A wholesale business purchases goods in bulk from a supplier and then sells them to other merchants in smaller quantities. The wholesaler relies on economies of scale to make a profit. Most wholesale businesses do not sell to the end-user. However, two exceptions are commodities trader Trafigura and big-box retailer Costco. Sysco is the largest wholesale foodservice distributor in the United States while McKesson Corporation is the largest distributor of pharmaceutical drugs and various other healthcare products and technology.
Introduction
A wholesale business purchases goods in bulk from a supplier and then sells them to other merchants in smaller quantities. The wholesaler relies on economies of scale to receive a discount price from the manufacturer and then adds mark-up before selling to the merchant. Most merchants are not the end-user of the product, but as we will discover later, there are exceptions to this rule.
Wholesalers play an important role in the market. They maintain supply-demand equilibrium by storing goods until there is merchant demand. What’s more, a wholesaler is responsible for the distribution and transportation of goods from their warehouse and bears the risks associated with product shrinkage or fluctuations in demand.
The rest of this article will be devoted to discussing some specific wholesale business examples.
Costco

Costco, also known as Costco Wholesale Corporation, is an American multinational big-box retail chain founded by James Sinegal, Jeffrey Brotman, Sol Price, and Robert Price in 1976.
Costco is a membership-only warehouse that requires consumers to purchase a membership before they can shop. The company is somewhat unusual in that it is a retailer and a wholesaler at the same time. In other words, Costco purchases wholesale products from the manufacturer and sells them to the end-user. However, the company also sells the same goods to other businesses under a more traditional wholesale business model.
Trafigura
Trafigura is a Singaporean commodity wholesaler that was established in 1993. The company sources raw commodities from miners and fossil fuel producers and, like Costco, supplies end-users which include power plants, construction companies, and state governments.
Despite only existing for approximately 30 years, Trafigura is the largest private metals trader in the world with total revenue for 2021 of $231.3 billion.
Sysco
Sysco Corporation is an American multinational involved in the wholesale distribution of kitchen equipment, food products, and tabletop items to restaurants, schools, and health facilities. The company also distributes products to hotels and other food services companies such as Sodexo and Aramark.
Sysco is the largest wholesale foodservice distributor in the United States with over 600,000 clients in 90 countries.
Toyota Tsusho
Toyota Tsusho is a trading arm of the Toyota Group of companies. The corporation’s primary function is to support Toyota’s automotive division and supply other vehicle manufacturers with wholesale parts.
However, Toyota Tsusho is a vast company with additional interests in metals, machinery, energy, chemicals, electronics, food and customer service, and logistics.
McKesson Corporation
McKesson Corporation is the largest distributor of pharmaceutical drugs, healthcare technology, care management devices, and medical supplies in North America.
The corporation distributes 33% of all pharmaceuticals across the continent with the company reporting full-year revenue of $238.2 billion in May 2021.
Key Highlights:
- Wholesale Business Overview: Wholesale businesses purchase goods in bulk from suppliers and sell them in smaller quantities to other merchants, relying on economies of scale for profitability. They often don’t sell directly to end-users, but there are exceptions.
- Role of Wholesalers: Wholesalers help maintain supply-demand balance by storing goods until merchant demand arises. They handle distribution, transportation, and sometimes even bear risks associated with products.
- Costco: Costco is a membership-based big-box retail chain that operates as both a retailer and a wholesaler. It purchases products in bulk and sells to both end-users and businesses under a single-step distribution strategy.
- Trafigura: Trafigura is a commodity wholesaler based in Singapore, sourcing raw commodities from miners and fossil fuel producers. It supplies end-users like power plants, construction companies, and state governments.
- Sysco Corporation: Sysco is the largest wholesale foodservice distributor in the United States, supplying kitchen equipment, food products, and more to restaurants, schools, health facilities, hotels, and other food service companies.
- Toyota Tsusho: Toyota Tsusho, a trading arm of the Toyota Group, supports Toyota’s automotive division and supplies wholesale parts to other vehicle manufacturers. It also has interests in various industries.
- McKesson Corporation: McKesson Corporation is North America’s largest distributor of pharmaceutical drugs, healthcare technology, medical supplies, and more. It plays a vital role in the healthcare industry.
- Business Diversity: Some wholesale companies diversify their interests beyond their primary industries, as seen with Toyota Tsusho’s involvement in metals, machinery, energy, and more.
- Market Influence: Wholesale businesses significantly impact various industries by connecting suppliers and merchants, ensuring a smooth flow of goods, and contributing to the overall supply chain.
Additional Case Studies
| Case Study | Description | Application in Wholesale |
|---|---|---|
| Costco | Costco Wholesale Corporation is a global retailer known for its warehouse club model. It offers bulk products to members at discounted prices. | – Membership-based model to provide exclusive access – Bulk purchasing and discounts to attract and retain customers – Efficient supply chain management to lower costs and prices |
| Sysco Corporation | Sysco is a leading foodservice distribution company that supplies restaurants, hotels, and healthcare facilities with food and related products. | – Streamlined distribution and delivery processes – Inventory management and just-in-time delivery to reduce waste – Extensive product variety to meet diverse customer needs |
| Grainger | W.W. Grainger, Inc. is a distributor of maintenance, repair, and operating (MRO) supplies. It serves businesses with essential products and services. | – Vast catalog of MRO products – Online ordering and e-commerce capabilities for convenience – Inventory management solutions to optimize supply chain – Focus on customer service and support |
| Alibaba Group | Alibaba is a global e-commerce and technology conglomerate. It operates various online marketplaces connecting wholesalers, retailers, and consumers. | – Digital platforms for B2B and B2C transactions – Facilitating global trade and cross-border transactions – Providing a wide range of products and suppliers – Data-driven insights to enhance sourcing |
| Cardinal Health | Cardinal Health is a healthcare services company specializing in pharmaceutical distribution and supply chain management. | – Efficient pharmaceutical distribution network – Compliance and regulatory expertise in healthcare – Inventory optimization for healthcare facilities – Value-added services to support healthcare providers |
| McKesson Corporation | McKesson is a pharmaceutical distribution and healthcare solutions company. It plays a vital role in delivering healthcare products to various healthcare providers. | – Extensive pharmaceutical distribution network – Technology solutions for healthcare providers – Streamlined logistics and supply chain management – Focus on patient safety and healthcare efficiency |
| HD Supply Holdings | HD Supply is a distributor of maintenance, repair, and construction (MRC) products primarily serving professional customers in the construction industry. | – Specialized focus on MRC products – Local and national distribution capabilities – E-commerce platform for easy ordering – Expertise in the construction industry to meet specific needs |
| DHL Supply Chain | DHL Supply Chain is a global logistics and supply chain management company that provides warehousing and distribution services to various industries. | – Warehousing and distribution services for various industries – Inventory management and supply chain optimization – Technology-driven solutions for visibility and efficiency – Focus on sustainability and environmental impact |
| Staples | Staples is a retailer specializing in office supplies, business services, and technology products. | – Wide range of office supplies and technology products – E-commerce platform for business customers – Customized procurement solutions for businesses – Focus on sustainability and responsible sourcing |
| C&S Wholesale Grocers | C&S Wholesale Grocers is one of the largest wholesale grocery supply companies in the United States, serving supermarkets and other retailers. | – Extensive distribution network for grocery products – Inventory management solutions for retailers – Private-label brands and customization options – Focus on sustainability and reducing environmental impact |
Read Next: Wholesale Business Model.
Main Free Guides:
- Business Models
- Business Competition
- Business Strategy
- Business Development
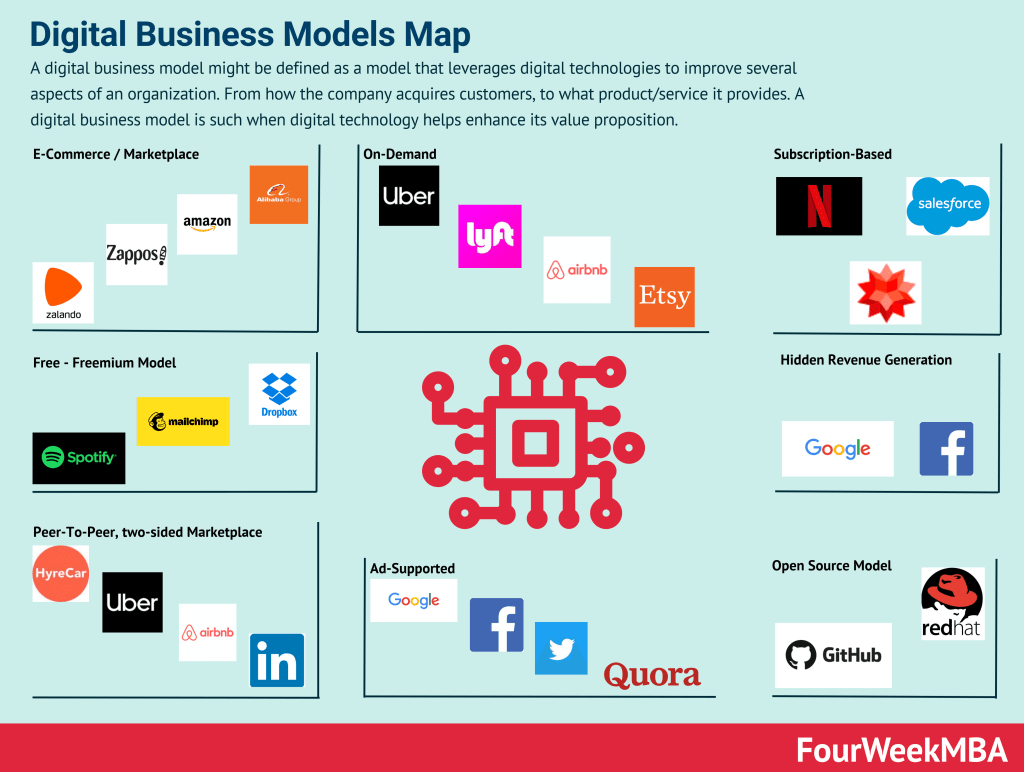
- Digital Business Models
- Distribution Channels
- Marketing Strategy
- Platform Business Models
- Revenue Models
- Tech Business Models
- Blockchain Business Models Framework
Connected Case Studies
Read Also: Costco Business Model

Read Also: Marketplace Business Models

Read Also: Food-Delivery Business Models

Connected Business Model Types And Frameworks







Attention Merchant Business Model
















Main Free Guides:









