- A production function is a mathematical expression that describes the relationship between inputs (factors of production) and outputs (quantity of goods or services produced) in a production process.
- It represents the technological relationship or process by which inputs are transformed into outputs, indicating the maximum quantity of output that can be produced given the available inputs and technology.
Components of the Production Function:
- Inputs (Factors of Production):
- The inputs or factors of production typically include labor, capital (machinery, equipment), land, and sometimes entrepreneurial ability.
- These inputs are combined in various proportions to produce goods or services, with each input contributing to the production process.
- Output (Quantity of Goods or Services):
- The output of the production function represents the quantity of goods or services produced as a result of combining the inputs.
- The level of output depends on the quantity and quality of inputs used, as well as the technology and production methods employed.
Types of Production Functions:
- Linear Production Function:
- In a linear production function, the relationship between inputs and outputs is linear, meaning that each additional unit of input contributes equally to the increase in output.
- For example, if labor and capital are the only inputs, the production function could be represented as Q = aL + bK, where Q is the quantity of output, L is the quantity of labor, K is the quantity of capital, and a and b are coefficients representing the marginal productivity of labor and capital, respectively.
- Cobb-Douglas Production Function:
- The Cobb-Douglas production function is a widely used functional form that exhibits constant returns to scale, meaning that if all inputs are increased proportionally, output also increases proportionally.
- It is expressed as Q = A * L^α * K^β, where Q is the quantity of output, L is the quantity of labor, K is the quantity of capital, A is a constant representing total factor productivity, and α and β are the output elasticities of labor and capital, respectively.
Applications of the Production Function:
- Efficiency Analysis:
- Production functions are used to analyze and measure the efficiency of production processes by assessing the relationship between inputs and outputs.
- Efficiency measures such as total factor productivity (TFP) and technical efficiency are derived from production function analysis.
- Resource Allocation:
- Production functions inform decision-making regarding resource allocation by identifying the optimal combination of inputs to achieve desired levels of output.
- Firms use production functions to determine the most cost-effective mix of labor, capital, and other inputs to maximize profits or minimize costs.
- Economic Growth and Development:
- Production functions play a central role in economic growth theory, where they are used to model the relationship between inputs, outputs, and technological progress over time.
- Governments and policymakers use production functions to formulate policies aimed at promoting productivity growth and sustainable economic development.
Conclusion:
The production function serves as a fundamental tool in economics for understanding the relationship between inputs and outputs in production processes. By analyzing the production function, economists, businesses, and policymakers gain insights into efficiency, resource allocation, and economic growth. Whether analyzing firm-level production decisions or formulating macroeconomic policies, the production function provides a framework for understanding the complex dynamics of production and technology in modern economies.
Connected Economic Concepts

Positive and Normative Economics








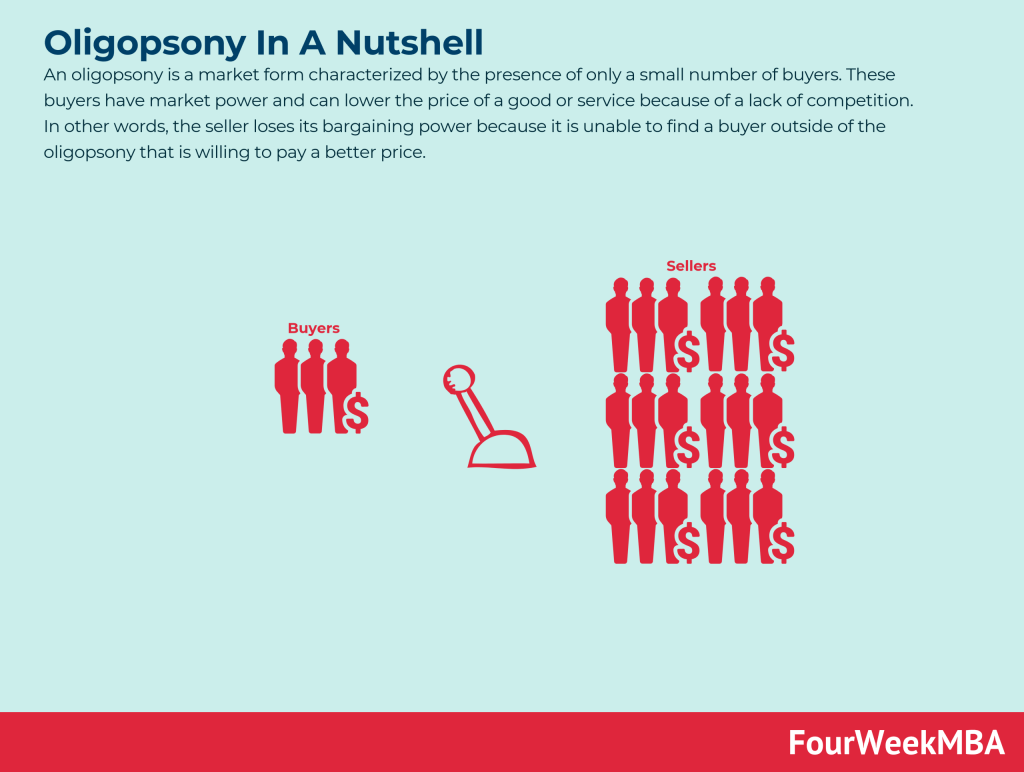











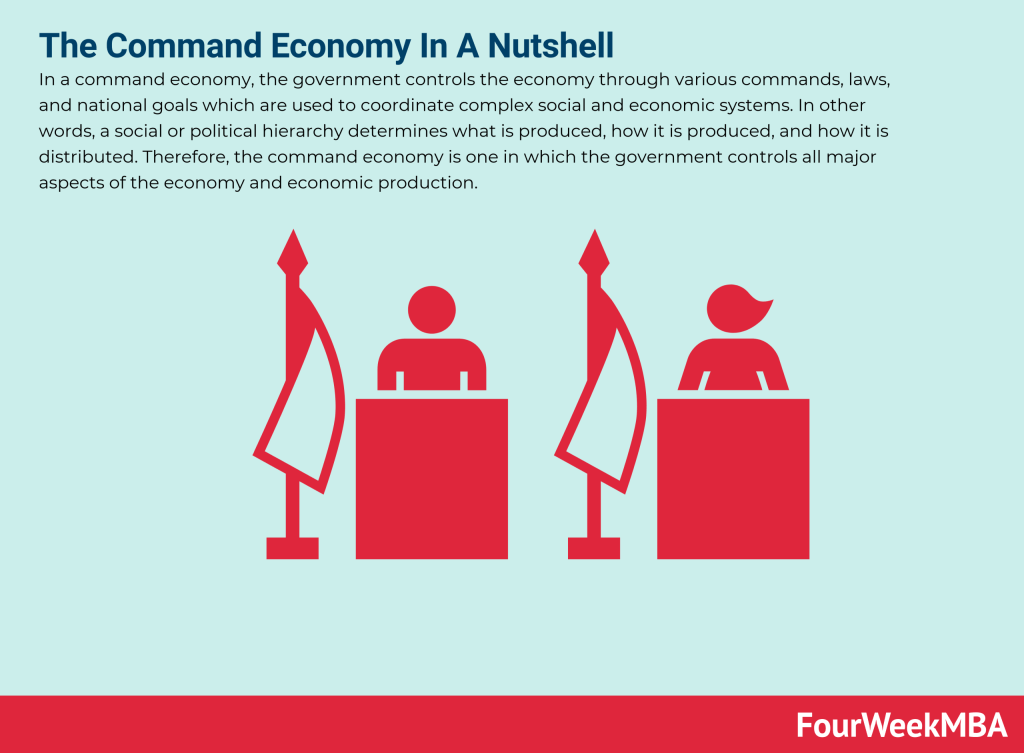









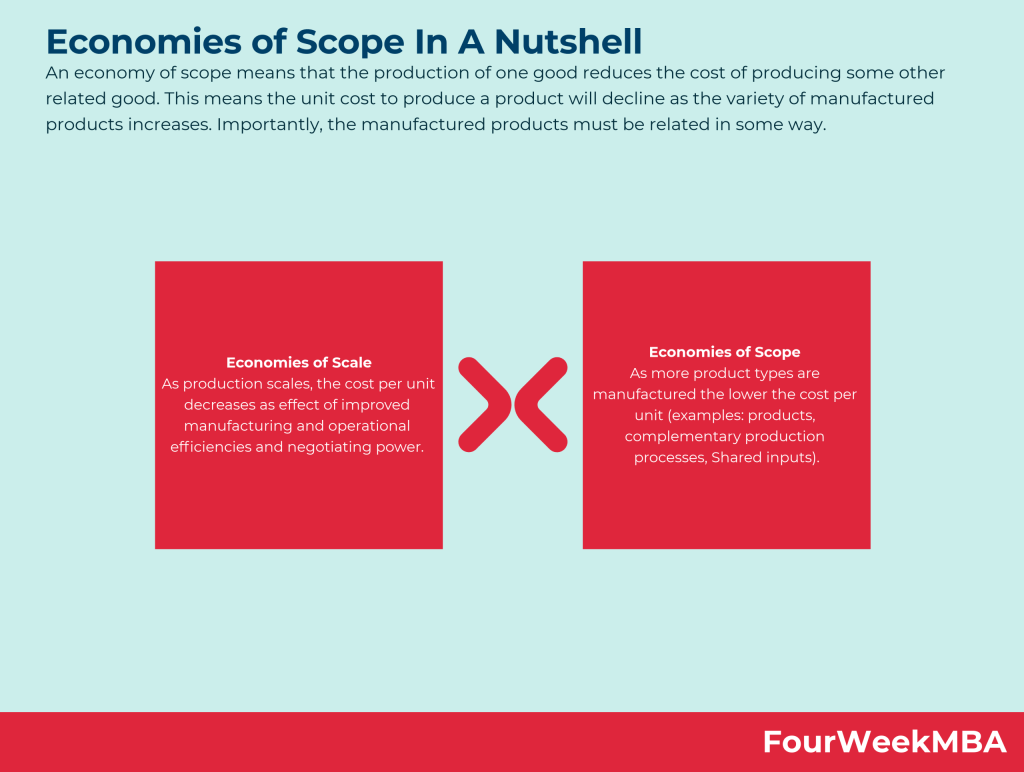



Main Free Guides:









