The MEDDIC sales process was developed in 1996 by Dick Dunkel at software company Parametric Technology Corporation (PTC). The MEDDIC sales process is a framework used by B2B sales teams to foster predictable and efficient growth.
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Concept | MEDDIC is a structured sales qualification and methodology used by sales teams to assess and prioritize opportunities in the B2B (business-to-business) sales environment. The acronym MEDDIC stands for Metrics, Economic Buyer, Decision Criteria, Decision Process, Identify Pain, and Champion. This approach helps sales professionals systematically evaluate and close complex deals. |
| Key Components | The MEDDIC sales process consists of six key components: – Metrics: Understand the customer’s key performance indicators (KPIs) and how your solution can positively impact them. – Economic Buyer: Identify and engage with the person who has the authority to make the purchasing decision and allocate budget. – Decision Criteria: Determine the specific criteria the customer will use to evaluate and select a solution. – Decision Process: Gain insights into the steps, timeline, and stakeholders involved in the decision-making process. – Identify Pain: Uncover the customer’s pain points, challenges, or needs that your solution can address. – Champion: Develop a strong relationship with an internal advocate or champion who can champion your solution within the customer’s organization. |
| Application | MEDDIC is typically applied in complex B2B sales situations, where deals involve multiple decision-makers, lengthy sales cycles, and significant financial commitments. It helps sales teams systematically assess and prioritize opportunities, allocate resources effectively, and increase win rates. |
| Process Flow | The MEDDIC process flows in a structured manner: – Metrics: Start by understanding the customer’s performance metrics and goals. – Economic Buyer: Identify and connect with the individual who has the authority to make purchasing decisions and control budget allocation. – Decision Criteria: Learn the specific criteria the customer will use to evaluate solutions. – Decision Process: Gain insights into the steps and timeline of the customer’s decision-making process. – Identify Pain: Explore and uncover the customer’s challenges, pain points, and needs. – Champion: Develop a strong relationship with a key contact within the customer’s organization who can advocate for your solution. |
| Benefits | The MEDDIC sales process offers several benefits: – Improved Qualification: It helps sales teams identify the most promising opportunities and allocate resources effectively. – Increased Win Rates: By systematically addressing key customer concerns and needs, sales professionals are more likely to close deals successfully. – Enhanced Customer Understanding: Sales reps gain a deeper understanding of the customer’s business, pain points, and decision-making process. – Stronger Internal Advocacy: Developing a champion within the customer’s organization can significantly boost your chances of success. |
| Challenges | Challenges associated with MEDDIC may include: – Resource Intensity: The thoroughness of the process may require more time and effort than some sales situations warrant. – Complexity: In very complex sales environments, navigating all the components of MEDDIC can be challenging. – Resistance to Change: Implementing a structured methodology may face resistance from sales teams accustomed to other approaches. |
| Real-World Application | MEDDIC is widely used by sales organizations, particularly in the technology, software, and enterprise sectors, where large deals and complex sales processes are common. |
Understanding the MEDDIC sales process
As a qualification framework, MEDDIC sets itself apart from other sales processes. It emphasizes extensive buyer qualification to ensure the business does not devote considerable resources to leads who will not convert. This process increases close rates and drives more predictable growth with better sales forecasting.
The qualification process itself is based on the twelve selling principles author Neil Rackham outlined in his 1988 book SPIN Selling. SPIN is an acronym for Situation, Problem, Implication, and Need-Payoff and is particularly suited to large or complex deals where the salesperson needs to become more of a trusted advisor to the client.
MEDDIC is a more evolved version of SPIN where sales teams are equipped with the tools and decision criteria to work closely with prospects and best meet their needs.
The six components of the MEDDIC sales process
The six components of MEDDIC are based on collaboration between Dunkel and individual PTC sales teams with a core focus on three questions:
- Why does PTC win?
- Why does PTC lose?
- Why do some PTC deals slip?
Let’s take a look at the six common components Dunkel defined below.
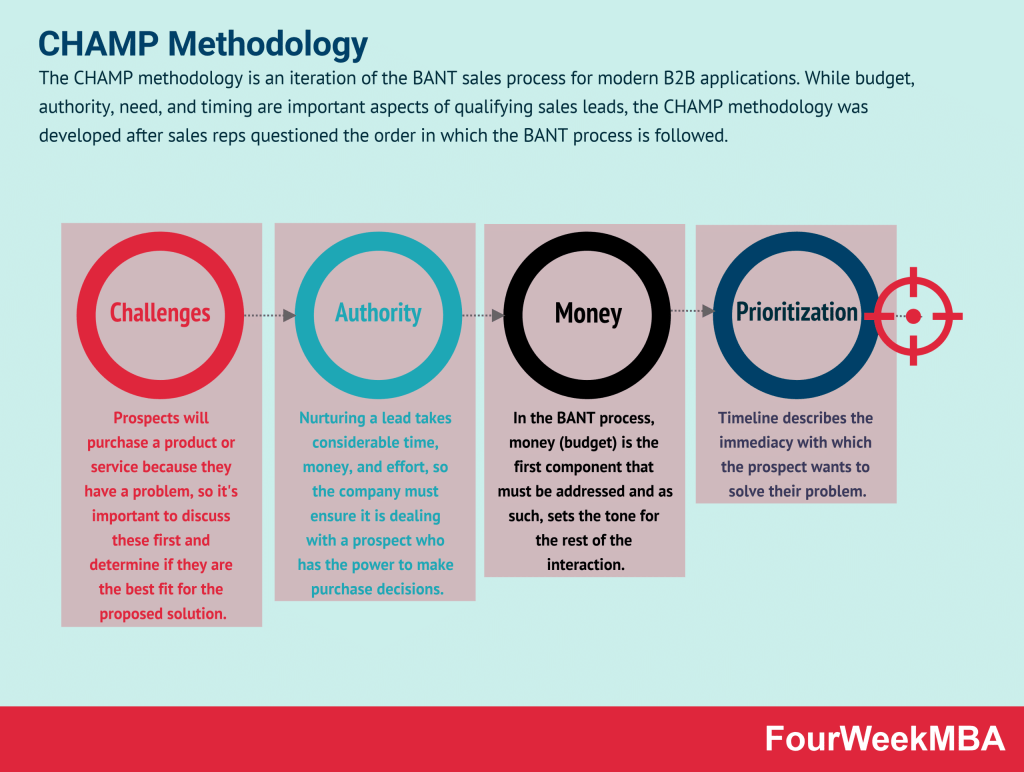
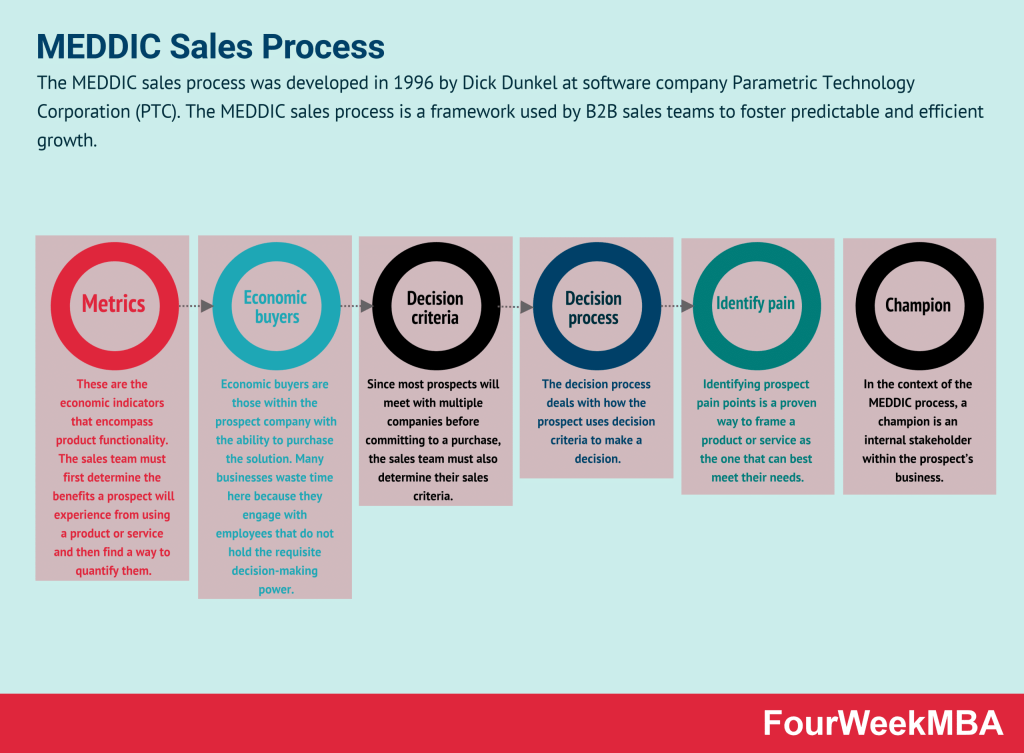
Metrics (M)
These are the economic indicators that encompass product functionality. The sales team must first determine the benefits a prospect will experience from using a product or service and then find a way to quantify them.
Metrics can then be incorporated into the pitch. For example: “Our service will save your business up to 25 working hours per week and increase productivity by 35%.”
Economic buyers (E)
Economic buyers are those within the prospect company with the ability to purchase the solution. Many businesses waste time here because they engage with employees that do not hold the requisite decision-making power.
LinkedIn is a good place to search a company’s employees based on job title. Otherwise, a meeting can be proposed with the sales team inviting the prospect to invite individuals who will be heavily involved in the project.
Decision criteria (D)
Since most prospects will meet with multiple companies before committing to a purchase, the sales team must also determine their sales criteria. This may take the form of:
- Technical criteria – how will the prospect implement a product or service? Indeed, does it have the technical ability to do what they need?
- Relationship criteria – is the prospect interested in working with the company? Are the needs, interests, and objectives of each party aligned?
- Economic criteria – does the product in question deliver an attractive ROI? What is the implementation cost? What about opportunity cost?
Decision process (D)
The decision process deals with how the prospect uses decision criteria to make a decision.
It tends to comprise two parts. The first part is a validation process where the prospect clarifies that the product or service can achieve what it says it can. The second part concerns receiving authorization from relevant stakeholders to move forward with a particular product or service.
Sales teams should make the decision-making process as smooth as possible by:
- Involving new stakeholders or others involved in decision-making.
- Reiterating or confirming the decision-making timeline, and
- Offering a free trial or product demonstration.
This is a crucial part of the deal forecasting process. Prospects that do not possess a clear decision process or who seem otherwise reticent represent a major red flag. Since the complex B2B deals to which MEDDIC is suited can last for months, reps need to keep the process moving forward wherever possible. Dedicated CRM software is one way to assist in this process.
Identify pain (I)
Identifying prospect pain points is a proven way to frame a product or service as the one that can best meet their needs. Most of these revolve around:
- The elimination of tedious tasks.
- The removal of complicated or convoluted solutions.
- Time or resource efficiency improvement.
These pain points can also be outlined in the context of a competitor. For example, the business may claim that its product is easier to use and more affordable than a rival offering.
Champion (C)
In the context of the MEDDIC process, a champion is an internal stakeholder within the prospect’s business who:
- Is selling the product or service to other stakeholders within the organization. The solution is afforded a certain degree of credibility when its benefits can be clearly linked to organizational objectives.
- Possess the power and influence to finalize the sale or at least ensure that it remains top-of-mind among decision-makers.
- Have a vested interest in the company’s success. This means the solution will remove a problem that makes their job easier or results in a promotion.
Principles of the MEDDIC Sales Process:
- Qualification: The MEDDIC framework is primarily a qualification tool used to assess the viability of sales opportunities. It ensures that resources are allocated to high-potential leads.
- Discovery: Sales professionals must engage in extensive discovery conversations with prospects to gather information related to each MEDDIC criterion. This involves asking probing questions and actively listening.
- Customization: Tailor your sales approach and solution based on the specific metrics, decision criteria, and pain points identified during the MEDDIC process.
- Continuous Evaluation: MEDDIC is not a one-time assessment. Sales teams should continuously evaluate and update the status of each MEDDIC criterion as the sales cycle progresses.
Advantages of the MEDDIC Sales Process:
- Effective Qualification: MEDDIC helps identify and prioritize sales opportunities, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently.
- Increased Win Rates: Focusing on opportunities that meet all MEDDIC criteria increases the likelihood of closing deals successfully.
- Streamlined Sales Cycles: MEDDIC-qualified leads often progress through the sales funnel more smoothly, resulting in shorter sales cycles.
- Improved Forecasting: Data gathered through MEDDIC assessments enhances sales forecasting accuracy and pipeline management.
Challenges of the MEDDIC Sales Process:
- Information Gathering: Obtaining complete information for all MEDDIC criteria can be challenging, especially in complex B2B sales.
- Complex Sales: MEDDIC is most suitable for complex B2B sales scenarios and may not be as relevant for simpler sales processes.
- Human Dynamics: Identifying the true Economic Buyer, navigating organizational politics, and understanding decision processes can be complex.
- Overemphasis on Criteria: Overemphasizing MEDDIC criteria may lead to missed opportunities with leads that don’t meet all criteria but could still become valuable customers.
When to Use the MEDDIC Sales Process:
- Complex Sales: MEDDIC is highly effective in complex B2B sales where understanding the prospect’s situation is critical.
- Resource Allocation: When sales teams have limited resources and need to prioritize leads efficiently.
- Customized Solutions: When your product or service can be tailored to meet specific decision criteria and metrics.
- Long Sales Cycles: MEDDIC is particularly valuable for sales cycles that involve multiple stages and evaluations.
What to Expect from Using the MEDDIC Sales Process:
- Improved Lead Quality: Expect a higher quality of leads in your sales pipeline.
- Efficiency Gains: Sales teams can work more efficiently by concentrating efforts on MEDDIC-qualified leads.
- Shorter Sales Cycles: MEDDIC-qualified leads often progress through the sales funnel more quickly.
- Enhanced Forecasting: Improved data leads to more accurate sales forecasting.
Long-Term Impact of the MEDDIC Sales Process:
- Revenue Growth: Over time, the MEDDIC process can contribute to consistent revenue growth by focusing efforts on high-potential opportunities.
- Data-Driven Culture: A commitment to MEDDIC fosters a data-driven culture within the sales organization, leading to better decision-making.
- Customer Satisfaction: By targeting leads with genuine needs, you’re more likely to deliver value and create satisfied customers.
- Competitive Edge: The MEDDIC process can provide a competitive edge by optimizing sales strategies and resource allocation.
In conclusion, the MEDDIC sales process is a structured framework that helps sales professionals qualify leads and prioritize sales efforts effectively. Its long-term impact includes revenue growth, the development of a data-driven culture, increased customer satisfaction, and a competitive advantage in the market. As businesses aim to improve their sales efficiency and effectiveness, the MEDDIC process remains a valuable tool in their sales toolkit.
Case Study
Metrics (M):
- Quantifying the benefits of a project management software by stating it can reduce project completion time by 20%.
- Demonstrating that an investment in a customer relationship management (CRM) system can increase revenue by 15% annually.
Economic Buyers (E):
- Identifying the CFO or Chief Procurement Officer as the economic buyer who has the authority to approve the purchase.
- Ensuring that the sales team engages with key decision-makers, not just lower-level employees.
Decision Criteria (D):
- Addressing technical criteria by explaining how the software integrates seamlessly with existing IT infrastructure.
- Covering economic criteria by showcasing the product’s attractive return on investment (ROI) compared to competitors.
Decision Process (D):
- Clarifying the validation process, which involves the prospect testing the software to ensure it meets their requirements.
- Confirming the timeline for obtaining authorization from stakeholders for the purchase.
Identify Pain (I):
- Identifying the prospect’s pain point in managing customer data and explaining how the CRM system simplifies the process.
- Highlighting the challenges the prospect faces with their current project management tools and how the new software can alleviate those issues.
Champion (C):
- Identifying an enthusiastic project manager within the prospect’s organization who actively promotes the software to decision-makers.
- Recognizing that the Head of Sales is a champion because implementing the CRM system aligns with their goal of increasing revenue.
Key takeaways:
- The MEDDIC sales process is a framework used by B2B sales teams to foster predictable and efficient growth.
- The qualification process inherent to the MEDDIC process is a more evolved version of the twelve selling principles outlined in Neil Rackham’s 1988 book SPIN Selling.
- The MEDDIC sales process is an acronym for six components: metrics, economic buyers, decision criteria, decision process, identify pain, and champion.
Key Insights
- MEDDIC Sales Process: A framework developed by Dick Dunkel at Parametric Technology Corporation (PTC) in 1996, used by B2B sales teams to achieve predictable and efficient growth.
- Qualification Framework: Emphasizes extensive buyer qualification to focus resources on leads that are likely to convert, increasing close rates and improving sales forecasting.
- SPIN Selling: A selling methodology by Neil Rackham, which serves as the basis for MEDDIC. SPIN stands for Situation, Problem, Implication, and Need-Payoff.
- Components of MEDDIC Sales Process:
- Metrics (M): Economic indicators that quantify product functionality and benefits for the prospect.
- Economic Buyers (E): Decision-makers within the prospect company who have purchasing authority.
- Decision Criteria (D): Sales criteria, including technical, relationship, and economic factors, considered by prospects during the decision-making process.
- Decision Process (D): How prospects use decision criteria to make decisions, involving validation and authorization from stakeholders.
- Identify Pain (I): Identifying prospect pain points to position the product as the best solution for their needs.
- Champion (C): Internal stakeholder within the prospect’s company who advocates for the product, possesses influence, and has a vested interest in the company’s success.
- Key Findings:
- MEDDIC focuses on buyer qualification and is an evolved version of SPIN Selling.
- It consists of six components: Metrics, Economic Buyers, Decision Criteria, Decision Process, Identify Pain, and Champion.
Case Studies
| Context | Description | Implications | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enterprise Software Sales | In enterprise software sales, applying MEDDIC involves identifying key metrics that the software will impact, understanding the economic buyer, determining the decision criteria, mapping the decision process, uncovering pain points, and cultivating a champion within the organization. | – Ensures alignment with the prospect’s strategic goals. – Helps in pinpointing the person or group with budget authority. – Guides the development of a tailored solution. – Provides insights into the decision-making dynamics. – Enables the identification of areas where the software can address pain points. – Facilitates relationship building and trust with a champion. | A sales team selling a complex ERP software solution applies MEDDIC by first quantifying how the software will improve operational efficiency and profitability (Metrics). They then identify the CFO as the Economic Buyer and align the software’s capabilities with the company’s decision criteria. The team maps out the decision process and identifies pain points in the current systems, while a sales representative works to cultivate a Champion within the finance department. |
| Medical Device Sales | In medical device sales, the MEDDIC process involves identifying metrics related to patient outcomes, understanding the economic buyer (often a hospital administrator or department head), determining the decision criteria for medical device adoption, mapping the decision process within the hospital, identifying pain points in current practices, and gaining a champion among the hospital staff. | – Demonstrates the value of the medical device in terms of patient care. – Ensures alignment with the person responsible for purchasing decisions. – Helps in meeting regulatory and clinical requirements. – Provides insights into the approval and procurement process. – Enables the identification of pain points and inefficiencies in current procedures. – Facilitates buy-in from medical professionals through a champion. | A medical device sales team applies MEDDIC by quantifying how their device improves patient outcomes (Metrics). They identify the hospital administrator as the Economic Buyer and ensure that the device meets the hospital’s decision criteria. The team maps out the decision process within the hospital, identifies pain points in current practices, and works to gain the support of a Champion among the surgical staff. |
| Industrial Equipment Sales | In industrial equipment sales, MEDDIC involves identifying metrics related to operational efficiency and cost savings, understanding the economic buyer (often a plant manager or director of operations), determining the decision criteria for equipment purchase, mapping the decision process within the organization, identifying pain points in current operations, and cultivating a champion within the plant. | – Demonstrates how the equipment can improve production efficiency and reduce costs. – Ensures alignment with the person responsible for facility decisions. – Guides the customization of the equipment to meet specific needs. – Provides insights into procurement and installation timelines. – Enables the identification of operational inefficiencies and bottlenecks. – Facilitates internal support for the purchase through a champion. | A sales team selling industrial equipment applies MEDDIC by quantifying how the equipment will improve production output and reduce energy consumption (Metrics). They identify the plant manager as the Economic Buyer and ensure that the equipment aligns with the facility’s decision criteria. The team maps out the decision process within the organization, identifies pain points in current operations, and works to cultivate a Champion within the plant’s engineering team. |
| Financial Services Sales | In financial services sales, the MEDDIC process involves identifying metrics related to ROI and risk mitigation, understanding the economic buyer (often a CFO or financial director), determining the decision criteria for financial services, mapping the decision process within the organization, identifying pain points in current financial strategies, and cultivating a champion within the finance department. | – Demonstrates the potential ROI and risk reduction associated with the financial services. – Ensures alignment with the person responsible for financial decisions. – Guides the customization of financial solutions. – Provides insights into the decision-making timeline and approval process. – Enables the identification of financial inefficiencies and potential cost savings. – Facilitates support for the services through a champion. | A financial services sales team applies MEDDIC by quantifying how their services can improve ROI and reduce financial risks (Metrics). They identify the CFO as the Economic Buyer and ensure that the financial services align with the organization’s decision criteria. The team maps out the decision process within the organization, identifies pain points in current financial strategies, and works to cultivate a Champion within the finance department. |
| SaaS Sales | In SaaS (Software as a Service) sales, MEDDIC involves identifying metrics related to increased productivity or cost savings, understanding the economic buyer (often a department head or CIO), determining the decision criteria for SaaS adoption, mapping the decision process within the organization, identifying pain points in current software solutions, and cultivating a champion within the user group. | – Demonstrates the value of the SaaS solution in terms of productivity gains or cost reduction. – Ensures alignment with the person responsible for software decisions. – Guides product customization and integration. – Provides insights into the software procurement process. – Enables the identification of pain points and limitations in current software. – Facilitates user adoption and support through a champion. | A SaaS sales team applies MEDDIC by quantifying how their software can increase productivity and reduce software licensing costs (Metrics). They identify the department head as the Economic Buyer and ensure that the SaaS solution meets the organization’s decision criteria. The team maps out the decision process within the organization, identifies pain points in current software solutions, and works to cultivate a Champion within the user group. |
| Telecom Services Sales | In telecom services sales, the MEDDIC process involves identifying metrics related to improved connectivity and cost savings, understanding the economic buyer (often a CTO or IT director), determining the decision criteria for telecom services, mapping the decision process within the organization, identifying pain points in current communication solutions, and cultivating a champion within the IT department. | – Demonstrates the value of improved connectivity and cost-effective solutions. – Ensures alignment with the person responsible for telecom decisions. – Guides customization of telecom packages and services. – Provides insights into the procurement process and technology adoption timeline. – Enables the identification of communication issues and inefficiencies. – Facilitates support and adoption through a champion. | A telecom services sales team applies MEDDIC by quantifying how their services can improve connectivity and reduce communication costs (Metrics). They identify the CTO as the Economic Buyer and ensure that the telecom services align with the organization’s decision criteria. The team maps out the decision process within the organization, identifies pain points in current communication solutions, and works to cultivate a Champion within the IT department. |
| Commercial Real Estate Sales | In commercial real estate sales, MEDDIC involves identifying metrics related to ROI and property value appreciation, understanding the economic buyer (often a property manager or investor), determining the decision criteria for property acquisition, mapping the decision process within the organization, identifying pain points in current property holdings or leases, and cultivating a champion among property stakeholders. | – Demonstrates the potential ROI and property value appreciation. – Ensures alignment with the person responsible for property decisions. – Guides property selection and negotiation. – Provides insights into the property acquisition process. – Enables the identification of property-related issues and inefficiencies. – Facilitates support and approval through a champion. | A commercial real estate sales team applies MEDDIC by quantifying how their property offering can deliver ROI and enhance property value (Metrics). They identify the property manager or investor as the Economic Buyer and ensure that the property aligns with the organization’s decision criteria. The team maps out the decision process within the organization, identifies pain points in current property holdings or leases, and works to cultivate a Champion among property stakeholders. |
| Pharmaceutical Sales | In pharmaceutical sales, the MEDDIC process involves identifying metrics related to patient health outcomes and cost savings, understanding the economic buyer (often a hospital or healthcare system administrator), determining the decision criteria for pharmaceutical adoption, mapping the decision process within the healthcare institution, identifying pain points in current treatment regimens, and cultivating a champion among healthcare professionals. | – Demonstrates the impact of the pharmaceutical product on patient health and cost savings. – Ensures alignment with the person responsible for healthcare decisions. – Guides the adoption of the pharmaceutical product within the institution. – Provides insights into the drug approval and procurement process. – Enables the identification of treatment-related issues and inefficiencies. – Facilitates support and adoption through a champion. | A pharmaceutical sales team applies MEDDIC by quantifying how their drug product can improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs (Metrics). They identify the hospital or healthcare system administrator as the Economic Buyer and ensure that the pharmaceutical product aligns with the institution’s decision criteria. The team maps out the decision process within the healthcare institution, identifies pain points in current treatment regimens, and works to cultivate a Champion among healthcare professionals. |
| Aspect | MEDDIC Sales Process | SPIN Selling | SNAP Selling |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | A structured sales methodology that stands for Metrics, Economic Buyer, Decision Criteria, Decision Process, Identify Pain, and Champion. | Focuses on asking Situation, Problem, Implication, and Need-Payoff questions to uncover customer needs and pain points. | Emphasizes Simplify, iNvaluable, Align, and Prioritize principles to quickly engage customers and drive sales conversations. |
| Objective | To qualify leads efficiently and focus on opportunities with a higher likelihood of closing by addressing key decision-making factors. | To uncover customer needs, create value, and build trust through effective questioning and problem-solving. | To simplify the sales process, demonstrate unique value, align with customer goals, and prioritize action to accelerate decision-making. |
| Customer Focus | Emphasizes identifying key stakeholders, understanding their needs, and aligning solutions with business objectives. | Focuses on understanding customer pain points, challenges, and aspirations to tailor solutions accordingly. | Prioritizes engaging customers in meaningful conversations, providing immediate value, and aligning solutions with their objectives. |
| Questioning Approach | Utilizes a structured set of questions to uncover specific information about the customer’s business, challenges, and decision-making process. | Relies on open-ended questions to explore customer needs, uncover pain points, and create opportunities for value-added solutions. | Emphasizes asking insightful questions to quickly identify customer needs, provide relevant solutions, and demonstrate value. |
| Sales Process Stages | Metrics, Economic Buyer, Decision Criteria, Decision Process, Identify Pain, Champion. | Situation, Problem, Implication, Need-Payoff. | Simplify, iNvaluable, Align, Prioritize. |
| Key Components | Metrics: Quantifiable objectives and key performance indicators. Economic Buyer: Identifying decision-makers with budget authority. Decision Criteria: Understanding customer requirements and evaluation criteria. Decision Process: Mapping out the steps involved in the buying process. Identify Pain: Discovering customer challenges and pain points. Champion: Cultivating internal advocates and influencers. | Situation: Understanding the customer’s current situation or context. Problem: Identifying specific issues or challenges the customer faces. Implication: Exploring the consequences or impact of the identified problems. Need-Payoff: Revealing the benefits and value of addressing the identified needs. | Simplify: Streamline the sales process and reduce complexity. iNvaluable: Provide unique value and insights to the customer. Align: Align solutions with customer objectives and priorities. Prioritize: Focus on high-potential opportunities and urgent customer needs. |
| Application | Suitable for complex B2B sales environments where multiple stakeholders are involved and long sales cycles are common. | Effective for uncovering customer needs and building rapport in consultative sales situations, particularly in industries with complex solutions. | Well-suited for fast-paced sales environments where quick engagement, value demonstration, and alignment with customer priorities are critical. |
Related Business Concepts






















Palantir Acquire, Expand, Scale Framework



Read: product development frameworks here.
Read Next: SWOT Analysis, Personal SWOT Analysis, TOWS Matrix, PESTEL Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces, TOWS Matrix, SOAR Analysis.
Main Free Guides:









