Business Engineering

Design Thinking

Business model canvas
The business model canvas aims to provide a keen understanding of your business model to provide strategic insights about your customers, product/service, and financial structure;
so that you can make better business decisions.
Blitzscaling canvas
In this article, I’ll focus on the Blitzscaling business model canvas. This is a model based on the concept of Blitzscaling.
That is a particular process of massive growth under uncertainty, and that prioritizes speed over efficiency. It focuses on market domination to create a first-scaler advantage in a scenario of uncertainty.
Pretotyping

Pretotyping is a mixture of the words “pretend” and “prototype,” and it is a methodology used to validate business ideas to improve the chances of building a product or service that people want.
The pretotyping methodology comes from Alberto Savoia’s work summarized in the book “The Right It: Why So Many Ideas Fail and How to Make Sure Yours Succeed.”
This framework is a mixture of the words “pretend” and “prototype,” and it helps to answer such questions (about the product or service to build) as: Would I use it? How, how often, and when would I use it? Would other people buy it? How much would they be willing to pay for it? How, how often, and when would they use it?
Value innovation and blue ocean strategy

A blue ocean is a strategy where the boundaries of existing markets are redefined, and new uncontested markets are created.
At its core, there is value innovation, for which uncontested markets are created, where competition is made irrelevant. And the cost-value trade-off is broken.
Thus, companies following a blue ocean strategy offer much more value at a lower cost for the end customers.
Growth hacking process

Growth hacking is a process of rapid experimentation, coupled with the understanding of the whole funnel, where marketing, product, data analysis, and engineering work together to achieve rapid growth.
The growth hacking process goes through four key stages of analyzing, ideating, prioritizing, and testing.
Pirate metrics

Venture capitalist, Dave McClure, coined the acronym AARRR which is a simplified model that enables us to understand what metrics and channels to look at. At each stage for the users’ path toward becoming customers and referrers of a brand.
Engines of growth

In the Lean Startup, Eric Ries defined the engine of growth as “the mechanism that startups use to achieve sustainable growth.”
He described sustainable growth as following a simple rule, “new customers come from the actions of past customers.”
The three engines of growth are the sticky engine, the viral engine, and the paid engine. Each of those can be measured and tracked by a few key metrics, and it helps plan your strategic moves.
RTVN model

The RTVN model is a straightforward framework that can help you design a business model when you’re at the very early stage of figuring out what you need to make it succeed.
Sales cycle

A sales cycle is the process that your company takes to sell your services and products.
In simple words, it’s a series of steps that your sales reps need to go through with prospects that lead up to a closed sale.
Planning ahead of time the steps your sales team needs to take to close a big contract can help you grow the revenues for your business.
Comparable analysis

A comparable company analysis is a process that enables the identification of similar organizations to be used as a comparison to understand the business and financial performance of the target company.
To find comparables, you can look at two key profiles: the business and economic profile. From the comparable company analysis, it is possible to understand the competitive landscape of the target organization.
Porter’s five forces

Porter’s Five Forces is a model that helps organizations to gain a better understanding of their industries and competition.
It was published for the first time by Professor Michael Porter in his book “Competitive Strategy” in the 1980s.
The model breaks down industries and markets by analyzing them through five forces which you can use to have a first assessment of the market you’re in.
Porter’s Generic Strategies

Porter’s Value Chain

Porter’s Diamond Model

Bowman’s Strategy Clock

VMOST Analysis

Fishbone Diagram

GE McKinsey Matrix

VRIO Framework

3C Analysis

Aida model

AIDA stands for attention, interest, desire, and action. This is a model that is used in marketing to describe the potential journey a customer might go through, before purchasing a product or service. The variation of the AIDA model is the CAB model and the AIDCAS model.
PESTEL analysis

The PESTEL analysis is a framework that can help marketers assess whether macro-economic factors are affecting an organization.
This is a critical step that helps organizations identify potential threats and weaknesses. That can be used in other frameworks such as SWOT or to gain a broader and better understanding of the overall marketing environment.
Technology adoption curve

The technology adoption curve is a model that goes through five stages. Each of those stages (innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, and laggard) has a specific psychographic that makes that group of people ready to adopt a tech product.
This simple concept can help you define the right target for your business strategy.
Business model essence
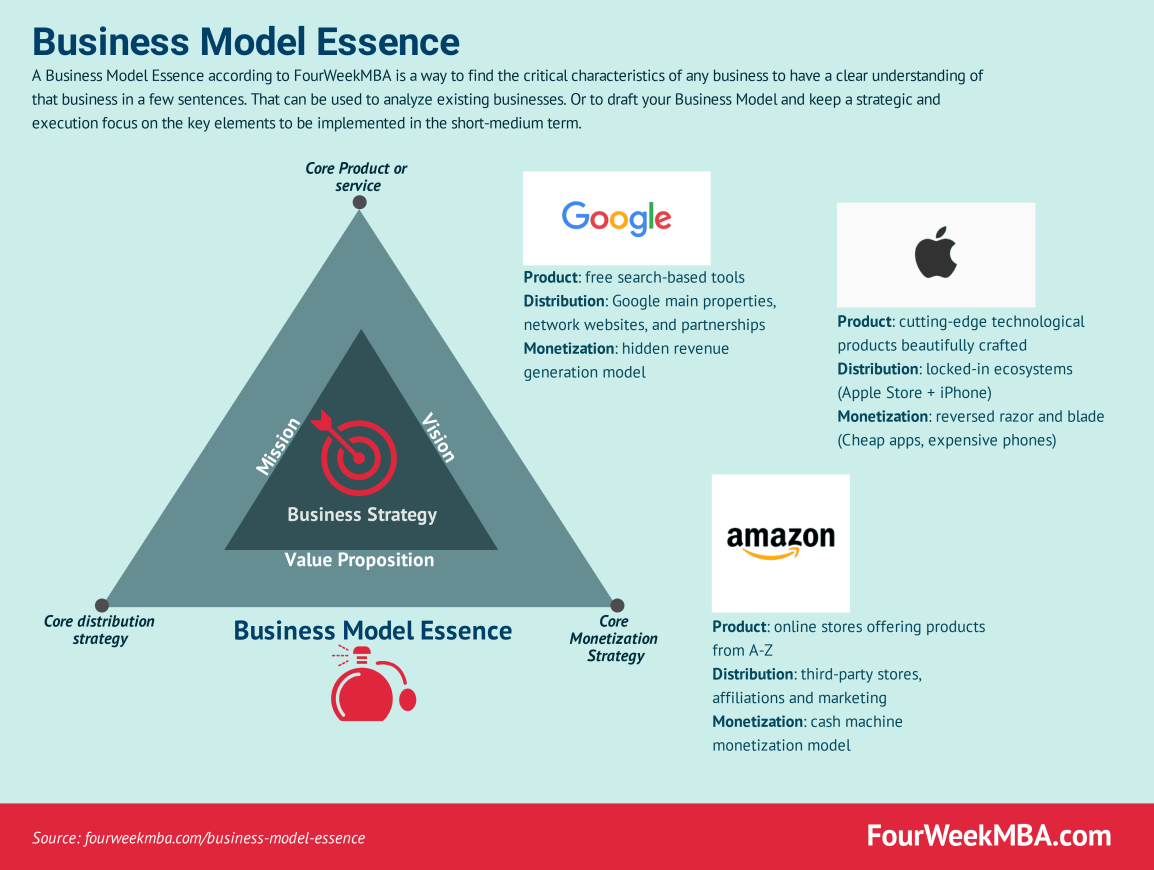
A Business Model Essence, according to FourWeekMBA, is a way to find the critical characteristics of any business to have a clear understanding of that business in a few sentences.
That can be used to analyze existing businesses. Or to draft your Business Model and keep a strategic and execution focus on the key elements to be implemented in the short-medium term.
FourWeekMBA business model framework

An effective business model has to focus on two dimensions: the people dimension and the financial dimension. The people dimension will allow you to build a product or service that is 10X better than existing ones and a solid brand.
The financial dimension will help you develop proper distribution channels by identifying the people that are willing to pay for your product or service and make it financially sustainable in the long run.
TAM, SAM, and SOM

Understanding your TAM, SAM and SOM can help you navigate the market you’re in and to have a laser focus on the market you can reach with your product and service.
Brand Building

Value Proposition Design

Product-Market Fit

Freemium Decision Model

Organizational Design And Structures

Speed-Reversibility Matrix

Minimum Viable Product

SWOT Analysis

Revenue Modeling

Business Experimentation

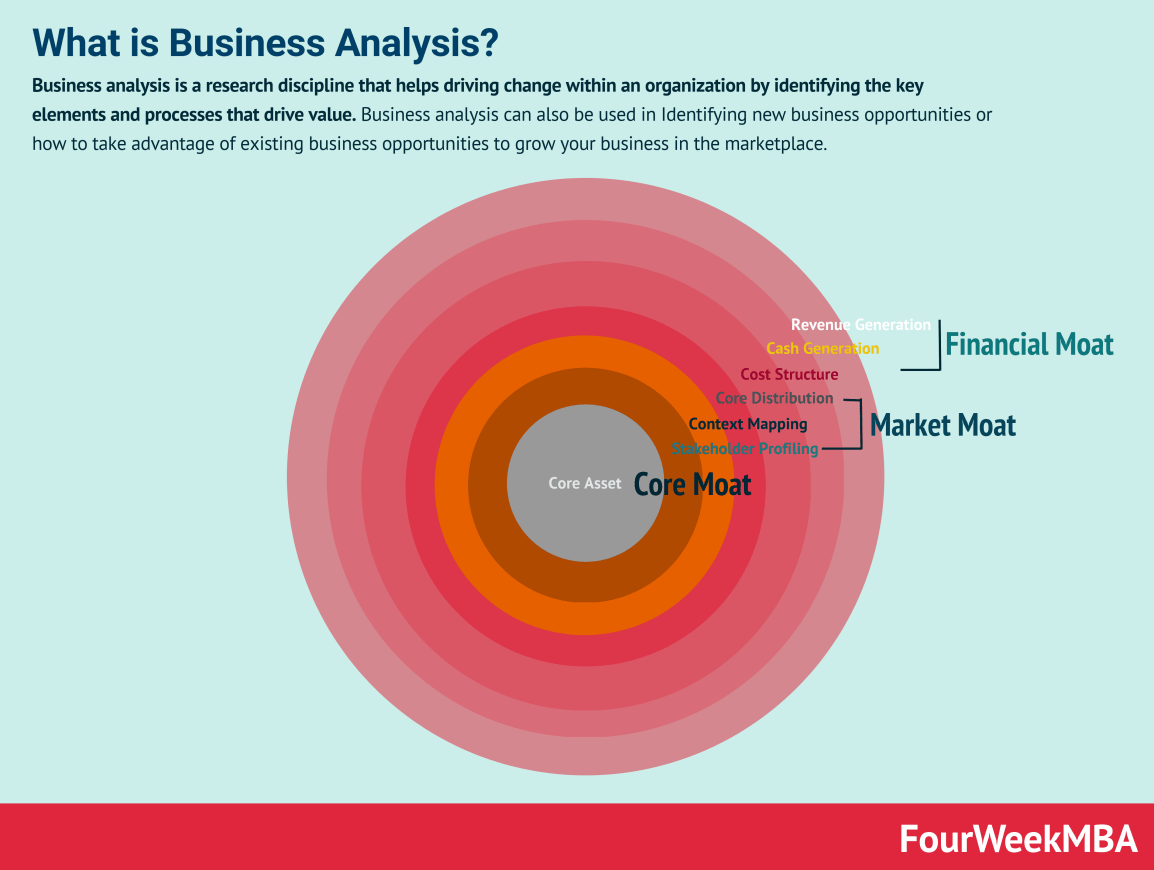
Business Analysis
BCG Matrix

Ansoff Matrix

Affiliate Marketing

Ambush Marketing

Brand Building

Brand Equity

Brand Positioning

Business Storytelling

Content Marketing

Digital Marketing

Growth Marketing

Guerrilla Marketing

Inbound Marketing

Integrated Marketing

Marketing Mix

Marketing Personas

Multi-Channel Marketing

Multi-Level Marketing

Niche Marketing

Relationship Marketing

Sustainable Marketing

Business Glossary Recap
- Design Thinking: A human-centered approach to innovation that balances desirability, feasibility, and viability to solve critical problems.
- Business Model Canvas: A tool for understanding and strategizing a business model by analyzing customers, products/services, and financial structure.
- Blitzscaling Canvas: A model focused on rapid growth under uncertainty, prioritizing speed over efficiency for market domination.
- Pretotyping: A methodology to validate business ideas and improve the chances of building products or services that people want.
- Value Innovation and Blue Ocean Strategy: Creating new uncontested markets and breaking the cost-value trade-off for competitive advantage.
- Growth Hacking Process: A process of rapid experimentation, combining marketing, product, data analysis, and engineering to achieve rapid growth.
- Pirate Metrics (AARRR): A simplified model for analyzing user paths towards becoming customers and referrers.
- Engines of Growth: Mechanisms used by startups to achieve sustainable growth, such as sticky, viral, and paid engines.
- RTVN Model: A simple framework to design a business model at the early stage of a startup.
- Sales Cycle: The process that a company takes to sell its services and products, leading up to a closed sale.
- Comparable Analysis: Identifying similar organizations for comparison to understand the performance of a target company.
- Porter’s Five Forces: A model to gain a better understanding of industries and competition by analyzing five forces.
- Porter’s Generic Strategies: Business strategies based on cost leadership, differentiation, or focus.
- Porter’s Value Chain: A collection of processes that create value for customers, leading to competitive advantage.
- Porter’s Diamond Model: Explains why specific industries become internationally competitive.
- Bowman’s Strategy Clock: A model for strategic positioning based on price and perceived value.
- VMOST Analysis: A tool to evaluate and analyze vision, mission, objectives, strategies, and tactics.
- Fishbone Diagram: A visual representation of cause and effect used in brainstorming.
- GE McKinsey Matrix: A tool for prioritizing investments among business units.
- VRIO Framework: Evaluates factors that give a company a competitive advantage (value, rarity, imitability, organization).
- 3C Analysis: Focuses on customers, competitors, and the company to develop an effective marketing strategy.
- AIDA Model: A marketing model describing a customer’s journey before purchasing a product or service.
- PESTEL Analysis: A framework to assess macro-economic factors affecting an organization.
- Technology Adoption Curve: Identifies stages of tech product adoption by different groups of users.
- Business Model Essence: Helps analyze existing businesses or draft a business model concisely.
- FourWeekMBA Business Model Framework: Focused on people dimension and financial dimension for sustainable growth.
- Brand Building: Activities to build a brand identity recognizable by the target audience.
- Value Proposition Design: Creating value for customers through demand generation and satisfaction.
- Product-Market Fit: Achieving a good market with a product that satisfies that market.
- Freemium Decision Model: A decision-making framework for the freemium business model.
- Organizational Design and Structures: Shaping business model and decision-making structures.
- Speed-Reversibility Matrix: Helps determine whether to focus on speed or reversibility in business decisions.
- Minimum Viable Product: The version of a new product that allows learning about customers with the least effort.
- SWOT Analysis: Evaluates an organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Revenue Modeling: Incorporates a sustainable financial model for revenue generation in a business.
- Business Experimentation: Testing hypotheses to define and solve problems effectively.
- Business Analysis: Identifying key elements and processes to drive value within an organization.
- BCG Matrix: Analyzes a product portfolio based on growth potential and market shares.
- Ansoff Matrix: A strategic framework based on market and product expansion.
- Affiliate Marketing: Earning a commission by selling another person or company’s products.
- Ambush Marketing: Covert advertising to raise brand awareness at events without paying for sponsorship.
- Brand Equity: The premium customers are willing to pay for a product due to brand perception.
- Brand Positioning: Creating a mental space in the target market’s mind for the brand.
- Business Storytelling: Developing a brand identity and story for better identification and engagement.
- Content Marketing: Leveraging content to attract a targeted audience and convert them into customers.
- Digital Marketing: Utilizing digital channels for marketing activities, including organic and paid methods.
- Growth Marketing: Rapid experimentation for fast growth on a limited budget.
- Guerrilla Marketing: Utilizing low-cost and unconventional tactics to raise brand awareness.
- Inbound Marketing: Attracting customers through valuable content and experiences.
- Integrated Marketing: Delivering consistent and relevant content across all marketing channels.
- Marketing Mix (Four Ps): Price, product, promotion, and place – the core elements of a marketing plan.
- Marketing Personas: Creating fictional representations of target audience segments.
- Multi-Channel Marketing: Executing marketing strategies across multiple platforms to reach a wider audience.
- Multi-Level Marketing (MLM): A strategy where individuals act as distributors and make money through direct sales and recruiting others.
- Niche Marketing: Focusing on a specific subset of potential customers within a niche market.
- Relationship Marketing: Building long-term relationships with customers to increase loyalty and engagement.
- Sustainable Marketing (Green Marketing): Incorporating social and environmental initiatives in marketing strategy.
- Technology Adoption Curve: Identifying stages of tech product adoption by different groups of users.
- Brand Building: Activities to build a brand identity recognizable by the target audience.
- Brand Equity: The premium customers are willing to pay for a product due to brand perception.
- Brand Positioning: Creating a mental space in the target market’s mind for the brand.
- Business Storytelling: Developing a brand identity and story for better identification and engagement.
- Content Marketing: Leveraging content to attract a targeted audience and convert them into customers.
- Digital Marketing: Utilizing digital channels for marketing activities, including organic and paid methods.
- Growth Marketing: Rapid experimentation for fast growth on a limited budget.
- Guerrilla Marketing: Utilizing low-cost and unconventional tactics to raise brand awareness.
- Inbound Marketing: Attracting customers through valuable content and experiences.
- Integrated Marketing: Delivering consistent and relevant content across all marketing channels.
- Marketing Mix (Four Ps): Price, product, promotion, and place – the core elements of a marketing plan.
- Marketing Personas: Creating fictional representations of target audience segments.
- Multi-Channel Marketing: Executing marketing strategies across multiple platforms to reach a wider audience.
- Multi-Level Marketing (MLM): A strategy where individuals act as distributors and make money through direct sales and recruiting others.
- Niche Marketing: Focusing on a specific subset of potential customers within a niche market.
- Relationship Marketing: Building long-term relationships with customers to increase loyalty and engagement.
- Sustainable Marketing (Green Marketing): Incorporating social and environmental initiatives in marketing strategy.
- Brand Building: Activities to build a brand identity recognizable by the target audience.
- Brand Equity: The premium customers are willing to pay for a product due to brand perception.
- Brand Positioning: Creating a mental space in the target market’s mind for the brand.
- Business Storytelling: Developing a brand identity and story for better identification and engagement.
- Content Marketing: Leveraging content to attract a targeted audience and convert them into customers.
- Digital Marketing: Utilizing digital channels for marketing activities, including organic and paid methods.
- Growth Marketing: Rapid experimentation for fast growth on a limited budget.
- Guerrilla Marketing: Utilizing low-cost and unconventional tactics to raise brand awareness.
- Inbound Marketing: Attracting customers through valuable content and experiences.
- Integrated Marketing: Delivering consistent and relevant content across all marketing channels.
- Marketing Mix (Four Ps): Price, product, promotion, and place – the core elements of a marketing plan.
- Marketing Personas: Creating fictional representations of target audience segments.
- Multi-Channel Marketing: Executing marketing strategies across multiple platforms to reach a wider audience.
- Multi-Level Marketing (MLM): A strategy where individuals act as distributors and make money through direct sales and recruiting others.
- Niche Marketing: Focusing on a specific subset of potential customers within a niche market.
- Relationship Marketing: Building long-term relationships with customers to increase loyalty and engagement.
- Sustainable Marketing (Green Marketing): Incorporating social and environmental initiatives in marketing strategy.
- Technology Adoption Curve: Identifying stages of tech product adoption by different groups of users.
- Business Model Essence: Helps analyze existing businesses or draft a business model concisely.
- FourWeekMBA Business Model Framework: Focused on people dimension and financial dimension for sustainable growth.
- TAM, SAM, and SOM: Understanding the Total Addressable Market, Serviceable Addressable Market, and Serviceable Obtainable Market for better market focus.
- Brand Building: Activities to build a brand identity recognizable by the target audience.
- Value Proposition Design: Creating value for customers through demand generation and satisfaction.
- Product-Market Fit: Achieving a good market with a product that satisfies that market.
- Freemium Decision Model: A decision-making framework for the freemium business model.
- Organizational Design and Structures: Shaping business model and decision-making structures.
- Speed-Reversibility Matrix: Helps determine whether to focus on speed or reversibility in business decisions.
- Minimum Viable Product: The version of a new product that allows learning about customers with the least effort.
- SWOT Analysis: Evaluates an organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.








