Growth Hacking

Scrum

Minimum Viable Product

Continuous Innovation

Leaner MVP

Engines of Growth

Lean Startup Canvas


Kanban

Business Engineering

Tech Business Model Template

Web3 Business Model Template

Asymmetric Business Models

Business Competition

Technological Modeling

Transitional Business Models

Minimum Viable Audience

Business Scaling

Market Expansion Theory

Speed-Reversibility

Asymmetric Betting

Growth Matrix

Revenue Streams Matrix

Revenue Modeling

Pricing Strategies

Bullseye Framework

Speed vs. Reversibility Matrix

STP Marketing

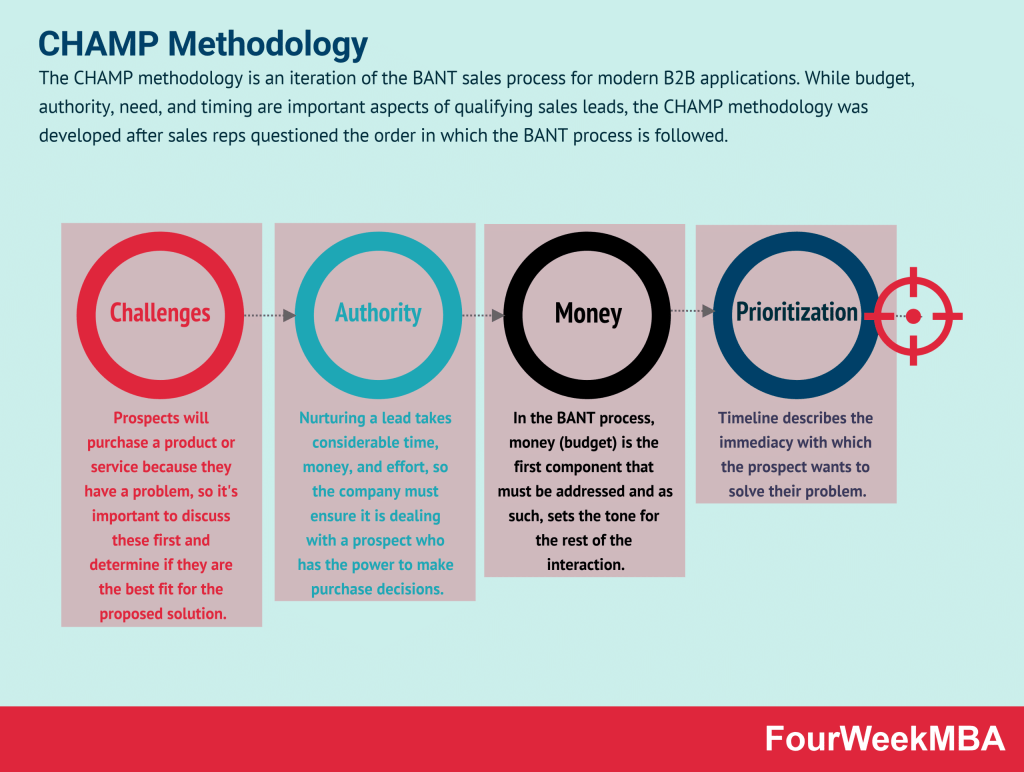
CHAMP Methodology
BANT Sales Process

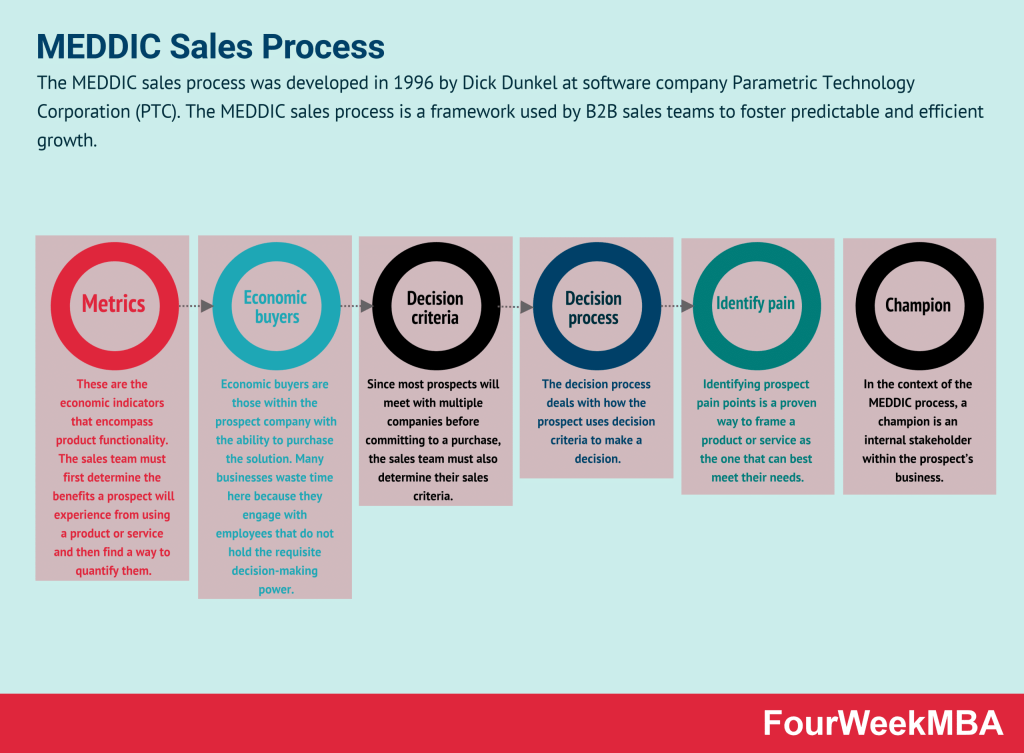
MEDDIC Sales Process
Highlights
| Concept | Description | When to Use | Advantages | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growth Hacking | Rapid experimentation for startups to achieve quick growth with a limited budget. | When aiming for rapid growth on a tight budget, typically in startup environments. | Speedy growth with resource constraints. | Requires continuous experimentation and testing. |
| Scrum | A methodology for effective team collaboration, primarily used in software development for frequent product delivery. | In complex product development projects, particularly in software development. | Enhances team collaboration and productivity. | May not be suitable for all project types. |
| Minimum Viable Product | A version of a new product that collects customer feedback with minimal effort, aligned with lean startup principles. | When developing a product to validate customer needs efficiently. | Reduces development time and risk. | May lack advanced features initially. |
| Continuous Innovation | The ongoing process of innovating products and processes to meet evolving customer needs. | When striving to stay competitive by adapting to changing market conditions. | Ensures adaptability and competitiveness. | Requires a culture of innovation and adaptability. |
| Leaner MVP | An evolution of the MVP approach that validates market risk before proceeding with development. | When seeking to further reduce risks and costs before building a minimum viable product. | Minimizes development investment early on. | May delay product development. |
| Engines of Growth | Three mechanisms (sticky, viral, paid) startups use to achieve sustainable growth by leveraging past customer actions. | When analyzing and strategizing growth for startups, focusing on user behavior. | Provides clear growth strategies. | Success depends on effective implementation. |
| Lean Startup Canvas | An adaptation of the business model canvas that emphasizes understanding problems before solutions. | When developing startups with a customer-centric approach, emphasizing problem-solving. | Focuses on customer needs and value. | May require iteration and refinement. |
| Lean Methodology | A continuous process of product development that aims to meet customer needs efficiently, rooted in lean manufacturing. | In industries where efficiency and customer-centricity are essential. | Streamlines product development. | Requires a shift in mindset and practices. |
| Kanban | A lean manufacturing framework for visualizing work, optimizing processes, and improving efficiency. | When managing work processes, particularly in manufacturing or service industries. | Enhances workflow visibility and efficiency. | May not address broader strategic concerns. |
| Business Engineering | A discipline that combines entrepreneurship, strategy, and scaling concepts for effective business innovation. | When seeking to innovate and scale business models effectively and systematically. | Integrates various aspects of business. | Requires a deep understanding of the framework. |
| Tech Business Model Template | Defines the components of a tech business model, including value, technology, distribution, and financial models. | When designing or analyzing tech-focused business models. | Offers a structured approach to tech business modeling. | Requires adaptation to specific tech contexts. |
| Web3 Business Model Template | Defines the components of a blockchain-based business model, encompassing value, blockchain, distribution, and economic models. | When analyzing or designing business models for blockchain or Web3 applications. | Offers a framework for understanding Web3 business models. | Requires expertise in blockchain and Web3 concepts. |
| Asymmetric Business Models | Monetization models that leverage data and technology platforms with key customers paying to sustain the core asset. | When exploring business models that leverage data and technology assets. | Enables new revenue streams and models. | Requires careful management of data and technology assets. |
| Business Competition | Analyzes competition in a technology-driven world, considering customer, technology, distribution, and financial model overlaps. | When assessing competitive forces and strategic positioning in evolving markets. | Offers a comprehensive view of competitive dynamics. | Requires continuous monitoring and adaptation. |
| Technological Modeling | A discipline to sustain innovation by developing both incremental and breakthrough products through technological strategies. | When aiming to innovate continuously while exploring transformative opportunities. | Balances short-term and long-term innovation. | Requires a clear understanding of technological trends. |
| Transitional Business Models | Used by companies to gain initial traction and validate ideas in a market, helping shape long-term scalable business models. | When entering new markets or niches to test concepts and secure needed capital. | Supports idea validation and adaptation. | Requires a transition to long-term models. |
| Minimum Viable Audience | Represents the smallest audience that can sustain a business and focuses on unmet needs within existing markets. | When identifying niche markets and microniche segments with unmet needs. | Targets specific unmet customer needs. | May limit growth potential beyond the minimum audience. |
| Business Scaling | Transformation of a business as the product is validated by wider market segments, aligning product, model, and organization. | When expanding from a niche product to broader market segments and achieving growth. | Enables growth and market penetration. | Requires alignment of product, model, and organization. |
| Market Expansion Theory | Involves providing products or services to a broader portion of an existing market or creating entirely new markets. | When considering strategies for expanding market reach and opportunities. | Supports scaling and market coverage. | May require adapting to changing market conditions. |
| Speed-Reversibility | Evaluates business decisions based on their speed of implementation and ease of reversal. | When assessing and prioritizing business decisions based on impact and reversibility. | Helps make informed decisions. | May not address all decision factors comprehensively. |
| Asymmetric Betting | Focuses on high-impact opportunities where market risk is validated before other investments. | When evaluating and prioritizing business ideas based on impact and risk. | Helps identify high-impact opportunities. | Not a standalone decision-making tool. |
| Growth Matrix | Categorizes growth strategies based on addressing existing or new problems for existing or new customers. | When planning growth strategies for a business or product. | Provides a framework for strategic growth planning. | May not cover all strategic growth scenarios. |
| Revenue Streams Matrix | Classifies revenue streams based on the frequency and ownership of interactions with key customers. | When analyzing and optimizing revenue generation strategies. | Offers insights into revenue sources and customer relationships. | Requires alignment with business strategy and goals. |
| Revenue Modeling | Examines revenue patterns to monetize business models effectively, considering short-term financial sustainability. | When designing revenue generation strategies and models. | Provides guidance for revenue planning and optimization. | Requires adaptation to fit specific business contexts. |
| Pricing Strategies | Establishing pricing formulas that align customer needs with profitability, enabling sustainable business models. | When setting prices for products or services to achieve profitability. | Aligns customer needs with business sustainability. | Considers market dynamics and competition. |
| Bullseye Framework | A method to prioritize marketing channels that will drive traction for a company effectively. | When planning marketing strategies to gain traction and optimize resources. | Focuses marketing efforts on high-impact channels. | Requires ongoing testing and adjustment. |
| Speed vs. Reversibility Matrix | Evaluates business decisions based on their speed of implementation and ease of reversal. | When assessing and prioritizing business decisions based on impact and reversibility. | Helps make informed decisions. | May not address all decision factors comprehensively. |
| STP Marketing | Simplifies market segmentation to select valuable segments, develop product positioning, and optimize marketing strategies. | In marketing, when identifying and targeting valuable customer segments efficiently. | Enhances commercial effectiveness. | May require comprehensive market research. |
| CHAMP Methodology | An iteration of the BANT sales process for B2B sales teams, focusing on customer challenges, authority, money, and prioritization. | In B2B sales, when qualifying leads and identifying prospects likely to make a purchase. | Addresses critical aspects of lead qualification. | May not fully align with certain sales processes. |
| BANT Sales Process | A sales process for identifying prospects based on budget, authority, need, and timing criteria. | In sales, when qualifying leads to prioritize those most likely to convert. | Simplifies lead qualification. | May not cover all aspects of lead qualification. |
| MEDDIC Sales Process | A framework for B2B sales teams to foster predictable and efficient growth by focusing on Metrics, Economic buyer, Decision criteria, Decision process, Identify pain, and Champion. | In B2B sales, when qualifying leads and ensuring efficient sales processes. | Provides a comprehensive approach to lead qualification. | May require significant training and implementation effort. |
Main Free Guides:









