Establishing a robust infrastructure is the cornerstone of cloud computing. It often accounts for a third of the total amount spent on IT in a majority of businesses. Instead of taking computer workloads through the internal IT team, this traditional approach seemed to be long gone. Modern industries that embrace digital transformation with open arms gradually transfer systems into the cloud. Whether the information is on a private or public cloud, it offers increased security and safety against cyber threats. The result of increased cloud usage opens doors for cloud computing services provided by vendors and enterprises.
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Definition of Cloud Computing | Cloud Computing is a technology paradigm that involves delivering a wide range of computing services over the internet. Instead of owning and maintaining physical hardware and software, users can access and use computing resources, such as servers, storage, databases, networking, and software, from cloud service providers on a pay-as-you-go basis. Cloud computing services are typically categorized into three main service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Cloud computing offers scalability, flexibility, cost-efficiency, and accessibility, making it a fundamental technology for businesses and individuals in various industries. It enables organizations to focus on their core objectives while outsourcing the management of IT infrastructure to specialized providers. Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals store, process, and access data and applications. |
| Key Concepts | Several key concepts define Cloud Computing: |
| – On-Demand Access | On-demand access is a central concept of cloud computing. Users can access computing resources and services as needed, without the need for extensive upfront investments in hardware or software. On-demand access promotes flexibility and cost-efficiency. |
| – Virtualization | Virtualization is a foundational technology in cloud computing. It involves creating virtual instances of physical hardware, allowing multiple virtual machines or containers to run on a single physical server. This optimizes resource utilization and enables scalability. Virtualization enhances resource efficiency. |
| – Service Models | Cloud computing offers multiple service models: – Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides virtualized computing resources, such as virtual machines and storage, allowing users to manage and control the operating systems and applications. – Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers a platform that includes development tools, databases, and infrastructure for building, testing, and deploying applications. – Software as a Service (SaaS) delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for installation and maintenance. Service models offer varying levels of control and management. |
| – Scalability | Scalability is a critical feature of cloud computing. It allows users to easily scale up or down their computing resources based on demand. Scalability ensures that organizations can handle fluctuations in workload without the need for significant hardware investments. Scalability supports business growth and efficiency. |
| Characteristics | Cloud Computing is characterized by the following attributes: |
| – Resource Pooling | Resource pooling involves the shared use of computing resources among multiple users. Cloud providers can allocate and reallocate resources dynamically to meet varying user demands. This pooling of resources optimizes utilization and leads to cost savings. Resource pooling enhances resource efficiency. |
| – Self-Service | Self-service is a key feature of cloud computing that enables users to provision and manage computing resources independently through web interfaces or APIs. This empowers users to have more control over their IT environments. Self-service promotes agility and reduces reliance on IT support. |
| – Broad Network Access | Cloud services are accessible over the internet from a variety of devices, including laptops, smartphones, and tablets. This broad network access ensures that users can access their data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. Broad network access enhances accessibility and mobility. |
| – Measured Service | Cloud computing services are metered, and users are billed based on their actual usage. This pay-as-you-go model allows organizations to pay only for the resources they consume, leading to cost savings and cost predictability. Measured service promotes cost-efficiency. |
| Examples of Cloud Computing | Cloud computing is applied in various contexts and industries: |
| – Web Hosting | Many websites and web applications are hosted on cloud infrastructure. Cloud web hosting services provide scalability and reliability, ensuring websites can handle traffic spikes and remain available. Cloud web hosting simplifies website management. |
| – Data Storage | Cloud storage services enable individuals and businesses to store and access data in the cloud. Cloud storage solutions offer redundancy and data replication, reducing the risk of data loss. Cloud storage enhances data durability and accessibility. |
| – Software Delivery | Software as a Service (SaaS) applications, such as email services, collaboration tools, and customer relationship management (CRM) software, are delivered over the cloud. Users can access and use these applications through web browsers, eliminating the need for software installation and maintenance. SaaS simplifies software deployment and updates. |
| – Big Data Processing | Cloud platforms offer services for big data processing and analytics. Organizations can leverage cloud-based data warehouses, analytics tools, and machine learning services to analyze large datasets and gain insights. Cloud-based big data solutions support data-driven decision-making. |
| Benefits and Considerations | Cloud Computing offers several benefits and considerations: |
| – Cost-Efficiency | Cloud computing allows organizations to reduce capital expenditures on hardware and infrastructure. It offers cost savings through pay-as-you-go pricing models and resource optimization. |
| – Scalability and Flexibility | Cloud computing enables organizations to scale resources up or down as needed, supporting rapid growth and agility. It accommodates changing business demands without major upfront investments. |
| – Accessibility | Cloud services are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, promoting remote work and collaboration. Accessibility fosters productivity and global reach. |
| – Security and Privacy | While cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, data security and privacy are considerations. Organizations must implement appropriate security practices and protocols to protect sensitive data in the cloud. |
| Revenue Models | Cloud computing providers typically utilize several revenue models: |
| – Subscription-Based | Many cloud services are offered on a subscription basis, where users pay a recurring fee to access and use the service. This model provides predictable and recurring revenue for providers. |
| – Pay-As-You-Go | Pay-as-you-go pricing allows users to pay only for the resources they consume, typically on an hourly or per-unit basis. This flexible model aligns costs with actual usage and encourages cost-efficient resource management. |
| – Freemium | In the freemium model, providers offer a basic version of their service for free, with the option to upgrade to a premium paid version with additional features or resources. This model attracts a wide user base and converts some users into paying customers. |
| – Tiered Pricing | Tiered pricing involves offering multiple pricing tiers with varying levels of features or resource allocations. Users can choose a tier that aligns with their needs and budget. This model caters to diverse user requirements. |
| Advantages | Cloud computing offers several advantages: |
| – Cost-Efficiency | Cloud computing reduces the need for significant upfront capital expenditures on hardware and infrastructure. It also eliminates the costs associated with hardware maintenance, upgrades, and physical space. |
| – Scalability and Flexibility | Organizations can easily scale their computing resources up or down based on demand, ensuring that they only pay for what they use. This scalability supports business growth and agility. |
| – Accessibility | Cloud services are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, facilitating remote work, collaboration, and global reach. |
| – Security and Reliability | Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, data redundancy, and disaster recovery. They often offer higher levels of security and reliability than many organizations can achieve on their own. |
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud delivery accounts for streamlining the delivery of services through the internet. When data gets stored in cloud software, servers in a comprehensive database secure it. IT professionals prefer data storage in the cloud instead of proprietary hard drives and local storage devices.
Cloud-storage is more convenient, allowing users to store and access files to a remote database. Almost everyone in the world has access to the internet.
Thus, you can run data and software through the cloud as long as you have an electronic device and internet connectivity.
Businesses are slowly adopting cloud computing into their existing framework for several reasons. Cloud offers convenience, speed, security, and cost-savings. Not only can it provide efficiency but it also increases the overall productivity of businesses.
How Does Cloud Computing Work?
As previously mentioned, cloud computing is used in both public and private clouds. Both public and private cloud services are networks that supply hosted services. Storing data in the public cloud means that you can acquire its services for free. In contrast, private cloud services require a fee that can only be accessed by many people.
In general, cloud computing features vast services, including the following:
- Consumer Services (cloud back-up for data on smartphones, desktop, and laptops)
- Hosted services to run several applications in the cloud (often used by companies)
A growing number of applications and software utilize cloud computing to offer innovative solutions and quality services. Extensive video streaming services like Hulu, Netflix, Disney+, and Amazon slowly transition to a subscription model. Through cloud computing, they can offer their applications as services instead of a standalone product. It may increase the costs for the users, but these often make up for the constant improvements made.
Types of Cloud Computing

Cloud computing is composed of the following services:
Software-as-a-service (SaaS)
SaaS refers to the license to apply the services offered by software applications. An example of this is Microsoft 365, or the entirety of Microsoft applications in a single cloud. There are different payment models for SaaS cloud computing services, depending on the product. Often, it is large enterprises that obtain these licenses.
Infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS)
IaaS yields the delivery of products and services through servers. Products, including operating systems and data, get stored through IP-based connectivity as part of an on-demand service. IaaS uses programs like IBM Cloud and Microsoft Azure. Instead of purchasing software, users can procure them as an on-demand service.
Platform-as-a-service (PaaS)
PaaS is often used interchangeably with SaaS. The main difference between the two is that the platform for establishing software gets delivered through the internet. Popular platforms that offer PaaS include Salesforce.com and Heroku.
Benefits of Cloud Computing to Digital Entrepreneurs
Cloud computing provides a plethora of benefits to different sectors of businesses. From the ability to manage software from any device on a native app or web browsers, users can handle data seamlessly. It is the foundation of a reliable IT infrastructure that aims to support business growth.
To better understand why more businesses are moving to the cloud, here are the benefits of cloud computing:
Scalability
Digital entrepreneurs and businesses that invest in cloud computing can take advantage of its efficiency and flexibility. Cloud-based services let companies use unlimited bandwidth and storage space, promoting scalability. Scalability means that companies can scale up and down, depending on their capacities and goals. Scalability in business plays a fundamental role in coping when traffic increases or fluctuates.
Simply put, playing your data in the cloud eliminates the need for the installation of programs on-site. On top of that, enterprises can update their software remotely, without the entire IT workforce present. Not only does it promote workforce flexibility but also convenience. Several uses can access applications and data anywhere and any time, as long as they have internet connectivity.
Reliability
A robust infrastructure supported by cloud computing means that businesses can rely on the cloud in case of issues that arise. Cloud-based services offer reliable disaster recovery and comprehensive back-up in the event of a system breach, malfunction, or cyber threat. It gives digital entrepreneurs peace of mind that they can recover data within a few hours. Cloud computing mirrors data across servers from the beginning to instantly provide back-up solutions, minimizing downtime.
Cost-Effective
One of the most valuable benefits of cloud computing is getting a lot of bang for your buck. It reduces IT operational costs with remote servers used for storage. Instead of gathering an in-house team to install applications and situate storage segments, you can simply leverage the cloud. From the overhead expenses, management efforts, and constant software upgrades, cloud computing does it all at a fraction of the price. Most cloud-based services are cost-effective and on a pay-per-use basis. This model means that businesses can obtain only the services they need at a given time.
Initiate Steadfast Collaboration
The cloud environment aims to initiate true collaboration across business sectors. Different departments can access, modify, and manage the same files without having to be in one room. Such a transparent form of collaboration eliminates the communication and geographical barriers since both parties can work with data as long as they have internet. With a true collaboration across teams, timeframes and scheduling is a much smaller issue.
Accelerate Business Growth
Cloud computing is applied to meet the ever-changing market demands and technological advancements. It is integrated into an existing framework to accelerate business growth. With increased storage space and bandwidth, webpages can handle considerable traction and anticipate traffic. The seamless deployment of the cloud makes it easier for digital entrepreneurs to grow. They can match their business operations with the growing IT requirements while maintaining optimum performance.
Automatic Software Updates and Integration
Cloud-based services feature regular software updates to meet the ever-changing IT demands. Constant monitoring is performed across cloud servers to make sure that systems are secured and safe. Instead of relying on your internal IT team, you can delegate the task to a cloud computing specialist. They are also the ones tasked to integrate software across cloud servers. Although it can occur automatically, professionals can modify software applications suitable for their business objectives.
Sustainability
Businesses are now taking the initiative of maintaining sustainability. One way to do so is through cloud computing. Cloud computing does not require much hardware equipment in the office. Cloud-based services reduce as much carbon footprint as possible, considering that they are remote. Data, applications, and servers can be stored and run in a virtual environment, meaning less energy consumption.
Case Studies
- Netflix
- Background: Netflix, a leading subscription-based streaming service, relies heavily on cloud computing to deliver content to its millions of subscribers worldwide. With a vast library of movies, TV shows, and original content, Netflix requires robust infrastructure to handle high volumes of streaming traffic and ensure seamless user experience.Implementation of Cloud Computing:
- Scalability: Netflix utilizes cloud computing to scale its infrastructure dynamically based on demand. During peak hours or when new content is released, the company can rapidly provision additional computing resources to accommodate increased traffic.Content Delivery: By leveraging cloud-based content delivery networks (CDNs), Netflix can distribute its content efficiently to users across the globe. CDNs reduce latency and ensure fast loading times for streaming media, enhancing the user experience.Cost-Efficiency: Cloud computing allows Netflix to optimize resource utilization and minimize operational costs. The pay-as-you-go pricing model ensures that the company only pays for the resources it consumes, avoiding upfront investments in hardware infrastructure.
- Netflix’s adoption of cloud computing has enabled the company to scale its streaming service globally and handle millions of concurrent users.
- By leveraging cloud-based infrastructure and CDNs, Netflix delivers high-quality streaming content with minimal interruptions and buffering.
- The cost-effective nature of cloud computing has allowed Netflix to allocate resources efficiently and invest more resources in content creation and platform enhancements.
- Background: Netflix, a leading subscription-based streaming service, relies heavily on cloud computing to deliver content to its millions of subscribers worldwide. With a vast library of movies, TV shows, and original content, Netflix requires robust infrastructure to handle high volumes of streaming traffic and ensure seamless user experience.Implementation of Cloud Computing:
- Airbnb
- Background: Airbnb, an online marketplace for lodging and homestays, relies on cloud computing to support its platform and facilitate bookings for millions of travelers worldwide. With a vast network of hosts and guests, Airbnb requires scalable and reliable infrastructure to handle fluctuating demand.Implementation of Cloud Computing:
- Scalability: Airbnb leverages cloud computing to scale its infrastructure dynamically based on seasonal demand and market trends. During peak travel seasons or promotional events, the company can allocate additional computing resources to handle increased traffic and bookings.Data Management: Cloud-based databases and storage solutions enable Airbnb to manage large volumes of user data, including property listings, reservations, and user profiles. By storing data in the cloud, Airbnb ensures data redundancy, availability, and security.Global Accessibility: Cloud computing allows Airbnb to offer its platform to users worldwide, regardless of their location or device. The company’s website and mobile apps are hosted on cloud servers, ensuring fast and reliable access for hosts and guests across the globe.
- Airbnb’s adoption of cloud computing has facilitated its rapid growth and global expansion, enabling the company to reach millions of users in diverse markets.
- By leveraging cloud-based infrastructure and data management solutions, Airbnb ensures seamless booking experiences for hosts and guests, leading to higher customer satisfaction and retention.
- The scalability and reliability of cloud computing have allowed Airbnb to innovate rapidly and launch new features and services to meet evolving customer needs and market demands.
- Background: Airbnb, an online marketplace for lodging and homestays, relies on cloud computing to support its platform and facilitate bookings for millions of travelers worldwide. With a vast network of hosts and guests, Airbnb requires scalable and reliable infrastructure to handle fluctuating demand.Implementation of Cloud Computing:
- Slack
- Background: Slack, a popular collaboration platform for teams, relies on cloud computing to provide real-time messaging, file sharing, and workflow automation to users worldwide. With a diverse user base spanning industries and geographies, Slack requires scalable and secure infrastructure to support its platform.Implementation of Cloud Computing:
- Real-Time Communication: Slack leverages cloud-based messaging infrastructure to enable real-time communication and collaboration among team members. Cloud servers handle message delivery, file sharing, and integration with third-party apps, ensuring seamless communication experiences.Scalability: Cloud computing allows Slack to scale its infrastructure horizontally to accommodate growing user demand and peak usage periods. Whether teams consist of a few members or thousands, Slack can allocate resources dynamically to maintain performance and reliability.Security and Compliance: Slack relies on cloud-based security solutions to protect user data and ensure compliance with data privacy regulations. Cloud providers offer robust security features, encryption protocols, and access controls to safeguard sensitive information transmitted through the platform.
- Slack’s adoption of cloud computing has transformed the way teams collaborate and communicate in the workplace, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
- By leveraging cloud-based infrastructure and security solutions, Slack provides a secure and reliable platform for organizations of all sizes, including enterprises with stringent compliance requirements.
- The scalability and flexibility of cloud computing have allowed Slack to innovate rapidly and introduce new features and integrations to meet the evolving needs of modern workplaces.
- Background: Slack, a popular collaboration platform for teams, relies on cloud computing to provide real-time messaging, file sharing, and workflow automation to users worldwide. With a diverse user base spanning industries and geographies, Slack requires scalable and secure infrastructure to support its platform.Implementation of Cloud Computing:
Key Highlights:
- Importance of Cloud Infrastructure: Robust cloud infrastructure is crucial in modern businesses, representing a significant portion of IT spending. Traditional internal IT management is giving way to cloud-based solutions, enabling digital transformation and enhanced security against cyber threats.
- Cloud Computing Defined: Cloud computing involves delivering services over the internet, storing data securely in comprehensive cloud databases. This approach offers convenience, accessibility, and efficiency compared to local storage devices.
- Benefits for Businesses: Cloud computing offers convenience, speed, security, and cost-savings to businesses. It enhances productivity and allows for streamlined operations.
- Public and Private Clouds: Cloud computing is employed in both public and private clouds. Public clouds provide services for free, while private clouds require fees for access. Both options offer various benefits.
- Types of Cloud Computing Services:
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS): License-based access to software applications, often used by large enterprises.
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS): Delivery of products and services via servers, offering flexibility and on-demand resources.
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS): Platforms delivered through the internet for software development and deployment.
- Benefits for Digital Entrepreneurs:
- Scalability: Cloud services promote scalability, allowing businesses to adjust resources as needed.
- Reliability: Cloud computing offers reliable disaster recovery and backup solutions, minimizing downtime and cyber threats.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud services reduce IT operational costs, offer pay-per-use models, and minimize the need for in-house resources.
- Collaboration: Cloud fosters collaboration by allowing seamless access to and modification of files across departments.
- Business Growth: Cloud integration accelerates business growth by providing scalable resources to match evolving IT requirements.
- Automatic Updates: Regular software updates and integration are managed by cloud specialists, reducing reliance on internal IT teams.
- Sustainability: Cloud computing contributes to sustainability by reducing hardware equipment, energy consumption, and carbon footprint.
Connected Business Model Types And Frameworks



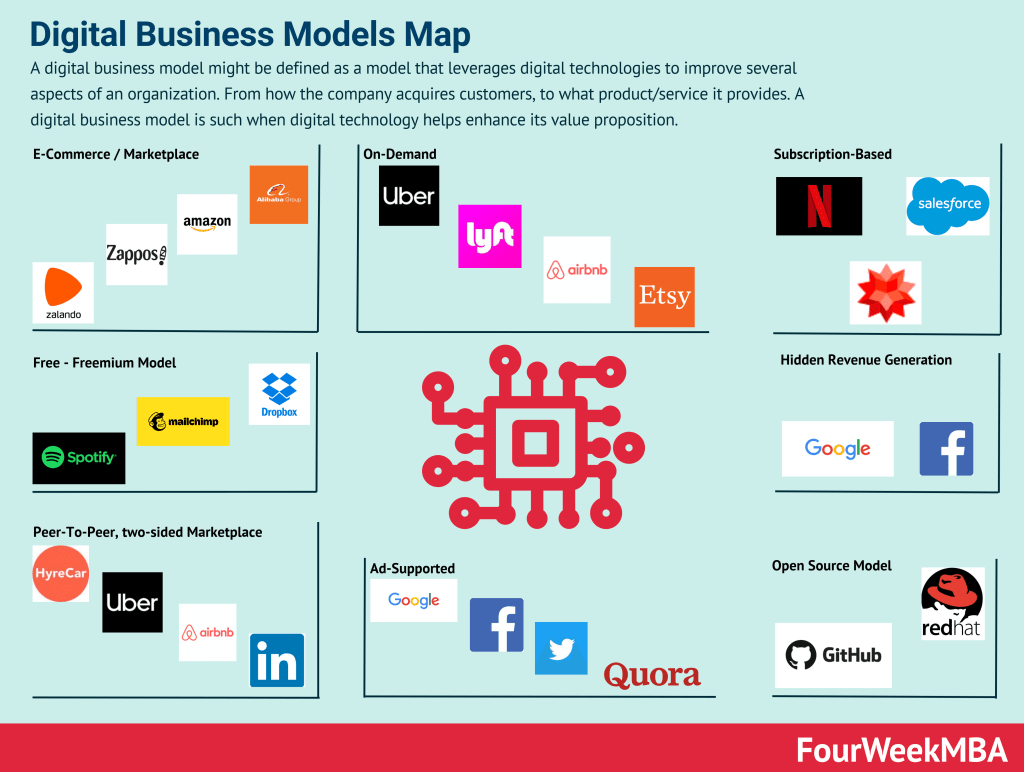





Attention Merchant Business Model

















Main Free Guides:









