Sales Enablement is a strategic, ongoing process that equips all salespeople with the ability to consistently and systematically have a valuable conversation with the right set of customer stakeholders at each stage of the customer’s problem-solving life cycle to optimize the return of investment of the selling system. It involves providing the sales organization with tools, training, and content to increase efficiency and effectiveness.
- Purpose and Scope: The goal is to ensure that every salesperson is equipped with the knowledge, skills, content, and tools to maximize every buyer interaction.
- Principal Concepts: Central to sales enablement is the integration of various functions such as marketing, training, management, and operations into the sales process.
Theoretical Foundations of Sales Enablement
Sales Enablement builds on concepts from strategic management, marketing, and organizational behavior, focusing on empowering sales teams through better resources and alignment across the company.
- Cross-Functional Integration: Bridging the gap between sales and other departments to ensure that sales strategies are well-informed and supported across the organization.
- Continuous Learning and Development: Incorporating ongoing training and development to adapt to changing market conditions and customer needs.
Methods and Techniques in Sales Enablement
Effective sales enablement involves a mixture of strategies tailored to enhance sales performance:
- Content Management: Developing and managing sales content such as case studies, product data sheets, and white papers that salespeople can use to engage clients effectively.
- Training and Coaching: Implementing comprehensive training programs that include onboarding, continuous learning, and coaching to improve sales skills and product knowledge.
- Analytics and Technology: Utilizing CRM systems, sales intelligence tools, and analytics to provide sales teams with data-driven insights to tailor their approach to the needs of potential buyers.
Applications of Sales Enablement
Sales enablement can be applied across various industries to boost sales efficiency and success by ensuring sales teams have the resources they need.
- B2B Enterprises: Particularly useful where complex products or services require a sophisticated understanding to sell effectively.
- Technology Sectors: Enables sales teams to stay current on rapidly evolving product features and industry trends.
Industries Influenced by Sales Enablement
- Pharmaceuticals: Sales reps are provided with up-to-date scientific data and regulatory information.
- Financial Services: Equipping salespeople with the latest market analyses and compliance regulations.
Advantages of Using Sales Enablement
Implementing a sales enablement strategy can significantly enhance the productivity and effectiveness of sales teams.
- Increased Sales Performance: Sales teams with thorough product knowledge and access to key selling tools are more likely to close deals successfully.
- Improved Sales Efficiency: Streamlining the sales process reduces the time salespeople spend looking for information and resources, allowing them to focus more on selling.
Challenges and Considerations in Sales Enablement
While sales enablement offers numerous benefits, there are challenges that need to be addressed to maximize its effectiveness:
- Alignment Across Departments: Ensuring that all parts of the organization contribute to and support the sales process can be challenging.
- Measuring Effectiveness: It can be difficult to track the direct impact of sales enablement initiatives on sales performance.
Integration with Broader Business Strategies
Sales enablement should be integrated into the company’s overall business strategy to ensure that sales efforts are aligned with broader business objectives.
- Strategic Alignment: Sales enablement initiatives should support the overall strategic goals of the company, such as entering new markets or growing specific product lines.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Regular feedback loops between sales, marketing, and product development teams help refine strategies and ensure that sales enablement tools and content are effective and up-to-date.
Future Directions in Sales Enablement
As markets and technologies evolve, so too will sales enablement, adapting to include new tools and methodologies.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI and machine learning could further personalize sales training and content distribution, enhancing the relevance for each sales interaction.
- Integration of Advanced Analytics: More sophisticated analytics will help in measuring the impact of sales enablement efforts more precisely, leading to better resource allocation and strategy adjustments.
Conclusion and Strategic Recommendations
Sales Enablement is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of the sales force by ensuring they have the necessary tools, skills, and support.
- Invest in Technology and Training: Continuous investment in the latest sales technologies and comprehensive training programs is essential.
- Foster Collaboration: Encourage ongoing collaboration between sales and other departments to ensure that sales enablement strategies are comprehensive and integrated across the company.
| Related Frameworks | Description | When to Apply |
|---|---|---|
| AIDA Model | – Describes the stages a customer goes through in the purchasing process: Attention, Interest, Desire, and Action. AIDA helps marketers and sales professionals understand and guide consumers through the sales funnel. | – When developing marketing or sales strategies. – Mapping out customer journey stages to create targeted messaging and promotional campaigns that guide prospects toward making a purchase. |
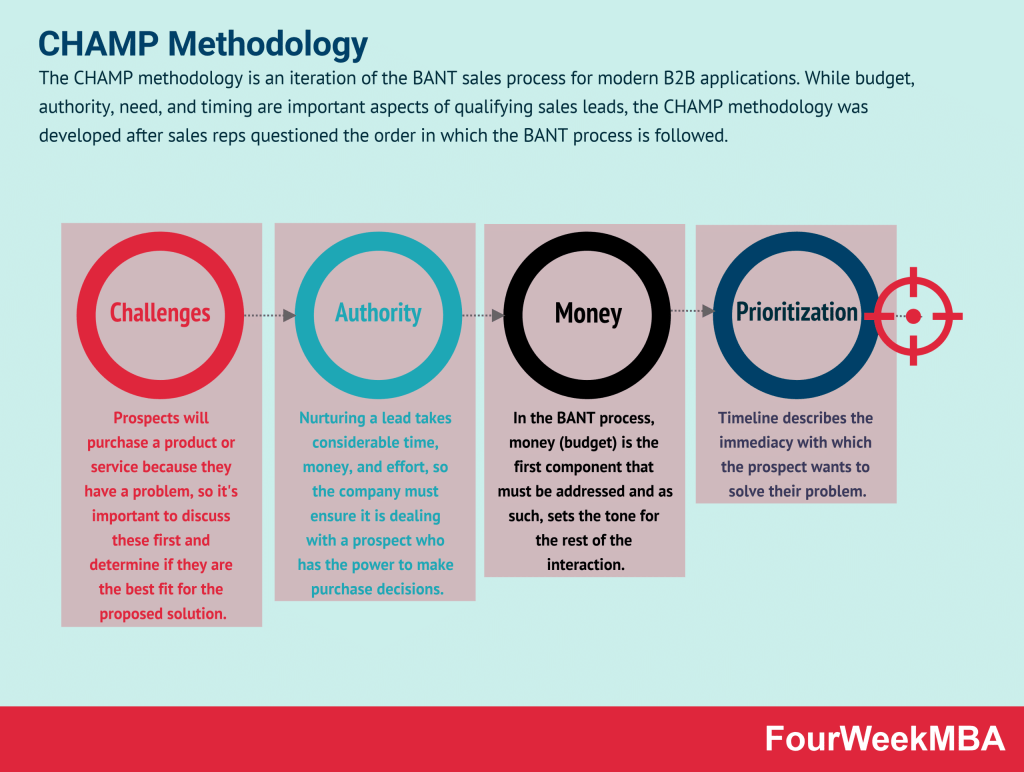
| BANT Criteria | – Stands for Budget, Authority, Need, and Timeline, used to qualify leads and prioritize sales efforts. BANT Criteria helps sales teams focus on prospects with the highest likelihood of conversion. | – When qualifying leads or prioritizing sales opportunities. – Assessing prospects based on their budget, decision-making authority, need for the product or service, and timeframe for purchase to allocate resources effectively. |
| SPIN Selling | – Focuses on asking situational, problem, implication, and need-payoff questions to uncover customer needs, address pain points, and provide tailored solutions. SPIN Selling emphasizes consultative selling and relationship-building. | – When engaging in complex B2B sales or consultative selling. – Using a structured questioning approach to understand customer challenges, build rapport, and offer solutions that align with their needs and objectives. |
| Solution Selling | – Involves identifying customer pain points and offering solutions that address their specific needs and objectives. Solution Selling emphasizes value proposition, relationship-building, and problem-solving. | – When selling complex or customizable products or services. – Tailoring sales pitches and proposals to demonstrate how the offered solution addresses the customer’s unique challenges and delivers measurable value. |
| Customer Journey Mapping | – Visualizes the stages and touchpoints a customer goes through when interacting with a brand or making a purchase decision. Customer Journey Mapping helps organizations understand customer experiences and identify opportunities for improvement. | – When analyzing and optimizing the customer experience. – Mapping out customer interactions across channels and touchpoints to identify pain points, gaps, and areas for enhancement throughout the sales funnel. |
| Lead Scoring | – Assigns numerical values to leads based on their characteristics, behaviors, and engagement levels to prioritize follow-up and tailor sales efforts. Lead Scoring helps sales teams focus on leads with the highest potential for conversion. | – When managing and qualifying leads in a CRM system. – Developing lead scoring criteria and algorithms to prioritize sales outreach and allocate resources effectively based on lead quality and likelihood of conversion. |
| Challenger Sale Model | – Proposes that successful sales professionals challenge customers’ assumptions, teach them something new, tailor solutions to their needs, gain consensus among stakeholders, and drive results. The Challenger Sale Model emphasizes insights-based selling and commercial teaching. | – When engaging with knowledgeable and skeptical buyers. – Providing insights, challenging assumptions, and guiding customers through the decision-making process to differentiate offerings and create value. |
| Inbound Marketing | – Focuses on attracting and engaging prospects through valuable content, personalized experiences, and relationship-building techniques. Inbound Marketing aligns with the modern buyer’s preference for self-directed research and engagement. | – When building brand awareness and generating leads. – Creating and distributing relevant and helpful content to attract, engage, and nurture prospects throughout their journey, from awareness to purchase and beyond. |
| Account-Based Marketing (ABM) | – Targets high-value accounts or companies with personalized marketing and sales efforts tailored to their specific needs and preferences. Account-Based Marketing fosters deeper relationships and alignment between marketing and sales teams. | – When pursuing strategic or enterprise-level accounts. – Collaborating with marketing and sales teams to develop and execute personalized campaigns and outreach strategies that resonate with target accounts and decision-makers. |
| Cross-Selling and Upselling | – Involves offering additional products or services (upselling) or complementary items (cross-selling) to existing customers to increase their lifetime value and maximize revenue. Cross-Selling and Upselling leverage customer relationships and understanding to drive incremental sales. | – When engaging with existing customers or clients. – Identifying opportunities to recommend related or upgraded offerings that enhance the value of the initial purchase and meet evolving needs or preferences. |
Related Business Concepts






















Palantir Acquire, Expand, Scale Framework



Read: product development frameworks here.
Read Next: SWOT Analysis, Personal SWOT Analysis, TOWS Matrix, PESTEL Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces, TOWS Matrix, SOAR Analysis.
Main Free Guides:








