A platform company generates value by enabling interactions, transactions, or relationships. A platform company leverages network effects (direct/same side or indirect). Platform companies are also known as platform business models, given their intrinsic way of creating value for users.
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Definition | A Platform Company is an organization that leverages digital technology and infrastructure to create and manage a platform ecosystem that connects various stakeholders, such as producers, consumers, and third-party developers. These platforms serve as a foundation for enabling interactions, transactions, and the exchange of goods, services, or information. Platform companies often facilitate and benefit from network effects, where the value of the platform increases as more participants join and engage with it. Examples of platform companies include Amazon, Uber, Airbnb, and Facebook. |
| Key Characteristics | – Ecosystem: Platform companies create an ecosystem where multiple stakeholders, including users, sellers, and developers, can interact and transact. – Network Effects: The value of the platform grows as more users and participants join, creating a positive feedback loop. – Digital Infrastructure: These companies heavily rely on digital technology, cloud computing, data analytics, and connectivity to operate and scale their platforms. – Scalability: Platform companies are designed to scale rapidly, accommodating millions or even billions of users and transactions. – Monetization Strategies: They employ various monetization models, including commission fees, subscription services, advertising, and data monetization. |
| Examples | – Amazon: Amazon operates a platform that connects buyers and sellers, enabling e-commerce transactions, third-party seller services, and Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud computing. – Uber: Uber’s platform connects riders and drivers, facilitating on-demand transportation services in multiple countries. – Airbnb: Airbnb provides a platform for hosts to offer short-term lodging services to travelers. – Facebook: Facebook operates a social media platform connecting users, advertisers, and developers. |
| Impact | – Platform companies have disrupted traditional industries and business models, reshaping how products and services are delivered, consumed, and monetized. – They have the potential to reach a global audience and generate substantial revenue and market capitalization. – Platform ecosystems can foster innovation by allowing third-party developers to create new applications and services on the platform. – However, concerns related to data privacy, market dominance, and regulatory issues have arisen as platform companies have grown in influence. |
| Challenges | – Competition: Platform companies often face fierce competition from other platforms and traditional businesses. – Regulatory Scrutiny: They may encounter regulatory challenges related to antitrust, data privacy, and market dominance. – Security and Trust: Ensuring the security and trustworthiness of the platform is crucial to maintaining user confidence. – User Data: Managing and protecting user data is a significant responsibility and potential source of risk. |
What is the level of digitalization?

Based on the research of FourWeekMBA, we identified four levels of digital transformation:
- Level one: tech and digitally-enabled
- Level two: tech-enhanced
- Level three: platforms and interactions
- Level four: business ecosystem
One of the most influential business models of the digital age is the platform business model, which created a paradigm shift.
The platform business model

The platform business model requires a paradigm shift, as you need to think about “how do I sell my product” to “how do I enable others to interact and transact on top of the platform?”
This is the essence of platform business models.

Platform business models are based on three main premises:
- Network effects.
- Control points.
- Economic/Non-Economic Incentives.
The most crucial aspect of kicking off a platform and scaling it is network effects.
Platforms and network effects

Network effects can help a platform kick off, scale and maintain its relevance to users as it builds momentum.
Yet, platform business models also require a considerable amount of maintenance, engineering, and understanding of complex dynamics.
And thus, they need to make sure negative network effects are prevented.
Beware of negative network effects

In general, negative network effects can be classified in:
To understand them to read the following case studies:
Inside business platforms

The next evolution of platform business models is business platforms/ecosystems.
The epitome of it is Apple’s ecosystem.

Key Highlights
- Level one: Tech and Digitally-enabled Transformation: At this level, businesses incorporate basic digital technologies but do not fundamentally change their traditional business models.
- Level two: Tech-enhanced Transformation: Businesses at this level leverage technology to enhance their existing models and operations, making processes more efficient and effective.
- Level three: Platforms and Interactions Transformation: This level involves the adoption of platform business models, focusing on creating value by enabling interactions and exchanges among users.
- Level four: Business Ecosystem Transformation: The highest level of digital transformation involves building business platforms or ecosystems like Apple’s, which encompass various interconnected products and services.
- Platform Business Models: These models create value by facilitating exchanges among consumers, relying on network effects, control points, and economic/non-economic incentives.
- Network Effects: A phenomenon where the value of a platform increases as more users join, creating positive momentum and relevance for users.
- Negative Network Effects: In some cases, as the platform grows, it may suffer from congestion or pollution, leading to reduced value for new users.
- Apple’s Ecosystem: An example of a business platform/ ecosystem, where various interconnected products and services are offered to users, creating a seamless experience.
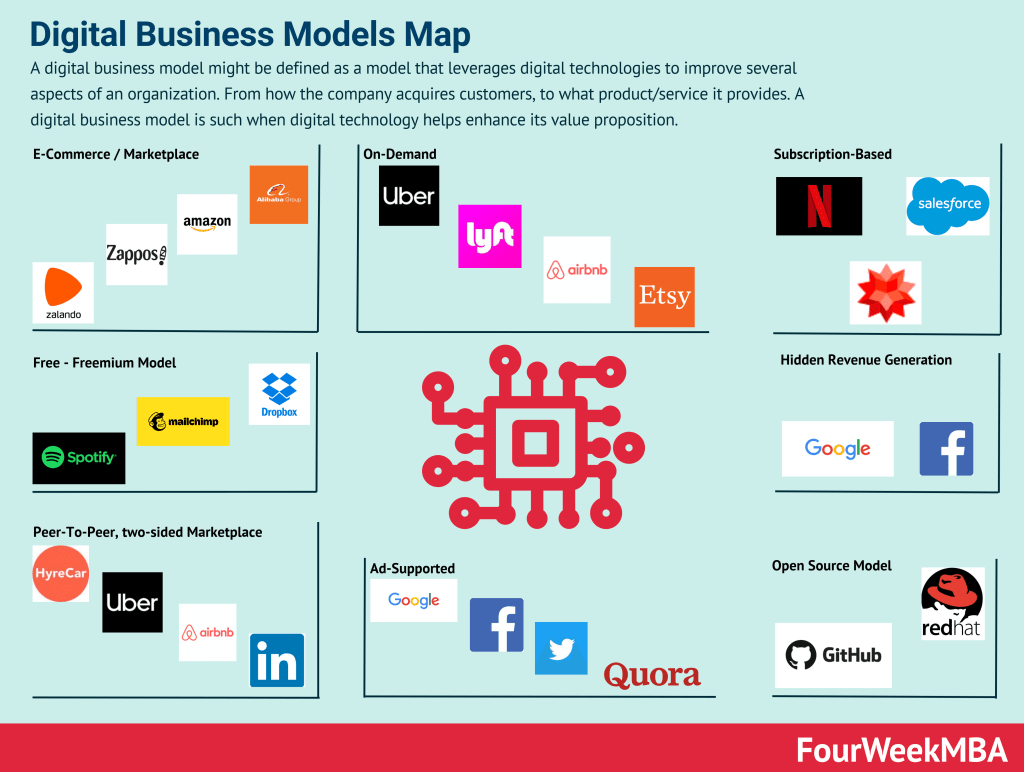
Platform Types
| Platform Business | Description | Examples | Revenue Models | Distribution Channels | Customer Segments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-commerce Marketplace | Connects buyers and sellers, facilitating transactions. | Amazon, eBay, Alibaba | Transaction fees, subscriptions, advertising. | Online, Mobile Apps, Partnerships, Affiliates | Consumers, Sellers, Retailers |
| Ride-Sharing | Connects passengers with drivers for transportation services. | Uber, Lyft, Grab | Commission on rides, surge pricing, ads. | Mobile Apps, Website, Referral Programs | Passengers, Drivers |
| Social Media | Enables content sharing and community building. | Facebook, Instagram | Advertising, sponsored content, data analytics. | Mobile Apps, Website, API | Users, Advertisers, Businesses, Developers |
| Crowdfunding | Connects project creators with backers for fundraising. | Kickstarter, Indiegogo | Platform fees, tiered rewards, payment processing. | Website, Email Campaigns, Social Media | Creators, Backers |
| App Stores | Distributes and sells applications developed by developers. | Apple App Store, Google Play Store | Revenue share from app sales, in-app purchases. | Pre-installed on devices, Mobile Apps | Developers, Users |
| Online Advertising | Connects advertisers with publishers for ad placements. | Google AdWords, Facebook Ads | Pay-per-click, pay-per-impression, subscriptions. | Self-service platforms, Ad networks | Advertisers, Publishers, Agencies |
| Content Streaming | Offers a library of digital content (e.g., movies, music). | Netflix, Spotify, Disney+ | Subscription fees, ads, licensing content. | Mobile Apps, Smart TVs, Web | Subscribers, Content Producers, Advertisers |
| Freelance Marketplaces | Connects businesses with freelancers for project work. | Upwork, Fiverr, Freelancer | Service fees, subscription plans, featured listings. | Website, Email Marketing, SEO | Freelancers, Businesses, Entrepreneurs |
| Real Estate Booking | Facilitates booking and rental of accommodations. | Airbnb, Booking.com, Vrbo | Booking fees, host service fees, subscription plans. | Website, Mobile Apps, Partnerships | Travelers, Property Owners, Property Managers |
| Job Matching | Matches job seekers with job openings and employers. | LinkedIn, Indeed, Monster | Premium subscriptions, job listings, ads. | Website, Mobile Apps, Email Campaigns | Job Seekers, Employers, Recruiters |
| Payment Processing | Provides a platform for online and mobile payments. | PayPal, Stripe, Square | Transaction fees, currency conversion, subscriptions. | Website, APIs, Payment Gateways | Individuals, Businesses, E-commerce Platforms |
| Cloud Computing | Offers infrastructure, platforms, or software services. | Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform | Subscription pricing, pay-as-you-go, data storage. | Online portals, Sales teams, Partnerships | Enterprises, Developers, IT Professionals |
| Food Delivery | Connects users with restaurants and delivery drivers for food orders. | Uber Eats, DoorDash, Grubhub | Commission on orders, delivery fees, ads. | Mobile Apps, Website, Partnerships | Consumers, Restaurants, Delivery Drivers |
| Related Concepts | Description | When to Apply |
|---|---|---|
| API Economy | The API Economy refers to the ecosystem of application programming interfaces (APIs) that enable the seamless integration, interoperability, and exchange of data and services between different software applications, platforms, and systems. Key components include APIs, providers, consumers, marketplaces, and monetization models. It fosters innovation, collaboration, and agility by facilitating the reuse and integration of services, data, and functionalities across applications. | – When developing or participating in digital ecosystems, platforms, or marketplaces that rely on APIs to enable seamless integration, interoperability, and exchange of data and services. |
| Digital Ecosystem | A Digital Ecosystem comprises interconnected digital platforms, applications, devices, and stakeholders collaborating within a shared environment. Participants contribute and benefit from the ecosystem’s offerings and innovations. Key features include interconnectivity, value co-creation, platform orchestration, ecosystem services, and data-driven insights. It fosters innovation, collaboration, and value creation across industries. | – When building or operating platforms, applications, or marketplaces that bring together diverse stakeholders to create value, drive innovation, and enhance user experiences within a shared digital environment. |
| Platform Company | A Platform Company operates a digital platform connecting multiple user groups, enabling interactions, transactions, and value exchange. Characteristics include network effects, ecosystem dynamics, scalability, data-driven insights, and diverse monetization strategies. It disrupts traditional business models, creates market opportunities, and transforms industries by facilitating interactions and value creation among stakeholders. | – When aiming to create or transform business models, leverage digital technologies, and build ecosystems to drive growth, innovation, and value creation in a networked economy. |
| Two-Sided Platform | A Two-Sided Platform connects and facilitates transactions between two distinct user groups, leveraging network effects and cross-subsidization. Key characteristics include balancing interests, cross-subsidization, network effects, platform governance, and various monetization strategies. It plays a crucial role in enabling marketplaces, ecosystems, and networks that drive economic activity and innovation. | – When building or operating platforms that connect and facilitate transactions between two distinct user groups, driving growth through network effects and cross-subsidization strategies. |
| Network Effects | Network Effects occur when the value of a product or service increases as more people use it. Positive network effects lead to a virtuous cycle of adoption and engagement, while negative network effects can result in diminishing value. Understanding network effects is essential for businesses aiming to leverage them to drive growth and create sustainable competitive advantages. | – When developing products, services, or platforms where user adoption and engagement play a critical role in driving value and achieving competitive advantage. |
| Digital Transformation | Digital Transformation refers to the integration of digital technologies into all aspects of a business, fundamentally changing how it operates and delivers value to customers. It involves leveraging digital tools and technologies to streamline processes, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation across the organization. Embracing digital transformation is crucial for organizations looking to remain competitive and adapt to the evolving digital landscape. | – When organizations seek to modernize their operations, processes, and customer interactions by leveraging digital technologies to drive efficiency, innovation, and growth. |
| Platform Governance | Platform Governance encompasses the rules, policies, and mechanisms established by platform companies to regulate interactions, ensure fairness, and maintain trust within their ecosystems. Effective platform governance is essential for fostering a thriving ecosystem, managing risks, and mitigating potential conflicts or abuses. It involves defining standards, enforcing policies, and resolving disputes to promote transparency, accountability, and integrity. | – When operating digital platforms or ecosystems that require establishing rules, policies, and mechanisms to govern interactions, ensure fairness, and maintain trust among participants. |
| Digital Disruption | Digital Disruption refers to the transformative effect of digital technologies on industries, markets, and business models, leading to the displacement of established incumbents by innovative newcomers. Digital disruptors leverage technology to challenge traditional practices, create new market opportunities, and redefine industry norms. Understanding digital disruption is crucial for organizations seeking to adapt to changing market dynamics and remain competitive. | – When organizations face the threat of digital disruptors or seek to leverage digital technologies to disrupt traditional industries, business models, or market dynamics. |
| Data Monetization | Data Monetization involves deriving economic value from data assets by converting them into revenue-generating opportunities. Organizations can monetize data through various means, such as selling raw data, offering data-as-a-service (DaaS), licensing data to third parties, or leveraging data insights to enhance products, services, and decision-making. Effective data monetization strategies enable organizations to unlock the value of their data assets and create new revenue streams. | – When organizations possess valuable data assets and seek to leverage them to generate revenue, create new business opportunities, or enhance existing products and services. |
| Ecosystem Innovation | Ecosystem Innovation involves fostering collaborative relationships and co-creating value with external partners, customers, and stakeholders within a broader ecosystem. It goes beyond internal R&D efforts and embraces open innovation principles to leverage external expertise, resources, and networks. Ecosystem innovation enables organizations to drive growth, expand market reach, and accelerate product development by tapping into diverse skillsets, perspectives, and capabilities. | – When organizations aim to drive innovation by collaborating with external partners, customers, or stakeholders within a broader ecosystem to co-create value, share resources, and leverage complementary expertise. |
Connected Business Model Types And Frameworks








Attention Merchant Business Model

















Main Free Guides:









