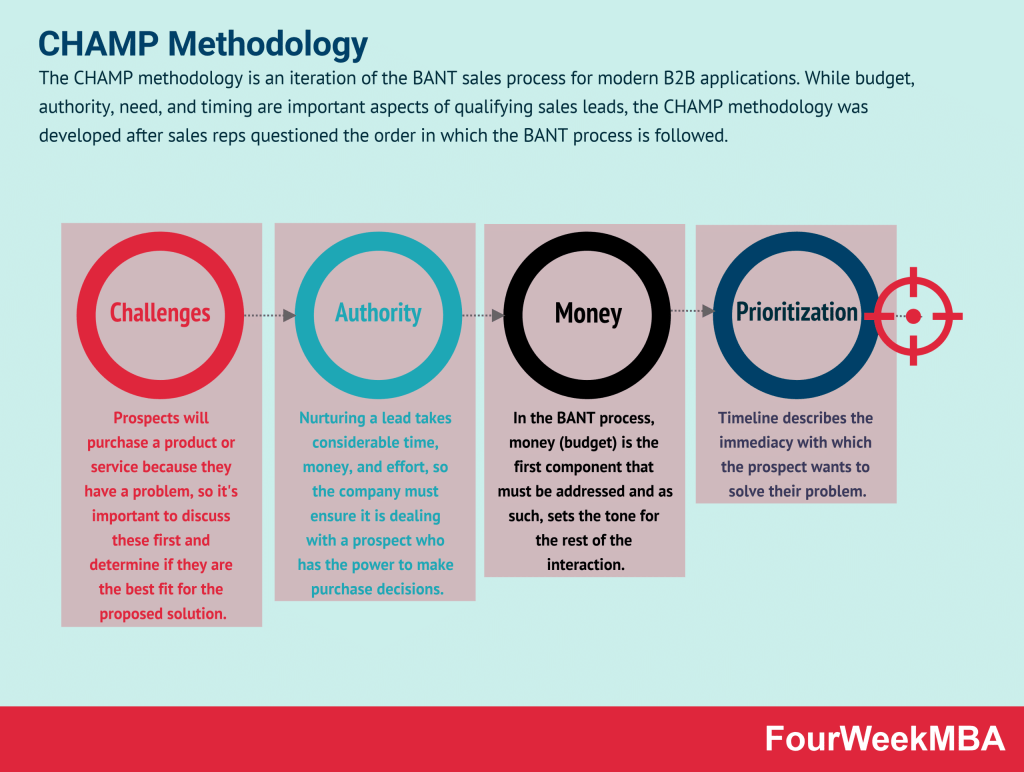
The CHAMP methodology is an iteration of the BANT sales process for modern B2B applications. While budget, authority, need, and timing are important aspects of qualifying sales leads, the CHAMP methodology was developed after sales reps questioned the order in which the BANT process is followed.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | The CHAMP (Creating High-impact Agile and Motivated Projects) methodology is an approach to project management that emphasizes agility, collaboration, and motivation. It aims to deliver high-impact results by promoting flexibility and responsiveness to changing circumstances. |
| Purpose | The primary purpose of the CHAMP methodology is to: – Foster a project environment that encourages collaboration and creativity. – Enable teams to adapt quickly to changes and uncertainties. – Deliver projects that have a meaningful and positive impact. – Enhance team motivation and engagement throughout the project. |
| Key Elements | The CHAMP methodology includes the following key elements: – Agility: The methodology prioritizes flexibility and the ability to respond to changing requirements and circumstances. – Collaboration: Emphasizes effective communication and teamwork among project stakeholders. – Motivation: A focus on maintaining team motivation and enthusiasm throughout the project lifecycle. – High Impact: Strives to achieve significant and valuable outcomes from projects. – Iterative Approach: Encourages iterative development and continuous improvement. – Customer-Centric: Prioritizes delivering value to the customer. – Adaptability: Embraces adaptability as a core principle to address uncertainties and challenges. |
| Benefits | The CHAMP methodology offers several benefits: – Agility: Helps teams adapt to changing requirements and market dynamics. – Collaboration: Enhances communication and cooperation among team members. – Motivation: Maintains high team motivation and engagement. – Value Delivery: Focuses on delivering high-impact results for customers and stakeholders. – Innovation: Encourages creative problem-solving and innovative solutions. – Risk Mitigation: Addresses risks and uncertainties effectively through adaptability. |
| Challenges | Challenges associated with the CHAMP methodology may include: – Cultural Shift: Requiring a cultural shift within organizations to embrace agility and collaboration. – Resistance to Change: Teams or stakeholders may resist adopting new practices and approaches. – Complexity: Managing iterative processes and adaptability can be complex. – Resource Allocation: Proper resource allocation and planning are essential for success. |
| Use Cases | The CHAMP methodology is well-suited for various use cases, including: – Software Development: Agile software development projects that require flexibility and collaboration. – Innovation Initiatives: Projects focused on innovation and creative problem-solving. – Product Development: Developing new products or improving existing ones. – Cross-functional Teams: Projects involving cross-functional teams that require effective collaboration. – Market Response: Initiatives aimed at responding quickly to changing market conditions. |
| Example | In a technology company, the CHAMP methodology might be employed for a software development project. The team would prioritize collaboration, adaptability, and delivering high-impact features based on customer feedback and changing market trends. |
| Best Practices | – Foster a collaborative and open work environment. – Embrace change and adapt to evolving project needs. – Maintain clear communication channels among team members. – Continuously assess and address risks and uncertainties. – Celebrate achievements and milestones to boost team motivation. – Encourage creative problem-solving and innovation throughout the project. |
Understanding the CHAMP methodology
The CHAMP methodology is a customer-centric lead qualification framework.
More specifically, they wondered if it might be more effective to lead with the client’s pain points rather than starting with their budget. After all, this was the primary reason a prospect would be motivated to reach out in the first place.
Re-arranging the BANT framework to reflect this customer-centrism resulted in an acronym that was difficult to pronounce.
In response, practitioners came up with the improved CHAMP acronym to encourage sales reps to prioritize empathy and relationship building over simply reaching their monthly quotas.
The four components of the CHAMP methodology
CHAMP stands for Challenges, Authority, Money, and Prioritization. Let’s take a brief look at each critical component below.
Challenges
Prospects will purchase a product or service because they have a problem, so it’s important to discuss these first and determine if they are the best fit for the proposed solution.
When a challenge is identified, a natural opportunity is created for the sales team to devise a strategy that addresses it.
Possible questions include:
- What challenges is the company facing and how long have they been occurring?
- What would the company look like if the problem were solved? Would processes or procedures be impacted?
- Has the company attempted to solve the problem with other solutions in the past?
- What would the potential ramifications be if the problem went unsolved?
Authority
Nurturing a lead takes considerable time, money, and effort, so the company must ensure it is dealing with a prospect who has the power to make purchase decisions.
Note that organizations have different ways of authorizing this power. Some appoint a board to oversee significant purchases while others leave the responsibility to human resources.
In any case, proper due diligence at the start avoids investing too much in a prospect who must first consult with someone else before making a decision.
Money
In the BANT process, money (budget) is the first component that must be addressed and as such, sets the tone for the rest of the interaction.
Whether a prospect can afford (or is prepared to pay for) a solution is important, but the CHAMP framework places it third.
This is done to give the sales rep more time to identify prospect pain points and link their solutions with spending money.
Prioritization
Prioritization is similar to the timing component of BANT, but it also considers the timeline in the context of other business priorities.
In many instances, company objectives can impact departmental objectives even if the latter is considered more important.
Understanding the interplay between these priorities is key to determining a realistic timeline.
Questions to ask at this stage include:
- When do you envisage the problem would be solved?
- How does the resolution of this problem compare to broader company objectives?
- If the current solution was canceled, would a fee be incurred?
- When does the solution expire?
- At what date would you like a decision to have been made?
Real-Wolrd Applications
Case Study 1: Salesforce
Challenge: Salesforce, a leading provider of customer relationship management (CRM) software, faced a challenge in penetrating new markets and acquiring enterprise-level customers who required complex solutions to meet their specific business needs.
History: Salesforce initially focused on small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) with its cloud-based CRM software. However, as the company expanded its offerings and capabilities, it aimed to target larger enterprises that demanded more sophisticated solutions and customization options.
Account Planning: Salesforce implemented the CHAMP methodology to approach enterprise-level accounts strategically. The sales team conducted thorough account planning sessions to understand the challenges, goals, and buying processes of target organizations.
Understanding Needs: Using the CHAMP framework, Salesforce sales representatives engaged with key stakeholders within target accounts to uncover their specific pain points, business objectives, and decision-making criteria. They conducted in-depth discussions and discovery sessions to gain insights into the customer’s unique requirements.
Mapping Solutions: Based on the information gathered through the CHAMP methodology, Salesforce sales professionals mapped their software solutions and services to address the identified needs and priorities of the target accounts. They tailored their offerings to deliver value propositions that resonated with the customer’s objectives and challenges.
Presenting Solutions: Salesforce sales representatives utilized the CHAMP methodology to deliver compelling presentations and demonstrations of their CRM platform, highlighting its features, capabilities, and benefits in addressing the customer’s specific requirements. They showcased case studies and success stories relevant to the customer’s industry and use cases.
Outcome: By leveraging the CHAMP methodology, Salesforce successfully expanded its presence in the enterprise market and secured significant deals with large organizations across various industries. The company’s strategic approach to account planning, understanding customer needs, and presenting tailored solutions enabled it to win the trust and confidence of enterprise customers and drive revenue growth.
Case Study 2: Oracle
Challenge: Oracle, a global leader in enterprise software and cloud solutions, faced a challenge in differentiating its offerings and effectively positioning them against competitors in highly competitive markets.
History: Oracle offers a wide range of products and services, including databases, enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, customer experience (CX) solutions, and cloud infrastructure. However, the company needed to articulate the unique value proposition of its solutions to address the specific needs and challenges of target customers.
Account Planning: Oracle implemented the CHAMP methodology to enhance its sales approach and engage more effectively with key accounts. The company conducted comprehensive account planning sessions to analyze customer requirements, competitive dynamics, and market trends.
Understanding Needs: Using the CHAMP framework, Oracle sales teams engaged with key stakeholders within target accounts to gain a deep understanding of their business objectives, pain points, and desired outcomes. They conducted thorough discovery sessions and needs assessments to uncover the customer’s specific challenges and priorities.
Mapping Solutions: Based on the insights gathered through the CHAMP methodology, Oracle sales professionals mapped their products and services to address the identified needs and requirements of target customers. They tailored their solutions to deliver tangible business outcomes and ROI aligned with the customer’s strategic objectives.
Presenting Solutions: Oracle sales representatives utilized the CHAMP methodology to deliver compelling presentations and demonstrations of their software and cloud solutions, showcasing their features, functionalities, and benefits in addressing the customer’s challenges. They leveraged case studies, testimonials, and proof-of-concept projects to demonstrate the value of Oracle’s offerings.
Outcome: By adopting the CHAMP methodology, Oracle improved its sales effectiveness and competitive positioning in the market. The company successfully engaged with key accounts, articulated the unique value proposition of its solutions, and won significant deals across industries and geographies. Oracle’s strategic approach to understanding customer needs, mapping solutions, and delivering compelling presentations enabled it to drive customer success and achieve revenue growth.
Case Studies
Software Sales:
- Challenges:
- Identify pain points related to project management processes.
- Conduct thorough research and ask probing questions.
- Uncover specific challenges such as communication gaps and missed deadlines.
- Authority:
- Identify key decision-makers responsible for implementing solutions.
- Build relationships with decision-makers.
- Gain insights into the organization’s decision-making process.
- Money:
- Present cost-effectiveness of software solution.
- Highlight potential savings from improved efficiency.
- Provide flexible payment options to accommodate budget constraints.
- Prioritization:
- Align solution with immediate needs and long-term objectives.
- Develop tailored implementation plan.
- Collaborate with team to address challenges and deadlines.
Manufacturing Solutions:
- Challenges:
- Identify pain points related to production processes.
- Discuss with operations team and observe production facilities.
- Identify inefficiencies, equipment downtime, and quality control issues.
- Authority:
- Identify decision-makers responsible for implementing solutions.
- Build rapport with plant managers, production supervisors, and senior management.
- Understand organizational structure and decision-making dynamics.
- Money:
- Highlight potential ROI from implementing solutions.
- Conduct cost-benefit analyses.
- Customize pricing plans to fit budget constraints.
- Prioritization:
- Align solutions with production schedule and operational goals.
- Develop phased implementation strategy.
- Prioritize areas with highest potential for improvement.
Consulting Services:
- Challenges:
- Identify pain points or challenges faced by the client organization.
- Conduct in-depth analysis and interviews to understand client needs.
- Uncover specific challenges such as inefficiencies, market disruptions, or regulatory compliance issues.
- Authority:
- Identify key stakeholders and decision-makers within the client organization.
- Build relationships with executives, department heads, and project sponsors.
- Understand decision-making processes and hierarchies.
- Money:
- Present the value proposition of consulting services.
- Demonstrate potential cost savings, revenue growth, or risk mitigation.
- Provide transparent pricing and flexible payment structures.
- Prioritization:
- Align consulting services with client’s strategic objectives.
- Develop a roadmap for implementation and deliverables.
- Prioritize initiatives based on impact and urgency.
Financial Services:
- Challenges:
- Identify financial goals, concerns, and pain points of the client.
- Conduct comprehensive financial analysis and risk assessment.
- Address specific challenges such as retirement planning, investment strategies, or debt management.
- Authority:
- Identify decision-makers or influencers involved in financial decision-making.
- Build trust and credibility with clients through expertise and personalized advice.
- Understand client’s risk tolerance and investment preferences.
- Money:
- Present tailored financial solutions aligned with client’s goals.
- Provide transparent fee structures and potential returns on investment.
- Offer diversified investment options and risk management strategies.
- Prioritization:
- Develop a personalized financial plan based on client’s priorities and timeline.
- Review and adjust the plan regularly to adapt to changing financial circumstances.
- Prioritize actions that have the greatest impact on achieving client’s financial objectives.
Healthcare Solutions:
- Challenges:
- Identify pain points or inefficiencies in healthcare delivery or patient care.
- Conduct needs assessments and data analysis to uncover specific challenges.
- Address issues such as patient wait times, staff shortages, or clinical errors.
- Authority:
- Identify key stakeholders in healthcare organizations, including administrators, physicians, and department heads.
- Build relationships with decision-makers and influencers in the healthcare industry.
- Understand organizational dynamics and decision-making processes.
- Money:
- Present the cost-effectiveness and ROI of healthcare solutions.
- Demonstrate potential cost savings, improved patient outcomes, or revenue generation.
- Provide flexible pricing options and financing arrangements.
- Prioritization:
- Align healthcare solutions with organizational priorities and patient needs.
- Develop implementation plans that address urgent issues while supporting long-term goals.
- Prioritize initiatives that improve quality of care, patient satisfaction, and operational efficiency.
Key takeaways:
- The CHAMP methodology is a customer-centric lead qualification framework.
- Re-arranging the BANT framework to reflect a focus on customer-centrism resulted in an acronym that was difficult to pronounce. The more memorable CHAMP acronym was then created to encourage sales reps to focus on empathy and relationship building and not their monthly quotas.
- The CHAMP methodology has four components: challenges, authority, money, and prioritization.
Key Highlights:
- Origin and Purpose: The CHAMP (Creating High-impact Agile and Motivated Projects) methodology is an iteration of the BANT sales process tailored for modern B2B applications. While BANT focuses on budget, authority, need, and timing, CHAMP reorders these elements to prioritize addressing customer challenges first and foremost.
- Components of CHAMP:
- Challenges: Identifying and understanding the prospect’s pain points or challenges.
- Authority: Determining if the prospect has the decision-making power within their organization.
- Money: Assessing the financial resources or willingness to invest in a solution.
- Prioritization: Understanding the urgency and alignment of the prospect’s needs with broader business objectives.
- Customer-Centric Approach: CHAMP places emphasis on empathy, relationship building, and understanding the customer’s perspective. It encourages sales reps to focus on addressing customer challenges rather than solely meeting sales quotas.
- Reordering of Components: Unlike the BANT framework where budget is the first consideration, CHAMP prioritizes challenges to align sales efforts with customer needs and pain points.
- Adaptability and Flexibility: The CHAMP methodology is adaptable to various industries and business contexts, emphasizing agility, collaboration, and motivation to deliver high-impact results.
- Practical Implementation: Sales professionals utilizing CHAMP methodology should ask targeted questions related to challenges, authority, money, and prioritization to effectively qualify leads and tailor solutions to customer needs.
- Key Takeaways: The CHAMP methodology underscores the importance of understanding and addressing customer challenges, engaging with decision-makers, assessing financial viability, and aligning solutions with customer priorities and timelines.
| Comparison’s Table | CHAMP Methodology | SPIN Selling | Solution Selling |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Sales methodology emphasizing building rapport, understanding needs, and guiding prospects through the buying process. | Sales technique focusing on asking Situation, Problem, Implication, and Need-payoff questions to uncover customer needs and pain points. | Sales approach centered on understanding customer challenges, offering tailored solutions, and building long-term relationships. |
| Purpose | To provide a structured approach for sales professionals to engage with prospects, uncover needs, and effectively close deals. | To help salespeople uncover customer needs, address pain points, and position their offerings as solutions to specific problems or challenges. | To assist sales professionals in identifying customer challenges, aligning offerings with needs, and building trust and credibility to win business. |
| Key Components | – Connect: Build rapport and establish credibility with the prospect. – Discover: Ask open-ended questions to uncover the prospect’s needs, challenges, and goals. – Diagnose: Explore the implications of the prospect’s challenges and pain points. – Propose: Present a tailored solution that addresses the prospect’s specific needs and offers value. – Close: Guide the prospect through the buying process and address any objections to secure the sale. | – Situation: Understand the prospect’s current situation and context. – Problem: Identify the prospect’s pain points, challenges, and areas for improvement. – Implication: Explore the consequences and impact of the prospect’s problems or challenges. – Need-payoff: Present the solution and demonstrate how it addresses the prospect’s needs, providing value and benefits. | – Introduction: Establish rapport and credibility with the prospect. – Discovery: Ask probing questions to uncover the prospect’s challenges, goals, and desired outcomes. – Offer: Present a customized solution that addresses the prospect’s specific needs and aligns with their goals. – Commitment: Gain the prospect’s commitment to move forward with the proposed solution. |
| Application | Used in various industries and sales environments to engage prospects, uncover needs, and guide them through the buying process effectively. | Commonly applied in complex B2B sales scenarios where understanding customer needs and pain points is crucial for closing deals successfully. | Widely used in consultative selling environments where building relationships, understanding customer challenges, and offering tailored solutions are key to sales success. |
| Focus | Focuses on building rapport, understanding prospect needs, and guiding them through a structured buying process to achieve successful outcomes. | Focuses on asking probing questions to uncover customer needs, challenges, and pain points and positioning offerings as solutions to address those issues. | Focuses on understanding customer challenges, aligning offerings with needs, and building trust and credibility to win business and foster long-term relationships. |
| Benefits | – Provides a structured approach for sales professionals to engage with prospects effectively and close deals. – Helps uncover customer needs, pain points, and motivations through active listening and questioning. – Guides prospects through a structured buying process, increasing the likelihood of successful outcomes. | – Facilitates deeper conversations with prospects to uncover their needs, challenges, and pain points effectively. – Helps sales professionals position their offerings as solutions to specific problems or challenges, adding value and relevance to the sales process. – Enables salespeople to address objections and concerns proactively, increasing the chances of closing deals successfully. | – Supports sales professionals in understanding customer challenges, needs, and goals comprehensively. – Enables the customization of solutions to address specific customer needs and deliver value effectively. – Fosters long-term relationships with customers based on trust, credibility, and mutual understanding. |
| Examples | – Connecting with a prospect by demonstrating empathy and active listening. – Asking probing questions to uncover the prospect’s pain points and challenges. – Presenting a tailored solution that addresses the prospect’s specific needs and offers value. – Guiding the prospect through the buying process and addressing objections to secure the sale. | – Understanding a prospect’s current situation, challenges, and goals through open-ended questioning. – Identifying the implications and consequences of the prospect’s problems or challenges. – Presenting the solution and demonstrating how it addresses the prospect’s needs, providing value and benefits. – Gaining the prospect’s commitment to move forward with the proposed solution. | – Establishing rapport and credibility with a prospect by understanding their business and industry. – Asking insightful questions to uncover the prospect’s challenges, goals, and desired outcomes. – Presenting a customized solution that addresses the prospect’s specific needs and aligns with their goals. – Gaining the prospect’s commitment to move forward with the proposed solution and building a long-term relationship. |
Related Business Concepts






















Palantir Acquire, Expand, Scale Framework



Read: product development frameworks here.
Read Next: SWOT Analysis, Personal SWOT Analysis, TOWS Matrix, PESTEL Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces, TOWS Matrix, SOAR Analysis.
Main Free Guides:








