| Framework | Description | When to Use | Advantages | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product-Market Fit | Being in a good market with a product that satisfies it, enabling traction for the company. | When assessing the alignment of a product with the market. | Drives business growth, validates product idea. | Subjective and challenging to measure precisely. |
| Minimal Viable Product (MVP) | A lean approach that validates market risk before further development. | When minimizing risk in product development. | Efficient validation, cost-effective. | Limited feature set, may not fully satisfy users. |
| Lean Methodology | A continuous product development process to meet customer needs, influenced by lean manufacturing. | Throughout product development for efficiency. | Focuses on customer value, reduces waste. | May require adaptation to unique industries. |
| Kanban | A framework for visualizing work, identifying bottlenecks, and optimizing processes using JIT manufacturing. | In manufacturing and process optimization. | Improves efficiency, identifies bottlenecks. | May not be suitable for all types of work. |
| Blue Ocean | A strategy creating new uncontested markets with value innovation, making competition irrelevant. | When seeking innovation and market expansion. | Offers unique value, reduces competition. | Risky, requires significant innovation. |
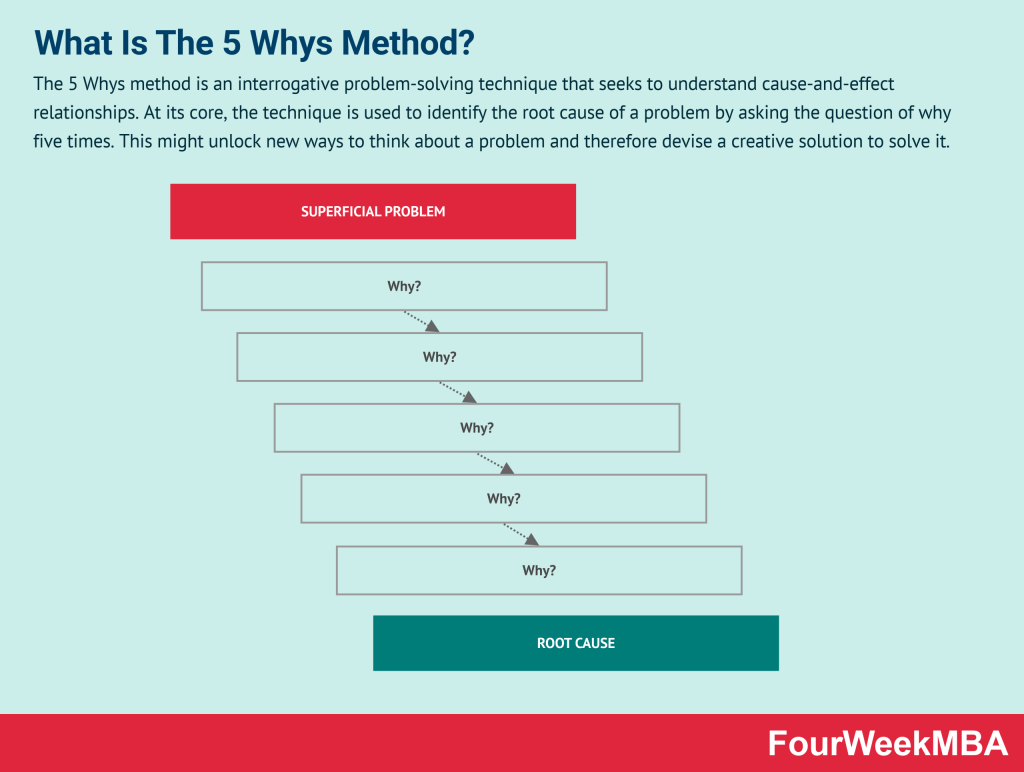
| 5 Whys | A problem-solving technique to identify the root cause by asking “why” five times. | For root cause analysis in problem-solving. | Uncovers deeper issues, promotes creativity. | May not be suitable for complex issues. |
| Pirate Funnel | A model (AARRR) to understand user paths toward becoming customers and brand referrers. | When analyzing user acquisition and retention. | Simplifies metrics, guides user funnel analysis. | May oversimplify complex user behaviors. |
| Growth Hacking | An approach focused on a north star metric (NSM) to achieve growth and simplify strategy execution. | When aiming for rapid business growth and innovation. | Streamlines growth strategy, focuses efforts. | Risk of overlooking other important metrics. |
Product-Market Fit

The Minimal Viable Product (MVP)

Lean Methodology

Kanban

Blue Ocean

5 Whys
Pirate Funnel

Growth Hacking

Key Highlights
- Product-Market Fit:
- Coined by Marc Andreessen, product-market fit is when a product or service satisfies a specific market’s needs, leading to traction and success for the company.
- Minimal Viable Product (MVP):
- The MVP approach involves creating a basic version of a product to validate market demand and reduce risk before investing further resources.
- Lean Methodology:
- The lean methodology originates from lean manufacturing and aims for continuous product development to meet customer needs efficiently.
- Kanban:
- Kanban, a framework developed by Toyota, visualizes work in progress and helps optimize processes using just-in-time manufacturing.
- Blue Ocean Strategy:
- Blue ocean strategy involves creating new markets and value innovation, offering customers more value at lower costs while breaking the cost-value trade-off.
- 5 Whys:
- The 5 Whys method is a problem-solving technique that seeks to identify the root cause of a problem by asking “why” multiple times.
- Pirate Funnel (AARRR):
- Coined by Dave McClure, the Pirate Funnel (AARRR) is a model that helps businesses understand metrics and channels at each stage of a user’s journey to becoming a customer and referrer.
- Growth Hacking:
- North Star Metric (NSM):
FourWeekMBA Business Toolbox
















Main Free Guides:








