Tech Business Model Template

Web3 Business Model Template

Asymmetric Business Models

Business Competition

Technological Modeling

Transitional Business Models

Minimum Viable Audience

Business Scaling

Market Expansion Theory

Speed-Reversibility

Asymmetric Betting

Growth Matrix

Revenue Streams Matrix

Revenue Modeling

Pricing Strategies

ADKAR Model

Ansoff Matrix

Business Model Canvas

Lean Startup Canvas

Blitzscaling Canvas

Blue Ocean Strategy

Business Analysis Framework

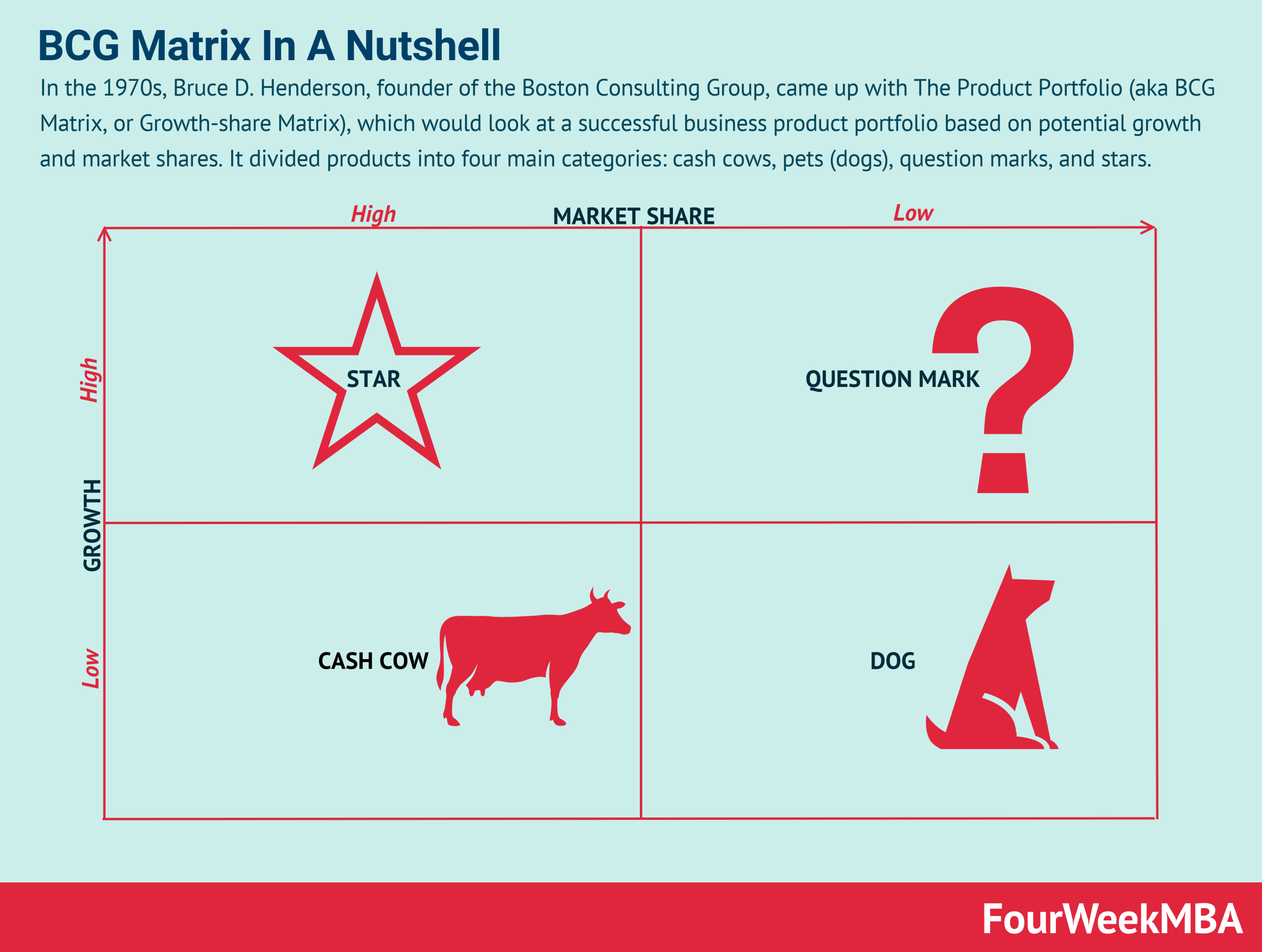
BCG Matrix

Balanced Scorecard

Blue Ocean Strategy

GAP Analysis

GE McKinsey Model

McKinsey 7-S Model

McKinsey’s Seven Degrees

McKinsey Horizon Model

Porter’s Five Forces

Porter’s Generic Strategies

Porter’s Value Chain Model

Porter’s Diamond Model

SWOT Analysis

PESTEL Analysis

Scenario Planning

STEEPLE Analysis

SWOT Analysis

Related Strategy Concepts: Go-To-Market Strategy, Marketing Strategy, Business Models, Tech Business Models, Jobs-To-Be Done, Design Thinking, Lean Startup Canvas, Value Chain, Value Proposition Canvas, Balanced Scorecard, Business Model Canvas, SWOT Analysis, Growth Hacking, Bundling, Unbundling, Bootstrapping, Venture Capital, Porter’s Five Forces, Porter’s Generic Strategies, Porter’s Five Forces, PESTEL Analysis, SWOT, Porter’s Diamond Model, Ansoff, Technology Adoption Curve, TOWS, SOAR, Balanced Scorecard, OKR, Agile Methodology, Value Proposition, VTDF
Main Free Guides: