Cloud as a service is a business model that combines the cloud infrastructure delivered to customers as a subscription-based service, where the customer can access a cloud infrastructure without running it on-premise. Therefore, the whole premise of the cloud as a service business model is to offer a more agile cloud infrastructure at a fraction of the costs compared to on-premise software, and that can be scaled up according to the need of the business.
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Definition | The Cloud as a Service (CaaS) business model is a cloud computing approach where cloud service providers offer a wide range of cloud-based services, applications, and resources to businesses and individuals on a pay-as-you-go or subscription basis. CaaS encompasses Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), enabling users to access, deploy, and manage computing resources, applications, and data over the internet. CaaS providers maintain and update the underlying infrastructure, allowing customers to focus on utilizing the services without the need for extensive hardware or software investments. It offers flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency, making it a popular choice for businesses and organizations of all sizes. |
| Key Concepts | – Service Models: CaaS includes IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, each catering to specific cloud service needs. – On-Demand: Users can access and provision resources and services as needed, often with self-service portals. – Scalability: CaaS allows for the rapid scaling up or down of resources to meet changing demands. – Managed Infrastructure: The cloud provider manages the underlying infrastructure, including servers, storage, and networking. – Cost Models: Payment is typically on a pay-as-you-go or subscription basis, reducing capital expenses. |
| Characteristics | – Scalability: CaaS offers the ability to scale resources up or down quickly based on demand, optimizing cost-efficiency. – Accessibility: Services and resources are accessible remotely over the internet, promoting remote work and collaboration. – Managed Services: Providers handle infrastructure maintenance, security, and updates, reducing the burden on customers. – Elasticity: CaaS allows for dynamic allocation of resources to meet fluctuating workloads. – Multi-Tenancy: Multiple users or organizations can share the same cloud infrastructure while maintaining data separation and security. |
| Implications | – Cost Efficiency: CaaS can reduce upfront infrastructure costs and lower total cost of ownership (TCO) by paying only for what is used. – Flexibility: Users can deploy a wide range of applications and services, adapting to evolving business needs. – Global Reach: CaaS providers typically have data centers in multiple regions, offering global availability. – Security and Compliance: Providers implement security measures and compliance standards to protect data and applications. – Innovation Acceleration: CaaS enables rapid development and deployment of new applications and services. |
| Advantages | – Cost Savings: Eliminates the need for significant capital investments in hardware and software. – Scalability: Resources can be adjusted to match business growth or seasonal demands. – Accessibility: Users can access services from anywhere with an internet connection. – Managed Infrastructure: Providers handle maintenance, security, and updates, reducing the IT workload. – Innovation: CaaS encourages innovation by enabling rapid development and deployment of applications. |
| Drawbacks | – Data Security: Concerns about data security and privacy when data is stored offsite. – Reliability: Downtime or service disruptions can occur if the provider experiences technical issues. – Vendor Lock-In: Migration of data and applications can be challenging when switching providers. – Compliance Challenges: Meeting specific industry or regulatory compliance requirements can be complex. – Cost Management: Overspending can occur if resources are not carefully monitored and controlled. |
| Applications | – Web Hosting: Hosting websites and web applications in the cloud. – Software Development: Developing, testing, and deploying software using cloud resources. – Big Data Analytics: Analyzing large datasets in the cloud for insights and business intelligence. – E-commerce: Running online stores and managing customer data securely in the cloud. – Collaboration Tools: Using cloud-based collaboration and communication tools for remote work. |
| Use Cases | – Startup Launch: Startups can quickly launch and scale their businesses without major upfront infrastructure costs. – Enterprise IT: Enterprises use CaaS for IT infrastructure, reducing complexity and capital expenditures. – Data Analysis: Organizations leverage cloud-based analytics platforms for data-driven decision-making. – Content Delivery: Media and entertainment companies distribute content globally using cloud-based CDNs. – Remote Work: Cloud-based collaboration tools support remote workforces, fostering productivity and flexibility. |
The new software paradigm: from proprietary to on-cloud premises
By the early 2000s software paradigms shifted. From on-premise, heavy software infrastructure to online-based, cloud infrastructure. Indeed, the web enabled companies to start building a cloud infrastructure that could host other servers.
This is part of the agile transformation. Where software infrastructure is hosted online, much lighter, and based on continuous updates so that it can be quickly iterated, and improved, based on users feedback loops.

This, in turn, brought also in the business world, to the phenomenon defined as continuous innovation, where business transformation is led by quick feedback loops between the company’s operations and its customers.

A further progression of this evolution is from a software-centered approach, where continuous innovation plays a key role, to a customer-centered approach; where continuous innovation coupled with continuous intelligence, dynamic technological stack, and continuous deployment and delivery become critical.

The cloud industry in a nutshell
With the advent of the Internet, and the fact the web scaled globally, cloud computing became the main paradigm.

Cloud computing expresses itself in three main business models: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.


These models ended up creating a new trillion-dollar industry, which is behind most of the digital and tech companies existing in today’s business panorama.
This paradigm proved much lighter and way more scalable than the previous, on-premise, software paradigm. However, it’s important to remark that while the cloud enabled many small businesses to run very heavy software operations by relying on massive cloud infrastructures.
These cloud infrastructures are managed centrally, by a few key players (like Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud, Google Cloud, and a few others). Therefore, the whole cloud infrastructure, powering up an entrepreneurial ecosystem worth trillions of dollars is also centrally managed by a few key players. Thus, making the whole system fragile.
Every software company will be an AI copany
As new algorithms are integrated within software products, an important trend is sharing the software world. of the 2020-the the 2030s is the transformation of software into AI-based workflows, in what has been called Artificial Intelligence as a Service:

In this new model, cloud players (like Microsoft, Amazon, Google, and IBM) integrate AI features within their platforms, so that whoever is picking up their services will also be able to leverage on an AI platform. This, in turn, is leading to the transformation of the “as a service” industry toward a consumption-based one. Where customers, beyond a subscription plan, will have the option to pay as they go. Thus, paying the use of the infrastructure, based on the consumption of the platform.
Cloud As A Service business model case studies
C3.ai

Microsoft Azure

As you can see from the visualizations above, cloud players are manufacturing models and algorithms, that becomes an integrated part of their cloud-based offering and platform. This is what attracts more AI developers and companies to become part of the ecosystem, thus, in turn, consuming more cloud infrastructure.
Google Cloud

Amazon AWS

IBM Cloud


Beyond Cloud As A Service and into decentralized data storage
The main weakness of the current paradigm is the centralization of the whole cloud-based industry (which today represents pretty much most of the digital and tech landscape) in the hands of a few, centrally managed players.
That is why blockchain-based business models are working toward a software paradigm that moves from centralization to decentralization. One example is Dfinity.

Whether or not this will prove viable, it’s important to work toward cloud-based models which can have a higher degree of diffusion to prevent the collapse of the whole cloud ecosystem, as it’s placed in the hands of a few players.
Key Highlights
- Shift to Cloud Infrastructure: In the early 2000s, there was a transition from on-premise software infrastructure to cloud-based solutions. The advent of the web enabled companies to build cloud infrastructure to host various servers, facilitating agility and scalability.
- Agile Transformation: Cloud-based software infrastructure allowed for continuous updates and quick iteration based on user feedback loops. This shift embraced agile methodologies, enabling companies to adapt and improve products rapidly.
- Continuous Innovation: Cloud adoption led to continuous innovation, where business transformation is driven by rapid feedback loops between a company’s operations and its customers. Products and services are designed around customers’ problems rather than just technical solutions.
- Customer-Centered Approach: The evolution continued from a software-centered approach to a customer-centered one. Continuous innovation, coupled with continuous intelligence, dynamic technological stack, and deployment, became critical for software operations.
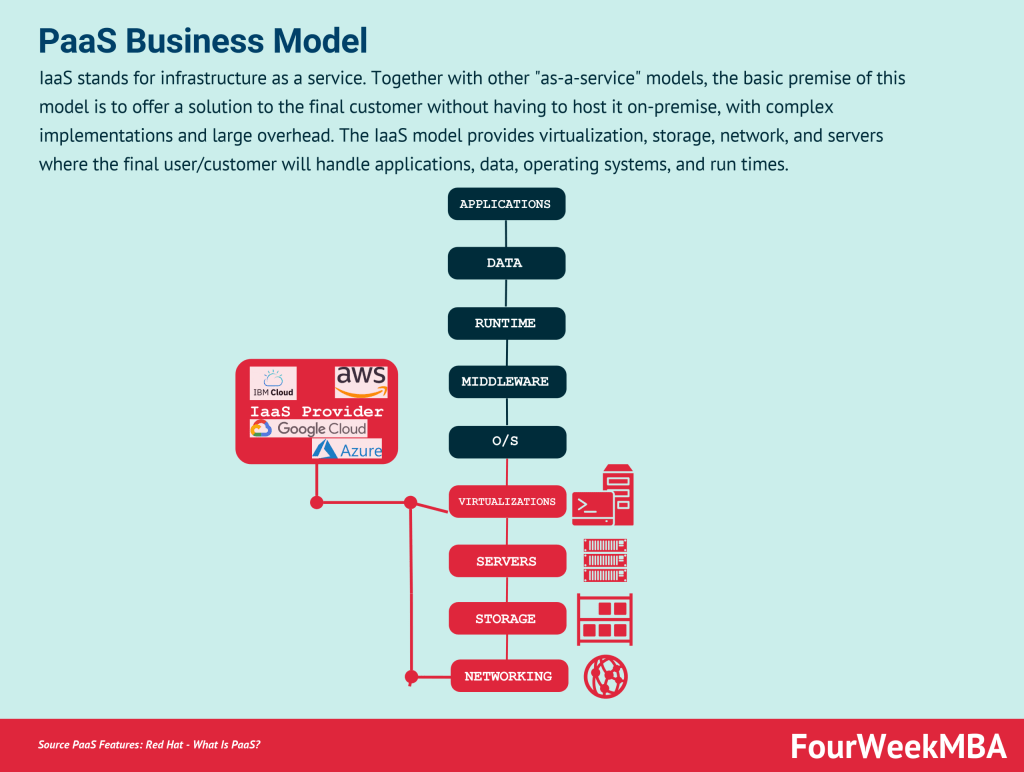
- Cloud Computing Models: Cloud computing introduced three main business models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). These models allowed for offloading the complexity of on-premise hosting and provided more scalability and flexibility.
- Trillion-Dollar Cloud Industry: The shift to cloud infrastructure created a new trillion-dollar industry, with key players like Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud, and Google Cloud managing massive cloud infrastructures.
- AI Integration: A trend emerged where software products incorporated AI algorithms, transforming software into AI-based workflows. This trend led to the rise of Artificial Intelligence as a Service (AlaaS), allowing organizations to integrate AI functionality without the expertise.
- Cloud Players and Consumption-Based Model: Cloud providers like Microsoft, Amazon, Google, and IBM integrated AI features into their platforms, leading to a transformation of the “as-a-service” industry toward a consumption-based model. Customers pay based on actual usage of the infrastructure.
- Cloud Service Case Studies:
- C3.ai: Offers cloud-based Enterprise AI SaaS with proprietary applications for digital transformation.
- Microsoft Azure: Part of the multi-billion dollar AI ecosystem, providing cloud infrastructure and AI services.
- Google Cloud: Offers models and algorithms integrated into its cloud-based offerings.
- Amazon AWS: Provides cloud services to enterprises and startups through a platform business model.
- IBM Cloud: Diverse technology company offering cloud services, including innovative products like Watson and Blockchain.
- Decentralized Data Storage: The centralization of the cloud industry in the hands of a few players is seen as a weakness. Blockchain-based business models, like Dfinity, aim to shift the paradigm from centralization to decentralization. Dfinity is working on a decentralized computer cloud for stable and cost-effective solutions.
| Related Frameworks, Models, or Concepts | Description | When to Apply |
|---|---|---|
| Software as a Service (SaaS) | Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud computing model that delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. It allows users to access and use software applications hosted on remote servers, eliminating the need for local installation and maintenance. By adopting SaaS, organizations can reduce IT costs, increase scalability, and access the latest software updates and features. | Consider Software as a Service (SaaS) when seeking to deploy software applications quickly and cost-effectively within your organization. Use it to access a wide range of software solutions, including customer relationship management (CRM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), and productivity tools, without the need for upfront investments in hardware or software licenses. Implement SaaS as a framework for driving agility, scalability, and cost savings in software deployment and management within your organization. |
| Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) | Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, including servers, storage, networking, and other infrastructure components. It allows organizations to provision and manage computing infrastructure on-demand, scaling resources up or down as needed. By leveraging IaaS, organizations can reduce capital expenditures, increase flexibility, and accelerate time-to-market for IT projects. | Consider Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) when seeking to deploy and manage computing infrastructure without the need for physical hardware or data centers. Use it to scale computing resources dynamically based on fluctuating demand, optimize resource utilization, and reduce operational overhead associated with managing on-premises infrastructure. Implement IaaS as a framework for driving agility, scalability, and cost efficiency in IT infrastructure provisioning and management within your organization. |
| Platform as a Service (PaaS) | Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides a development platform and environment over the internet for building, deploying, and managing applications. It offers developers access to tools, libraries, and middleware for application development, testing, and deployment. By leveraging PaaS, organizations can accelerate application development, reduce development costs, and improve collaboration and innovation. | Consider Platform as a Service (PaaS) when seeking to develop and deploy applications quickly and efficiently within your organization. Use it to access a range of development tools and services, including databases, frameworks, and application hosting environments, without the need for managing underlying infrastructure. Implement PaaS as a framework for fostering innovation, collaboration, and agility in application development and deployment within your organization. |
| Public Cloud | Public Cloud is a cloud computing deployment model where cloud services are delivered over the internet by third-party providers on a shared infrastructure. Public cloud services are available to multiple users on a pay-as-you-go basis, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency. By leveraging public cloud services, organizations can access a wide range of computing resources and services without the need for upfront investments in hardware or infrastructure. | Consider Public Cloud when seeking to leverage scalable and cost-effective computing resources and services for your organization. Use it to access a variety of cloud services, including compute, storage, networking, and applications, on-demand and without the need for managing physical infrastructure. Implement Public Cloud as a framework for driving agility, scalability, and cost savings in IT infrastructure and services provisioning within your organization. |
| Private Cloud | Private Cloud is a cloud computing deployment model where cloud services are delivered over a private network or infrastructure dedicated to a single organization. Private cloud environments offer greater control, security, and customization compared to public cloud services, making them suitable for organizations with specific compliance, security, or performance requirements. By adopting private cloud, organizations can maintain data sovereignty, ensure regulatory compliance, and customize cloud environments to meet their unique needs. | Consider Private Cloud when seeking to leverage cloud computing while maintaining control over data, security, and performance within your organization. Use it to deploy cloud services in a dedicated and isolated environment, providing greater security, privacy, and customization compared to public cloud offerings. Implement Private Cloud as a framework for addressing specific compliance, security, or performance requirements within your organization while still leveraging the benefits of cloud computing. |
| Hybrid Cloud | Hybrid Cloud is a cloud computing deployment model that combines public and private cloud environments, allowing organizations to leverage the benefits of both. It involves integrating and orchestrating workloads across multiple cloud environments, enabling seamless data and application portability. By adopting hybrid cloud, organizations can optimize resource utilization, improve flexibility, and address diverse business requirements effectively. | Consider Hybrid Cloud when seeking to leverage the advantages of both public and private cloud environments within your organization. Use it to deploy workloads across multiple cloud environments based on their specific requirements, such as security, compliance, performance, or cost. Implement Hybrid Cloud as a framework for optimizing resource utilization, improving agility, and addressing diverse business needs effectively within your organization. |
| Cloud Native Computing | Cloud Native Computing is an approach to software development and deployment that leverages cloud-native technologies and architectures to build and run applications at scale in cloud environments. It involves designing applications as a set of loosely coupled microservices that can be deployed and managed independently in containerized environments. By adopting cloud-native computing, organizations can achieve greater agility, resilience, and scalability in application development and delivery. | Consider Cloud Native Computing when seeking to develop and deploy modern, scalable, and resilient applications in cloud environments. Use it to adopt cloud-native technologies and practices, such as containerization, microservices, and DevOps, to accelerate application development, improve scalability, and enhance agility within your organization. Implement Cloud Native Computing as a framework for building and operating cloud-native applications that are optimized for scalability, resilience, and agility in dynamic and distributed computing environments. |
| Serverless Computing | Serverless Computing is a cloud computing model that abstracts infrastructure management from application development, allowing developers to focus on writing code without worrying about underlying servers or infrastructure. Serverless platforms automatically scale resources based on demand and charge users only for the resources consumed during execution. By adopting serverless computing, organizations can reduce operational overhead, improve scalability, and accelerate time-to-market for applications. | Consider Serverless Computing when seeking to develop and deploy event-driven or scalable applications without the need for managing infrastructure or provisioning servers. Use it to build and deploy serverless applications that automatically scale based on demand, reduce operational complexity, and optimize resource utilization within your organization. Implement Serverless Computing as a framework for accelerating application development, improving scalability, and reducing costs associated with infrastructure management within your organization. |
| Cloud Security | Cloud Security encompasses practices, technologies, and policies designed to protect cloud environments, data, and applications from cyber threats, vulnerabilities, and unauthorized access. It involves implementing security controls, encryption, identity management, and compliance measures to safeguard cloud assets and mitigate security risks. By prioritizing cloud security, organizations can build trust, ensure compliance, and protect sensitive data and assets in cloud environments. | Consider Cloud Security when adopting cloud computing services within your organization. Use it to assess and mitigate security risks associated with cloud adoption, implement security best practices, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards. Implement Cloud Security as a framework for building a secure and resilient cloud infrastructure, protecting sensitive data and applications, and fostering trust and confidence in cloud services within your organization. |
Read More: Cloud Business Models, IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS, AIaaS Business Model.
Connected Business Model Types And Frameworks








Attention Merchant Business Model

















Main Free Guides:









