Blended learning is a broad and imprecise field that makes it difficult to define. However, in most cases, it is considered to be a form of hybrid learning that combines online and offline instructional methods.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Blended Learning, often referred to as hybrid learning, is an educational approach that combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online or digital learning methods. It integrates both in-person and virtual elements to create a comprehensive learning experience. |
| Purpose | The primary purpose of blended learning is to leverage the advantages of both traditional classroom teaching and online learning. It aims to enhance engagement, flexibility, and effectiveness in education, accommodating diverse learning styles and preferences. |
| Key Elements | – In-Person Instruction: Traditional classroom sessions or physical meetings with educators or peers. – Online Components: Digital resources, including videos, quizzes, discussion forums, and webinars. – Flexibility: Allows learners to access content and interact with instructors at their convenience. – Interaction: Encourages collaboration, discussions, and feedback through online platforms. |
| Implementation | Blended learning can take various forms, such as the flipped classroom, rotation model, flex model, or self-blend model, depending on the mix of in-person and online activities and the specific educational goals. |
| Analysis | – Educators assess the effectiveness of blended learning by analyzing learning outcomes, student engagement, and feedback. – Continuous improvement is achieved by fine-tuning the balance between online and in-person components. |
| Benefits | – Enhanced Engagement: Combines active learning strategies with technology to keep students engaged. – Flexibility: Allows learners to access materials and collaborate outside traditional class hours. – Personalization: Tailors learning experiences to individual needs and pacing. – Scalability: Suits various educational levels and subjects, from K-12 to higher education and corporate training. – Data-Driven: Provides data on student progress and engagement for informed decision-making. |
| Drawbacks | – Technology Dependence: Requires reliable internet access and digital devices, which may not be universally accessible. – Instructor Training: Educators may need training to effectively blend in-person and online elements. – Design Complexity: Developing well-structured blended courses can be challenging. – Student Readiness: Students need digital literacy and self-discipline for online components. |
| Applications | – Education: Widely used in K-12 and higher education settings to provide more interactive and flexible learning experiences. – Corporate Training: Employed by organizations to upskill employees and offer flexible training solutions. – Language Learning: Popular for learning languages, where multimedia resources and interactive activities enhance language acquisition. – Professional Development: Used for ongoing education and certification programs in various industries. |
| Examples | – In a flipped classroom, students watch pre-recorded lectures online before attending in-person classes for discussions and hands-on activities. – A corporate training program combines on-site workshops with online modules accessible at employees’ convenience. – A language learning platform offers virtual language labs, online quizzes, and live conversation sessions to complement traditional classroom instruction. |
Understanding blended learning
Blended learning is a combination of online learning and more traditional forms of face-to-face learning where each serves to enhance the other.
Indeed, in a typical blended course, instruction that occurs in a classroom is reinforced or supported by activities that take place in an online environment.
For teachers, blended learning is an approach that enables them to cater to all types of learners.
Students who prefer to learn in a structured environment will appreciate direct interaction with an instructor, while those who prefer to learn alone will find the semi-autonomous nature of learning online more to their tastes.
While schools and universities are the most obvious institutions to benefit from blended learning, businesses with diverse workforces can also use the approach to cater to a mix of learning styles.
Types of blended learning models
Some of the models of blended learning include:
Flipped
Where teachers prioritize active learning in face-to-face classes by distributing resources and materials before the class takes place.
For many organizations, this occurs in a learning management system (LMS).
Face-to-face
In this case, traditional classroom instruction is supplemented with technology so that students can learn at their own pace.
Flex
The flex model describes students that learn via an LMS and choose the direction of their study.
Teachers are present, but in more of a mentoring capacity to answer questions when required.
Enriched virtual
Where most of the coursework is completed online and supplemented with face-to-face online webinars led by an instructor.
Note that attendance at these webinars is at the discretion of the student.
Self–blend–motivated students
Who want to delve deeper into a subject can use the self-blend model.
Here, face-to-face instruction is augmented with additional content such as white papers, video tutorials, case studies, and industry blogs that are conveniently organized under an LMS.
When to Use Blended Learning:
Blended Learning is suitable in various educational scenarios:
- K-12 Education: In primary and secondary education, it can support differentiated instruction and student engagement.
- Higher Education: In colleges and universities, it facilitates flipped classrooms, online discussions, and hybrid courses.
- Corporate Training: In professional development, it offers a flexible and cost-effective approach to upskilling employees.
- Language Learning: In language education, it combines classroom practice with online exercises and resources.
- Skill Development: For acquiring technical or practical skills, Blended Learning offers a mix of hands-on and online training.
How to Implement Blended Learning Effectively:
To effectively implement Blended Learning, consider the following steps:
- Clear Learning Objectives: Define clear learning objectives and outcomes for both in-person and online components.
- Curriculum Design: Develop a curriculum that integrates face-to-face and online activities, ensuring a seamless flow.
- Technology Integration: Choose and integrate appropriate educational technology and online platforms that enhance learning.
- Student Engagement: Promote active student engagement through discussions, collaborative projects, and interactive online activities.
- Assessment Strategies: Design assessment methods that align with the learning objectives and evaluate both in-person and online learning.
- Support and Training: Provide support and training for both educators and students in using digital tools and navigating the Blended Learning environment.
Drawbacks and Limitations of Blended Learning:
While Blended Learning offers numerous advantages, it also has drawbacks and limitations:
- Resource Requirements: Implementing and maintaining the necessary technology and resources can be costly.
- Technical Challenges: Technical issues, such as connectivity problems or platform glitches, can disrupt the learning process.
- Teacher Preparedness: Effective Blended Learning requires educators to adapt their teaching methods and become proficient in using digital tools.
- Student Discipline: Students may require strong self-discipline and time-management skills for successful participation in online components.
What to Expect When Applying Blended Learning:
When applying Blended Learning, expect the following outcomes and considerations:
- Enhanced Flexibility: Students benefit from the flexibility to access content and engage in learning activities at their own pace.
- Personalized Learning: Blended Learning allows for personalized learning experiences tailored to individual student needs.
- Improved Engagement: The combination of in-person and online activities often leads to higher student engagement.
- Resource Optimization: Educational resources, including time and physical space, are optimized through Blended Learning.
Relevance in Various Educational Contexts:
Blended Learning is relevant in various educational contexts, including K-12 education, higher education, corporate training, language learning, and skill development.
It provides a versatile approach to meet diverse learning needs and objectives.
Examples of blended learning
In the final section, we will describe some real-world examples of blended learning in action.
Sales
Blended learning in the context of sales training may comprise the following elements:
- Important topics such as CRM, negotiation skills, and effective communication are offered via mobile-based videos. Gamification is also used to maintain student engagement.
- Virtual instructor-led training (VILT) encompasses scenario-based discussion and role-play situations. Best practices, aids, and guidelines are made available as downloadable resources.
- Simulated environments where role-play situations are explored in more detail and incorporated into VILT or face-to-face sessions.
- A flipped blended learning model where students attend face-to-face classes and raise issues encountered while completing online exercises.
Healthcare
In a course to train healthcare professionals, a combination of learning methods was used to teach the skill of cannulation. In layman’s terms, this is the intravenous delivery of fluids, blood, and antibiotics to improve patient health.
Below is a list of learning outcomes and their associated instructional styles:
- List the main veins in the forearm – online.
- Name the primary components of the cannula. This is the thin tube that is inserted into the body – online.
- Learning how to correctly insert the cannula – classroom.
- Provide cannulation to patients – the bedside (mentored).
Compliance
Compliance training by its very nature needs to be rigorous, strict, and standardized to ensure the necessary outcomes are met.
How might this look in terms of blended learning?
- Immersive learning is important for compliance training since most of the content will be learned by the student on their own. For best results, a self-paced style that incorporates micro-learning, scenario-based learning, and gamification is ideal.
- To maintain student engagement and increase learning, various concepts, scenarios, and important case studies can be used to demonstrate the impact of non-compliance. This can either be a virtual or face-to-face training session.
- Webinars run by business leaders can also be useful to add a human touch to the subject of compliance and clarify any trainee questions.
Key takeaways
- Blended learning is a broad and imprecise field that makes it difficult to define. However, in most cases, it is considered to be a form of hybrid learning that combines online and offline instructional methods.
- There are various blended learning models which educators use to disseminate online and offline content. These include flipped, face-to-face, flex, enriched virtual, and self-blend.
- Blended learning is useful in limitless real-world scenarios. These include non-compliance training, sales training, and training for healthcare professionals.
Key Highlights
- Definition of Blended Learning: Blended learning is a hybrid approach that combines both online and traditional face-to-face instructional methods. It aims to enhance learning experiences by leveraging the strengths of both modes of learning.
- Enhancing Learning: In a blended learning course, in-person classroom instruction is complemented and reinforced with online activities and resources. This approach aims to cater to various learning preferences and create a more engaging and effective learning environment.
- Catering to Different Learners: Blended learning allows educators to accommodate different learning styles. It provides structured interaction with instructors for those who prefer it, as well as a semi-autonomous online learning experience for those who prefer to learn independently.
- Types of Blended Learning Models: There are several models of blended learning, including:
- Flipped Model: Resources and materials are provided online before face-to-face classes, prioritizing active learning.
- Face-to-Face Model: Traditional classroom instruction is supplemented with technology to enable self-paced learning.
- Flex Model: Learning occurs mainly online, with teachers serving as mentors for guidance and support.
- Enriched Virtual Model: Most coursework is online, supplemented by occasional face-to-face online webinars.
- Self-Blend Model: Face-to-face instruction is augmented with additional online content for deeper learning.
- Examples of Blended Learning in Action:
- Sales Training: Blended learning in sales training may involve mobile-based videos for important topics, virtual instructor-led training (VILT) with role-play scenarios, simulated environments for detailed exploration, and a flipped model combining face-to-face sessions with online exercises.
- Healthcare Training: A healthcare training course on cannulation combines online learning for theory, classroom learning for practical skills, and bedside mentoring for hands-on practice.
- Compliance Training: In compliance training, immersive self-paced learning using micro-learning and scenario-based methods can be combined with webinars by business leaders for clarification.
Connected Learning Frameworks












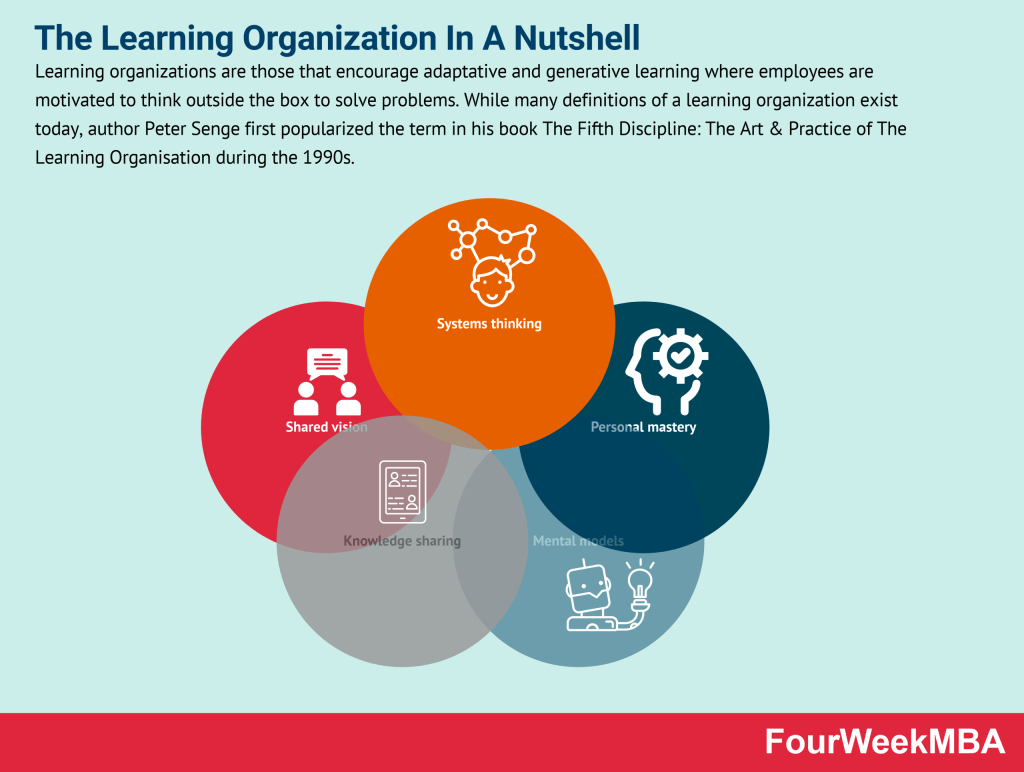


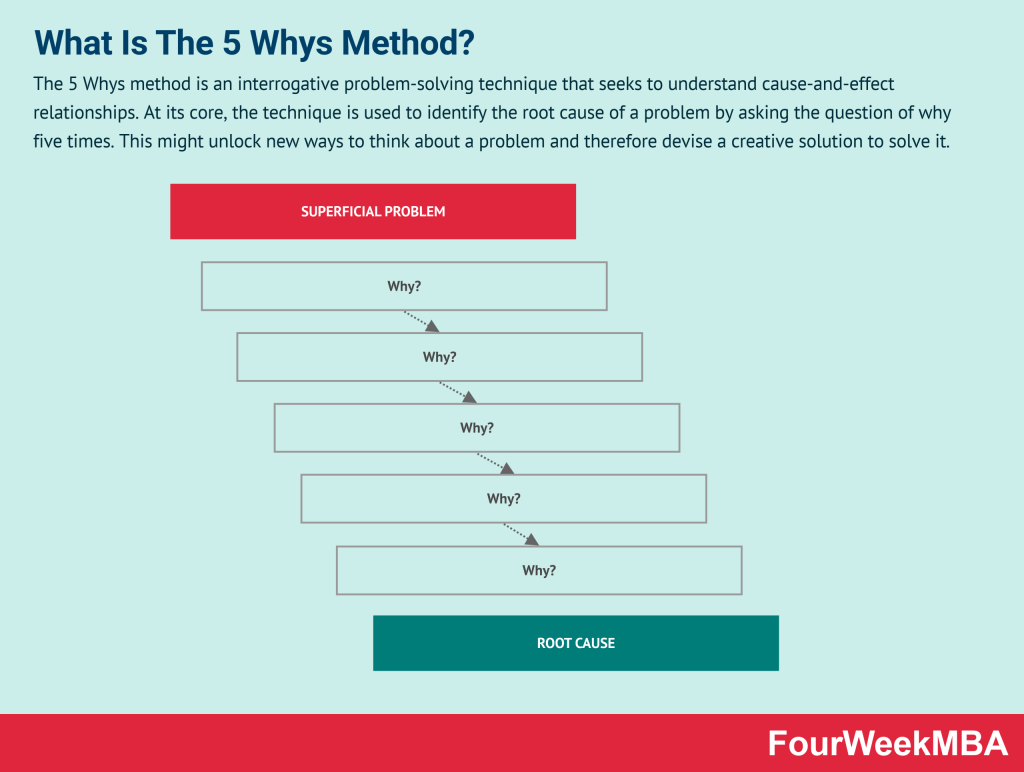








Related Strategy Concepts: Read Next: Mental Models, Biases, Bounded Rationality, Mandela Effect, Dunning-Kruger Effect, Lindy Effect, Crowding Out Effect, Bandwagon Effect, Decision-Making Matrix.
Main Free Guides:









