Visa Inc. is a multinational financial services company that provides electronic payment services to consumers, businesses, and governments worldwide. In most instances, the services are provided via the company’s branded credit, debit, and prepaid cards.
Visa started life as a credit card program launched by the Bank of America in 1958. The program, known as BankAmericard, was the brainchild of leader Joseph P. Williams, the Customer Research Services Group, and an internal product development think tank.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Value Proposition | Visa offers a range of value propositions for its customers: – Payment Acceptance: Visa provides a widely accepted payment network, allowing businesses to accept Visa payments from customers worldwide. – Security and Fraud Prevention: Visa offers advanced security measures and fraud prevention tools to protect both consumers and merchants. – Global Reach: Visa’s extensive global network enables cross-border transactions and international payments. – Digital Innovation: The company invests in digital payment solutions, including mobile wallets and contactless payments. – Financial Inclusion: Visa promotes financial inclusion by providing access to digital payments for underserved populations. – Data Insights: Visa offers data analytics and insights to help businesses make informed decisions and improve customer experiences. |
| Core Products/Services | Visa’s core products and services include: – Payment Network: Visa operates a global payment network that connects financial institutions, merchants, and consumers, facilitating electronic payments. – Payment Cards: Visa issues debit and credit cards, which are widely used by consumers for making payments and accessing funds. – Payment Processing: The company provides payment processing services, enabling the authorization, clearing, and settlement of transactions. – Digital Payment Solutions: Visa offers digital payment solutions, including Visa Checkout and Visa Direct, to streamline online and mobile payments. – Security and Fraud Prevention: Visa provides security features like EMV chip technology and real-time transaction monitoring to prevent fraud. – Data Analytics: Visa offers data analytics services to help businesses analyze payment trends and customer behavior. |
| Customer Segments | Visa’s customer segments include: – Financial Institutions: Banks and credit unions partner with Visa to issue Visa-branded debit and credit cards to their customers. – Merchants and Businesses: Retailers and businesses of all sizes accept Visa payments, benefiting from access to a broad customer base. – Consumers: Individuals use Visa cards for everyday purchases, online shopping, and access to cash through ATMs. – Government and Public Sector: Government entities may use Visa payment solutions for various purposes, including tax collection and disbursements. – Global Corporations: Multinational corporations often use Visa for employee expenses, corporate cards, and cross-border payments. – Underserved Populations: Visa’s financial inclusion initiatives aim to reach underserved and unbanked populations, providing access to digital payments. |
| Revenue Streams | Visa generates revenue through several revenue streams: – Payment Processing Fees: Visa charges fees to financial institutions for processing payments through its network. – Card Issuance Fees: The company earns fees for card issuance, including annual fees from cardholders. – Interchange Fees: Visa collects interchange fees from merchants for processing transactions and providing access to its payment network. – Cross-Border Fees: Revenue is generated from cross-border transaction fees when consumers make purchases in foreign currencies. – Digital Payment Solutions Fees: Visa may charge fees for the use of its digital payment solutions and value-added services. – Data Analytics and Insights: Income may be earned from data analytics services provided to businesses for decision-making purposes. |
| Distribution Strategy | Visa’s distribution strategy focuses on expanding its network and partnerships: – Global Network: Visa’s global presence ensures its payment network is widely accessible to financial institutions, merchants, and consumers worldwide. – Financial Institution Partnerships: The company partners with banks and credit unions to issue Visa cards to their customers. – Merchant Acceptance: Visa encourages merchant acceptance by offering payment processing solutions and benefits to businesses. – Technology Partnerships: Visa collaborates with technology providers to enhance digital payment solutions and expand its offerings. – Financial Inclusion Initiatives: The company works with governments and organizations to promote financial inclusion and expand access to digital payments. – Marketing and Branding: Visa invests in marketing and branding efforts to promote its payment network and drive consumer usage. |
Understanding Visa’s business model
The Visa business model revolves around facilitating the movement of money between consumers, merchants, businesses, strategic partners, governments, and financial institutions. In an industry where innovation has created new ways to pay, the company has had to evolve to stay relevant.
To that end, Visa extends, enhances, and invests in a proprietary electronic payments network known as VisaNet. The network is the largest and most sophisticated in the world and provides telecommunications, payment processing, payment authorization, and numerous value-added services such as fraud control and risk management.
According to its 2022 Annual Report, Visa also hopes to “become a network of networks, offering a single connection point for senders and receivers to enable money movement to all endpoints and to all form factors, using all available networks.”
How does Visa make money?
Visa makes money from four primary revenue streams:
- Service (fiscal year 2022 revenue of $13.4 billion) – revenue from services provided to clients in support of Visa payment service patronage.
- Data processing ($14.4 billion) – revenue earned from value-added services, payment authorization, payment settlement, and network access. This also includes any other maintenance or support service that facilitates transaction and information processing.
- International transaction ($9.8 billion) – revenue collected from currency conversions and the processing of cross-border transactions.
- Other ($2.0 billion) – a smaller stream that consists mostly of value-added services. These include license fees Visa collects for the use of its brand or technology and other fees related to account holder services, licensing, and certification.
Key foundations of Visa’s business model
Visa also defines four key pillars which fortify the core infrastructure of its business model. Let’s take a brief look at each to round out this article.
Technology platforms
These encompass hardware, software, data centers, and telecommunications infrastructure. Each has a unique operational footprint and architecture wrapped in multiple layers of security. Visa operates three data centers worldwide which serve as a critical part of continuous payment system availability.
Security
Visa’s security approach devalues sensitive and personal data via various cryptographic means. Security is embedded into the software development lifecycle, while management controls prevent unauthorized account access.
To ensure the integrity of its network and also to maintain service availability, the company has invested heavily in cybersecurity measures.
Brand
Visa’s brand equity enables the company to deliver added value to customers, merchants, partners, and financial institutions. The brand is associated with a diverse range of products and services that facilitate mutually beneficial relationships with key stakeholders.
The company also notes that it is the only brand in the world that serves as a top sponsor of FIFA, the NFL, and the Olympic Games.
Talent
Lastly, Visa recognizes that training and advancing the best global talent is vital to its long-term success. Visa employs around 26,500 staff from 80 countries, and each is supported to pursue personal career interests while also meeting their performance objectives
By considering an employee’s particular background, skills, accomplishments, and future ambitions, Visa can support meaningful dialogue about performance and drive development to help it meet its own growth objectives. It will also enable the company to retain talent in a competitive global market.
Key takeaways:
- Visa Inc. is a multinational financial services company that provides electronic payment services to consumers, businesses, and governments worldwide. In most instances, the services are provided via the company’s branded credit, debit, and prepaid cards.
- The Visa business model revolves around facilitating the movement of money between consumers, merchants, businesses, strategic partners, governments, and financial institutions. This is primarily offered via the proprietary network VisaNet.
- Visa also defines four key pillars which fortify the core infrastructure of its business model. These include technology platforms, security, brand, and talent.
Key Highlights
- Multinational Financial Services: Visa Inc. is a global financial services company that offers electronic payment services to individuals, businesses, and governments through its branded credit, debit, and prepaid cards.
- Origin and Evolution: Visa originated as the BankAmericard program launched by the Bank of America in 1958, initially created by Joseph P. Williams and the Customer Research Services Group.
- Facilitating Money Movement: Visa’s core business model centers around enabling the transfer of funds among consumers, merchants, businesses, governments, and financial institutions.
- VisaNet Network: The company heavily invests in VisaNet, a sophisticated electronic payments network that handles payment processing, authorization, telecommunications, fraud control, and risk management.
- Diverse Revenue Streams: Visa generates revenue through four primary streams:
- Service Revenue: Revenue from services supporting Visa payment service patronage.
- Data Processing Revenue: Earned from payment authorization, settlement, network access, and value-added services.
- International Transaction Revenue: From currency conversions and cross-border transactions.
- Other Revenue: Includes brand and technology license fees, account holder services, and more.
- Key Pillars of Business Model:
- Technology Platforms: Infrastructure encompassing hardware, software, data centers, and security protocols.
- Security: Focus on data security, encryption, and cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive information.
- Brand: Leveraging brand equity to deliver value to stakeholders and build meaningful relationships.
- Talent: Recognizing the importance of a skilled workforce to drive growth and innovation.
- Global Presence: Visa employs around 26,500 individuals from 80 countries, fostering a diverse talent pool that drives performance and innovation.
- Value Proposition: Visa’s services provide added value to customers, partners, merchants, and financial institutions, facilitating secure and efficient financial transactions worldwide.
- Global Partnerships: Visa is a top sponsor of major events such as FIFA, the NFL, and the Olympic Games, further enhancing its brand presence.
Connected Business Models
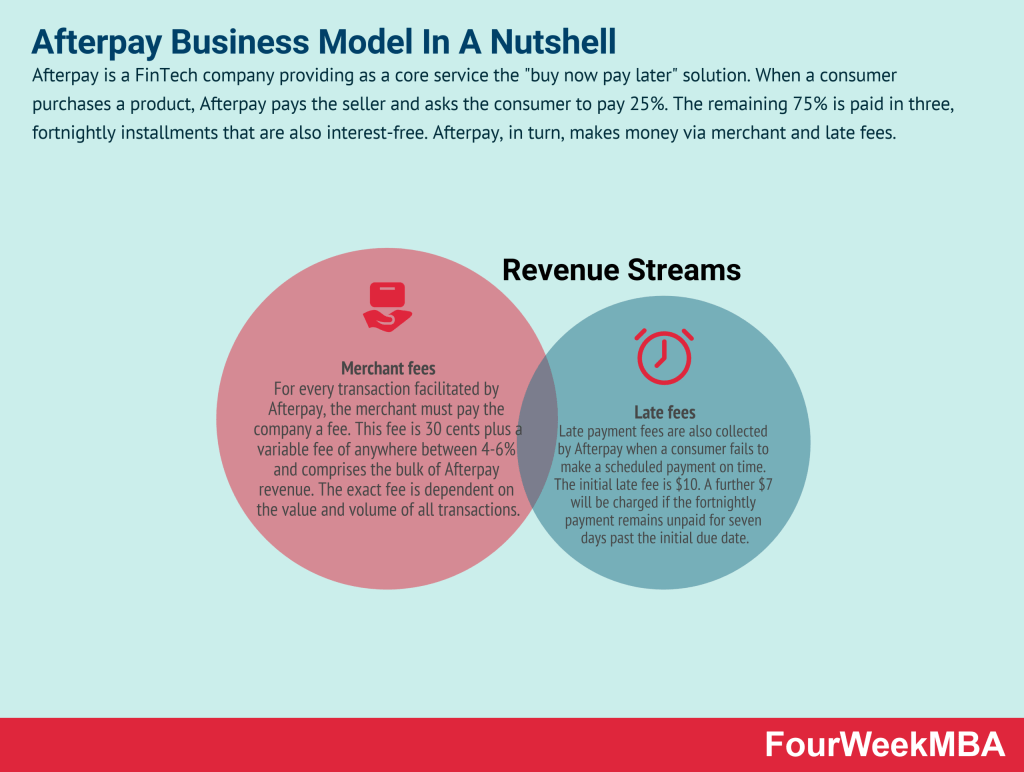
Afterpay Business Model
Quadpay Business Model

Klarna Business Model

SoFi Business Model

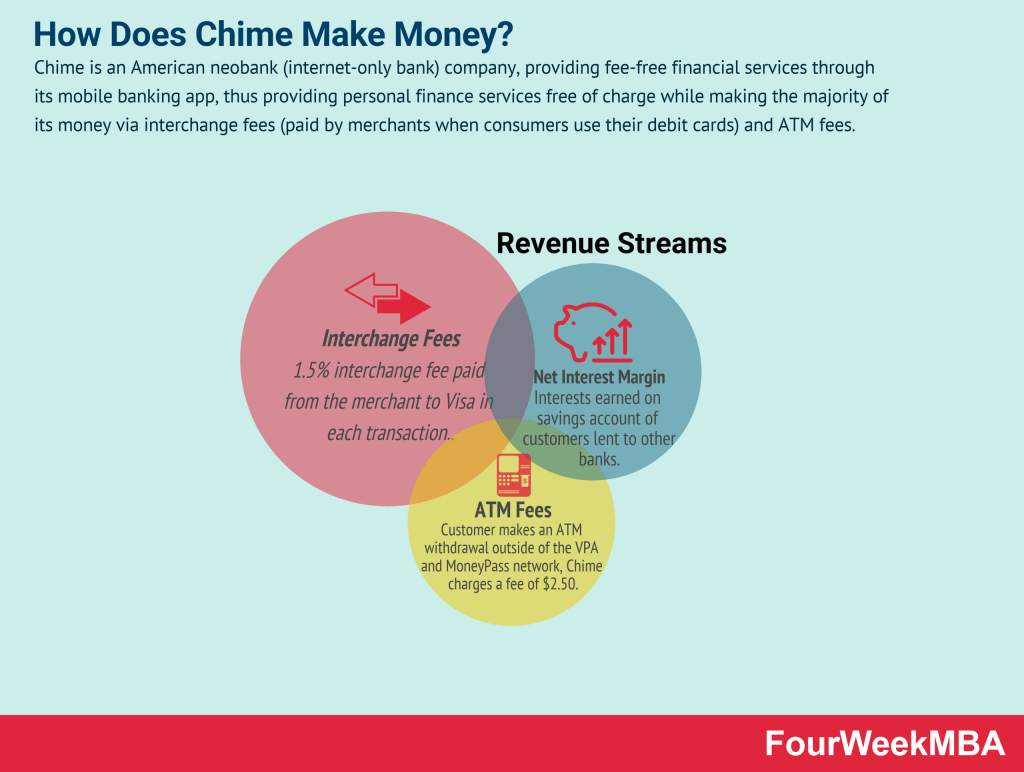
Chime Business Model
How Does Venmo Make Money

FinTech Business Models

List of FinTech Business Models




Braintree



















Read Next: Fintech Business Models, IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, Enterprise AI Business Model, Cloud Business Models.
Read Next: Affirm Business Model, Chime Business Model, Coinbase Business Model, Klarna Business Model, Paypal Business Model, Stripe Business Model, Robinhood Business Model.
Main Free Guides:








