In the Business Model Canvas, the Revenue Streams building block details the way a business intends to solve customer problems for financial gain. Revenue streams represent the various ways a business generates cash from each customer segment.
Understanding revenue streams in the Business Model Canvas
In determining revenue streams, the business must answer the following questions:
- For what value are customers ultimately willing to pay? This is determined by how big a problem is in their life.
- How much does each revenue stream contribute to overall revenue in terms of percentage contribution?
- How do customers prefer to pay? In other words, how will these preferences influence the revenue stream(s) chosen?
There are two types of revenue streams. The first is a transaction-based stream, where customers make a one-time payment for a product or service. The second is a recurring stream, where customers make continuous payments to maintain access to the product or certain product features.
Note that this section of the Business Model Canvas represents the cash the company generates – not the profit.
Revenue stream pricing mechanisms
Pricing mechanisms refer to the impact of pricing on the expected supply and demand of a product. Each company revenue stream can have its own pricing mechanism, which can be divided into two types.
1 – Fixed pricing
Fixed pricing mechanisms have predefined prices based on a static set of variables. Examples include:
List price
Where prices are fixed and non-negotiable. The main courses on a restaurant menu are list price. Every diner pays the same amount for the same dish.
Product feature dependent
Here, the price depends on product quality or value proposition features. Organic foods tend to attract a higher price than their non-organic equivalents.
Customer segment dependent
Where the price is determined by a customer segment. Some businesses offer discounts to seniors or those with a qualifying membership card.
Volume dependent
Where the price is a function of the volume purchased. Costco shoppers who purchase in bulk tend to be charged less per item than customers who shop in traditional supermarkets.
2 – Dynamic pricing
Dynamic pricing mechanisms, on the other hand, change according to fluctuating market conditions.
There are also four types in this category:
Yield management
Product pricing is determined by inventory levels at the time of purchase.
Yield management is a feature of airline and hotel reservation systems, with prices fluctuating according to supply and demand.
Negotiated pricing
Where the buyer and seller negotiate a mutually beneficial price. Negotiation is often involved in the sale of a home or vehicle.
Real-time market
Prices are determined by broader supply and demand factors.
The stock market is perhaps the best example, with share prices based on the number of buyers and sellers at any given time.
Oil, iron, coal, uranium, and other commodity prices also fluctuate for the same reasons.
Auction
Where the price is determined by a competitive bidding process.
Revenue stream models
How are revenue streams generated? Let’s take a look at a few models below:
Asset sales
Where a company sells the rights to a physical product to consumers. Amazon and eBay are two examples.
Subscription fees
Which are paid by consumers for constant access to a product or service. Examples include Spotify and Netflix.
Usage fees
In this case, the company earns revenue based on how much a consumer uses its services. Pricing for smartphone contracts depends on how much data the customer desires.
Licensing
This involves a company charging customers access to copyrighted or patented intellectual property. Licensing is a common revenue stream in the music, sports, media, and technology industries.
Lending, renting, and leasing
As the names suggest, money is made by the company selling temporary access to its products or services for a set period.
Key takeaways
- In the Business Model Canvas, the Revenue Streams building block details the way a business intends to solve customer problems for financial gain. These revenue streams may be transaction-based or recurring.
- Revenue streams are based on fixed or dynamic pricing mechanisms, with both mechanisms influencing price via broad and sometimes more localized supply and demand factors.
- Examples of revenue stream models include asset sales, usage fees, subscription fees, licensing, lending, renting, and leasing.
Key Highlights
- Revenue Streams Definition: Revenue streams represent the different ways a business generates cash from its customers in exchange for the value it provides to them. It focuses on how the company plans to solve customer problems for financial gain.
- Types of Revenue Streams: There are two main types of revenue streams: transaction-based and recurring. Transaction-based revenue streams involve one-time payments for products or services, while recurring streams involve continuous payments to maintain access to products or specific features.
- Revenue Stream Pricing Mechanisms: Pricing mechanisms in revenue streams refer to how pricing affects the supply and demand of a product or service. Pricing can be fixed, with predefined prices based on static variables, or dynamic, changing according to fluctuating market conditions.
- Fixed Pricing Mechanisms: Examples of fixed pricing mechanisms include list prices (non-negotiable prices), product feature-dependent prices, customer segment-dependent prices, and volume-dependent prices.
- Dynamic Pricing Mechanisms: Dynamic pricing mechanisms change based on market conditions. Examples include yield management (pricing based on inventory levels), negotiated pricing (mutually beneficial price negotiation), real-time market pricing (based on broader supply and demand factors), and auction pricing (competitive bidding).
- Revenue Stream Models: Revenue streams can be generated through various models, including:
- Asset Sales: Selling physical products to consumers (e.g., Amazon, eBay).
- Subscription Fees: Charging consumers for constant access to a product or service (e.g., Spotify, Netflix).
- Usage Fees: Earning revenue based on consumer usage (e.g., smartphone contracts based on data usage).
- Licensing: Charging customers for access to copyrighted or patented intellectual property (e.g., music, sports, media, technology).
- Lending, Renting, and Leasing: Selling temporary access to products or services for a set period.
Case Studies
| Company | Revenue Model | Case Study | Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Netflix | Subscription-Based Model | Netflix’s subscription streaming service | Netflix relies on monthly subscription fees, providing access to a vast library of content with no ads. |
| Spotify | Freemium Model | Spotify’s free and premium music streaming | Spotify offers both free ad-supported and premium ad-free subscriptions, generating revenue from premium users and advertisers. |
| Amazon | E-commerce and Marketplace Model | Amazon’s online retail and third-party sellers | Amazon generates revenue through product sales, third-party seller fees, and Amazon Web Services (AWS). |
| Advertising Model | Google’s online advertising, AdWords, and AdSense | Google earns revenue by displaying ads on its search results pages and partner websites. | |
| Apple | Hardware and Ecosystem Model | Apple’s sale of hardware and services | Apple generates revenue from the sale of hardware (iPhone, Mac) and services (Apple Music, App Store). |
| Airbnb | Commission Model | Airbnb’s commission from host and guest bookings | Airbnb earns a percentage from hosts and guests for each booking facilitated on its platform. |
| Uber | Commission and Ride Fees Model | Uber’s commission from drivers and ride fees | Uber takes a commission from driver earnings and charges riders based on distance and time. |
| Subscription and Recruitment Model | LinkedIn’s premium subscriptions and job postings | LinkedIn generates revenue from premium subscriptions, talent solutions, and marketing solutions. | |
| Dropbox | Freemium and Subscription Model | Dropbox’s cloud storage and file-sharing | Dropbox offers free storage with premium subscriptions for additional features and space. |
| Facebook (Meta) | Advertising and Data Monetization Model | Facebook and Instagram’s advertising and user data | Meta earns revenue by displaying targeted ads to users and monetizing user data. |
| Etsy | Handmade and Artisanal Goods Marketplace | Etsy’s platform for artisans and crafters | Etsy provides a platform for artisans to sell their unique handmade products to a global audience. |
| Upwork | Freelance Talent Marketplace | Upwork’s platform for freelancers and clients | Upwork connects businesses with freelance talent for various projects, spanning from writing to programming. |
| eBay | Online Auction and Sales Marketplace | eBay’s platform for auctions and sales | eBay allows individuals and businesses to buy and sell a wide range of goods through auctions and direct sales. |
| Alibaba Group | B2B and B2C E-commerce Marketplace | Alibaba’s e-commerce and wholesale platforms | Alibaba connects global buyers and sellers, facilitating trade and e-commerce transactions on a massive scale. |
| Turo | Peer-to-Peer Car Rental | Turo’s platform for car owners and renters | Turo enables individuals to rent their vehicles to travelers, disrupting the traditional car rental industry. |
| Fiverr | Freelance Services Marketplace | Fiverr’s platform for freelance services | Fiverr offers a marketplace for freelancers to offer a wide range of services, from graphic design to content writing. |
| TaskRabbit | On-Demand Task and Service Marketplace | TaskRabbit’s platform for taskers and clients | TaskRabbit connects individuals with skilled taskers who can complete a variety of household and business tasks. |
| OpenTable | Restaurant Reservation Marketplace | OpenTable’s platform for restaurant reservations | OpenTable allows users to book restaurant reservations and helps restaurants manage their tables efficiently. |
| StockX | Sneaker and Collectibles Marketplace | StockX’s platform for sneakers and collectibles | StockX provides a marketplace for authenticated sneaker and collectible sales, ensuring transparency and trust. |
| Poshmark | Fashion Resale Marketplace | Poshmark’s platform for fashion resale | Poshmark connects fashion enthusiasts to buy and sell gently used clothing and accessories. |
| Thumbtack | Local Services Marketplace | Thumbtack’s platform for local service providers | Thumbtack helps users find and hire local service professionals, from plumbers to wedding photographers. |
| HomeAway (Vrbo) | Vacation Rental Marketplace | HomeAway’s platform for vacation rentals | HomeAway offers a marketplace for vacation rentals, connecting travelers with property owners. |
| Booking.com | Hotel and Accommodation Booking | Booking.com’s online travel agency platform | Booking.com enables travelers to book hotels and accommodations worldwide, serving as an intermediary between customers and hotels. |
| Zillow | Real Estate Marketplace | Zillow’s platform for buying and selling homes | Zillow provides tools for home buyers, sellers, and renters, simplifying the real estate process. |
| Freelancer.com | Freelance Job Marketplace | Freelancer.com’s platform for freelance jobs | Freelancer.com connects employers with freelancers to complete a wide range of projects, from software development to graphic design. |
| Rover | Pet Services Marketplace | Rover’s platform for pet care services | Rover connects pet owners with pet sitters and walkers, offering a range of pet care services. |
| 99designs | Design Services Marketplace | 99designs’ platform for design contests | 99designs hosts design contests, allowing businesses to receive custom designs from a global community of designers. |
| Subscription and In-App Purchases Model | WhatsApp’s subscription and in-app sticker purchases | WhatsApp offers a free messaging service with revenue generated from subscriptions and in-app purchases. | |
| Patreon | Membership and Crowdfunding Model | Patreon’s support for content creators | Patreon allows creators to offer exclusive content to paying members, generating income through memberships. |
| Shopify | Subscription and E-commerce Model | Shopify’s e-commerce platform and subscription fees | Shopify offers e-commerce solutions and earns revenue through monthly subscription fees and transaction fees. |
| HubSpot | Inbound Marketing and SaaS Model | HubSpot’s inbound marketing and SaaS services | HubSpot provides inbound marketing and sales software on a subscription basis, generating recurring revenue. |
| Airbnb for Work | Corporate Travel and Service Fees Model | Airbnb for Work’s service fees for corporate travel | Airbnb for Work charges service fees for businesses booking accommodations and experiences. |
| Coursera | Online Education and Certification Model | Coursera’s online courses and specialization certificates | Coursera offers courses for free or as part of a subscription, with revenue generated from paid certificates. |
| Yelp | Advertising and Local Business Model | Yelp’s advertising and partnerships with local businesses | Yelp offers advertising and business solutions, generating revenue through partnerships. |
| LinkedIn Talent Solutions | Recruitment and Subscription Model | LinkedIn’s recruitment tools and premium subscriptions | LinkedIn Talent Solutions provides tools for talent recruitment and generates revenue through premium subscriptions. |
| Square | Payment Processing and Financial Services | Square’s payment processing and financial services | Square offers payment processing and financial services, earning revenue through transaction fees and subscriptions. |
| Salesforce | CRM and Enterprise Software Model | Salesforce’s customer relationship management (CRM) | Salesforce generates revenue from its CRM software and cloud services for enterprises. |
| Udemy | Online Learning and Course Sales Model | Udemy’s marketplace for online courses | Udemy allows instructors to sell courses, with revenue shared between the platform and instructors. |
| GoFundMe | Crowdfunding and Platform Fees Model | GoFundMe’s crowdfunding platform and fees | GoFundMe facilitates fundraising campaigns and charges platform fees on donations. |
| Shutterfly | Photo Printing and Personalized Products | Shutterfly’s photo books, gifts, and printing services | Shutterfly generates revenue by selling personalized photo products. |
| Robinhood | Commission-Free Stock Trading Model | Robinhood’s commission-free stock and crypto trading | Robinhood offers commission-free trading and generates revenue through order flow payments. |
| Salesforce Marketing Cloud | Marketing Automation Model | Salesforce Marketing Cloud’s marketing automation | Salesforce’s marketing automation tools generate revenue through subscription and usage fees. |
| DoorDash | Food Delivery and Service Fees Model | DoorDash’s food delivery and service fees | DoorDash charges service fees to customers and restaurants for food delivery services. |
| Expedia | Online Travel Booking and Commissions | Expedia’s online travel booking and commissions | Expedia earns revenue by facilitating online travel bookings and taking commissions from hotels and airlines. |
| GitHub | Developer Tools and Enterprise Services | GitHub’s code hosting and collaboration platform | GitHub provides free and paid developer tools and earns revenue from enterprise subscriptions. |
| SurveyMonkey | Survey and Data Insights Model | SurveyMonkey’s survey creation and data analysis | SurveyMonkey offers survey tools and generates revenue from premium plans and data insights. |
| ZoomInfo | B2B Sales and Marketing Intelligence | ZoomInfo’s B2B sales and marketing intelligence | ZoomInfo offers B2B data and intelligence services, earning revenue through subscriptions and sales. |
| Related Frameworks, Models, or Concepts | Description | When to Apply |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model Canvas | The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management tool that provides a visual framework for describing, analyzing, and innovating business models. Revenue Streams are one of the nine building blocks of the Business Model Canvas, representing the various sources of revenue generated by a business. | Apply the Business Model Canvas to analyze and design business models, including the identification and evaluation of different revenue streams. Use it during the business planning stage or when considering business model innovation to understand how revenue is generated and how it contributes to overall business sustainability and growth. |
| Value Proposition Design | Value Proposition Design is a methodology for creating compelling value propositions that address customer needs and pain points. Revenue Streams are closely linked to value propositions, as they reflect the value captured by the business from its customers. | Utilize Value Proposition Design to develop value propositions that resonate with target customers and drive revenue generation. Incorporate Revenue Streams analysis to ensure that the value created for customers translates into revenue opportunities for the business, aligning value creation with revenue capture effectively. |
| Subscription Business Model | The Subscription Business Model involves offering products or services to customers on a recurring subscription basis, typically with regular payments. Revenue Streams in a subscription model consist of subscription fees paid by customers in exchange for ongoing access to the product or service. | Apply the Subscription Business Model to create recurring revenue streams and establish long-term customer relationships. Use it when developing subscription-based offerings or transitioning from traditional one-time sales models to subscription-based revenue models to enhance revenue predictability and customer lifetime value. |
| Freemium Model | The Freemium Model offers basic features or services for free while charging users for premium features or additional functionalities. Revenue Streams in a freemium model come from a combination of free users (who may generate revenue through advertising or data monetization) and premium users (who pay for access to premium features). | Utilize the Freemium Model to attract a large user base with free offerings and monetize premium features or upgrades. Apply it when developing digital products, software applications, or online platforms to maximize user acquisition and engagement while capturing revenue from users willing to pay for enhanced functionality or value-added features. |
| E-commerce Business Model | The E-commerce Business Model involves selling products or services online through digital channels. Revenue Streams in an e-commerce model come from online sales transactions, including product sales, service fees, subscription charges, and other revenue-generating activities conducted on e-commerce platforms or websites. | Apply the E-commerce Business Model to establish an online presence and sell products or services directly to customers over the internet. Use it when launching an online store, marketplace, or digital platform to leverage digital channels and technology to reach a wider audience and generate revenue through online sales and transactions. |
| Platform Business Model | The Platform Business Model facilitates interactions and transactions between multiple groups of users or participants on a digital platform. Revenue Streams in a platform model can come from various sources, such as transaction fees, subscription charges, advertising revenue, data monetization, and value-added services offered to platform users. | Utilize the Platform Business Model to create a digital platform that connects buyers and sellers, service providers and customers, or other user groups to facilitate transactions and exchanges. Apply it when building online marketplaces, social networking platforms, or sharing economy platforms to capture revenue from platform usage, transactions, and ecosystem growth. |
| Advertising Business Model | The Advertising Business Model relies on generating revenue through advertising placements and sponsorships. Revenue Streams in an advertising model come from advertisers who pay for displaying ads to target audiences on various media channels, such as websites, social media platforms, search engines, and traditional media outlets. | Apply the Advertising Business Model to monetize digital content, websites, apps, or media channels by displaying ads to target audiences. Use it when offering free content, services, or platforms to users and monetizing audience attention and engagement through advertising placements, sponsorships, or branded content partnerships. |
| Affiliate Marketing Model | The Affiliate Marketing Model involves promoting third-party products or services and earning commissions for driving sales or referrals. Revenue Streams in an affiliate marketing model come from affiliate commissions earned for each successful sale, lead, or referral generated through affiliate marketing activities. | Apply the Affiliate Marketing Model to monetize online content, blogs, websites, or social media channels by promoting affiliate products or services to target audiences. Use it when partnering with affiliate programs or networks to earn commissions for driving sales or referrals and leveraging existing audience reach and engagement to generate revenue through affiliate marketing partnerships. |
| Licensing and Royalties | Licensing and Royalties involve granting permission to use intellectual property, proprietary technology, or brand assets in exchange for licensing fees or royalties. Revenue Streams from licensing and royalties come from licensing agreements, franchise fees, patent royalties, or other forms of intellectual property licensing arrangements. | Utilize Licensing and Royalties agreements to monetize intellectual property assets, technology innovations, or brand properties. Apply it when licensing out patents, trademarks, copyrights, or proprietary know-how to third parties, franchising business concepts or brand names, or entering into partnership agreements that involve revenue-sharing arrangements based on intellectual property usage or exploitation. |
| Partnership and Sponsorship Model | The Partnership and Sponsorship Model involves collaborating with other businesses, organizations, or individuals to co-create value, drive brand awareness, or support mutual objectives. Revenue Streams from partnerships and sponsorships come from partnership agreements, sponsorship deals, co-branding initiatives, or revenue-sharing arrangements with partner entities. | Apply the Partnership and Sponsorship Model to leverage strategic alliances, collaborations, or sponsorships to generate additional revenue streams and support business objectives. Use it when partnering with complementary businesses, industry associations, influencers, or event organizers to co-market products or services, access new customer segments, or enhance brand visibility and credibility through sponsorship or co-branding opportunities. |
Use Revenue Modeling Instead


Read: Revenue Model, Pricing Model.
Alternatives to the Business Model Canvas
FourWeekMBA Squared Triangle Business Model
This framework has been thought for any type of business model, be it digital or not. It’s a framework to start mind mapping the key components of your business or how it might look as it grows. Here, as usual, what matters is not the framework itself (let’s prevent to fall trap of the Maslow’s Hammer), what matters is to have a framework that enables you to hold the key components of your business in your mind, and execute fast to prevent running the business on too many untested assumptions, especially about what customers really want. Any framework that helps us test fast, it’s welcomed in our business strategy.

FourWeekMBA VTDF Framework For Tech Business Models
This framework is well suited for all these cases where technology plays a key role in enhancing the value proposition for the users and customers. In short, when the company you’re building, analyzing, or looking at is a tech or platform business model, the template below is perfect for the job.


Download The VTDF Framework Template Here
FourWeekMBA VBDE Framework For Blockchain Business Models
This framework is well suited to analyze and understand blockchain-based business models. Here, the underlying blockchain protocol, and the token economics behind it play a key role in aligning incentives and also in creating disincentives for the community of developers, individual contributors, entrepreneurs, and investors that enable the whole business model. The blockchain-based model is similar to a platform-based business model, but with an important twist, decentralization should be the key element enabling both decision-making and how incentives are distributed across the network.

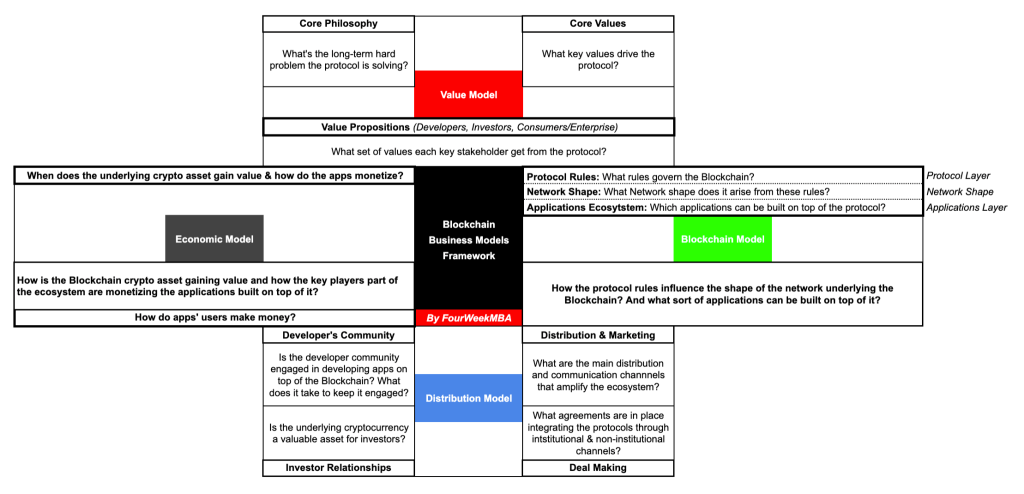
Download The VBDE Framework Template Here
FourWeekMBA Business Toolbox
















Main Free Guides:







