Active recall enables the practitioner to remember information by moving it from short-term to long-term memory, where it can be easily retrieved. The technique is also known as active retrieval or practice testing. With active recall, the process is reversed since learning occurs when the student retrieves information from the brain.
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Definition | Active Recall is a powerful learning and study technique that involves actively stimulating memory recall during the learning process. Instead of passively reviewing notes or textbooks, learners actively attempt to remember and retrieve information from memory. This technique is often used in the form of quizzes, flashcards, or self-testing. Active recall engages the brain in the retrieval of learned material, reinforcing neural pathways and strengthening memory retention. It is based on the principle that actively retrieving information from memory is more effective for learning and long-term retention than simply rereading or re-exposing oneself to the material. Active recall is a fundamental component of many successful study strategies and is particularly effective for improving knowledge retention, comprehension, and recall. |
| Key Concepts | – Recall Practice: Active recall involves repeated attempts to remember and retrieve information from memory. – Self-Testing: Learners create questions or prompts related to the material and actively answer them from memory. – Retrieval Strength: The act of recalling information strengthens the neural pathways associated with that knowledge. – Spacing Effect: Combining active recall with spaced repetition enhances long-term retention. – Feedback: Immediate feedback from self-testing can guide further study and correction of mistakes. |
| Characteristics | – Active Engagement: Learners actively participate in the learning process by recalling information. – Self-Paced: Active recall can be self-paced and tailored to individual learning needs. – Versatile: It can be applied to various subjects and types of learning material. – Effective Retrieval: Active recall reinforces memory retrieval pathways, making it easier to recall information later. – Efficient Learning: This technique optimizes learning by focusing on the most challenging and relevant content. |
| Implications | – Enhanced Memory: Active recall significantly improves memory retention and recall. – Deep Understanding: Engaging with the material actively promotes a deeper understanding of the content. – Efficient Study: It reduces the time required to learn and retain information effectively. – Effective Test Preparation: Active recall is an excellent method for preparing for exams and assessments. – Lifelong Learning: This technique can be applied to lifelong learning and skill acquisition. |
| Advantages | – Effective Learning: Active recall is highly effective for learning and knowledge retention. – Efficient Study: It makes the most efficient use of study time by focusing on challenging content. – Deep Comprehension: Engaging in active recall promotes a deeper and more comprehensive understanding of the material. – Applicability: It is applicable to various subjects and types of learning material. – Long-Term Retention: Active recall enhances long-term memory retention. |
| Drawbacks | – Initial Difficulty: Some learners may find active recall initially challenging, especially if they are not accustomed to this study technique. – Time-Consuming: Creating self-tests or flashcards can be time-consuming. – Not Suitable for All Content: Active recall may not be suitable for certain types of content, such as highly complex or creative subjects. – Requires Effort: It requires active effort and engagement, which may not be appealing to all learners. – Mistakes: Learners may make mistakes during self-testing, which can be frustrating. |
| Applications | – Academic Learning: Active recall is commonly used by students to improve comprehension and retention in subjects like science, history, and languages. – Professional Development: Professionals use active recall for ongoing learning and skill development. – Exam Preparation: It is a valuable tool for preparing for exams, including standardized tests and certifications. – Language Learning: Active recall is integral to language learning methods that involve vocabulary and grammar practice. – Self-Paced Learning: Self-learners use active recall to master a wide range of topics and skills. |
| Use Cases | – Flashcards: Flashcards are a classic example of active recall tools where learners create questions or prompts on one side and provide answers on the other. – Quizzes: Self-administered quizzes or practice exams are effective for active recall. – Online Learning Platforms: Many online learning platforms incorporate active recall through interactive quizzes and self-assessment tools. – Exam Review: Students often use active recall extensively when reviewing for exams. – Language Apps: Language learning apps like Duolingo incorporate active recall exercises for vocabulary and language practice. |
Understanding active recall
Active recall is an effective way to study, memorize, and retrieve information as required.
Imagine you’re studying for a certification exam or want to memorize some key points for a sales presentation.
Instead of underlining the information or reading and then re-reading it, simply close your eyes and try to remember the material without the assistance of cues.
If you can do this successfully, you’ve reached the point of active recall. If not, revisit the information once more, learn it, and try to remember it.
Active recall is based on the premise that the act of retrieving information increases our ability to retain said information. In a 2013 study that analyzed the effectiveness of numerous revision techniques, researchers noted that:
“we rate practice testing as having high utility. Testing effects have been demonstrated across an impressive range of practice-test formats, kinds of material, learner ages, outcome measures, and retention intervals.”
How does active recall work?
Most learning techniques advocate that students read information to store in their brains.
With active recall, however, the process is reversed since learning occurs when the student retrieves information from the brain.
The student starts with a list of questions on a topic and tests their ability to answer them repeatedly.
In so doing, they force their brain to retrieve information which provides clarity on their level of comprehension and which areas require more attention.
This process of actively retrieving information from the brain is more effective than passive learning techniques such as reading from notes.
In addition to exam preparation, the ability to answer numerous questions about a topic may also beneficial for careers in healthcare, sales, education, and financial planning.
Active recall techniques
Here are some active recall techniques that respect the idea’s basic premise.
Whiteboard method
In this technique, the student writes what they know about a topic on a whiteboard, reads the information out loud, turns away from the whiteboard, and tries to recall the information.
The student then turns back to the whiteboard to verify their level of understanding and repeats the process as many times as needed.
Excel spreadsheet method
Excel spreadsheets can be used such that the questions are listed in one column and the answers in an adjacent column.
With the answer text color changed to white to make the column invisible, the student can then try to answer the questions. When they answer successfully, they are allowed to change the text color back to black.
Those who especially love spreadsheets can color cells with green, yellow, and red for correct, partial, and incorrect answers respectively.
Flashcard method
One of the simplest active recall methods where the student writes basic information about a topic on one side of the flashcard and an answer or explanation on the other.
This technique is often used to learn a new language, but it is also effective in other contexts.
Once the student has a basic understanding of the topic in question, they read the explanation side of the flashcard and actively try to recall the word, concept, or topic summary it is associated with.
Some recommend that students create three piles of flashcards based on whether they believe their understanding is low, medium, or high, and devote more time accordingly.
Case Studies
- Sales Training and Product Knowledge:
- Industry: Sales and Marketing
- Description: Sales professionals can use active recall techniques to memorize product features, benefits, and key selling points. By repeatedly testing their knowledge through self-quizzing or flashcards, sales reps can enhance their product expertise and recall during customer interactions.
- Case Study: A pharmaceutical sales representative preparing for a sales pitch might use flashcards to memorize the features and benefits of a new medication. Through active recall, the rep reinforces their understanding of the drug’s mechanism of action, indications, contraindications, and side effects, leading to more confident and effective communication with healthcare providers.
- Customer Service Training:
- Industry: Retail, Hospitality, Service Industries
- Description: Customer service representatives can employ active recall methods to internalize company policies, procedures, and best practices. By practicing scenarios and self-testing on common customer inquiries or service scenarios, employees can improve their ability to provide accurate and timely assistance.
- Case Study: A hotel front desk associate may use active recall techniques to learn the hotel’s check-in process, loyalty program details, and response protocols for guest complaints. By regularly reviewing flashcards or self-quizzing on various scenarios, the employee develops the confidence and competence to deliver exceptional customer service experiences.
- Compliance Training and Regulatory Requirements:
- Industry: Banking, Finance, Healthcare
- Description: Professionals in regulated industries can utilize active recall to ensure compliance with laws, regulations, and industry standards. By testing their knowledge of compliance policies, ethical guidelines, and risk management protocols, employees can mitigate legal and operational risks.
- Case Study: A financial advisor studying for regulatory exams may employ active recall techniques to memorize compliance rules related to client disclosures, investment suitability, and anti-money laundering regulations. Through regular self-testing and review of case studies, the advisor reinforces their understanding of regulatory requirements, reducing the likelihood of compliance violations.
- Training for Technical Skills and Procedures:
- Industry: Information Technology, Manufacturing, Aviation
- Description: Employees in technical roles can benefit from active recall when learning complex procedures, troubleshooting techniques, or software applications. By practicing hands-on tasks, simulating scenarios, and self-assessing their knowledge, technicians and engineers can improve their proficiency and problem-solving abilities.
- Case Study: An IT support specialist undergoing training for a new software deployment may use active recall methods to learn troubleshooting steps, command syntax, and system configurations. Through repeated practice and self-assessment in a simulated environment, the specialist gains the confidence and competence to resolve technical issues efficiently, minimizing downtime and user disruptions.
Key takeaways:
- Active recall is an effective way to study, memorize, and retrieve information as required. The technique is also known as active retrieval or practice testing.
- With active recall, learning takes place when the student retrieves information from the brain. The student starts with a list of questions on the topic and tests their ability to answer them repeatedly, which clarifies their level of understanding and identifies areas for improvement.
- There exist numerous active recall methods that respect the technique’s underlying premise. These include the whiteboard, flashcard, and Excel spreadsheet methods.
Key Highlights
- Active Recall Technique: Active recall, also known as active retrieval or practice testing, involves the process of retrieving information from memory to enhance learning and retention. Unlike passive learning methods, where information is read and stored, active recall emphasizes retrieving information from the brain.
- Process of Active Recall: To engage in active recall, an individual poses questions related to the topic they’re learning and tries to answer them repeatedly. This process stimulates the brain’s retrieval of information and provides insights into their comprehension level and areas needing further attention.
- Effectiveness: Active recall has been shown to be highly effective in enhancing memory and understanding. Research indicates that practice testing across various formats, subjects, ages, outcomes, and retention intervals is beneficial.
- Methods of Active Recall:
- Whiteboard Method: Write down information on a whiteboard, read it aloud, turn away from the board, and attempt to recall the information. Verify understanding by looking back and repeat the process.
- Excel Spreadsheet Method: List questions and answers in adjacent columns, initially hiding the answers. Answer questions and reveal correct answers to reinforce learning.
- Flashcard Method: Write basic information on one side of a flashcard and an explanation or answer on the other. Read the explanation side and actively recall associated information.
- Adaptation to Various Fields: Active recall is valuable not only for exam preparation but also for careers in fields like healthcare, sales, education, and financial planning. It enhances comprehension and retention across various domains.
Connected Learning And Growth Frameworks












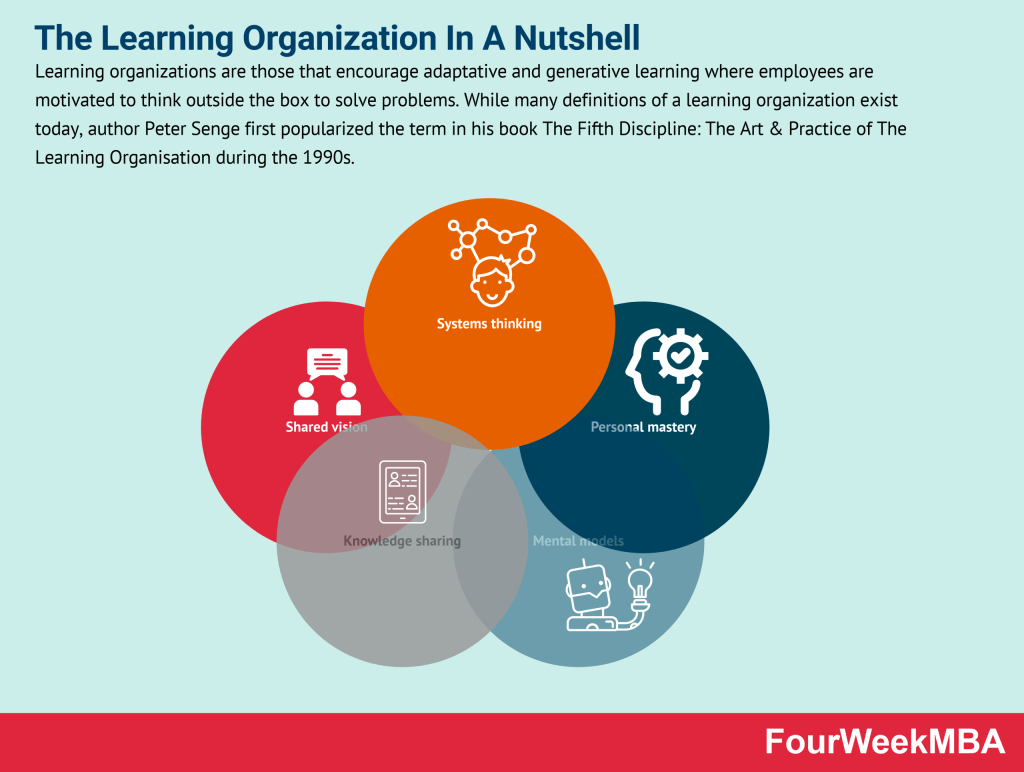


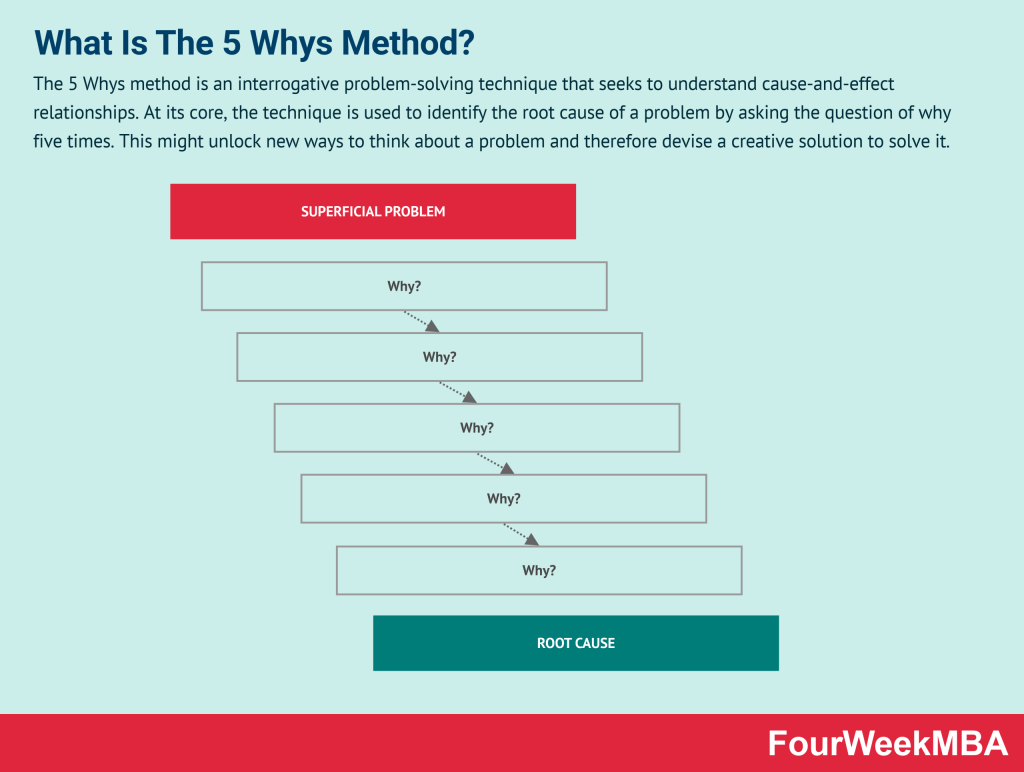








Related Strategy Concepts: Read Next: Mental Models, Biases, Bounded Rationality, Mandela Effect, Dunning-Kruger Effect, Lindy Effect, Crowding Out Effect, Bandwagon Effect, Decision-Making Matrix.
Main Free Guides:









