Understanding a company’s values helps assess how the company makes decisions at scale. In Uber’s case, the company is defined by 7 core values:
- Do the right thing.
- Go get it.
- Trip obsessed.
- Build with heart.
- Stand for safety.
- See the forest and the trees.
- One Uber.
- Great minds don’t think alike.
Do the right thing
Period.
Go get it: Bring the mindset of a champion.
Our ambition is what drives us to achieve our mission. How we define a champion mindset isn’t based on how we perform on our best days, it’s how we respond on our worst days. We hustle, embrace the grind, overcome adversity, and play to win for the people we serve. Because it matters.
Uber has been following a blitzscaling strategy, since the onset.
In part, this has been due to the fact the company has been trying to open up a new industry, within a highly regulated and lobbied environment.
This pushed the company to move at the edge of regulation, and push on growth, as a priority, since its inception.
Trip obsessed: Make magic in the marketplace.
The trip is where the marketplace comes to life. The earner, rider, eater, carrier, and merchant are the people who connect in our marketplace – and we see every side. This requires judgment to make difficult trade-offs, blending algorithms with human ingenuity, and the ability to create simplicity from complexity. When we get the balance right for everyone, Uber magic happens.
Uber’s marketplace is central to its mission.
In fact, the marketplace is where network effects are built and how the service becomes valuable and stays valuable over time.

When Uber kicks off network effects, those are usually local networks, where liquidity needs to be created, almost from scratch.
Build with heart: We care.
We work at Uber because our products profoundly affect lives and we care deeply about our impact. Putting ourselves in the shoes of people who connect in our marketplace helps us build better products that positively impact our communities and partners. Our care drives us to perfect our craft.
Uber has been pushing on a market expansion strategy, where it tried to build upon the existing mobility market, by enlarging it and redefining it.

Stand for safety: Safety never stops.
We embed safety into everything we do. Our relentless pursuit to make Uber safer for everyone using our platform will continue to make us the industry leader for safety. We know the work of safety never stops, yet we can and will challenge ourselves to always be better for the communities we serve.
Safety is a core component of the service.
Just like for software companies like Google, or for media platforms like Twitter, the amount of spam on the platform as it scales, can stall the network and reduce its value drastically.
When it comes to Uber, safety is the spam equivalent.
In short, safety can actually reduce the value of the network, and it can do it quickly.
That is why this must be one of the core company’s values.
See the forest and the trees: Know the details that matter.
Building for the intersection of the physical and digital worlds at global scale requires seeing the big picture and the details. Knowing the important details can change the approach, and small improvements can compound into enormous impact over time.
This value is critical because Uber is a company operating at the intersection of digital and physical.
It has some advantages of being a digital player, but also many disadvantages of operating in a highly regulated, and local environment.
This enabled the company to create a built-in playbook that is at the intersection of digital and physical, with a focus on local and understanding of complex regulations.
One Uber: Bet on something bigger.
It’s powerful to be a part of something bigger than any one of us, or any one team. That’s why we work together to do what’s best for Uber, not the individual or team. We actively support our teammates, and they support us – especially when we hit the inevitable bumps in the road. We say what we mean, disagree and commit, and celebrate our progress, together.
Uber has created one of the most interesting companies of the last decade.

And as its network has become valuable, it expanded in other areas, like delivery, with Uber Eats, which now, has become a huge company, within Uber.

Great minds don’t think alike: Diversity makes us stronger.
We seek out diversity. Diversity of ideas. Identity. Ethnicity. Experience. Education. The more diverse we become, the more we can adapt and ultimately achieve our mission. When we reflect the incredible diversity of the people who connect on our platform, we make better decisions that benefit the world.
In this case, diversity helps have a strong mindset, able to navigate complex situations and make decisions in a fast and ambiguous context.
Key Highlights
Do the right thing:
This value emphasizes ethical decision-making and integrity. It’s about making choices that align with ethical standards and doing what’s right, even when faced with challenges.
Go get it:
This value reflects a champion mindset and ambition. It’s about striving to achieve the company’s mission even in the face of adversity, hustling, embracing challenges, and playing to win.
Trip obsessed:
This value highlights the significance of the marketplace and customer experience. It involves making trade-offs, blending algorithms and human judgment, and creating balance to create the “magic” in the marketplace.
Build with heart:
This value focuses on caring about the impact of the company’s products on people’s lives. It’s about understanding the users, partners, and communities and using that empathy to build better products.
Stand for safety:
Safety is a paramount value for Uber. It emphasizes embedding safety into all aspects of the business to ensure the platform’s reliability and industry leadership in safety.
See the forest and the trees:
This value pertains to a balanced perspective that considers both the big picture and the crucial details. It’s essential in the context of operating at the intersection of the physical and digital worlds and understanding the complexities of local regulations.
One Uber:
This value promotes teamwork and collaboration, focusing on the collective success of the company rather than individual achievements. It encourages support, communication, and celebrating progress together.
Great minds don’t think alike:
Diversity is celebrated as a strength in this value. It highlights the importance of diverse perspectives, experiences, and backgrounds in decision-making, which leads to better outcomes for the company and its mission.
Read Next:
Visual Stories Related To Uber Business Model





In 2022, Uber mobility took 27% of each booking on the platform. At the same time, Uber Eats took 20% of each booking on the delivery platform. The take rate varies according to demand and supply but also market dynamics. In short, in periods of increased competition, the service might charge lower take rates to keep up with it. In 2022, Uber pushed on efficiency, thus raising its take rates, to move toward profitability.
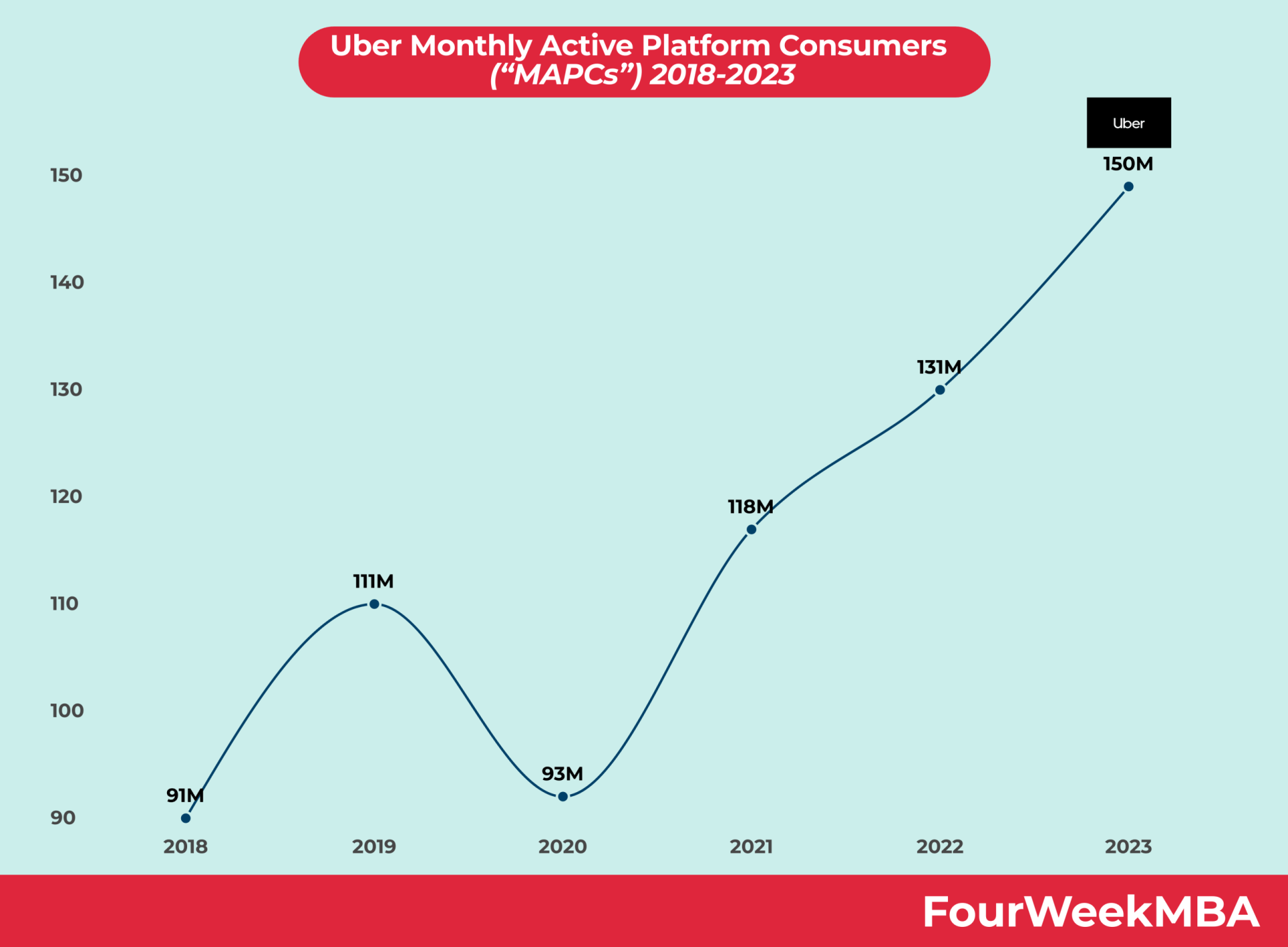
Uber Platform Users