Google mission statement is to “organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.” Its vision statement is to “provide an important service to the world-instantly delivering relevant information on virtually any topic.” In 2019, Sundar Pichai emphasized a renewed mission to allow people “to get things done!”
| Aspect | Details | Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Mission | “Organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.” | – Clear and concise mission focused on organizing information for global accessibility and usefulness. |
| Vision | “Provide an important service to the world by instantly delivering relevant information on virtually any topic.” | – Vision emphasizes the provision of instant and relevant information as a valuable global service. |
| Evolving Mission | Sundar Pichai emphasized a renewed focus on allowing users “to get things done!” | – Google’s evolving mission aligns with an emphasis on user-centricity and practicality, reflecting its commitment to enhancing users’ productivity and experiences. |
| Business Model Essence | – Google’s core mission involves organizing information and making it universally accessible and useful. – Main properties, such as search, YouTube, and Gmail, generate substantial advertising revenue through a cost-per-click mechanism. – Google Analytics, Google Search Console, and Google Trends aid publishers in creating user-friendly and relevant content. | – Google’s business model centers around data organization, accessibility, and monetization through advertising. – Tools and algorithms support publishers in delivering content aligned with user preferences. |
| User-Centric Approach | – Google focuses on users by providing quality, relevant, and user-friendly content. – Google’s algorithms and tools help publishers create content that meets user preferences. | – A user-centric approach ensures content serves users’ needs, maintaining Google’s value as a search engine. – Google’s tools empower publishers to produce relevant content. |
| Impact on Publishers and Industries | Google’s influence and changes sometimes raise concerns for publishers and industries reliant on its services. | – Publishers and industries must adapt to Google’s evolving algorithms and guidelines. – Google’s dominance in search can impact the visibility and traffic of websites. |
| Long-Term Vision | – Google aims for high-risk, high-reward projects, emphasizing non-incremental innovation. – The company values long-term success and invests accordingly. | – Google’s approach to innovation prioritizes long-term impact and transformative change. |
| Attention Merchant Model | – Google operates as an attention merchant, monetizing traffic multiple times through advertising. – Its vertically integrated structure allows control over data acquisition from consumers. | – Google’s revenue model relies on effectively capturing and monetizing user attention. – Vertical integration provides control over data and advertising revenue. |
| Competition and Adaptation | – Google faces competition in the digital advertising landscape from Amazon, Apple, and emerging players. – Maintaining dominance in a competitive market may pose challenges. | – Increased competition requires Google to adapt and innovate continually to retain its position. – New entrants may disrupt the digital advertising landscape, impacting Google’s market share. |
| Diversification and Bets | – Google explores diverse areas, including AI, search enhancements, and technological innovations. | – Diversification allows Google to explore new opportunities beyond its core mission. – Investment in various projects reflects Google’s commitment to staying at the forefront of technology. |
Breaking down Google’s mission statement
Both the mission and vision statement informs Google’s overall business strategy, and we’re going to break them down to dissect the core elements of the company.

Google‘s mission is to “organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.”
Let’s break down this statement to capture the Google business model essence. At this stage, it is important to highlight that Google today is Alphabet Inc. and it isn’t anymore just a search engine but a company that diversified in several areas. However, the search engine is still Alphabet Inc.’s cash cow.

Having clarified that we can look at the core of the Google business model. Google highlights four key concepts of its mission:
- Organize.
- Information.
- Universally accessible.
- Useful.
Google “organizes” the “information.” Google doesn’t create content. Indeed, Google assembles billion web pages and returns an accurate result in a matter of milliseconds. That information is “universally accessible” as Google is free and available to billion of users each day.
When the information served is useful (relevant) that’s when that information becomes knowledge. If you didn’t get it yet, Google has been so far a media company, and its corporate structure reflects that. Indeed, it has a dual-class stock structure which reflects the structure of other media companies like The New York Times.
It is a free tool for users, but a paid tool for businesses. It is an amplification and distribution channel for publishers (Google organic traffic is as of 2019 the channel that still brings the most traffic to websites all over the world).
Source: Jumpshot – SparkToro
And a free tool for publishers and content producers. Indeed, tools like Google Analytics, Google Search Console, and Google Trends help publishers analyze the content that is more searched by users, by limiting their risk of producing content that isn’t relevant.
Example of data from Google Trends on most popular queries by country
Google is changing at a fast pace and as AI grows and the search engine can put together content on its own (by scraping content from websites to offer direct answers or by feeding it to its AI algorithms) publishers are becoming less relevant.
Therefore from the three key players:
- Users.
- Publishers.
- Marketers/Businesses.
There is one player that wins over the others: users. In short, Google knows that as soon as its search engine is extremely valuable to its users, then it will be so also for publishers and advertisers.
That doesn’t mean Google always defends users’ interests. Indeed, one of the recurring polemic around Google practices in collecting massive users’ data even though it might not use it “yet.”
To understand why users always come first for Google, we need to look at Google‘s vision!
Breaking down Google’s long-term vision
Google’s Founders in the IPO letter of 2004, started with:
Google is not a conventional company. We do not intend to become one. Throughout Google’s evolution as a privately held company, we have managed Google differently. We have also emphasized an atmosphere of creativity and challenge, which has helped us provide unbiased, accurate and free access to information for those who rely on us around the world.
That is also the reason Google has picked dual-class stocks corporate structure, where Bring and Page maintained control over the company while instituting several boards of directors to make other important decisions.
As highlighted in the Alphabet annual report for 2018:
Many companies get comfortable doing what they have always done, making only incremental changes. This incrementalism leads to irrelevance over time, especially in technology, where change tends to be revolutionary, not evolutionary. People thought we were crazy when we acquiredYouTubeand Android and when we launched Chrome, but those efforts have matured into major platforms for digital video and mobile devices and a safer, popular browser. We continue to look toward the future and continue to invest for the long-term. As we said in the original founders’ letter, we will not shy away from high-risk, high-reward projects that we believe in because they are the key to our long-term success.
This point is critical as Google is a company that doesn’t think incrementally. Indeed, the 10X better has been its paradigm since the start, and that is also why Google has been using Moonshot Thinking also to bet in other areas that have nothing to do with the search:

In the 2004 Founders’ letter, Page also highlighted:
Sergey and I founded Google because we believed we could provide an important service to the world-instantly delivering relevant information on virtually any topic. Serving our end users is at the heart of what we do and remains our number one priority.
To notice that Page specified, “serving our end users is at the heart of what we do and remains our number one priority.”
If you do understand that, then you can grasp why Google (the search engine) “behaves” the way it does!
Google wants to provide users with what it thinks is “quality and relevant content.”
What does that mean?
Let’s start via negativa by defining low-quality content according to Google:
Low quality pages may have been intended to serve a beneficial purpose. However, Low quality pages do not achieve their purpose well because they are lacking in an important dimension, such as having an unsatisfying amount of MC, or because the creator of the MC lacks expertise for the purpose of the page.
This comprises things like:
- An inadequate level of Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-A-T).
- The quality of the MC is low.
- There is an unsatisfying amount of MC for the page.
MC stands for the main content, “which is determined by how much time, effort, expertise and talent/skill have gone into the creation of the page and also informs the E-A-T of the page.”
Google also points out that user-friendly content should:
- Give visitors the information they’re looking for.
- Make sure that other sites link to yours.
- Make your site easily accessible.
Don’t fill your page with lists of keywords, attempt to “cloak” pages, or put up “crawler only” pages. If your site contains pages, links, or text that you don’t intend visitors to see, Google considers those links and pages deceptive and may ignore your site.
Today hundreds of millions of websites are adapting their content guidelines to Google’s definition of quality content to be up to date with Google’s changes! That is what happens when a company scales up to the point of influencing billions of stakeholders worldwide!
Thus, when we think of Google (the search engine) moving in a particular direction, we have to ask, “will this benefit users?”
For instance, in the publishing world, or in other industries where Google might have a massive impact, the companies involved start to ask “whether this is good for them” and complain about Google taking over a specific industry. However, they are pondering the wrong question.
At the same time, those same publishers also raise significant concerns, as Google is massive and influential and it can crash overnight those same publishers.
Has Google’s mission changed?
At the annual conference Google holds each year, the Google I/O for 2019, its CEO, Sundar Pichai highlighted that Google’s mission stays the same, and now more than ever its mission is strong.
However, he highlighted how the way Google approaches its mission has changed. Indeed, Google is moving more and more from “access to information and knowledge” to allowing you “to get things done!”
The switch and change in its approach are critical to understanding as Google will be developing tools that control a larger part of the users’ experience. This becomes clear with tools like Google Duplex and AI applied to search and voice.
Understanding Google’s incentives

To understand Google’s underlying incentives, it’s critical to emphasize the fact, that the company remains an attention merchant.
This is what makes up the Google business model.

This means that Google needs to be able to monetize its traffic many times over.

Something, that the company has become very good at in the last decades, as it built its vertically integrated business machine:

Today, Google is able to monetize its traffic many times over.
And part of the revenue and resources generated by the Google advertising platform, is invested back into it, go continuously maintain and grow it.
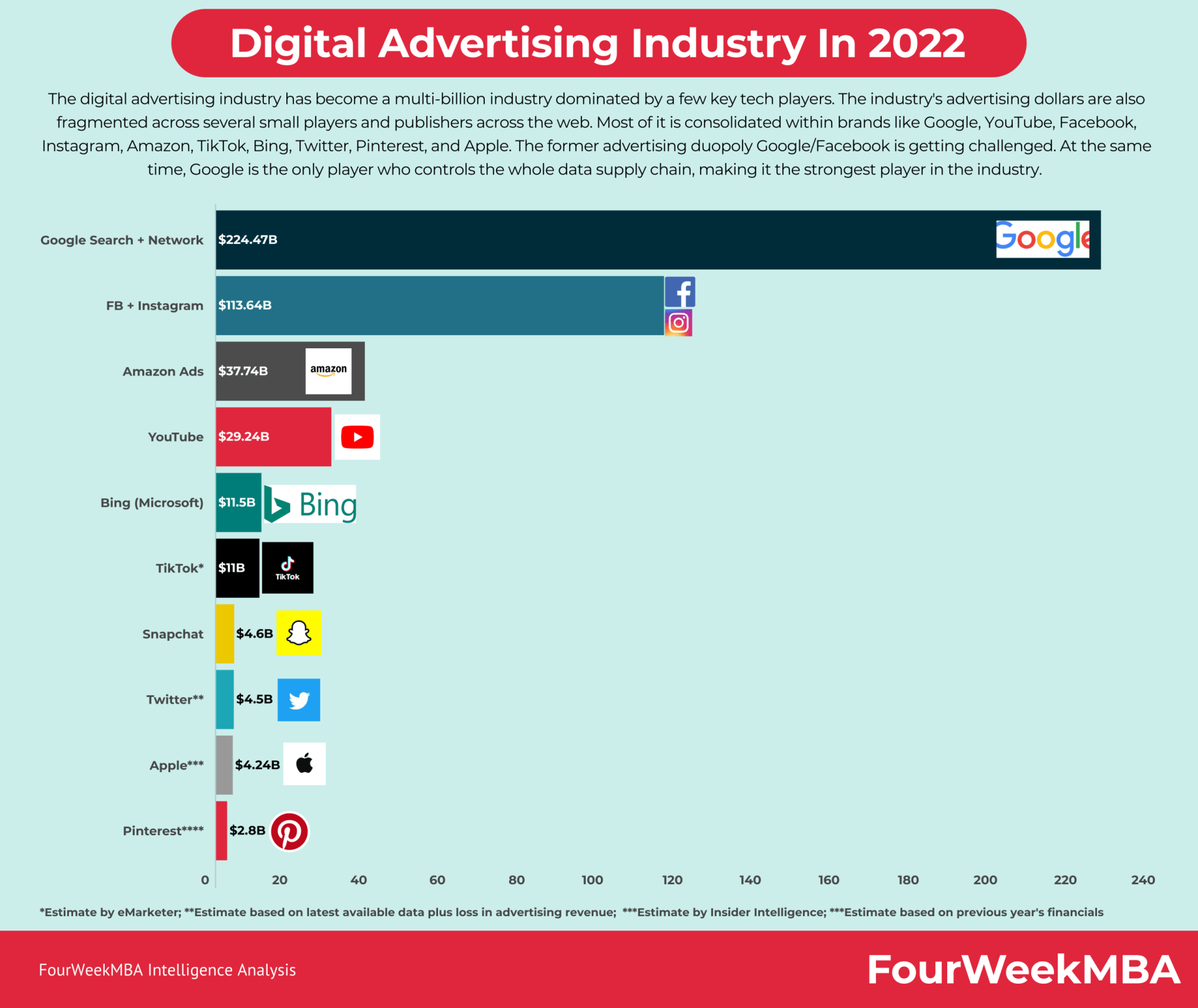
And the digital advertising landscape is getting way more competitive, with players like Amazon and Apple ramping up their advertising operations.
And players like TikTok growing at an exponential rate. This makes the whole advertising landscape potentially more fragmented, thus, making it difficult for Google to maintain its dominant position in the long term.
While on the other hand, Google also places bets elsewhere.
Key Highlights
- Mission and Vision Statements:
- Google’s Evolving Mission:
- Sundar Pichai, Google’s CEO, emphasized a renewed focus on allowing users “to get things done!” while maintaining the core mission.
- Google’s Business Model Essence:
- Google’s core mission involves organizing information and making it universally accessible and useful.
- Google’s main properties, such as search engine, YouTube, and Gmail, are monetized primarily through a cost-per-click mechanism, generating significant advertising revenue.
- User-Centric Approach:
- Google’s focus on users is central to its business model, and it aims to provide quality, relevant, and user-friendly content.
- Google’s algorithms and tools like Google Analytics and Google Trends help publishers create content that aligns with users’ preferences.
- Impact on Publishers and Industries:
- Google’s focus on user interests sometimes creates concerns for publishers and other industries that rely on Google’s influence and changes.
- Google’s Long-Term Vision:
- Google’s approach is non-incremental; it aims for high-risk, high-reward projects that can lead to revolutionary change.
- The company values innovation and is willing to invest for the long-term to ensure its success.
- Attention Merchant Model:
- Google remains an attention merchant, monetizing traffic multiple times over through its advertising platform.
- The company’s vertically integrated structure allows it to control data acquisition from consumers.
- Competition and Adaptation:
- Google faces increasing competition in the digital advertising landscape from players like Amazon and Apple.
- Maintaining its dominant position may become challenging as new players enter the market.
- Diversification and Bets:
- Google places bets in various areas beyond its core mission, such as AI, search enhancements, and other technological innovations.
Related: Apple Mission Statement and Vision Statement In A Nutshell
Other resources:
- How To Write A Mission Statement
- Successful Types of Business Models You Need to Know
- Business Strategy: Definition, Examples, And Case Studies
- What Is a Business Model Canvas? Business Model Canvas Explained
- Blitzscaling Business Model Innovation Canvas In A Nutshell
- What Is a Value Proposition? Value Proposition Canvas Explained
- What Is a Lean Startup Canvas? Lean Startup Canvas Explained
- What Is Market Segmentation? the Ultimate Guide to Market Segmentation
- Marketing Strategy: Definition, Types, And Examples
Read: Mission Statement Examples.
Mission Statement Case Studies











What is Alphabet's mission statement?
Google’s mission statement is to “organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.” Its vision statement is to “provide an important service to the world-instantly delivering relevant information on virtually any topic.” In 2019, Sundar Pichai emphasized a renewed mission to allow people “to get things done!”
How do you write a mission statement?
A mission statement helps an organization to define its purpose in the now and communicate it to its stakeholders. That is why a good mission statement has to be concise, clear, and able to articulate what’s unique about an organization.
What is Starbucks mission statement?
What is Apple mission statement?
Apple’s Mission is “to bring the best user experience to its customers through its innovative hardware, software, and services.” And in a manifesto dated 2009 Tim Cook set the vision specified as “We believe that we are on the face of the earth to make great products and that’s not changing.”
What is Nike mission statement?
Nike’s vision is “To bring inspiration and innovation to every athlete in the world.” While its mission statement is to “do everything possible to expand human potential. We do that by creating groundbreaking sports innovations, by making our products more sustainably, by building a creative and diverse global team, and by making a positive impact in communities where we live and work.”
What is Amazon mission statement?
Amazon’s mission statement is to “serve consumers through online and physical stores and focus on selection, price, and convenience.” Amazon’s vision statement is “to be Earth’s most customer-centric company, where customers can find and discover anything they might want to buy online, and endeavors to offer its customers the lowest possible prices.”