A business plan is a document that details key operational and financial goals for a business and how they will be achieved in the future. Essentially, a business plan is an exercise in due diligence. While no business plan can accurately predict the future, they do demonstrate and give insight into the likelihood of eventual profitability. This in turn removes some of the entrepreneurial risk associated with investing large amounts of time and capital into a new venture.
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Definition | A Business Plan is a formal written document that outlines a company’s goals and how it plans to achieve them. It serves as a roadmap for the business, providing a detailed description of its products or services, target market, competition, financial projections, and strategies for growth. A business plan is typically used to secure financing, attract investors, guide internal decision-making, and communicate the business’s vision to stakeholders. |
| Key Components | – Executive Summary: A concise overview of the business, including its mission, vision, and the main points of the plan. – Company Description: Detailed information about the company’s history, structure, and its legal form (e.g., LLC, corporation). – Market Analysis: Research on the industry, market trends, target audience, and competitive analysis. – Organization and Management: Information about the management team, key personnel, and organizational structure. – Products or Services: Description of what the business offers, including features, benefits, and unique selling points. – Marketing and Sales Strategy: Plans for marketing, advertising, and sales, including pricing, distribution, and promotion. – Funding Request: If seeking financing, this section outlines the amount of funding needed and its intended use. – Financial Projections: Detailed financial forecasts, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. – Appendix: Supplementary materials such as resumes, market research, and additional data. |
| Importance | – Guidance: A business plan provides a roadmap for the business, helping owners and managers make informed decisions and set clear objectives. – Investor Attraction: Investors and lenders often require a business plan to evaluate the company’s potential for profitability and growth. – Strategic Direction: It defines the company’s goals, strategies, and tactics, ensuring that everyone is aligned with the same objectives. – Risk Mitigation: By conducting thorough market research and financial analysis, a business plan helps identify and mitigate potential risks. |
| Types of Business Plans | – Startup Business Plan: Created by entrepreneurs when launching a new business, it focuses on securing initial funding and establishing a strong foundation. – Internal Business Plan: Aimed at guiding the internal operations and strategies of an existing company, often used for planning and decision-making. – Strategic Business Plan: Developed for a specific project, product launch, or expansion initiative within an established business. – Operational Business Plan: Concentrates on the day-to-day operations, processes, and resources required to run the business effectively. |
| Audience | The primary audience for a business plan includes potential investors, lenders, partners, and stakeholders who want to understand the company’s vision, viability, and growth potential. Internally, it serves as a reference for employees and management. |
| Real-World Example | A tech startup preparing to pitch to venture capitalists creates a detailed business plan that outlines its innovative product, market potential, revenue projections, and the team’s qualifications. This plan helps secure funding for development and growth. |
A typical business plan structure
Business plan structure varies considerably across industries, but most incorporate these parts as a part of a 10 to 20-page document.
Business concept
What is the nature of the industry the business intends to operate in?
What is the structure of the business and what are the products or services it will offer? How will it achieve success?
Marketplace analysis
Who is the potential target audience and why are they motivated to buy? Is there an existing demand for the product or service? In this part, it’s crucial to be as detailed as possible.
Develop a target demographic and associated buyer persona through in-depth research.

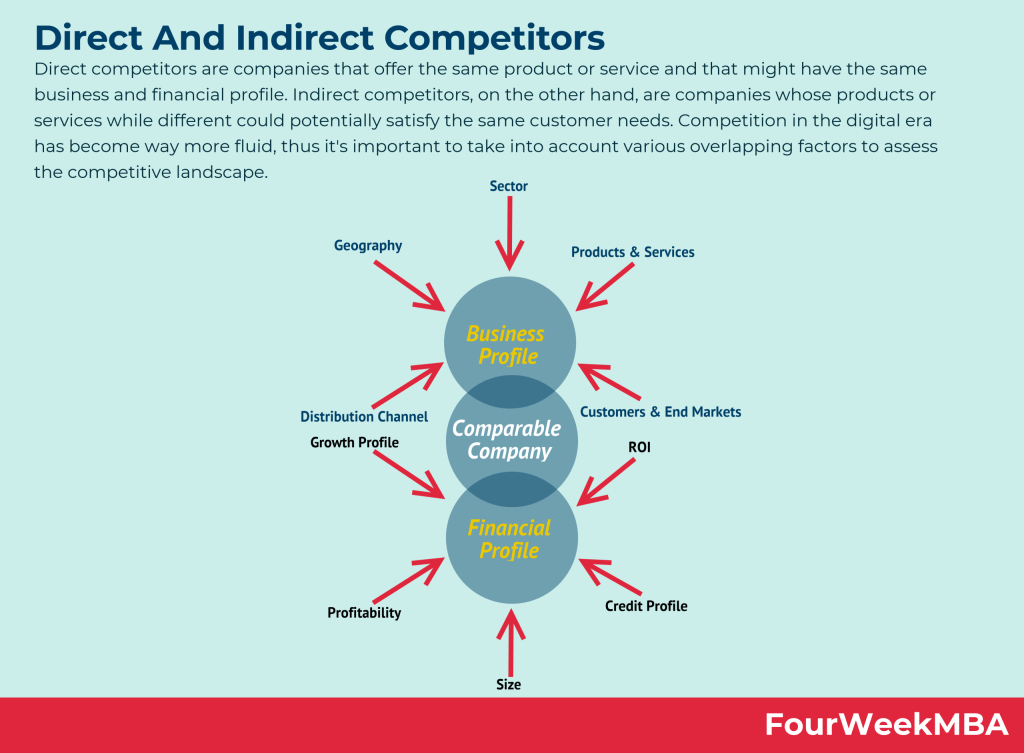
Competitive analysis
Who are the main competitors and what are their strengths and weaknesses? Is the market saturated or impenetrable?
If the market does have established players, then strategies must be devised to acquire market share.
Financial plan
If financing is required, then a sound financial plan will be key in attracting capital from banks, investors, or venture capitalists.
As best as possible, develop income and cash flow statements, balance sheets, and break-even analyses.
The goal here is to convince interested parties that the business has a realistic chance of success.
Management and legal structure
How will the company be structured and who will lead it? What skills do management bring to the table and how will they contribute to success?
A sound business plan should also define the intended legal structure, whether that be incorporated, partnership, sole proprietor, or LLC.
The four main categories of business plans
Business plans usually fall under one of four main categories:
The mini-plan
Used to quickly test a concept or gauge the interest of a prospective investment partner. Mini-plans are typically short at 1-10 pages in length.
The working plan
Used to describe how a business could operate once established.
The working plan is primarily an internal document; it does not need to look attractive with supporting photography, formatting, and appendices.
The presentation plan
Or a working plan submitted to interested external parties. Industry jargon and slang should be removed in favor of standard business language.
The presentation plan should incorporate all aspects of a typical business plan structure.
Attention to detail is also a must. Figures must be correct and words free of typing errors. The plan should also be professionally bound and printed.
The electronic plan
In the digital age, many organizations find it useful to keep electronic copies of their business plans.
These are useful for savvy investors who want to delve into complex spreadsheets for analysis. They are also ideal for presentations and virtual meetings.
How to build an effective business plan according to Peter Thiel

According to Pether Thiel, former CEO of PayPal and founder of the software company Palantir, there are seven questions to answer if you want to create a company that will go from Zero to One.
Those questions are critical to building a business that will be able to capture value in the long run. In fact, according to Peter Thiel the value of a business isn’t to go from 1 to n but to real value is to go from Zero to One.
In short, build a company that creates new things, rather than building a business based on the existing “best practices,” which according to Peter Thiel, leads to dead ends.
This framework of going from Zero to One can be summarised in seven questions to answer if you want to have a great business plan.
In fact, you don’t need complicated Excel models or reasonings. You only need to address now these seven questions.
Indeed, that is how Peter Thiel puts it in Zero to One:
Whatever your industry, any great business plan must address every one of them.If you don’t have good answers to these questions, you’ll run into lots of “bad luck” and your business will fail. If you nail all seven you’ll master fortune and succeed.
The Engineering Question
Can you create breakthrough technology instead of incremental improvements?
The Timing Question
Is now the right time to start your particular business?
The Monopoly Question
Are you starting with a big share of a small market?
The People Question
Do you have the right team?
The Distribution Question
Do you have a way to not just create but deliver your product?
The Durability Question
Will your market position be defensible 10 and 20 years into the future?
The Secret Question
Have you identified a unique opportunity that others don’t see?
Key takeaways
- A business plan is a comprehensive document that highlights the goals of a business and how it plans to achieve them.
- A business plan is essential for new businesses where due diligence is crucial in attracting external investment or predicting long-term viability. All businesses – regardless of maturity – should use and adhere to such a plan.
- There are four main categories of business plans, with each category suited to a particular stage of the business life cycle.
Key Highlights:
- Business Plan Definition: A business plan is a detailed document outlining a business’s operational and financial goals, along with strategies for achieving them. It serves as a tool for due diligence, demonstrating the potential profitability of a venture and reducing entrepreneurial risk.
- Components of a Business Plan: Business plans typically include the following sections:
- Business Concept: Describes the industry, business structure, products/services, and success strategies.
- Marketplace Analysis: Identifies the target audience, demand, and buyer persona through detailed research.
- Competitive Analysis: Assesses main competitors, their strengths and weaknesses, and market saturation.
- Financial Plan: Presents income statements, cash flow projections, balance sheets, and break-even analyses.
- Management and Legal Structure: Defines the company’s structure, leadership, and legal status.
- Four Main Categories of Business Plans:
- Mini-Plan: Brief, used to test concepts or attract investment partners.
- Working Plan: Describes how a business will operate, primarily for internal use.
- Presentation Plan: Tailored for external parties, incorporates all aspects of a typical plan.
- Electronic Plan: Digital copies useful for analysis, presentations, and virtual meetings.
- Building an Effective Business Plan (According to Peter Thiel):
- Peter Thiel, co-founder of PayPal, outlines seven critical questions to address in a business plan.
- These questions guide businesses to create new value and avoid dead-end practices.
- The seven questions include: Engineering Question, Timing Question, Monopoly Question, People Question, Distribution Question, Durability Question, and Secret Question.
- Addressing these questions enhances a company’s chances of success by creating breakthrough technology, timing the market entry, targeting a niche market, forming the right team, ensuring product delivery, building defensible market positions, and identifying unique opportunities.
- Key Takeaways:
- A business plan outlines a business’s goals and strategies for achieving them.
- It is essential for attracting investment, reducing risk, and guiding business operations.
- The plan’s components include business concept, marketplace analysis, competitive analysis, financial plan, and management structure.
- Business plans can fall into four categories: mini-plan, working plan, presentation plan, and electronic plan.
- Addressing Peter Thiel’s seven questions can enhance a business plan’s effectiveness and increase the chances of long-term success.
Examples
| Industry/Business Type | Description | Business Plan Example | Key Components and Objectives |
|---|---|---|---|
| Restaurant | Opening a new restaurant. | A restaurant business plan outlining the concept, location, menu, target market, pricing strategy, and financial projections. | Objectives include securing funding, attracting customers, and achieving profitability within a specified time frame. |
| Technology Startup | Launching a new software application. | A tech startup business plan detailing the problem the app solves, the market need, product features, marketing plan, and financial forecast. | Objectives include securing seed funding, developing the product, gaining users, and achieving profitability or acquisition. |
| Retail Store | Establishing a boutique clothing store. | A retail store business plan describing the store’s niche, location, inventory, pricing, visual merchandising, and marketing strategy. | Objectives include securing startup capital, attracting customers, and achieving sustainable sales and profits. |
| E-commerce | Starting an online marketplace. | An e-commerce business plan outlining the niche, website features, product sourcing, digital marketing strategy, and financial projections. | Objectives include securing initial investment, building a user base, and achieving profitability and growth. |
| Manufacturing | Launching a new product manufacturing company. | A manufacturing business plan detailing product design, production processes, supply chain, quality control, and sales strategy. | Objectives include securing funding, optimizing production, and expanding market reach. |
| Consulting Services | Offering management consulting services. | A consulting business plan explaining the expertise, target industries, service offerings, marketing approach, pricing, and growth strategy. | Objectives include acquiring clients, establishing industry partnerships, and achieving revenue and profitability goals. |
| Healthcare Startup | Developing a telehealth platform. | A healthcare startup business plan describing the telehealth concept, technology infrastructure, healthcare provider network, and regulatory compliance. | Objectives include raising capital, attracting healthcare providers, and expanding the user base while maintaining compliance. |
| Renewable Energy Project | Building a solar energy farm. | A renewable energy business plan outlining the project scope, financing, engineering, environmental impact, and power purchase agreements. | Objectives include securing project financing, constructing the facility, and generating clean energy revenue. |
| Fitness Center | Opening a fitness gym. | A fitness center business plan detailing the gym’s location, equipment, fitness programs, pricing structure, marketing, and membership growth strategy. | Objectives include securing financing, attracting members, and achieving membership and revenue targets. |
| Agricultural Farming | Starting an organic vegetable farm. | An agricultural business plan outlining land use, crop selection, organic farming practices, distribution channels, and revenue projections. | Objectives include securing funding, optimizing crop yields, and marketing to local markets or restaurants. |
| Real Estate Development | Developing a mixed-use real estate project. | A real estate development business plan describing the project scope, financing sources, market analysis, construction timeline, and property management strategy. | Objectives include securing financing, completing construction, and generating rental income or property sales revenue. |
| Nonprofit Organization | Establishing a nonprofit to address a social issue. | A nonprofit business plan explaining the mission, target beneficiaries, programs, fundraising strategies, and organizational structure. | Objectives include securing grants and donations, implementing programs, and achieving social impact goals. |
| Financial Services | Launching a financial planning firm. | A financial services business plan detailing services offered, target client demographics, fee structure, marketing, compliance, and revenue projections. | Objectives include acquiring clients, building a client portfolio, and achieving revenue growth and profitability. |
| Food Truck | Starting a mobile food truck business. | A food truck business plan outlining the menu, food truck design, location strategy, pricing, marketing, and sales projections. | Objectives include securing funding, building a customer base, and achieving profitability with mobile food sales. |
| Event Planning | Launching an event planning company. | An event planning business plan describing services offered, target events, vendor relationships, pricing, marketing, and growth strategy. | Objectives include acquiring event contracts, delivering successful events, and achieving revenue growth. |
| Educational Institution | Starting a private school. | An educational business plan outlining the curriculum, facilities, enrollment strategy, tuition structure, and accreditation process. | Objectives include securing initial funding, enrolling students, and maintaining educational quality and growth. |
| Transportation Services | Establishing a ride-sharing service. | A transportation business plan detailing the app platform, driver recruitment, pricing, marketing, and expansion strategy to attract riders and drivers. | Objectives include securing initial funding, launching the service, and growing the user base and geographic reach. |
| Green Energy Startup | Developing new renewable energy technology. | A green energy startup business plan explaining the technology innovation, research and development, market potential, and funding requirements. | Objectives include securing research grants, advancing technology development, and entering the renewable energy market. |
| Fashion Design | Launching a fashion design label. | A fashion design business plan detailing the brand concept, clothing lines, production, pricing, marketing, and distribution strategy. | Objectives include securing funding, gaining brand recognition, and achieving sales and growth in the fashion industry. |
| Related Concepts | Description | When to Apply |
|---|---|---|
| Business Plan | A Business Plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the goals, objectives, strategies, and operations of a business venture. It typically includes sections on executive summary, company description, market analysis, organization and management, products or services, marketing and sales, funding and financial projections, and appendices. A well-crafted business plan serves as a roadmap for entrepreneurs, guiding decision-making, attracting investors, and communicating the business vision to stakeholders. | – When launching a new business venture or seeking funding. – Particularly in understanding the market landscape, defining business objectives, and outlining strategies to achieve growth and profitability, and in exploring techniques to develop a detailed business plan, conduct market research, and analyze financial feasibility to secure funding, align stakeholders, and drive business success. |
| Market Analysis | Market Analysis is the process of evaluating market dynamics, trends, opportunities, and competitors to assess the viability of a business idea or venture. It involves gathering and analyzing data on industry size, growth potential, customer needs, preferences, and behaviors, as well as competitive landscape, pricing strategies, and regulatory factors. Market analysis provides insights into market segmentation, target audience, and positioning strategies, informing business decisions and marketing efforts. | – When entering a new market or launching a new product. – Particularly in understanding customer needs, market demand, and competitive landscape, and in exploring techniques to conduct market research, analyze industry trends, and assess market attractiveness to identify growth opportunities, mitigate risks, and develop effective market entry or expansion strategies that align with business objectives and target market needs. |
| Financial Projections | Financial Projections are forecasts of a company’s future financial performance, including revenues, expenses, profits, cash flow, and financial position. They typically include income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and break-even analysis, projecting financial outcomes over a specific period, such as one to five years. Financial projections help assess business feasibility, estimate funding requirements, and evaluate investment returns, guiding strategic planning and resource allocation decisions. | – When planning budgets or forecasting revenue growth. – Particularly in understanding revenue streams, cost structures, and investment needs, and in exploring techniques to develop financial models, forecast cash flows, and project profitability to support business planning, fundraising efforts, and investment decisions, and to monitor financial performance and adjust strategies to achieve financial goals and sustainability. |
| Marketing Strategy | Marketing Strategy is a plan of action for promoting and selling products or services to target customers. It involves defining target markets, positioning offerings, and developing marketing mix elements, such as product, price, place, and promotion strategies, to achieve marketing objectives and drive business growth. Marketing strategies may include digital marketing, content marketing, social media, advertising, and other tactics to reach and engage audiences effectively. | – When launching a new product or expanding into new markets. – Particularly in understanding customer needs, competitive advantages, and market opportunities, and in exploring techniques to develop marketing plans, set marketing goals, and implement marketing campaigns to acquire customers, increase brand awareness, and generate demand, and to measure marketing performance and adjust strategies based on feedback and market insights to achieve business objectives and sales targets. |
| Operations Management | Operations Management is the design, execution, and control of business processes and activities to deliver products or services efficiently and effectively. It involves planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling operational functions, such as production, inventory management, supply chain logistics, quality control, and customer service, to meet customer needs and organizational goals while maximizing productivity and minimizing costs. | – When streamlining workflows or improving productivity. – Particularly in understanding production processes, resource allocation, and performance metrics, and in exploring techniques to optimize operations, reduce waste, and enhance efficiency, such as lean management, Six Sigma, and process automation, to improve business performance, deliver value to customers, and achieve competitive advantage in the marketplace. |
| Strategic Planning | Strategic Planning is the process of setting goals, defining strategies, and allocating resources to achieve long-term objectives and competitive advantage. It involves assessing internal strengths and weaknesses, external opportunities and threats, and industry trends to formulate strategic initiatives and action plans that align with the organization’s mission, vision, and values. Strategic planning guides decision-making, resource allocation, and performance evaluation at all levels of the organization. | – When setting long-term goals or repositioning the company. – Particularly in understanding market dynamics, competitive positioning, and growth opportunities, and in exploring techniques to develop strategic plans, conduct SWOT analysis, and define strategic objectives, initiatives, and performance metrics to align stakeholders, allocate resources effectively, and drive organizational success and sustainability in dynamic business environments. |
| Risk Management | Risk Management is the process of identifying, assessing, prioritizing, and mitigating risks that may impact business objectives or operations. It involves analyzing potential risks, such as financial, operational, legal, regulatory, or reputational risks, and developing strategies and controls to manage or minimize their impact on business continuity and performance. Risk management aims to protect assets, reduce liabilities, and enhance resilience against uncertainty and adverse events. | – When evaluating investment opportunities or anticipating threats. – Particularly in understanding risk exposures, vulnerabilities, and consequences, and in exploring techniques to assess risk likelihood and impact, develop risk mitigation plans, and implement risk controls and monitoring mechanisms to minimize losses, exploit opportunities, and ensure business continuity, compliance, and resilience in volatile and uncertain environments. |
| Human Resource Management | Human Resource Management is the process of managing human capital to achieve organizational goals and objectives. It involves recruiting, selecting, training, developing, compensating, and retaining employees to build a skilled and motivated workforce that contributes to business success. Human resource management addresses various HR functions, such as workforce planning, performance management, employee relations, diversity and inclusion, and talent development, to optimize organizational effectiveness and employee engagement. | – When scaling operations or developing organizational culture. – Particularly in understanding workforce needs, skills gaps, and talent requirements, and in exploring techniques to attract, retain, and develop employees, such as recruitment strategies, training programs, performance incentives, and employee engagement initiatives, to build a high-performing organization, foster a positive work environment, and achieve strategic objectives and growth targets. |
| Business Model Innovation | Business Model Innovation involves creating new or modifying existing business models to deliver value to customers, capture market opportunities, and achieve sustainable competitive advantage. It encompasses rethinking key elements of the business model, such as value proposition, revenue streams, cost structure, distribution channels, and customer relationships, to adapt to changing market conditions, disruptive technologies, and evolving customer needs. Business model innovation drives business growth and transformation. | – When responding to market disruptions or exploring new revenue streams. – Particularly in understanding customer preferences, market trends, and competitive dynamics, and in exploring techniques to innovate business models, such as value proposition design, revenue model experimentation, and ecosystem partnerships, to create differentiated offerings, unlock new sources of value, and seize growth opportunities in dynamic and competitive markets. |
| Strategic Partnerships | Strategic Partnerships are collaborative relationships between organizations to achieve mutual goals, leverage complementary strengths, and create value. They involve establishing formal or informal alliances, joint ventures, or co-development agreements with other companies, suppliers, distributors, or industry stakeholders to share resources, capabilities, risks, and rewards and pursue strategic objectives that may be difficult to achieve independently. Strategic partnerships enable organizations to expand market reach, access new capabilities, and drive innovation and growth. | – When entering new markets or accelerating innovation. – Particularly in understanding market trends, competitive positioning, and growth opportunities, and in exploring techniques to identify and engage potential partners, negotiate partnership agreements, and align strategic objectives and incentives to create synergistic relationships that drive value creation, market expansion, and competitive advantage for all parties involved. |
Read also: Business Strategy, Examples, Case Studies, And Tools
Read Next: Lean Canvas, Agile Project Management, Scrum, MVP, VTDF.
The FourWeekMBA Business Strategy Toolbox

Blockchain Business Model Framework











Methodologies & Frameworks
- Business Model Canvas Guide
- Business Model Patterns
- Business Model Navigator
- Build An Exceptional Viable Product
- Blitzscaling Canvas Guide
- Lean Startup Canvas
- Business Model Framework
- Flywheel And Virtuous Sales Cycles
- Growth Marketing
- Pretotyping Methodology
- SEO Hacking Framework
- Technology Adoption Curve
- Value Proposition Canvas
- What Is OKR
- What Is Scrum?
Business Models Case Studies
- Amazon Business Model
- Netflix Business Model
- Starbucks Business Model
- LinkedIn Business Model
- Google Business Model
- Uber Business Model
- Lyft Business Model
- Robinhood Business Model
- Nike Business Model
- DuckDuckGo Business Model
- ALDI Business Model
- Apple Business Model
- TOMS Business Model
- Slack Business Model
- Fiverr Business model
- Pinterest Business Model
- Telegram Business Model
- TripAdvisor Business Model
- Booking Business Model
Startup Resources






