E-business models utilize advanced communication technologies and digital information to streamline various business processes online. These processes include customer relationship management (CRM), supply chain management, payment processing, employee services and recruitment, and information sharing.
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Definition of E-business Model | An E-business Model is a framework and strategy that defines how a business conducts its operations, engages with customers, and generates revenue primarily through digital channels and technologies. E-business models leverage the internet and electronic platforms to facilitate various business functions, including sales, marketing, customer service, and supply chain management. These models can encompass a wide range of online activities, from e-commerce and online marketplaces to digital services and subscription-based offerings. The overarching goal of an E-business model is to create value for customers, streamline processes, and drive profitability in the digital realm. |
| Key Concepts | Several key concepts define E-business Models: |
| – Digital Transformation | E-business models are a manifestation of digital transformation, where businesses adapt to the digital age. This concept encompasses the integration of digital technologies and strategies throughout an organization to fundamentally change how it operates and delivers value. Digital transformation is central to E-business models, as they rely on digital tools and platforms for their core operations. |
| – E-commerce | E-commerce is a critical component of many E-business models. It involves the buying and selling of goods or services over the internet. E-commerce platforms, whether business-to-consumer (B2C) or business-to-business (B2B), play a significant role in enabling online transactions and revenue generation. |
| – Digital Marketing | Digital marketing strategies are integral to E-business models. They encompass various online advertising, content marketing, social media, and search engine optimization (SEO) techniques to reach and engage a digital audience effectively. E-business models leverage digital marketing channels to acquire and retain customers, promote products or services, and build brand awareness. |
| – Customer Experience | A focus on enhancing the digital customer experience is vital in E-business models. This includes ensuring user-friendly websites, efficient online shopping processes, personalized recommendations, and responsive customer support. Providing a seamless and enjoyable digital experience is key to attracting and retaining customers in the digital landscape. |
| Characteristics | E-business Models are characterized by the following attributes: |
| – Online Presence | E-business models primarily operate online, with a strong online presence being a hallmark characteristic. Businesses often have websites or digital platforms where customers can interact, transact, and obtain information. |
| – Global Reach | Digital technologies enable E-business models to have a global reach. They can attract customers from around the world and engage in international commerce. This global reach opens up new markets and opportunities for growth. |
| – Scalability | Scalability is a feature of many E-business models. They can often scale rapidly to accommodate increased demand without significant increases in operational costs. This scalability is facilitated by digital infrastructure and automation. |
| – Data-Driven Decision-Making | E-business models rely on data analytics for decision-making. Data collected from online interactions and transactions provide valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and market trends. Data-driven decision-making is a fundamental aspect of E-business models, guiding marketing, product development, and operational strategies. |
| Examples of E-business Models | E-business models are prevalent across various industries: |
| – Amazon | Amazon is a prime example of an E-business model that includes e-commerce, digital content services (Amazon Prime Video and Kindle), and cloud computing (Amazon Web Services). It leverages a vast online platform to offer a wide range of products and services to a global audience. |
| – Netflix | Netflix is a subscription-based E-business model that provides online streaming of movies and television series. It demonstrates how a digital platform can deliver content to millions of subscribers globally, emphasizing personalization and user experience. |
| – Uber | Uber is an E-business model that operates in the transportation industry. It connects drivers and riders through a digital platform, facilitating ridesharing services. Uber’s model relies on mobile apps for both drivers and riders to coordinate rides, payments, and ratings. |
| – Shopify | Shopify offers an E-business model that enables entrepreneurs and businesses to set up online stores and e-commerce websites. It provides a comprehensive platform for selling products online, including website creation, payment processing, and inventory management. |
| Benefits and Considerations | E-business models offer several benefits and considerations: |
| – Global Market Access | E-business models have the potential to reach a global audience, expanding market access beyond geographical boundaries. This can lead to increased sales and revenue opportunities. |
| – Efficiency and Automation | Digital technologies enable automation of various business processes, leading to increased efficiency and reduced operational costs. E-business models can streamline workflows, improve inventory management, and enhance customer service through automation. |
| – Data-Driven Insights | E-business models can gain valuable insights from customer data. These insights inform strategic decision-making, allowing businesses to optimize marketing efforts, product offerings, and user experiences. However, handling and protecting customer data come with responsibilities and privacy considerations. |
| – Competitive Landscape | The digital landscape is highly competitive, with many businesses operating E-business models. Competition can be fierce, requiring businesses to continually innovate, provide exceptional customer experiences, and differentiate themselves to succeed. |
Understanding E-business models
E-business models are used by companies to create value and become profitable online.
E-business models were developed in response to the increasing prevalence and technological capabilities of the internet.
Seemingly overnight, the internet removed geographical barriers and allowed businesses to operate wherever it was available.
Businesses can now enter new markets with ease and can be open 24 hours a day, 7 days a week for very little outlay.
This shift has resulted in four broad transformations:
- Domestic business to multinational business.
- An economy based on industrial manufacturing to one that characterized by knowledge-based services.
- Enterprise resource management to enterprise network management, and
- Manual, document-driven business processes to those that are electronic, automated, and paperless.
With e-business models developed to take advantage of these transformations, they have virtually rendered traditional models of organizational design obsolete.
The four components of E-business models
In general terms, E-business models should have four components:
Value proposition

Advances in IT and communications have enabled many E-businesses to create and deliver various forms of customer value.
For example, Dell uses the internet to sell customizable, direct-to-consumer PCs.
Other companies offer value in the form of reduced prices, fast delivery, or access to more diverse inventories.
Customer relationships
There is a limit to how much an offline business can interact with its customers.
For the e-business, however, customer relationships have benefitted from data collection, increased communication, order tracking, and personalized support.
Revenue streams

When clarifying revenue streams, it’s important to look beyond obvious sources of income such as eCommerce.
Other sources include advertising, licensing, sales commissions, syndication, subscription, and sponsorship.
Activities, capabilities, and resources
Like traditional business models, e-business models must define how the mission or vision of the company will be carried out and how much it will cost.
Some of these methods may be patented – such as Amazon’s 1-click checkout process – while others can be utilized for free.
E-business models also place more of an emphasis on less tangible resources such as intellectual property, software, customer data, and other IT infrastructure.
E-business model types
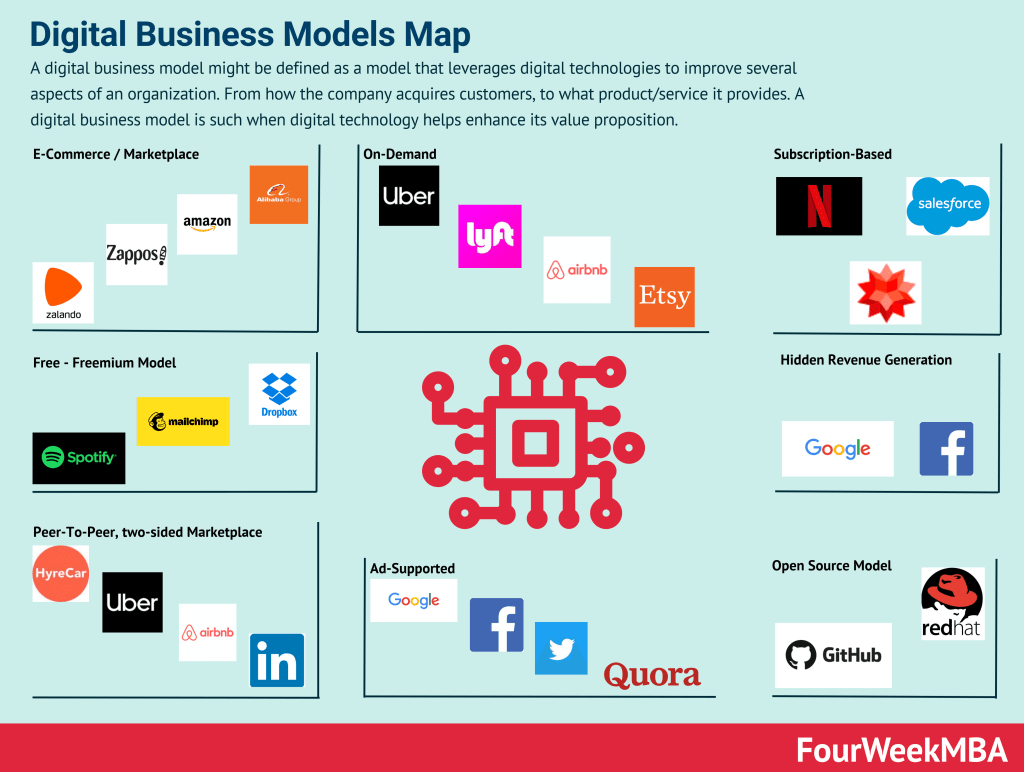
Let’s conclude by taking a look at some common e-business model types categorized according to functionality and transaction type.
Functionality
- Community model – a model used by Facebook, Wikipedia, and Flickr where communities share information, photos, or opinions. Revenue is earned via donations, advertising, and subscriptions.
- Advertising model – where businesses such as newspapers and journals provide content to readers and serve ads to generate revenue.
- Brokerage model – companies such as eBay and Amazon make money by bringing buyers and sellers together.
Transaction type
- Business-to-consumer (B2C) – where merchants sell products and services to buyers who then purchase them online.
- Business-to-business (B2B) – electronic transactions that occur between two businesses. Many SaaS companies follow this model.
- Consumer-to-business (C2B) – the reverse of B2C where consumers sell to businesses. A freelance graphic designer may sell a logo to a company, for example.
- Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) – this model is prevalent on online auction sites and other marketplaces for consumers.
- Business-to-government (B2G) – where government procures products, services, or information from external contractors. For example, governments that require city and open space maintenance will solicit these services from private companies.
Case Studies
Functionality-Based E-business Models:
- Community Model:
- Facebook: A social media platform where users share information, photos, and opinions. Revenue is earned through advertising.
- Wikipedia: An online encyclopedia where the community collaboratively creates and edits articles. It relies on donations for funding.
- Advertising Model:
- Google: Provides search engine services and earns revenue through targeted advertising.
- YouTube: A video-sharing platform that generates income through advertising and premium subscriptions.
- Brokerage Model:
- eBay: Connects buyers and sellers for online auctions and sales, earning fees from successful transactions.
- Amazon: Facilitates online shopping by bringing together sellers and buyers while selling its own products.
Transaction-Based E-business Models:
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C):
- Amazon: Sells a wide range of products directly to online consumers.
- Netflix: Offers streaming services directly to individual subscribers.
- Business-to-Business (B2B):
- Alibaba: Connects businesses with suppliers and manufacturers, facilitating wholesale transactions.
- Salesforce: Provides cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) solutions to businesses.
- Consumer-to-Business (C2B):
- Upwork: A platform where freelancers offer their services to businesses or individuals looking to hire.
- Fiverr: Allows individuals to offer various digital services and products to businesses.
- Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C):
- eBay: Enables individuals to sell products to other individuals through online auctions and fixed-price listings.
- Airbnb: Lets individuals rent their properties or accommodations to other individuals for short-term stays.
- Business-to-Government (B2G):
- FedBid: Connects businesses with government agencies for procurement and contracting.
- Grants.gov: Facilitates the application process for government grants and funding opportunities.
Key takeaways:
- E-business models are used by companies to create value and become profitable online. These models have taken advantage of the proliferation and technological advancement of the internet, rendering offline models almost obsolete.
- Most e-business models will incorporate four components: value proposition, customer relationships, revenue streams, and activities, capabilities, and resources.
- Various e-business model types have been developed over the years. In terms of functionality, some examples include the community model, advertising model, and brokerage model. The ever-evolving and diverse transaction types include B2C, B2B, C2B, C2C, and C2G.
Key Highlights:
- E-business Models Overview: E-business models utilize digital technologies and the internet to optimize various business processes, including customer relationship management, supply chain management, payment processing, employee services, and information sharing.
- Evolving Due to the Internet: The development of e-business models is a response to the internet’s transformative capabilities, which have removed geographical barriers and allowed businesses to operate globally 24/7 with minimal overhead.
- Four Transformations: E-business models have brought about four significant transformations: from domestic to multinational business, from industrial manufacturing to knowledge-based services, from enterprise resource management to enterprise network management, and from manual, document-driven processes to electronic, automated, and paperless operations.
- Components of E-business Models: E-business models typically consist of four key components:
- Value Proposition: Focused on delivering customer value through various means such as customization, reduced prices, fast delivery, and more.
- Customer Relationships: Enhanced through data collection, increased communication, order tracking, and personalized support.
- Revenue Streams: Diverse revenue sources beyond e-commerce, including advertising, licensing, sales commissions, syndication, subscription, and sponsorship.
- Activities, Capabilities, and Resources: Define how the company’s mission or vision will be executed, emphasizing intellectual property, software, customer data, and IT infrastructure.
- Types of E-business Models: E-business models can be categorized based on functionality and transaction types.
- Functionality:
- Community Model: Examples include Facebook, Wikipedia, and Flickr, with revenue from donations, advertising, and subscriptions.
- Advertising Model: Used by newspapers and journals, providing content to readers while generating revenue from ads.
- Brokerage Model: Companies like eBay and Amazon profit by connecting buyers and sellers.
- Transaction Type:
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C): Merchants sell products and services directly to online buyers.
- Business-to-Business (B2B): Electronic transactions occur between two businesses, commonly seen in SaaS companies.
- Consumer-to-Business (C2B): Consumers sell to businesses, such as freelance graphic designers offering services to companies.
- Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C): Found on online auction sites and marketplaces where consumers engage in transactions.
- Business-to-Government (B2G): Governments procure products, services, or information from external contractors, such as city maintenance services.
- Functionality:
Connected Business Model Types And Frameworks









Attention Merchant Business Model

















Main Free Guides:









