Asymmetric Betting

Critical Thinking

Divergent Thinking

Vertical Thinking

Convergent Thinking

Brand Association

Metaphorical Thinking

Affirmations

Cognitive Restructuring

Second-Order Thinking

Choice Overload

Business Valuation Diagram

Scaled Agile Framework

Nadler-Tushman Congruence Model

Toulmin Model

RevOps

OODA Loop

MoSCoW Method

SIPOC Diagram

Six Thinking Hats Model

Straw Man Fallacy

Porter Operational Model

Lightning Decision Jam

Jobs-To-Be-Done

Empathy Mapping

Business model canvas
The business model canvas aims to provide a keen understanding of your business model to provide strategic insights about your customers, product/service, and financial structure;
so that you can make better business decisions.
Blitzscaling canvas
In this article, I’ll focus on the Blitzscaling business model canvas. This is a model based on the concept of Blitzscaling.
That is a particular process of massive growth under uncertainty, and that prioritizes speed over efficiency. It focuses on market domination to create a first-scaler advantage in a scenario of uncertainty.
Pretotyping

Pretotyping is a mixture of the words “pretend” and “prototype,” and it is a methodology used to validate business ideas to improve the chances of building a product or service that people want.
The pretotyping methodology comes from Alberto Savoia’s work summarized in the book “The Right It: Why So Many Ideas Fail and How to Make Sure Yours Succeed.”
This framework is a mixture of the words “pretend” and “prototype,” and it helps to answer such questions (about the product or service to build) as: Would I use it? How, how often, and when would I use it? Would other people buy it? How much would they be willing to pay for it? How, how often, and when would they use it?
Value innovation and blue ocean strategy

A blue ocean is a strategy where the boundaries of existing markets are redefined, and new uncontested markets are created.
At its core, there is value innovation, for which uncontested markets are created, where competition is made irrelevant. And the cost-value trade-off is broken.
Thus, companies following a blue ocean strategy offer much more value at a lower cost for the end customers.
Growth hacking process

Growth hacking is a process of rapid experimentation, coupled with the understanding of the whole funnel, where marketing, product, data analysis, and engineering work together to achieve rapid growth.
The growth hacking process goes through four key stages of analyzing, ideating, prioritizing, and testing.
Pirate metrics

Venture capitalist, Dave McClure, coined the acronym AARRR which is a simplified model that enables us to understand what metrics and channels to look at. At each stage for the users’ path toward becoming customers and referrers of a brand.
Engines of growth

In the Lean Startup, Eric Ries defined the engine of growth as “the mechanism that startups use to achieve sustainable growth.”
He described sustainable growth as following a simple rule, “new customers come from the actions of past customers.”
The three engines of growth are the sticky engine, the viral engine, and the paid engine. Each of those can be measured and tracked by a few key metrics, and it helps plan your strategic moves.
RTVN model

The RTVN model is a straightforward framework that can help you design a business model when you’re at the very early stage of figuring out what you need to make it succeed.
Sales cycle

A sales cycle is the process that your company takes to sell your services and products.
In simple words, it’s a series of steps that your sales reps need to go through with prospects that lead up to a closed sale.
Planning ahead of time the steps your sales team needs to take to close a big contract can help you grow the revenues for your business.
Comparable analysis

A comparable company analysis is a process that enables the identification of similar organizations to be used as a comparison to understand the business and financial performance of the target company.
To find comparables, you can look at two key profiles: the business and economic profile. From the comparable company analysis, it is possible to understand the competitive landscape of the target organization.
Porter’s five forces

Porter’s Five Forces is a model that helps organizations to gain a better understanding of their industries and competition.
It was published for the first time by Professor Michael Porter in his book “Competitive Strategy” in the 1980s.
The model breaks down industries and markets by analyzing them through five forces which you can use to have a first assessment of the market you’re in.
Porter’s Generic Strategies

Porter’s Value Chain

Porter’s Diamond Model

Bowman’s Strategy Clock

VMOST Analysis

Fishbone Diagram

GE McKinsey Matrix

VRIO Framework

3C Analysis

Aida model

AIDA stands for attention, interest, desire, and action. This is a model that is used in marketing to describe the potential journey a customer might go through, before purchasing a product or service. The variation of the AIDA model is the CAB model and the AIDCAS model.
PESTEL analysis

The PESTEL analysis is a framework that can help marketers assess whether macro-economic factors are affecting an organization.
This is a critical step that helps organizations identify potential threats and weaknesses. That can be used in other frameworks such as SWOT or to gain a broader and better understanding of the overall marketing environment.
Technology adoption curve

The technology adoption curve is a model that goes through five stages. Each of those stages (innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, and laggard) has a specific psychographic that makes that group of people ready to adopt a tech product.
This simple concept can help you define the right target for your business strategy.
Business model essence
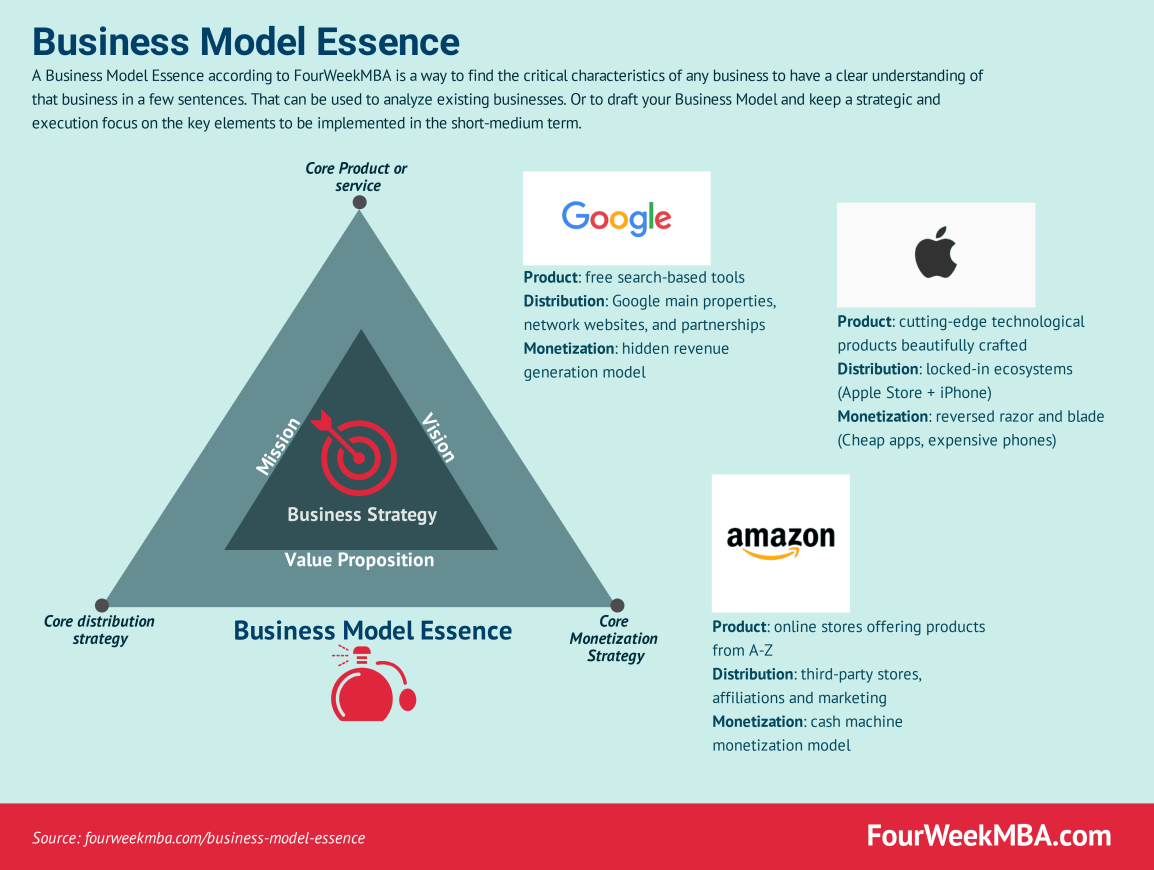
A Business Model Essence, according to FourWeekMBA, is a way to find the critical characteristics of any business to have a clear understanding of that business in a few sentences.
That can be used to analyze existing businesses. Or to draft your Business Model and keep a strategic and execution focus on the key elements to be implemented in the short-medium term.
FourWeekMBA business model framework

An effective business model has to focus on two dimensions: the people dimension and the financial dimension. The people dimension will allow you to build a product or service that is 10X better than existing ones and a solid brand.
The financial dimension will help you develop proper distribution channels by identifying the people that are willing to pay for your product or service and make it financially sustainable in the long run.
TAM, SAM, and SOM

Understanding your TAM, SAM and SOM can help you navigate the market you’re in and to have a laser focus on the market you can reach with your product and service.
Brand Building

Value Proposition Design

Product-Market Fit

Freemium Decision Model

Organizational Design And Structures

Speed-Reversibility Matrix

Minimum Viable Product

SWOT Analysis

Revenue Modeling

Business Experimentation

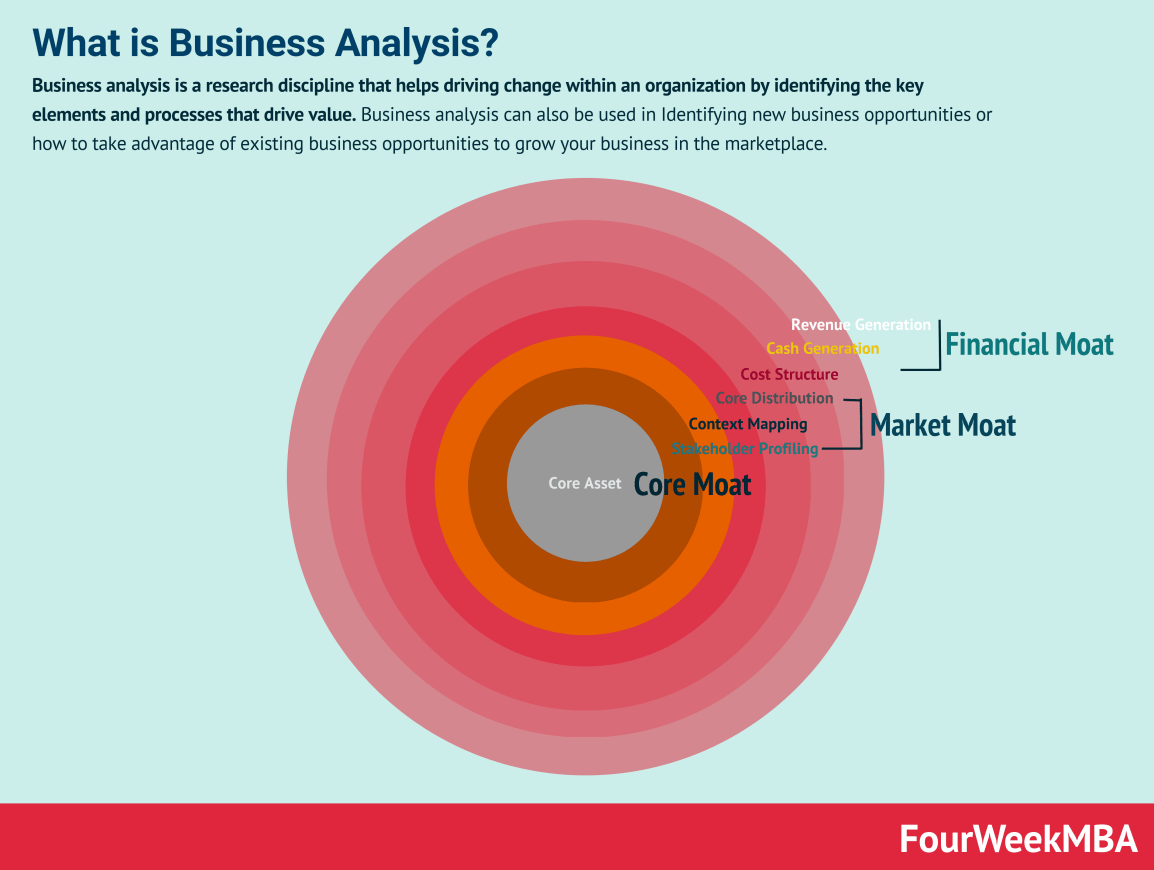
Business Analysis
BCG Matrix

Ansoff Matrix

Key Highlights On Top 30 Frameworks
- Asymmetric Betting: Asymmetric betting refers to making high-impact bets that are easy to reverse, often associated with “Jackpot” and “All-In-Mode” actions.
- Critical Thinking: Critical thinking involves analyzing observations, facts, evidence, and arguments to form a judgment about what someone reads, hears, says, or writes.
- Divergent Thinking: Divergent thinking is a thought process used to generate creative ideas by exploring multiple possible solutions to a problem in a short amount of time.
- Vertical Thinking: Vertical thinking is a structured and analytical problem-solving approach, aiming to arrive at a defined solution.
- Convergent Thinking: Convergent thinking occurs when a problem’s solution can be found by applying established rules and logical reasoning to narrow down the possibilities to the best solution.
- Brand Association: Brand association is the mental connection between a brand and a concept in a consumer’s mind.
- Metaphorical Thinking: Metaphorical thinking involves making comparisons between qualities of objects from different classifications.
- Affirmations: Affirmations are positive statements or phrases repeated to reinforce positive thinking and boost self-esteem.
- Cognitive Restructuring: Cognitive restructuring is the process of changing negative thought patterns to bring about a positive change in behavior and emotions.
- Second-Order Thinking: Second-order thinking involves considering future consequences and implications of decisions beyond the immediate outcomes.
- Choice Overload: Choice overload occurs when consumers are overwhelmed by too many options, leading to decision-making difficulties.
- Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe): SAFe is a framework used by larger organizations to manage the challenges of practicing agile at an enterprise scale.
- Nadler-Tushman Congruence Model: The Nadler-Tushman Congruence Model is a diagnostic tool used to identify problem areas within a company.
- Toulmin Model: The Toulmin model is a system of argumentation used to analyze and categorize arguments based on their structure and effectiveness.
- RevOps (Revenue Operations): RevOps is a framework that aims to maximize revenue potential by aligning sales, marketing, and customer success departments.
- OODA Loop: The OODA Loop is a decision-making process that involves observing, orienting, deciding, and acting quickly to adjust strategies.
- MoSCoW Method: The MoSCoW method is a task prioritization framework that categorizes tasks as Must have, Should have, Could have, and Won’t have.
- SIPOC Diagram: SIPOC diagrams are used for high-level process mapping to provide a common reference point for project teams and identify problem areas.
- Six Thinking Hats Model: The Six Thinking Hats model is a problem-solving approach that considers different perspectives and personalities to generate ideas.
- Straw Man Fallacy: The straw man fallacy involves misrepresenting an opponent’s argument to make rebuttal easier.
- Porter Operational Model: The Porter Operational Model is a visual representation of a business’s value chain to build a viable business model.
- Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ): LDJ is a fast decision-making process designed to provide quick direction in business meetings.
- Jobs-To-Be-Done (JTBD): JTBD framework identifies and organizes consumer needs based on the premise that consumers buy products to get specific jobs done.
- Empathy Mapping: Empathy mapping is a visual representation of user behavior and attitudes to gain insights into user needs.
- Business Model Canvas: The business model canvas is a strategic tool that provides a comprehensive understanding of a business model, enabling better decision-making.
- Blitzscaling Canvas: Blitzscaling canvas is a model based on the concept of blitzscaling, which involves rapid growth under uncertainty.
- Pretotyping: Pretotyping is a methodology to validate business ideas and improve the chances of building a product or service that people want.
- Value Innovation and Blue Ocean Strategy: Blue ocean strategy involves creating new uncontested markets where competition becomes irrelevant by offering much more value at a lower cost.
- Growth Hacking Process: Growth hacking is a process of rapid experimentation and collaboration among marketing, product, data analysis, and engineering teams to achieve rapid growth.
- Pirate Metrics (AARRR): Pirate metrics represent a simplified model that enables businesses to understand metrics and channels in each stage of a user’s path towards becoming a customer and referrer.
- Engines of Growth: The engines of growth are sticky, viral, and paid engines that help startups achieve sustainable growth.
Table Summary
| Framework Name | Description | When to Use | Advantages | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asymmetric Betting | Involves high-impact bets that are easy to reverse. | When you have asymmetric bets with high impact. | Potential for high returns, easy reversibility. | High risk involved. |
| Critical Thinking | Analyzing observations, facts, evidence, and arguments for forming judgments. | In decision-making and problem-solving processes. | Better decision-making, problem-solving skills. | Requires time and practice to develop. |
| Divergent Thinking | Generates creative ideas by exploring multiple solutions to a problem. | When seeking innovative solutions to a problem. | Encourages creativity, explores multiple options. | May lead to unstructured approaches. |
| Vertical Thinking | Favors analytical, structured, sequential problem-solving. | When a structured and reasoned solution is needed. | Systematic problem-solving, defined solutions. | May limit creative thinking. |
| Convergent Thinking | Seeks the single best solution through logical reasoning. | When a single, optimal solution is required. | Efficient problem-solving, clear outcomes. | Limits exploration of alternative solutions. |
| Brand Association | Describes the mental connection between a brand and a concept. | When building brand identity and influencing purchase intent. | Influences consumer decisions, brand recognition. | Complex and difficult to measure. |
| Metaphorical Thinking | Connects qualities of separate objects through metaphorical comparisons. | When seeking creative or abstract insights. | Expands creative thinking, unique perspectives. | May not always lead to practical solutions. |
| Affirmations | Repeating positive statements to boost self-esteem and overcome negativity. | For personal development, overcoming negative thoughts. | Improves self-confidence, promotes positivity. | Effectiveness may vary among individuals. |
| Cognitive Restructuring | Changes negative thought patterns by altering perceptions and reactions. | In cognitive-behavioral therapy and personal growth. | Empowers individuals to change their thinking. | Requires professional guidance in therapy settings. |
| Second-Order Thinking | Assesses decisions by considering future consequences and thinking outside the box. | When making strategic decisions and anticipating outcomes. | Encourages strategic foresight, minimizes risks. | Can lead to overanalysis or indecision. |
| Choice Overload | Deals with the phenomenon of consumers being overwhelmed by too many choices. | In marketing and product design to simplify choices. | Enhances decision-making experience, reduces stress. | May limit variety and personalization. |
| Business Valuation Diagram | Analyzes key aspects of a business to determine its economic value. | When evaluating the worth of a business or company unit. | Provides a structured approach to valuation. | Subjective factors can impact valuations. |
| Scaled Agile Framework | Helps larger organizations implement agile practices at an enterprise scale. | In large organizations to manage agile challenges. | Facilitates agile implementation, role guidance. | May face resistance to change in traditional setups. |
| Nadler-Tushman Model | Identifies problem areas within a company by assessing congruence among different goals. | When assessing organizational performance and alignment. | Pinpoints areas for improvement, alignment clarity. | Complex to implement, requires data collection. |
| Toulmin Model | A system of argumentation that categorizes and evaluates arguments for validity and effectiveness. | In evaluating and developing persuasive arguments. | Helps structure and assess arguments effectively. | May be too structured for some contexts. |
| RevOps | Maximizes revenue potential by aligning sales, marketing, and customer success departments. | In organizations seeking revenue growth and alignment. | Increases collaboration, revenue optimization. | Requires cross-functional coordination. |
| OODA Loop | A decision-making process involving observe, orient, decide, and act, designed for quick adjustments. | In dynamic and fast-changing environments to make rapid decisions. | Adapts to changing situations, promotes agility. | May not suit all decision-making scenarios. |
| MoSCoW Method | Prioritizes tasks into four categories: Must have, Should have, Could have, and Won’t have. | When prioritizing tasks and features within a project. | Clear prioritization, efficient resource allocation. | May require ongoing adjustments as priorities change. |
| SIPOC Diagram | Illustrates high-level process maps and identifies key points in a process for better understanding. | In process improvement and problem-solving efforts. | Simplifies process visualization, identifies issues. | May oversimplify complex processes. |
| Six Thinking Hats Model | A tool for different perspectives in problem-solving, including analytical, emotional, and creative viewpoints. | In group decision-making and brainstorming sessions. | Encourages diverse thinking, balanced discussions. | May require structured facilitation. |
| Straw Man Fallacy | Describes a misrepresentation of an opponent’s argument to make it easier to rebut. | In critical thinking and debate analysis. | Highlights flawed arguments, aids in debate. | Can be used deceptively in arguments. |
| Porter Operational Model | Visualizes the organization’s processes and how it delivers value, helping to build a viable business model. | In designing and optimizing operational processes. | Enhances understanding of value delivery. | May require significant process analysis. |
| Lightning Decision Jam | A fast decision-making method inspired by design sprints, aiming to provide quick direction. | When quick decisions are needed to address challenges or opportunities. | Speeds up decision-making, aligns teams quickly. | May not be suitable for complex decisions. |
| Jobs-To-Be-Done | Defines, categorizes, captures, and organizes consumer needs based on the idea that consumers “hire” products to get jobs done. | In product development and market research. | Focuses on real customer needs, informs product design. | Requires a deep understanding of customer needs. |
| Empathy Mapping | Visualizes user behavior and attitudes to gain insights into user experiences and improve products. | In user research and product design to enhance user understanding. | Enhances user-centric design, identifies pain points. | Interpretation of data may vary. |
| Business Model Canvas | Provides a framework to understand and analyze key aspects of a business model, including customers, products, and finances. | When assessing or designing a business model. | Offers a holistic view of the business model. | May oversimplify complex business situations. |
| Blitzscaling Canvas | Focuses on rapid growth under uncertainty, prioritizing speed over efficiency and market domination. | In startups aiming for rapid and massive growth. | Drives aggressive growth, creates market dominance. | High risk and resource-intensive approach. |
| Pretotyping | A methodology to validate business ideas by pretending to have a product or service before building it. | When testing the viability of a product or service concept. | Minimizes development costs, validates concepts early. | Limited to concept validation, not full development. |
| Value Innovation and Blue Ocean Strategy | Focuses on creating uncontested markets with value innovation, offering more value at a lower cost. | When seeking to redefine markets and create new value propositions. | Breaks away from competition, maximizes value. | Requires innovative thinking and execution. |
| Growth Hacking Process | Rapid experimentation and data-driven approach to achieve fast growth by aligning marketing, product, data analysis, and engineering. | In startups and companies aiming for rapid growth. | Accelerates growth, data-focused decision-making. | May not suit all business models or industries. |
| Pirate Metrics | A framework for tracking user behavior through Acquisition, Activation, Retention, Revenue, and Referral stages. | In assessing and improving user engagement and conversion. | Provides a clear view of user journey and conversions. | May require complex tracking and analytics tools. |
| Engines of Growth | Identifies the mechanisms startups use for sustainable growth, including the sticky engine, viral engine, and paid engine. | In understanding and optimizing growth strategies. | Guides growth strategy, measures effectiveness. | Strategies may require ongoing adjustments. |
| RTVN Model | A simple framework to design a business model by focusing on vision, target, value, and network. | In the early stages of defining a business model. | Provides a structured approach to model development. | May lack depth for complex business models. |
| Sales Cycle | The process a company follows to sell its products or services, involving a series of steps with prospects leading to a closed sale. | In sales and revenue generation processes. | Guides sales teams, improves revenue generation. | May vary in complexity depending on industry. |
| Comparable Analysis | Analyzes similar organizations to understand the business and financial performance of a target company. | In assessing competitive landscapes and target organizations. | Provides valuable insights for strategic decision-making. | Requires access to relevant data and thorough analysis. |
| Porter’s Five Forces | A model to understand industry dynamics by analyzing competitive forces: rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, threat of substitutes, and threat of new entrants. | In evaluating market competitiveness and strategic positioning. | Helps identify competitive advantages and threats. | May not cover all relevant industry factors. |
| Porter’s Generic Strategies | Defines competitive advantage through cost leadership, differentiation, or focus on a narrow market segment. | In developing competitive strategies for a business. | Provides clear strategic directions for businesses. | May not address unique strategic challenges. |
| Porter’s Value Chain | Analyzes a company’s value chain, consisting of processes that create value for consumers, to identify areas for optimization. | In improving operational efficiency and competitive advantage. | Enhances understanding of value creation and optimization. | Requires thorough analysis and process mapping. |
| Porter’s Diamond Model | Explains why some industries in a nation become internationally competitive, considering factors like firm strategy, structure, factor conditions, demand conditions, and related industries. | In analyzing factors influencing international competitiveness. | Offers insights into industry competitiveness and strategies. | May not apply to all industries or regions. |
| Bowman’s Strategy Clock | A model for strategic positioning based on price and perceived value, categorizing products or services into different market positions. | In assessing and choosing market positioning strategies. | Helps identify distinct market positioning strategies. | May not cover all possible market positions. |
| VMOST Analysis | Analyzes core strategies by assessing vision, mission, objectives, strategies, and tactics, providing clarity on strategic alignment. | In evaluating and aligning strategic elements within an organization. | Promotes strategic alignment and clarity. | Requires a clear understanding of strategic elements. |
| Fishbone Diagram | A visual tool for identifying potential causes of a problem by mapping out various factors contributing to an issue. | In root cause analysis and problem-solving efforts. | Visualizes complex problems, aids in identifying root causes. | Interpretation of factors may vary. |
| GE McKinsey Matrix | A portfolio management tool that helps prioritize investments among business units based on market attractiveness and competitive position. | In evaluating and managing a diverse portfolio of business units. | Guides investment decisions, optimizes portfolio. | Requires data and ongoing assessment. |
| VRIO Framework | Evaluates factors that give a company a long-term competitive advantage: value, rarity, imitability, and organization. | In assessing and protecting competitive advantages. | Identifies and protects key competitive factors. | Requires thorough analysis and ongoing monitoring. |
| 3C Analysis | Focuses on Customers, Competitors, and the Company to develop a marketing strategy and gain a competitive advantage. | In formulating marketing strategies and assessing market dynamics. | Provides a comprehensive view of market and competition. | Requires accurate market research and analysis. |
| AIDA Model | Describes the stages of the customer journey: Attention, Interest, Desire, and Action, to guide marketing and sales efforts. | In planning marketing and sales campaigns. | Maps the customer journey, aids in conversion strategies. | May oversimplify the complexity of customer behavior. |
| PESTEL Analysis | Analyzes macro-economic factors (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, Legal) to assess their impact on an organization. | In evaluating external factors affecting a business. | Provides insights into external factors and risks. | May not cover all relevant external factors. |
| Technology Adoption Curve | Describes stages of technology adoption: Innovators, Early Adopters, Early Majority, Late Majority, and Laggards. | In targeting specific user segments based on technology adoption. | Helps identify target user groups and market timing. | Assumes homogeneous behavior within segments. |
| Business Model Essence | Distills the critical characteristics of a business model into a concise description for strategic focus. | In summarizing and communicating essential elements of a business model. | Provides a clear and focused understanding of the business. | May oversimplify complex business models. |
| FourWeekMBA Framework | Focuses on people and financial dimensions for building effective business models and sustainable value. | In designing and evaluating business models for sustainable growth. | Emphasizes both product/service and financial aspects. | Requires a holistic understanding of business dynamics. |
| TAM, SAM, and SOM | Identifies Total Addressable Market (TAM), Serviceable Addressable Market (SAM), and Share of Market (SOM) to target specific market segments effectively. | In market sizing and targeting strategies. | Provides insights into market potential and target segments. | Accuracy depends on market research and data sources. |
| Brand Building | Activities aimed at creating a recognizable brand identity through core values, trust, and long-term relationships. | In establishing and nurturing brand recognition and loyalty. | Builds brand equity and trust with stakeholders. | Requires consistent and long-term efforts. |
| Value Proposition Design | Focuses on creating value for customers through product/service design, aligning with customer needs and generating demand. | In product/service development and market positioning. | Enhances value creation and demand generation. | Requires a deep understanding of customer needs. |
| Product-Market Fit | A state where a product/service fits well with the market’s needs, leading to customer traction and success. | In evaluating and adjusting product-market alignment. | Drives customer engagement and growth. | Requires continuous validation and adaptation. |
Main Guides:








