Pain Points refer to the challenges and issues customers or businesses encounter, requiring effective solutions. By identifying specific, urgent, and impactful problems through market research, businesses can address customer needs, gain a competitive edge, and uncover untapped market opportunities. However, understanding pain points and offering suitable solutions amidst market competition can pose challenges.
Defining Pain Points
Pain points are specific problems, challenges, or inconveniences that individuals or groups encounter in their interactions with products, services, or systems.
These issues often cause frustration, dissatisfaction, or hindrance to achieving desired outcomes. Pain points can manifest in various forms and across diverse domains, including business, technology, healthcare, and everyday life.
Significance of Pain Points
Recognizing the importance of pain points is crucial for individuals and organizations alike:
- Customer Satisfaction: In the business world, addressing customer pain points is vital for enhancing satisfaction and loyalty. Identifying and resolving issues that customers find troublesome can lead to increased trust and retention.
- Innovation Catalyst: Pain points often serve as catalysts for innovation. Identifying areas where improvement is needed can inspire creative solutions and drive technological advancements.
- Product Development: Understanding pain points is integral to product development. Designing products that effectively address customer needs and pain points can lead to successful market adoption.
- Efficiency and Productivity: In organizational settings, identifying and mitigating pain points among employees can enhance workplace efficiency and productivity. Streamlining processes and reducing friction can lead to improved performance.
Identifying Pain Points
Effectively identifying pain points is a critical first step in the process of addressing them. Here are some strategies for identifying pain points:
- Customer Feedback: Collect feedback from customers through surveys, interviews, or online reviews. Analyzing customer comments and complaints can reveal recurring pain points.
- Observation: Observe how customers interact with products or services in real-world settings. Identifying moments of frustration or inefficiency can highlight pain points.
- Employee Input: Encourage employees to provide insights into areas where they face challenges or obstacles in their work. Their firsthand experiences can uncover internal pain points.
- Competitive Analysis: Study the offerings of competitors and identify gaps or shortcomings in their products or services. These gaps can represent potential pain points to address.
- Data Analytics: Analyze data related to customer behavior, such as website analytics or purchase history. Patterns in data may reveal pain points in the customer journey.
Addressing Pain Points
Once pain points are identified, addressing them effectively becomes the next crucial step. Here are strategies for addressing pain points:
- Prioritization: Prioritize pain points based on their impact and feasibility. Focus on addressing high-impact pain points that can lead to substantial improvements.
- User-Centered Design: Apply user-centered design principles to create products or services that directly address pain points. Involve users in the design process to ensure their needs are met.
- Continuous Improvement: Establish a culture of continuous improvement within your organization. Regularly review and update processes and offerings to address evolving pain points.
- Innovation: Embrace innovation as a means of addressing pain points. Encourage creative thinking and experimentation to develop novel solutions.
- Collaboration: Collaborate with cross-functional teams to address pain points comprehensively. Engage experts from various disciplines to find holistic solutions.
Role of Innovation
Innovation plays a pivotal role in addressing pain points effectively. Here’s how innovation can be leveraged:
- Creative Problem Solving: Innovation involves thinking outside the box and exploring unconventional solutions to pain points. Encouraging a culture of creative problem-solving can lead to breakthroughs.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in technology often provide new tools and capabilities for addressing pain points. Automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics can offer powerful solutions.
- Iterative Development: Innovators often iterate on ideas, refining them based on feedback and real-world testing. This iterative approach is effective in fine-tuning solutions to pain points.
- User-Centric Innovation: Innovation should be driven by a deep understanding of user needs and pain points. Engaging with end-users throughout the innovation process ensures that solutions directly address their concerns.
- Disruption: Innovation can disrupt traditional models and paradigms, challenging the status quo. Disruptive innovations have the potential to not only address pain points but also transform entire industries.
Examples of Pain Points and Innovation
To illustrate the relationship between pain points and innovation, consider these real-world examples:
- Healthcare: In the healthcare industry, long wait times for medical appointments are a common pain point for patients. Innovative solutions include telemedicine platforms that offer virtual consultations, reducing wait times and increasing access to care.
- Transportation: Traffic congestion in urban areas is a significant pain point for commuters. Innovations such as ride-sharing services and autonomous vehicles aim to address this challenge by improving traffic flow and reducing congestion.
- E-commerce: Cart abandonment is a pain point for online retailers. Innovations like one-click checkout and personalized product recommendations help streamline the purchasing process and reduce abandonment rates.
- Education: High student-to-teacher ratios in schools can hinder personalized learning. EdTech innovations, including adaptive learning platforms, address this pain point by tailoring instruction to individual students.
- Finance: Complex and lengthy loan approval processes are pain points for borrowers. Fintech innovations, such as peer-to-peer lending and online loan marketplaces, offer streamlined and efficient lending solutions.
Key Highlights of Pain Points:
- Pain Points Overview:
- Pain Points are challenges and problems that customers or businesses encounter, requiring effective solutions.
- Identifying specific, urgent, and impactful problems helps address needs, gain a competitive edge, and discover market opportunities.
- Characteristics:
- Specific: Clearly defined issues or difficulties.
- Urgent: Requiring immediate attention or resolution.
- Impactful: Significantly affecting well-being or performance.
- Use Cases:
- Market Research: Identifying needs and challenges for product development.
- Sales Pitch: Addressing pain points for relevant solutions.
- Business Strategy: Creating offerings catering to specific market pain points.
- Examples of Pain Points:
- Healthcare: Patients facing long wait times for appointments.
- E-commerce: Customers concerned about high shipping costs.
- Project Management: Teams struggling with communication processes.
- Benefits of Addressing Pain Points:
- Customer Satisfaction: Enhancing customer experience by meeting needs.
- Competitive Edge: Standing out by solving pressing challenges.
- Market Opportunities: Identifying untapped markets with unaddressed pain points.
- Challenges in Addressing Pain Points:
- Research Complexity: Thoroughly understanding customer pain points.
- Solution Suitability: Ensuring solutions effectively address the challenges.
- Market Competition: Facing rivals targeting the same pain points.
| Related Frameworks | Description | When to Apply |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Journey Mapping | – Customer Journey Mapping is a framework used to visualize and understand the end-to-end experience of customers as they interact with a product, service, or brand. It helps identify pain points, opportunities, and moments of truth in the customer journey. | – When seeking to understand the customer experience holistically and identify pain points, friction, and opportunities for improvement. |
| Service Blueprinting | – Service Blueprinting is a framework for mapping the entire service delivery process, including front-stage and back-stage activities, interactions, and touchpoints. It helps identify pain points, bottlenecks, and opportunities to enhance service delivery and customer experience. | – When analyzing complex service processes and interactions to identify pain points and opportunities for improvement. |
| Root Cause Analysis | – Root Cause Analysis is a problem-solving technique used to identify the underlying causes of issues or pain points. It involves systematically analyzing symptoms, identifying potential causes, and probing deeper to uncover the root cause or causes of the problem. | – When investigating recurring issues, problems, or pain points to determine their underlying causes and develop effective solutions. |
| Design Thinking | – Design Thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation and problem-solving that emphasizes empathy, creativity, and iteration. It involves understanding user needs, ideating solutions, prototyping, and testing to address pain points and create meaningful experiences. | – When tackling complex problems or pain points in a user-centric and iterative manner, fostering innovation and empathy in problem-solving. |
| Voice of the Customer (VoC) Analysis | – Voice of the Customer (VoC) Analysis involves gathering and analyzing feedback from customers to understand their preferences, needs, and pain points. It helps organizations prioritize improvements and innovations that address customer pain points and drive satisfaction and loyalty. | – When seeking insights into customer preferences, needs, and pain points to inform product development, service enhancements, or process improvements. |
| SWOT Analysis | – SWOT Analysis is a strategic planning tool used to assess an organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It helps identify internal weaknesses and external threats that may contribute to pain points or challenges within the organization. | – When conducting a strategic assessment of organizational capabilities, identifying areas for improvement, and addressing potential pain points or vulnerabilities. |
| Gap Analysis | – Gap Analysis is a technique used to compare the current state of an organization’s performance or capabilities with its desired future state. It helps identify gaps or discrepancies that may be causing pain points or hindering progress toward organizational goals. | – When assessing performance or capabilities against strategic objectives, identifying areas of improvement or optimization, and addressing pain points or obstacles to progress. |
| Empathy Mapping | – Empathy Mapping is a tool used to understand the thoughts, feelings, and motivations of users or stakeholders. It helps teams gain empathy for their target audience and identify pain points, needs, and opportunities for innovation or improvement. | – When seeking to understand the perspectives and experiences of users or stakeholders, uncovering pain points, and designing solutions that meet their needs and expectations. |
| Lean Six Sigma | – Lean Six Sigma combines the principles of Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma to improve process efficiency, reduce waste, and minimize variation. It involves systematically identifying and eliminating defects, errors, or inefficiencies that contribute to pain points or customer dissatisfaction. | – When optimizing processes, reducing defects or errors, and improving quality and efficiency to address pain points and enhance customer satisfaction. |
| Business Process Reengineering (BPR) | – Business Process Reengineering (BPR) is a strategy for redesigning and restructuring business processes to achieve dramatic improvements in performance, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. It involves analyzing and reimagining workflows to eliminate pain points, streamline operations, and drive innovation. | – When seeking to radically transform organizational processes, eliminate bottlenecks or pain points, and drive significant improvements in performance, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. |
Related Business Concepts











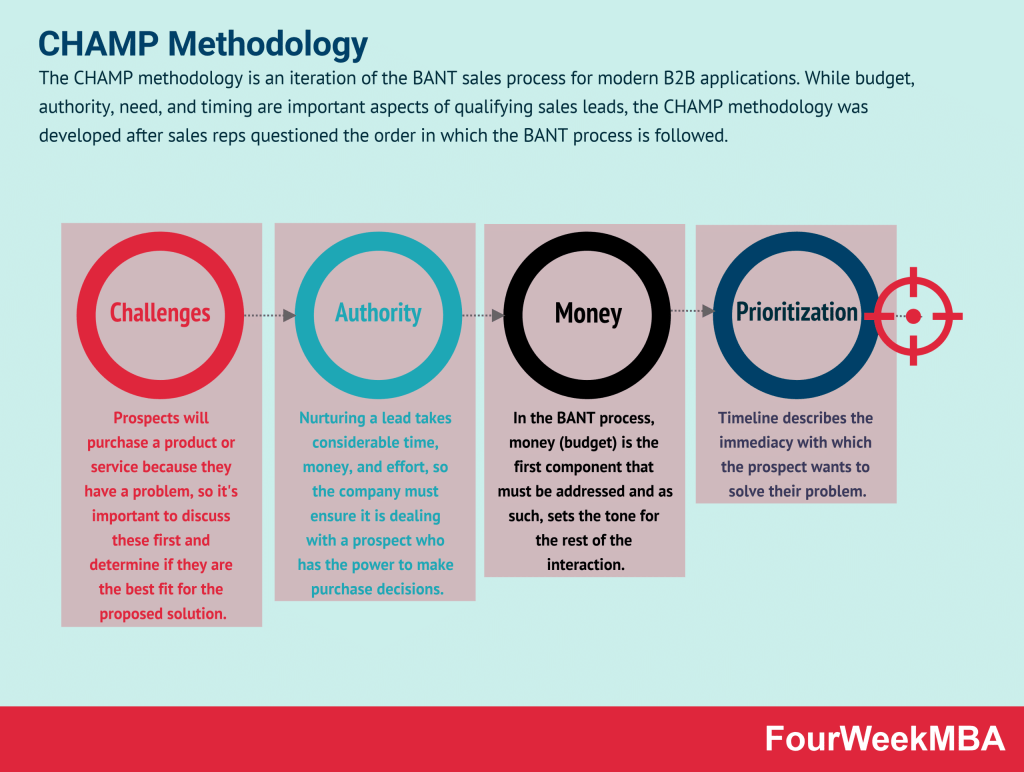

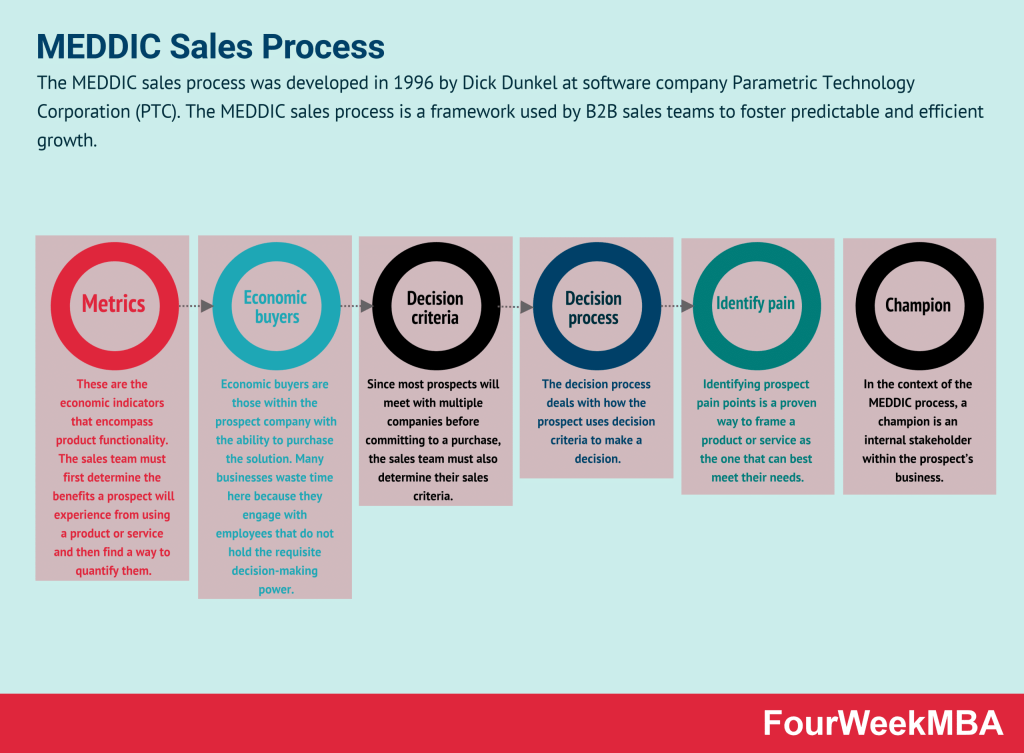










Palantir Acquire, Expand, Scale Framework



Read: product development frameworks here.
Read Next: SWOT Analysis, Personal SWOT Analysis, TOWS Matrix, PESTEL Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces, TOWS Matrix, SOAR Analysis.
Main Free Guides:



