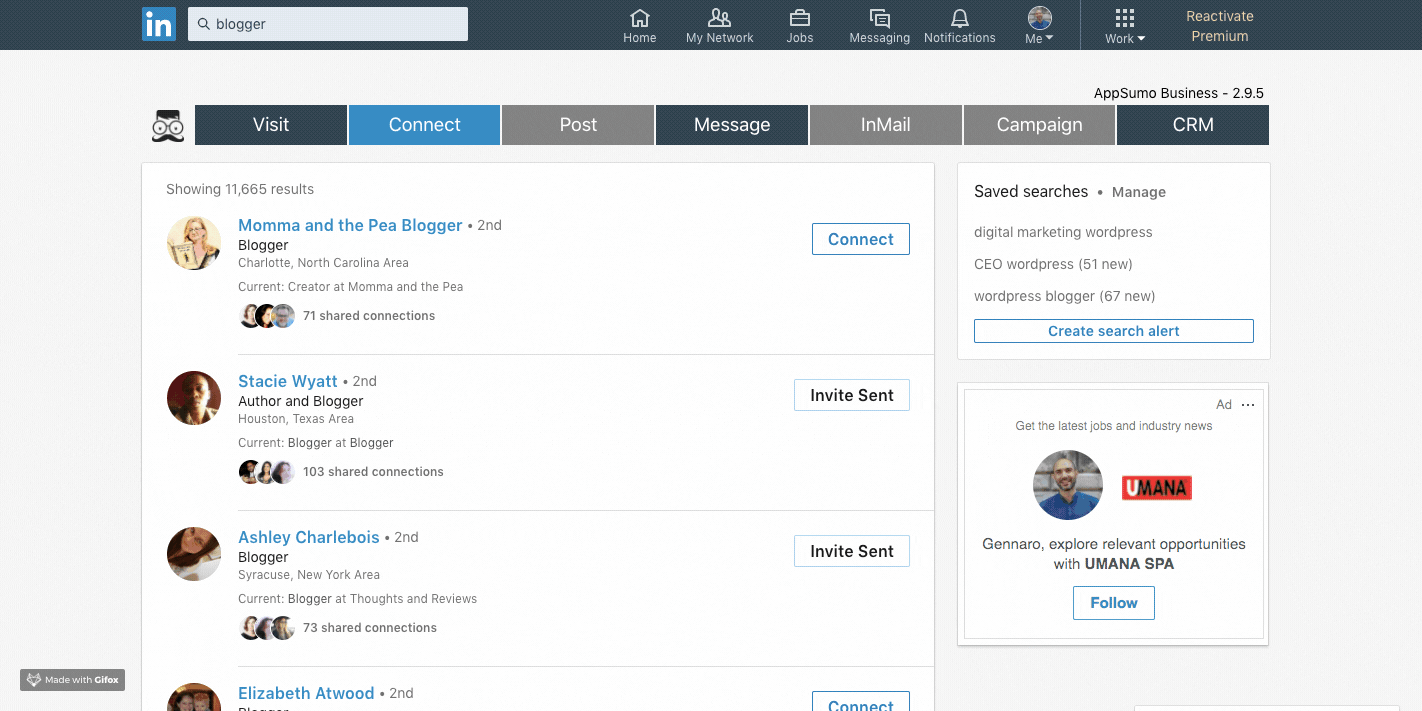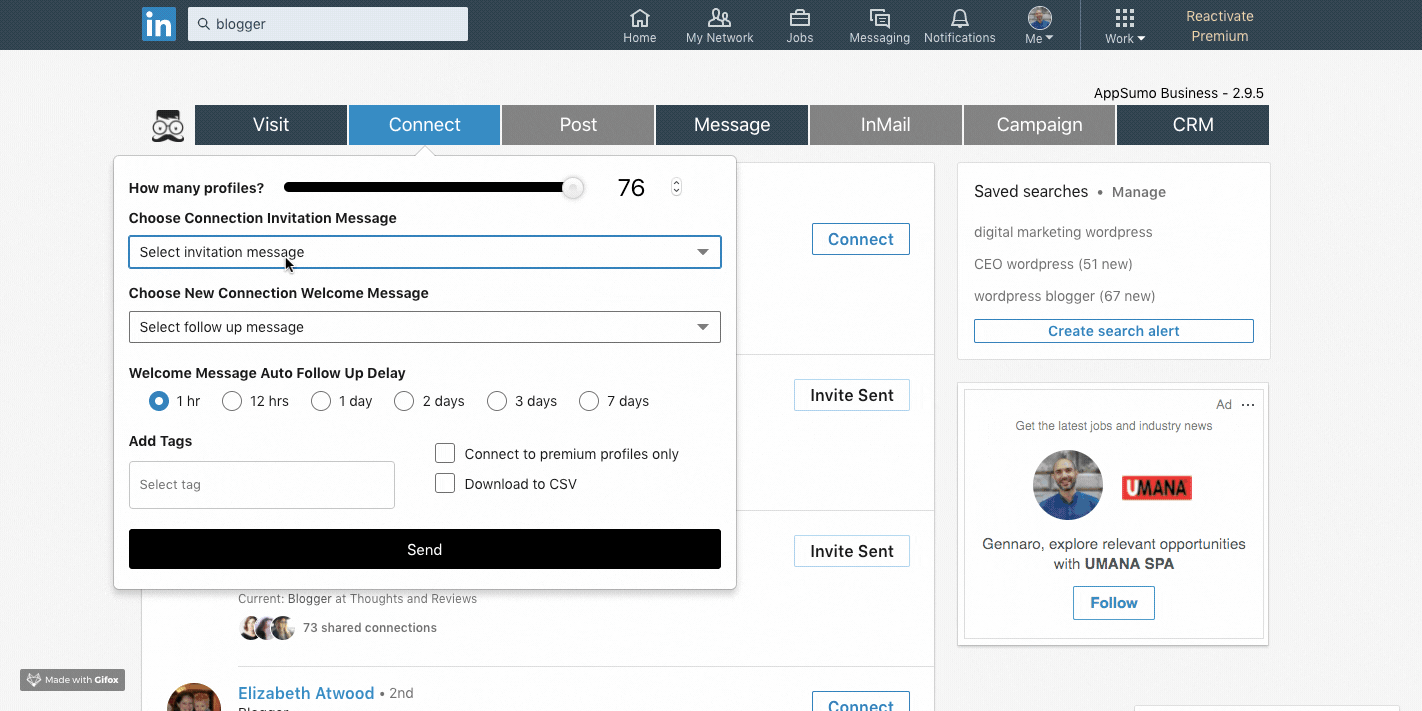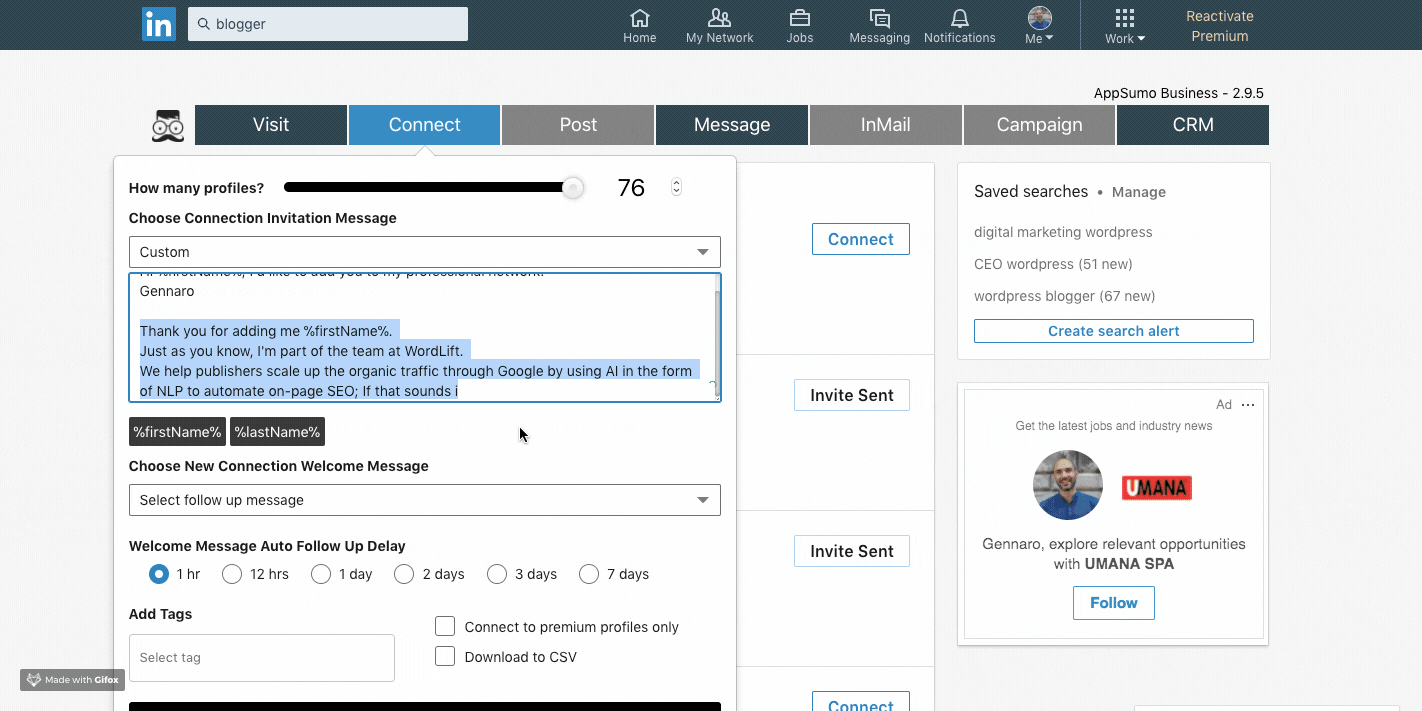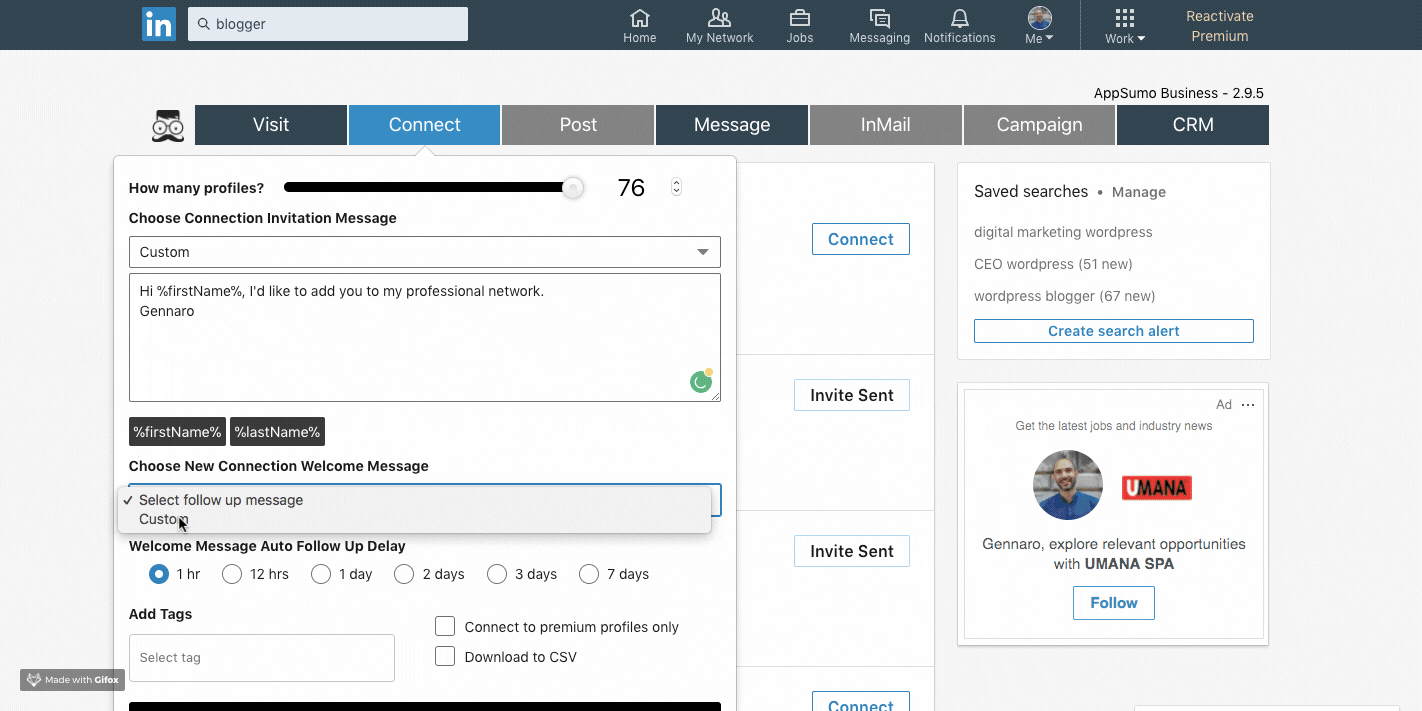
Social selling is a process of developing trust, rapport, and a relationship with a prospect to enhance the sales cycle. It usually happens through tech platforms (like LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and more), which enable salespeople to engage with potential prospects before closing the sale, thus becoming more effective.
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Definition | Social Selling is a sales strategy that leverages social media platforms and networks to build and nurture relationships with potential customers. It involves using social media tools and techniques to identify, connect with, and engage prospects in a more personalized and authentic manner. The goal of social selling is to move prospects through the sales funnel by providing them with valuable content, insights, and solutions, ultimately leading to a conversion or sale. This approach recognizes the changing dynamics of buyer behavior and emphasizes building trust and credibility through online interactions. Social selling is commonly used in B2B (business-to-business) and B2C (business-to-consumer) sales environments. |
| Key Concepts | – Relationship Building: Social selling prioritizes the development of relationships with potential customers through social media platforms. – Content Sharing: Sales professionals share relevant and valuable content to educate and engage prospects. – Personalization: Interactions are tailored to individual prospect needs and preferences. – Authenticity: Authenticity and transparency in communication are essential for building trust. – Online Presence: Maintaining a professional and visible online presence is crucial. |
| Characteristics | – Social Media Usage: Social selling relies on various social media platforms such as LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook. – Content Creation: Sales professionals create and curate content, including articles, videos, and infographics. – Listening and Monitoring: Monitoring social media conversations and listening to prospect needs is an integral part. – Engagement: Active engagement with prospects through comments, messages, and shares. – Data and Analytics: The use of data and analytics tools to track engagement and measure the effectiveness of social selling efforts. |
| Implications | – Enhanced Prospecting: Social selling expands the pool of potential prospects by tapping into online networks. – Relationship Building: It facilitates the development of deeper and more meaningful relationships with prospects. – Trust and Credibility: Building trust through transparent and authentic interactions can lead to higher conversion rates. – Adaptation to Buyer Behavior: Recognizing and adapting to changing buyer behavior, which often includes researching products and services online, is essential. – Competitive Advantage: Effectively using social selling can provide a competitive edge in sales efforts. |
| Advantages | – Wider Reach: Social selling allows sales professionals to reach a larger and more diverse audience. – Personalization: Interactions can be highly personalized, increasing the relevance of sales messages. – Cost-Effective: Compared to traditional sales methods, social selling can be cost-effective. – Measurable Results: Data and analytics tools provide insights into the impact of social selling efforts. – Builds Trust: Authentic and transparent communication builds trust and credibility with prospects. |
| Drawbacks | – Time-Consuming: Effective social selling requires time and effort in building relationships and creating content. – Not Instantaneous: It may not lead to immediate results, as building trust can take time. – Content Quality: Poor-quality content or inappropriate interactions can harm credibility. – Privacy Concerns: Sales professionals must navigate privacy concerns and data protection regulations. – Saturation: Some social media platforms may be saturated with sales messages, making it harder to stand out. |
| Applications | Social selling is widely used across various industries, including technology, finance, real estate, and consumer goods. It is applicable in both B2B and B2C sales scenarios, where building relationships and trust play a crucial role in the sales process. |
| Use Cases | – B2B Sales: Sales professionals in the B2B sector use social selling to connect with decision-makers and influencers within target companies. – B2C Sales: In B2C sales, social selling helps companies engage with individual consumers, understand their preferences, and provide personalized recommendations. – Personal Branding: Sales professionals often build their personal brands online to establish credibility and trust. – Lead Generation: Social selling is an effective method for generating leads through online engagement and content sharing. – Customer Relationship Management: After a sale, social selling can continue to nurture customer relationships and gather feedback. |
My experience as a “social seller”
In the last years, I’ve been using LinkedIn as a tool to meet people that could help me grow professionally. Yet never thought of it as a social selling tool. That is also because as a former financial analyst I wasn’t focused on sales, lead generation or digital marketing. Yet for more than three years, I’ve been using advanced social selling tactics through LinkedIn.
In fact, as a Head of Business Development, I’ve spent time and resources (a lot of trial and errors) to master this tool that turned out to be the most effective weapon for the biz-dev guy. Indeed, LinkedIn can help you generate conversions and relationships very quickly. Those conversations often turn in deals, partnerships, PR and more.
In this article, I want to show you what tactics I’ve been using but also how to use LinkedIn as your primary social selling tool.
Related: What Is Business Development? The Complete Guide To Business Development
What is Social Selling?
LinkedIn defines it as:
Social selling is about leveraging your social network to find the right prospects, build trusted relationships, and ultimately, achieve your sales goals. This sales technique enables better sales lead generation and sales prospecting process and eliminates the need for cold calling. Building and maintaining relationships is easier within the network that you and your customer trust.
Instead, hubspot.com defines Social Selling in 100 words as:
Social selling is when salespeople use social media to interact directly with their prospects. Salespeople will provide value by answering prospect questions and offering thoughtful content until the prospect is ready to buy.
Some argue how social selling is reinventing cold calling and bringing that to another level. Truth is whatever you want to call it, LinkedIn is an excellent tool to build relationships with key players in your industry. From those relationships, business opportunities might or might not arise.
Therefore, that is my first social selling tip: don’t focus on the sale at first but only about creating a conversation.
Be ready to accept that conversation might not turn out into a business relationship. In fact, although in sales many terms such as lead generation, or prospecting are useful to create a consistent process it is essential to realize that on the other hand, you have people that have a business objective that comes before yours.
Thus, social selling tip number two: think about how you can help the other person how to achieve his/her business objective
Once clarified those two aspects you’re ready to start. By keeping in mind that LinkedIn is just a tool for others. However, the LinkedIn team could create a business-driven platform where people are primed to think entrepreneurially. It might sound trivial, yet that is what makes LinkedIn so compelling, I argue. In fact, if you go on Facebook and start a business conversation a person might get offended “how dare you, PM me about business?!”
On the other hand, LinkedIn is the perfect environment and context to start business conversations openly. People are primed to think business on LinkedIn compared to any other social media platform. That is also why LinkedIn is so tailored for social selling.
In other words, my social selling tips number three is: don’t be scared to start business conversations as soon as you’re providing value
I know that “providing value” might seem too generic. But it really depends on a few factors. For instance, in my case, as I’m a Business Developer for a startup that offers a tool for SEO and content marketing I found content creation a great lever to start a business relationship. In fact, my principle is: content first, money then.
However, this works for me and in my industry. Would this work anywhere else? Not sure. On the other hand, I find content powerful enough to be leveraged in any other industry too. For instance, let’s say you work in a very traditional industry like real estate commercial development. You also have a company blog that talks about real estate. Why not use the blog to interview and therefore create critical strategic relationships with players in that industry? That is not going to guarantee more profits, yet in the worst-case scenario, you will have great content for your blog, a new acquaintance (we abuse too much of the word “friend” over the internet, but friendship takes years and effort to cultivate) and a potential future business partner!
Why social selling on LinkedIn is important: Social selling vs. traditional selling
Social Selling on LinkedIn is based on four pillars:
- Create a professional brand
- Focus on the right prospects
- Engage with insights
- Build trusted relationships
Social selling is just another way to grow your network and business. In my experience, I found that some other traditional tactics, like cold calling, have become bothering most people. There is no data to back it up as this is my personal experience. In short, some people might be extremely good at that, that is not my case. In fact, as a Business Developer, I tried several tactics to bring new leads. When I used cold calling, I found that people, in any case, told me to send the information over email and that only made the sales cycle longer and more painful.
In short, cold calling not only has become me superfluous but it actually added steps to my sales process.
Using LinkedIn for social selling means to learn how to connect with the right people. In fact, when you start using LinkedIn you’ll need to expand your network by inviting people to join. When connecting you will need to have clear in mind who do you want to talk to. Is it the CEO? Is it the CMO? Or the Editor in Chief? Those searches will help you clarify who is your best interlocutor.

To determine that I’d look at three things:
- Is my tool service solving an actual problem for the person in this role?
- Has this person the ability to influence decisions internally?
- Does this person manage a budget?
- If so, is this budget in line with my business objectives?
Some of those questions will help you clarify who the person within an organization you need to talk to is.
Also, LinkedIn has managed to create an engaged audience ready to comment and interact with you. For instance, a few people have become influencers thanks to LinkedIn publishing and by just posting short content or videos on LinkedIn.
Lately, I also started to experiment with that, and in some cases, the reach of a post can be very powerful. Indeed, a short post can reach thousands of people:

That helps you to establish your personal branding beyond the company or organization you manage, represent or work for.
Where can you start with social selling on LinkedIn?
Make your profile rock!
The first step is to optimize your profile. Over time once you’ve done it right you’ll see the “All-Star” badge on it:

Don’t confuse the symbol with personal recognition. That All-Star badge is only an indicator that your profile is optimized to be found through LinkedIn search.
Make sure to optimize your profile to get found by the people in your industry that can become business partners.
Follow these six tips to have an impressive LinkedIn profile:
The six suggestions are summarised below:
- Professional picture: here professional also depends on the context. For instance, since I work now in digital marketing I don’t wear a suit and tie anymore. However, I did have an old picture with a suit when I worked in the financial industry
- Use a proper headline: I see many kinds of headlines on LinkedIn, but I like to keep it simple. For instance, I have “Business Developer at WordLift and Creator of FourWeekMBA.com” which professionally are the two things that describe me best
- “what I can do for you oriented profile summary”: don’t use buzzwords, or talk only about you but what problems you help to solve on a daily basis
- Work Experience: short and sweet
- show off your recommendations: One way is to ask people you’ve been working together for sincere feedback on LinkedIn
- Put your contact details: that might seem trivial but many people make it too hard to be contacted on LinkedIn
Once you have followed those tips and set up your profile, you can see where you’re at with LinkedIn Social Selling Index.
How to calculate your Social Selling Index (SSI)?
LinkedIn Social Selling Index is a synthetic score from 1 up to 100 that tells you where you’re at regarding professional branding, network, and influence.
As any synthetic rating, you don’t want to take it literally, yet it is an excellent proxy to track the advancement of your LinkedIn profile over time.
You can check your Social Selling Index from here:

For instance, in the last year, I’ve been working on my profile, and I was able to bring my Social Selling Index to 72 out of 100.

Compared to other people in my industry my profile ranks in the top 1% and on the top 10% for my network.

To put things in context sales professionals in the Marketing and Advertising have an average Social Selling Index (SSI) of 25.
Once again, this is only a synthetic indicator. This means having your Social Selling Index as high won’t bring you any sale to the door. That just means that you’re ready now to present your professional brand in the best way possible. Nothing more, nothing less. However, if you want to increase your Social Selling Index see next.
How to increase your LinkedIn Social Selling Index (SSI)?
To improve your Social Selling Index, you have to develop four areas:
- Establish a professional brand
//www.slideshare.net/slideshow/embed_code/key/1FA7ziCECtFRZV
Establish Your Professional Brand from LinkedIn Sales Solutions
- Find the right people
//www.slideshare.net/slideshow/embed_code/key/LOlTzCP0vgK047
Find the Right People from LinkedIn Sales Solutions
- Engage with insights
//www.slideshare.net/slideshow/embed_code/key/qTLLw6KQRTxV3u
Engage with Insights from LinkedIn Sales Solutions
- Build relationships
//www.slideshare.net/slideshow/embed_code/key/4gAz5TyAYgcfed
Build Relationships from LinkedIn Sales Solutions
Top google chrome extensions for social selling on LinkedIn
To maximize and power up your LinkedIn capabilities, there are a few Google Chrome Extensions which over time I found very useful.
Snovio for email capturing
Working on a single channel is not effective. Therefore, when you visit someone’s profile on LinkedIn, it is also a good idea to get his/her email for the future. Many people don’t use LinkedIn much and contacting them through email can be way more efficient.
Snovio is a must-have tool to make this process of email capturing straightforward.
Rapportive to connect on LinkedIn through your mail inbox
Another Google Chrome extension I can’t live without is Rapportive. That is an extension that allows you to communicate with anyone when opening an email from your inbox.
For more Google Chrome extension not related to LinkedIn read this:
A crash course on LinkedIn Automation
LinkedIn is a powerhouse to build and grow a professional network that can accelerate and scale up your business growth. Anyone seems to be an expert, but a few have told you the truth about the professional social network that can make or break a company’s business model. I used LinkedIn in the last years for PR, direct sales, prospecting, networking, and personal branding.
In this guide, I want to show you everything I’ve learned. I’m not going to keep secrets or tell you the obvious (like many others do). I’ll let you know what real sales and marketing professionals do on LinkedIn and how they use it to their advantage to bring value back to their business. From prospecting to automation. No secret sauce, but just a lot of tinkering.
Related: What Is Business Development? The Complete Guide To Business Development
The truth about LinkedIn Automation and how to do it right!
In this article, I want to show how I pushed LinkedIn automation tools to the limit to test until which extent you could use them “safely” and get the most out of them.
I want to show you why automating some of your lead generation activity over LinkedIn makes sense, but it needs to be done very carefully if you don’t want to end up like that:

A little caveat: the account suspension was the result of a tool I’ve used that is not in the article. The tool that I recommend later in the article also suggests you best practices. If you don’t follow them and your account gets blocked this is your responsibility!
Do you need LinkedIn automation at all?
You don’t need LinkedIn automation. That’s right, you don’t have to use it, neither I suggest you do. In fact, that is against LinkedIn user agreement and policy. However, I know for a fact that many people that are focused on growing businesses quickly use those tools. Many others want to know how to use them. In fact, each month 590 people search on Google the keyword “LinkedIn automation.”

That is also why I decided to run a few tests and see LinkedIn free tools for automation work. LinkedIn is a goldmine for businesspeople. With over 467 million profiles, it is probably the most significant professional database on the internet. Many believe that only by using those tools would get your account permanently suspended. I didn’t think that myth.
However, until I didn’t test that I couldn’t know for sure; in fact, I safely used LinkedIn automation tools for more than a month, and nothing happened. Then I decided to push it to the limit (we’re going to see in a bit what those limits are) to see to which extent you can use those tools for your business workflow.
When does it make sense to use LinkedIn automation?
There are a few LinkedIn tools that allow you to automate everything. From adding new contacts to set up a flow of follow up messages. Although very powerful I don’t suggest you use that because it barely works and the risk to compromise a relationship might be too high. So when does it make sense to use it?
Prospecting
In the prospecting phase in a traditional sales funnel you might need a few hundred leads that can help you grow your business. You can argue that LinkedIn is for relationships. In fact, it is. But how do you deal with a boss that asks you to produce a constant flux of prospects? Let’s not fool us. If you work in sales besides results, you’re asked to do a day to day or weekly reporting. We know that is useless. In fact, at the end of the day what matters is conversion and how many real relationships you’ve built!
Related: What Is Business Development? The Complete Guide To Business Development
Pushing the algorithm
Many argue that optimizing for the algorithm doesn’t make sense. All you need is to post great content. That is BS! In fact, many times I posted things which I believed were way more interesting than many others I posted in the past, yet for some reason the algorithm made it go through to just a few dozens people. For other posts that are qualitatively lower, the opposite happens. Since there is no way to know exactly how the algorithm works, rather than waiting for that to show people your content, you can automate the reach out so you make sure each time people in your network you know might be interested will see that.
Triggering business conversations
Today like in the past business conversations are critical because they might turn into business opportunities. Leave a discussion on an algorithm might be too risky. Especially if you run a business based on complex sales. In fact, any algorithm or automation isn’t smart enough yet to get all the subtleties of a conversation. Even though chatbots are moving quickly and they might be good at generating those conversations. If you want to get to the next stage, you have to make sure you can emotionally connect with that person. People want to do business with people. If they perceive you’re a bot, automatically the conversation gets devalued. So the risk of losing a business opportunity is too high. However, it is true that automation can work to trigger those conversations, which leads us to the next point.
Testing what works and what doesn’t, fast!
LinkedIn automation can be useful also to speed up the process of testing several messages copies fast. In fact, imagine you have a copy vs. another copy. How do you know which works best? You can send one by one to a set of people, have slight variations and see what converts best. However, this is true only in part. From my experience with outreach what works best is personalization.
First, because if you’re reaching someone out that person doesn’t care about you or your business but only what you can offer to her/him. Thus, if you didn’t take the time to research that person profile and study its business the message will have a meager conversion rate.
Also, if you are about to reach out to an online publisher about SEO service, there is no doubt that organic traffic growth will be a critical hook. Second, you have to make sure your message won’t sound automated. In fact, as soon as it does, the person, on the other hand, won’t bother caring about your message.
The one tool you need to Automate LinkedIn Meet Leonard
To put together this guide, I’ve been trying several tools in the last weeks. But I want to show you one tool which I found extremely powerful. That is a LinkedIn bot, called Leonard, that will do anything for you. It will actually perform four main tasks:

Why, When and How to Visit Profiles
As you might or might not know, one of the main feature of LinkedIn (if you don’t have it blocked in the privacy) allows users to see who visited their profile:

This is useful also as a prospecting tool. In fact, when you visit someone’s else profile, that person will notice. Thus, this should improve your profile visibility. It is also useful to make that person comfortable with you before you reach out. As repetition is the mother of sales. If you allow a person to see you a few times before you reach out, then it’s almost like you already know each other. Therefore, that will improve your chances of generating a business conversation, while it will decrease your likelihood of getting rejected.
Auto Visit Profiles with Meet Leonard
With Leonard for LinkedIn, you can set up automation to visit people’s profile in or outside your network:

Automated and Customized Connection Request with Leonard
You can also set up automatic and customized connection requests with a defined flow:
Automated and Customized Follow up with Leonard
After the first contact you can automate the follow up:

Automated and Customized Messages to first degree connections with Leonard
As a way to share fast some content you believe a group of people in your network might like you can also automate an outreach campaign to amplify your content reach:

Just like I did with this article that ended up getting a lot of traffic from LinkedIn:
Start with the push but get geared for the pull
Many believe that all you need to do is to build a so-called pull strategy and hundreds of people will contact you, just because you’ve become a celebrity, and you won’t bother anymore in reaching out to anyone. Even if you might become one day a so-called “top influencer” there will be many times when without reaching out you won’t be able to talk to the right people.
Certain activities are geared for the pull strategy, but that will work overtime. In the meanwhile, you have to become quite good at reaching out. What activities will gear you toward the pull?
- write blog posts on your site
- publish guest posts
- get interviewed/featured on other blogs
- public speaking
- build your social media personal brand
- attend offline events
- get interviewed on podcasts
Start small, very small
Automation is powerful but also dangerous if it goes out of hand. That is why you might want to start small. Thus, instead of automating right away for hundreds of contacts, begin with 10-20 touches. If your screw up rate is 10%, you might be wrong in contacting 1-2 persons. So the damage is limited and the potential high. That small automation will also allow you to see what works and what doesn’t.
Do your keyword research
Do you know who your ideal customer is? No? Then think about it deeply before moving forward. In other words, before starting this process of automation, you want to make sure you know which set of people you can create value with your offer. If not sure yet, do your homework. Look at your customer’s profiles, conversations and past deals you closed. Once you have that clear in mind, put down a list of keywords that represent your ideal customer. The process won’t need to be complicated and require a lot of time. Just start with a simple test. Trial and error is the key here.
Craft the message
When you start small and contact a few groups of people with an automated message. You want to look at conversion rates. Rather than keep using the same message over and over again, apply some variations. Don’t get lost in optimizing for small changes. Rather try several words. You want to go with the one that increases your open rates by 10x rather than 10%
How to make an article go viral on LinkedIn according to Larry Kim
According to Larry Kim, founder of WordStream, there are 11 ways to sort of hack the LinkedIn algorithms and the can be summarized as follow:
- Keep your titles short
- Use eye-catching images
- Grow your network
- Publish regularly
- Get on LinkedIn channels
- Optimize your posts
- Contact pulse editors
- Use social ads
- Promote your page
- Repost content
- Syndicate your best content

Source: wordstream.com
Key takeaway on LinkedIn Automation
Many will pretend not to use automation tools on LinkedIn for several reasons. However, it is undeniable to automation tools if used correctly can help you out in growing your business. I am not crazy about automating my LinkedIn activity, but this is because most of what I do now is a complex sale that requires since the start a more sophisticated interaction with customizations that the automation tool can’t do (For instance, I might need to send a personalized report for a potential client).
However, for those that don’t get that deal with a more streamlined sales process those tools might be beneficial. In this article, we saw why when, and how to use automation. I hope my experiment and the fact that I was kicked off by LinkedIn for a few hours will give you the awareness to use any LinkedIn automation tool with the proper caution. The most important part is not to push the algorithm too much and just run minimal automation at the time.
The crash course in content optimization for LinkedIn
By reading the article “Serving Top Comments in Professional Social Networks” on the LinkedIn engineering blog I stumbled upon the signals that the LinkedIn machine-learning model looks at to rank top comments on the platform. While this seems to be limited to comments – I argue – those signals can teach us how LinkedIn’s team think about the relevance of content. Thus, in a way, it makes you better at communicating on LinkedIn.
In short, my argument is this: if the LinkedIn team decided to use the following signals for its machine-learning model to rank top comments, those signals might actually be relevant also for other kinds of contents on the platform.
However, I want to repeat – here I must use the conditional – those “might” be the signals LinkedIn algorithms look at in general when ranking content.
Related: What Is Business Development? The Complete Guide To Business Development
The 14 Signals to take into account when publishing content over LinkedIn
In its machine-learning model LinkedIn ranks 14 signals to allow top comments to be shown:

Source: engineering.linkedin.com
The content in the comment is judged by using four parameters:
Commenter (is this someone I care about?)
- connected / following
- edge affinity / connections strength
- Influencer
- profile views
- locale & industry
- likes & replies received in the past
We have commenter features that characterize each commenter’s reputation and popularity (i.e., their profile view counts, influencer status, etc.). We also match the commenter and the viewers on the basis of industry, location, and other shared attributes. At LinkedIn, we have access to various mature machine-learned signals to represent the engagement affinity between two members. We take into account their connection/follow relationships, their profile similarity, and past interactions on the feed. These signals are crucial inputs that help us select high quality comments that are personalized to each viewer.
Content (is this about something I’m interested in?)
- length of comment
- language of comment
- mentions & #hashtags
- mentions me, my connections, an influencer
As far as the actual comment content is concerned, we leverage our in-house Natural Language Processing (NLP) library to characterize the language, the comment length, the grammatical structure, the presence/absence of hashtags, and other content features. We also attempt to infer whether the comment includes mentions of LinkedIn members or other entities.
Popularity (does the community think this is valuable?)
- likes & replies overall
- likes & replies from people in the industry, by influencers, by author
- unique replies in the thread
Social engagement features generated on the feed are segmented by industries for the machine learning model to capture when a particular comment might only be popular for a segment of members.
Time (is it fresh?)
Comment freshness features capture recent actions on the comment. We capture the timestamp of comment creation, the last reply, and the last like. Viewers have a tendency to read fresh comments or recently discussed topics.
LinkedIn looks at over 100 features for online ranking
We’ve only scratched the surface here. There are close to 100 features that we capture and use in online ranking.
Those features might turn into thousands of signals. In fact, as soon as you access to your LinkedIn feed, a machine learning algorithm identifies in a fraction of a second the posts that are most relevant to you. This means the algorithm has to be able to rank tens of thousands of posts in that fraction of a second.
As specified by LinkedIn engineering team:
Flowing into this algorithm are thousands of signals that help us understand a member’s preferences and enable us to personalize the feed for a specific member. These signals fall into three broad categories:
- Identity: Who are you? Where do you work? What are your skills? Who are you connected with?
- Content: How many times was the update viewed? How many times was it “liked”? What is the update about? How old is it? What language is it written in? What companies, people, or topics are mentioned in the update?
- Behavior: What have you liked and shared in the past? Who do you interact with most frequently? Where do you spend the most time in your news feed?
Thus, based on three major/broad categories, related to your identity (company, skills, connections), content (likes, comments, share for that update), and behavior (for instance, who you interact with more frequently) that is how LinkedIn builds your feed.
What are other signals?
These range from well-known metrics, like time spent reading, to insights from your social graph. We also incorporate a variety of findings from other sources in our models, such as user experience research.
One indication is given by the LinkedIn engineering team regarding what’s next for LinkedIn feed and that in some ways answers to those who assert that LinkedIn is becoming way more like Facebook is this:
Creator-side optimization: Many recommendation systems focus on optimizing for discreet, short-term gains in member activities (click, like, share) as a proxy for member engagement and value. In the future, we’re investing in models that specifically optimize for members who create high-quality content on LinkedIn over time.
Source: engineering.linkedin.com
If high-quality content remains the long-term focus of LinkedIn, then you can expect a high ROI from investing time and resources on this platform.
Key takeaway on LinkedIn content optimization
In this article, we’ve looked at some of the signals used by the LinkedIn machine-learning model to rank top comments. If those signals are applied to classify top comments they might also be used to rank online content on LinkedIn – I argue.
Of course, as LinkedIn AI-powered algorithm built on top of a vast knowledge graph, becomes smarter the more signals it might take into account. In fact, as pointed out by the LinkedIn engineering team, as of now there are thousands of signals taken into account to personalize the feed and a hundred features used for online ranking.
Looking at the signals, LinkedIn engineering team takes into account for ranking top comments also help you understand the aim of the platform, thus making you more effective at communicating on LinkedIn.
Some of the interesting aspects and questions to ask when posting on LinkedIn are related to content quality. In fact, as LinkedIn will invest more resources at looking for quality of content rather than traditional signals used on social media (likes and shares), it becomes critical to assess whether you are publishing quality content.
How can that be defined according to what we’ve seen in this article?
- Is this something useful for my audience?
- Am I mentioning relevant people to whom I have built a trusted relationship over time?
- Does my community find it valuable?
- Do I post often?
The crash course on LinkedIn features to grow your business
In the last few years I’ve been using LinkedIn for meeting key people that helped me out in finding jobs, I’ve used it to bring traffic to my blog and to bring revenues to my online businesses. Now LinkedIn has also become a powerful tool to build your community and true fans. No matter how you look at it, investing some of your time to understand this platform has become a must. I spent the last two years of my professional life using LinkedIn on a daily basis. There are a few features you need to know about to make the most out of LinkedIn. I’ve listed them all.
Related: What Is Business Development? The Complete Guide To Business Development
LinkedIn Social Selling Index (SSI)
The LinkedIn Social Selling Index (SSI) is a useful metric to look at to understand how the LinkedIn algorithm perceives you from time to time.

This metric will not only allow you to see how you’re doing in four areas of your profile but also how you rank respectively in your industry and your network.
You might want to align those two metrics (how you rank in your industry and network). In fact, the more you grow your profile compared to the industry, the more you want to make sure your network SSI is growing.
A strong network is also what makes your communication effort over LinkedIn more effective. Also, you can track how the Social Selling Index is progressing over time:

This feature, of course, is the starting point. Indeed, if on the one hand understanding how the LinkedIn algorithm is perceiving you is critical. On the other hand, understanding how people in your network perceive you is even more critical. How can you track that? There is another essential feature for that.
LinkedIn People Also Viewed Feature
The People Also Viewed Feature allows you to understand how people perceive you on LinkedIn based on three main things:
- The keywords you have in your profile: in fact, people find you on LinkedIn thanks to the keywords you use within your profile
- The things that you post and publish: on LinkedIn, you can use the self-publishing platform to publish or re-purpose your content. You can also publish posts and video which are native. Those can reach thousands of people over LinkedIn
- What you like and share: LinkedIn Feed Algorithm is quite powerful. In fact, everything you do becomes part of your activity graph. Thus when you like or share something on LinkedIn, you’re putting the face on that. Therefore make sure to be aware when you like or share something
That is why based mostly on those activities, that is how your network will perceive you. For instance, if look at Neil Patel profile, which is public, you will see a few interesting things:

As of now, when you look for Neil Patel and dive into the People Also Viewed feature you will mostly notice profiles of people that work in the SEO industry (like Rand Fishkin and Brian Dean) or other entrepreneurs profile (like Brian Chesky from Airbnb).
This makes sense as Neil Patel is one of the most knowledgeable entrepreneurs, focused on SEO. Thus, this means that Neil Patel is pretty good at communicating over LinkedIn. Besides, this also tells you that he has a strong brand (which he has built over the years).
Thus, you might want to make sure when people visit your profile; they also view profiles that are related to your industry or in any case to sectors tied to your bottom line.
LinkedIn Search Appearances
When you go to your LinkedIn page, click on your image to access your dashboard. On that dashboard, there are interesting information and data. Some data is pretty important to understand whether your business effort over LinkedIn is paying back. You need to look at search appearances:

When you click on those search appearances you will notice the breakdown of companies that have been looking at your profile each week:

You can also find out where the people that looked at your profile which industry they belong to:

In my specific case, this information is critical. Because when I communicate over LinkedIn, I want to connect to people that have specific roles within the organizations. In most cases, as I handle a complex sale, the more I get closer to the spending decision center, the more I improve my chances to close a deal.
Thus, when I talk to founders, executive directors and website managers, that informs me whether my communication effort is working. Thus, try to have in mind who’s the ideal person within the organization you might want to talk to and mold your communication on that. What role does that person have? How senior the profile needs to be? Do you want to target small organizations or a more structured company?
There is also another part of the LinkedIn Search Appearances that is critical: the keywords through which people are finding you on LinkedIn. Thus, this leads us to the next point.
LinkedIn Keywords Optimization
Within the LinkedIn Search Appearances you can also look through the keywords that are allowing you to be found on LiknedIn:

For instance, of those keywords, I realized that just the last one was relevant to me. The others seemed to be out of place. What to do when you get found for the wrong keywords? Simple: you have to update your profile to reflect the keywords you want to be found.
Where to focus your effort?
- reorganize your skills
- include relevant keywords in your headline and summary
- complete the information on your profile by keeping in mind who’s your target
LinkedIn Who’s Viewed Your Profile Feature
LinkedIn offers plenty of analytic data from your profile, that can help you adjust the target from time to time. This includes how your profile is getting viewed over time. To access this feature go on your LinkedIn homepage and click on “who’s viewed your profile”:

You will get access to the Linkedin analytical dashboard:
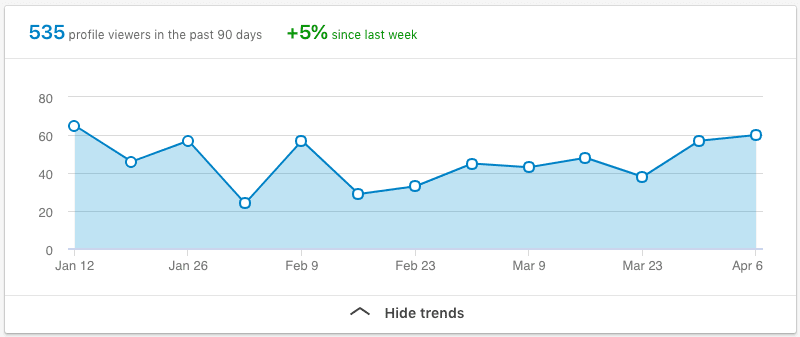
Although LinkedIn doesn’t show you all the profile viewers unless you have the premium version. This feature is useful to track whether you’re getting more visibility over time.
LinkedIn Views of Your Post
As posts on LinkedIn have become quite important, LinkedIn also allows you to track how those posts are performing. You can access the analytics of your post from the LinkedIn homepage:

Posts that are well drafted and on target with your audience, you can reach a few thousand people easily on LinkedIn:

This allows you to monitor how many views, shares you’re getting; and from which companies, roles, and cities those views are coming from:

Monitoring which posts work best and which ones generate business conversations is critical to growing your influence over LinkedIn.
However, it’s essential to strike a balance. For instance, posting inspirational phrases might get you tons of likes. Yet I wonder from the business perspective if that adds any value.
It’s easy to get likes, less to generate business conversations.
People You May Know Feature
Growing your network is critical to improving your reach. Thus the business conversations you can generate over LinkedIn. LinkedIn’s algorithm can help you out in building your network more quickly and efficiently. In fact, from the homepage, if you click on “My network,” you will access a page, that shows you the pending invitations you might have.
It will also show the people you may know:

Use this feature wisely, don’t just add anyone. Keep in mind that from the selection you’re doing you’re also training the LinkedIn algorithm to work for you. So the better you’ll select the people you might want to have in your network the more the algorithm might give you better suggestions.
Withdraw LinkedIn Pending Invitations
When you click on “My network” on the home page, you will access the page where you can see the pending invitation and the people you may know. From there, click on manage all:
It will open up a page where you can see all the invitations you’ve sent:

Why do you want to withdraw contacts request? If you added someone because it represented a good fit for a business conversation; if after a week or so you didn’t get accepted it makes sense to withdraw the invitation for a few reasons. Frist, the other person doesn’t see you as a good fit. Second, you might have used the wrong message, thus by withdrawing you can retry with a more personalized message. Third, that person might be not that active on LinkedIn, so it makes sense to find other channels to talk to her/him.
LinkedIn Native Video
I’m not an expert on LinkedIn videos, not because they don’t work or because they’re not effective. Quite the opposite. If you master videos, you can reach a broad audience. However, this is not my strength.
Yet people like Allen Gannet reach thousands of people with each video published on LinkedIn:

I admire Allen’s work because he’s pretty effective at personal branding. This is clear from the engagements each of his videos has. But he is also able to grow his business. How do I know? I bought his book, The Creative Curve, thanks to his videos on LinkedIn.
The above video is an example of a forty seconds video getting viewed by over sixty thousand people. Of course, Allen Gannet didn’t reach those numbers overnight. Yet if you become comfortable with publishing short video interviews, tips and in any case find the format the suits you best you might be able to reach thousands of people with a little effort.
LinkedIn Self-Publishing
A few years back the LinkedIn self-publishing platform was the most powerful tool to get noticed over LinkedIn;. However, as you can imagine that also lead people outside the feed. This makes the publishing platform less interesting for LinkedIn from the monetization standpoint. In fact, in the feed, LinkedIn learns many things about us. That data we give it allows the company to monetize in several ways.
For instance, by showing sponsored ads. Or prompting us to buy a subscription plan or an online course part of the LinkedIn learning platform. Thus, over time the publishing platform has been taken over by posts and videos that instead are featured on the LinkedIn feed. Therefore, more valuable for the company from a financial standpoint.
Having said that I still believe the self-publishing platform is a powerful syndication tool. In short, if you use a company blog as a way to generate leads. Then from time to time, it makes sense to republish that content over LinkedIn. Just like I did below:

This article that was previously published on my blog got re-published on LinkedIn. Over a thousand people looked/read it. That means that over ten thousand people might have seen it in their feed. This is not bad for a republished article that only took a few minutes to set up. Also, since at the end of the article I included a link that says “originally published on my blog” which points toward the article on my blog, this also brings traffic back to your website.
You could alternatively also include a call to action, such as “subscribe to my newsletter.”
LinkedIn Advanced Search
When prospecting to find the key people that can help you grow your business LinkedIn advanced search is a great tool. You can filter people based on locations, a degree of connections (1st, 2nd, 3rd) and current companies they work for:

Besides people, you can use the same advanced search to look for jobs, content, companies, groups, and schools.
LinkedIn Career Advice
This is a feature implemented in November 2017. As explained by the LinkedIn team:
That’s why we’re launching Career Advice, a new feature that helps connect members across the LinkedIn network with one another for lightweight mentorship opportunities. Whether you need advice on your career path, switching to a new industry or best practices for a project you’re working on, Career Advice can help you find and connect with the right person who can help.
You can get started from here:

Click on get started:

You can specify from whom you want to get a career advice based on the job function and industry:

Eventually, you can specify what kind of advice you’re looking for:

Why and how can this feature affect your businessbottom line? LinkedIn is a powerful tool to generate conversations that lead to business deals. What is great about that is the fact that LinkedIn puts its members in a business-friendly mindset. Thus, if tools like career advice can help you out to learn from people in your industry and create a potential partnership, why not take advantage of it?
LinkedIn Groups Revival
LinkedIn as any other platform has a digital marketing community that from time to time spreads new trends, buzzwords, and myth. One of those potential myths developing lately is the revival of LinkedIn groups. In short, LinkedIn groups seemed to be dead, yet many digital marketers say they are again an effective way to improve your reach.
I’m honestly not able to tell you whether this is true or only marketing buzz. In fact, in the last period, which I’m posting in some of the groups I didn’t get any useful result. However, there is one thing for which groups might be useful. Once you joined a group, you automatically have access to an incredible database of contact.
In fact, even though you’re not connected with a person on LinkedIn you can still reach her/him directly if that person is in the group:
This is going to open up the database of members, which you can contact, even though you’re not connected with them directly:

With this feature, it gets easier to know people that are outside your network, yet share the same interests.
LinkedIn Slideshare
Slideshare is another section of LinkedIn entirely dedicated to presentations. If you work in the corporate world or participated as a speaker at various conferences for sure you’ll have a few presentations that might be interesting to an audience. Create an account and upload some of those presentations. The effort required is minimal. Yet if you get featured in the daily top slide shares you might get hundreds of thousands of views:

LinkedIn Recruiter Toggle On
If you go inside your privacy settings you can let privately know to recruiters on LinkedIn that you’re open to job opportunities:

Within that you can specify things like:
- What job titles are you considering?
- What locations would you work in?
- What types of jobs are you open to?
- Which industries do you prefer?
- What size company would you like to work for?
Once activated you can also create a 300 characters note for recruiters:
Why would you use this feature if you’re an entrepreneur or not really looking for a job? The answer is simple. Recruiters know a lot of people. It’s their job. So getting to know recruiters can also open up conversations with other companies, which might lead to business deals or partnerships. So why not give it a try?
Key take away about social selling
LinkedIn is an awesome tool for social selling. Remember the three tips we saw at the beginning:
- Don’t focus on the sale at first but only about creating a conversation.
- Think about how you can help the other person how to achieve his/her business objective
- Don’t be scared to start business conversations as soon as you’re providing value
Additional steps to take to get going with Social Selling with LinkedIn is to complete your profile, improve your social selling index by posting relevant insights, connecting with people you share professional interests, use LinkedIn publishing to build a strong professional brand. Engage with other top experts in your industry to create trust!
After all the objective is clear: build as many relationships as possible in the shortest time and with the minimum effort.
Related Frameworks
In this example, the ratio is reasonably high which means the shoe company is acquiring customers profitably.
Key takeaways:
- CAC payback is a metric used in SaaS and eCommerce that determines how long it will take to recoup the costs of customer acquisition.
- A payback period of 12 months is considered to be ideal, but a wiser strategy is to consider competitor benchmarks in conjunction with metrics such as logo (customer) retention and net dollar retention.
- To determine how much should be spent on customer acquisition, businesses should calculate the CAC payback to lifetime value (LTV) ratio.
Related Business Concepts






















Palantir Acquire, Expand, Scale Framework



Read: product development frameworks here.
Read Next: SWOT Analysis, Personal SWOT Analysis, TOWS Matrix, PESTEL Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces, TOWS Matrix, SOAR Analysis.
Main Free Guides:









