensing agreements for the Nike brand. Nike’s digital fitness apps may generate additional income through premium subscriptions and in-app purchases. | Revenue from footwear and apparel sales represents the bulk of income, driven by brand popularity. Equipment, accessories, and licensing agreements contribute to diversified revenue streams. Digital fitness apps offer potential subscription and in-app purchase income. | Revenue from athletic footwear and apparel sales, income from equipment and accessories, licensing agreements for the Nike brand, potential income from premium subscriptions and in-app purchases in digital fitness apps. |
| Customer Segments | Nike serves a diverse customer base, including athletes, sports enthusiasts, fitness-conscious individuals, and casual wearers of athletic fashion. The brand appeals to consumers seeking performance-oriented sportswear and fashion-forward athletic styles. | Nike’s target demographic spans athletes, sports enthusiasts, fitness-conscious individuals, and fashion-conscious consumers. The brand’s focus on both performance and style broadens its appeal. Athlete endorsements enhance brand credibility. | Athletes seeking performance gear, sports enthusiasts valuing sport-specific equipment, fitness-conscious individuals using Nike for workouts, fashion-conscious consumers wearing Nike for everyday style. |
| Distribution Channels | Nike distributes its products through various channels, including its own branded retail stores, online sales through the official website and mobile app, and authorized retail partners. The company also operates the Nike Training Club (NTC) and Nike Run Club (NRC) apps for digital fitness and training content. | Branded retail stores provide a physical shopping experience. Online sales and mobile apps cater to digital-savvy customers. Authorized retail partners extend brand reach. Digital fitness apps enhance customer engagement. | Nike-branded retail stores (e.g., Niketown), online retail through the official website and mobile app, authorized retail partners (e.g., sporting goods stores), digital fitness apps (Nike Training Club, Nike Run Club). |
| Key Partnerships | Nike collaborates with professional athletes and sports teams for endorsements and sponsorships. The company also forms partnerships with authorized retailers and distributors to sell its products. Additionally, Nike may have licensing partnerships for branded merchandise. | Collaborations with professional athletes and teams build brand credibility and promotion. Partnerships with retailers ensure product availability and distribution. Licensing agreements expand the reach of Nike-branded merchandise. | Endorsement partnerships with athletes like LeBron James, partnerships with authorized retailers (e.g., Foot Locker), licensing agreements for Nike-branded merchandise (e.g., Nike x NBA apparel). |
| Key Resources | Nike’s key resources include its brand reputation, innovative product design and technology, manufacturing capabilities, retail stores, online platforms, marketing and advertising efforts, athlete endorsements, and a commitment to performance and style. | The Nike brand signifies performance and style. Innovation in product design and technology sets it apart. Manufacturing capabilities maintain product quality. Retail stores provide a physical presence. Online platforms expand accessibility. Marketing and advertising promote the brand. Athlete endorsements boost credibility. A commitment to both performance and style appeals to diverse customers. | Nike brand recognition, innovative product design and technology, manufacturing facilities, Nike retail stores, online retail platforms, marketing campaigns, athlete endorsements, commitment to performance and style. |
| Cost Structure | Nike incurs costs in product design and development, manufacturing of athletic apparel and footwear, marketing and advertising campaigns, athlete endorsements, employee salaries (including designers and athletes), retail store operations, and maintaining digital fitness apps. | Costs associated with product design and development are significant due to innovation. Manufacturing of high-quality athletic gear requires resources. Marketing and advertising campaigns are essential for brand promotion. Employee salaries, including athletes and designers, are substantial. Retail store operations entail expenses. Maintaining digital fitness apps has associated costs. | Costs related to product design and development, manufacturing of athletic gear, marketing and advertising campaigns, athlete endorsements (e.g., endorsement deals with LeBron James), employee salaries, retail store operations, maintenance of digital fitness apps. |
| Competitive Advantage | Nike’s competitive advantage lies in its iconic brand name, innovative product designs and technology, athlete endorsements, commitment to performance and style, and a diverse customer base. The brand targets athletes and fashion-conscious consumers, offering a blend of performance and style. | The Nike brand is synonymous with athletic excellence and style. Innovation in product design and technology keeps the brand ahead. Athlete endorsements provide credibility and promotion. A focus on both performance and style broadens its appeal. A diverse customer base ensures a wide reach. | Nike’s iconic brand name, innovative products like Nike Air technology, athlete endorsements by LeBron James and Serena Williams, commitment to performance and style, a wide range of customer segments. |
| Value Proposition | Nike offers customers high-performance athletic gear and stylish sportswear that empowers them to excel in their sports and activities. The brand provides innovative products, athlete endorsements, and fashion-forward styles, catering to diverse customer preferences. | Nike’s value proposition centers on delivering high-quality athletic products that enhance performance and style. Innovative technologies improve athletic performance. Athlete endorsements inspire confidence. Fashion-forward designs make a style statement. | Enhancing sports performance with Nike’s innovative products, gaining confidence from athlete endorsements, making a fashion statement with Nike sportswear and footwear. |
Understanding the difference between Class A and Class B stocks
In many instances, in companies (especially in those organizations where the initial founding team or family want to keep tight control over the company in the long term), two types of stocks are created: Class A and Class B.
The way each class of stock works in detail depends upon the way the statute has defined them.
The main take is that Class A and B stocks will have different purposes.
Generally, a class of stock is issued primarily for ownership, while another type is allocated for control.
By balancing Class A and B, key shareholders can keep tight control over strategic decisions while selling only the ownership of the companies to other shareholders interested in the stock appreciation rather than participating in the company’s decision-making.
This works exceptionally well when a listed company reaches over $100 billion in value.
It becomes interesting for large institutional investors (like pension funds) who can invest billions into the stock, thus making it much more liquid on the market.
Those institutional investors, though, will be much less active.
In the case of Nike, in 2022, the company had 304,903,252 shares of Class A Stock and 1,263,652,653 of Class B Stock.
As Nike specifies, each share of Class A and Class B Stock is entitled to one vote.
Yet, holders of Class B Stock are currently entitled to elect 25 percent of the Board.
In short, Class B stock gives more power to elect the board of the company, which
While Class A Stockholders are currently entitled to elect the remaining directors.
Under this formula, holders of Class B Stock will elect three directors at the Annual Meeting, and holders of Class A Stock will elect seven directors.
This means that Class B holders have more power over the company’s decision-making process, as they can elect most of the board members, which usually are involved into making strategic decisions.
In addition, the Knight family controls Nike via two main entities, Swoosh LLC and the Travis Knight Family Trust. Trust is an entity usually built to pass ownership from generation to generation.
Phil Knight and his family are worth $40 billion in 2023. And they have tight control over the company.

Nike is a major global brand.

Incorporating other incredible brands like Jordan.

Indeed, thanks to the incredible deal between Nike and Jordan, Michael Jordan has become a billionaire today.

Key Highlights
- Nike Ownership and Control:
- Knight Family Dominance: The Knight family, with Philip Knight as a co-founder, holds a significant influence over Nike. Travis A. Knight, Philip Knight’s son, is the top individual shareholder with a 7% stake in Class A stocks and a 2.7% stake in Class B stocks.
- Control Entities: The Knight family extends its control through Trusts and an LLC named Swoosh, which aligns with the Nike logo’s “swoosh” shape. Collectively, the Knight family, including Swoosh LLC and Travis Knight’s irrevocable trust, controls over 97.1% of Class A and 21.4% of Class B stocks.
- Class A vs. Class B Stocks:
- Purposeful Distinction: Companies often create two classes of stocks, A and B, to balance ownership and control, a practice commonly employed by founding families to retain influence.
- Ownership vs. Control: Class A shares generally signify ownership, while Class B shares are allocated for control.
- Strategic Decision-Making: This arrangement allows key stakeholders to maintain decision-making control while selling ownership shares to investors interested in stock appreciation.
- Suitable for Large Companies: This structure is particularly effective for companies surpassing $100 billion in value, making them appealing to large institutional investors.
- Nike’s Stock Structure:
- Stock Count in 2022: In 2022, Nike had 304,903,252 shares of Class A Stock and 1,263,652,653 shares of Class B Stock.
- Voting Rights: Each Class A and Class B share entitles one vote.
- Board Representation: Class B holders elect 25% of the Board, while Class A holders elect the remaining directors. This grants Class B holders more influence over strategic decisions.
- Knight Family’s Influence:
- Entities of Control: The Knight family wields authority through Swoosh LLC and the Travis Knight Family Trust, typically designed for generational ownership transfer.
- Phil Knight’s Stake: With a personal stake of 7% ownership, Phil Knight, the founder, controls Nike through shares held by Swoosh LLC and his son’s Trust. His holdings are valued at over $40 billion.
- Nike’s Brand and Revenue:
- Global Brand Status: Nike, a globally recognized brand, derives substantial revenue from various sources.
- Footwear Dominance: Nike’s revenue sources include over $29 billion from footwear, $13.5 billion from apparel, $2.35 billion from equipment, and $1.6 billion from the Converse brand in 2022.
- The Impact of Jordan Brand: The Jordan brand, integrated under Nike, follows a demand generation model. It generated more than $5 billion in revenue in 2022, contributing over 10% to Nike’s total revenue.
- Michael Jordan’s Royalties: Michael Jordan, while not owning the Jordan brand outright, receives 5% royalties from its sales. As of May 31, 2022, Nike owed him royalties of over $250 million for that year, with estimated payments nearing a billion dollars from 2018 to 2022.
Read Also: Nike Business Model, Nike Mission Statement, Nike Value Proposition, Marketing Strategy, Business Models.
Related to Nike








Related Tech Ownership Case Studies




















Read More:









