Uber Freight is a platform that connects carriers with shippers, which generated $5.24 billion in revenue in 2023, slowing down from $6.95 billion in revenue in 2022, and it’s now one of the three core segments (Mobility, Delivery, and Freight) within the Uber Business Model.
Within Uber, there is another crucial segment called Uber Freight, which has become a company for its own sake.
Indeed, Uber Freight allows carriers to book a shipment, transportation management, and other logistics services.
Uber Freight powers a managed transportation and logistics network and connected Shippers and Carriers in a digital marketplace to move shipments.
Indeed, that is an on-demand platform to automate and accelerate logistics transactions end-to-end while providing visibility and control of logistics networks.
Uber Freight comprises services such as:
- TMS (transportation management system): visibility into shipments, weather, and traffic analytics
- Instant Booking.
- Instant Quote.
The platform has 200K+ users and $17B freight under management.
Value Proposition:
- Efficient Freight Matching: Uber Freight offers a platform that efficiently matches carriers with shippers, reducing empty truck miles and improving resource utilization.
- Digital Logistics: The platform provides digital tools such as a Transportation Management System (TMS), instant booking, and instant quotes, streamlining logistics processes.
- Visibility and Control: Uber Freight enhances visibility and control of logistics networks, providing shippers and carriers with real-time insights into shipments, weather conditions, and traffic analytics.
- Network Connectivity: The platform operates a managed transportation and logistics network, connecting shippers and carriers in a digital marketplace.
- End-to-End Automation: Uber Freight’s platform automates and accelerates logistics transactions end-to-end, simplifying the booking and management of shipments.
Customer Segments:
- Carriers: Uber Freight serves carriers, including truck drivers and transportation companies, who seek efficient load matching, automated booking, and access to logistics services.
- Shippers: Shippers, including businesses and organizations that need to transport goods, benefit from Uber Freight’s platform for finding reliable carriers, managing shipments, and optimizing their supply chain.
- Logistics Industry: The platform caters to the broader logistics and transportation industry, offering tools like TMS and analytics for logistics professionals.
- Businesses of All Sizes: Uber Freight’s services are suitable for businesses of all sizes, from small enterprises to large corporations, looking to streamline their freight operations.
Distribution Strategy:
- Digital Marketplace: Uber Freight operates as a digital marketplace, allowing carriers and shippers to connect and transact online.
- Technology-Driven: The platform leverages technology to automate logistics transactions, making it accessible to users through a mobile app and web platform.
- Nationwide Reach: Uber Freight’s services have a nationwide presence, connecting users across the United States.
Marketing Strategy:
- Digital Marketing: Uber Freight employs digital marketing strategies to reach carriers and shippers, promoting its platform through online channels and advertisements.
- Partnerships: Collaborations and partnerships with carriers, shippers, and logistics industry stakeholders enhance the platform’s reach and user base.
- User Education: The company provides educational resources and support to help users maximize the benefits of its platform.
- Visibility and Transparency: Uber Freight emphasizes the visibility and transparency it offers to carriers and shippers as a key selling point.
Cost Structure:
- Technology Infrastructure: Investments in technology infrastructure, including app development and platform maintenance.
- Marketing and Promotion: Expenses related to marketing and promotional activities to acquire and retain users.
- Operations: Costs associated with platform operations, customer support, and logistics management.
- User Acquisition: Expenses related to acquiring carriers and shippers onto the platform.
- Partnerships: Costs associated with establishing and maintaining partnerships within the logistics industry.
Key Highlights
- Platform and Revenue Generation: Uber Freight connects carriers with shippers and generated $6.95 billion in revenue in 2022.
- Segment in Uber’s Business Model: Uber Freight is a core segment within Uber’s business model, along with Mobility and Delivery.
- Independent Entity: Operating as its own company within Uber, Uber Freight focuses on freight and logistics.
- Carrier Services: Uber Freight empowers carriers to book shipments, access transportation management, and other logistics services.
- Managed Network: Uber Freight operates a managed transportation and logistics network, digitally linking shippers and carriers.
- End-to-End Automation: The platform automates and accelerates logistics transactions, enhancing visibility and control over networks.
- Service Offerings: Uber Freight provides services like Transportation Management System (TMS), Instant Booking, and Instant Quote.
- User Base and Freight Management: With over 200,000 users, Uber Freight manages over $17 billion worth of freight.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Value Proposition | Uber Freight offers a compelling value proposition for its users, including: – Efficient Freight Matching: Streamlining the process of matching shippers with carriers. – Transparent Pricing: Providing clear and upfront pricing for shipments. – Reduced Administrative Burden: Simplifying paperwork and documentation. – Real-Time Tracking: Enabling real-time tracking of shipments for visibility. – Driver Support: Offering support and resources for carriers and drivers. – Payment Assurance: Ensuring timely and guaranteed payments to carriers. – Access to Loads: Providing access to a wide range of available freight loads. – Digital Platform: Offering a user-friendly and digital platform for logistics. – Reduced Empty Miles: Optimizing routes to reduce empty miles for carriers. – Safety and Compliance: Promoting safety and compliance within the industry. |
| Core Products/Services | Uber Freight’s core products and services encompass: – Digital Freight Marketplace: Operating an online platform for matching shippers and carriers. – Load Booking: Allowing shippers to book available freight loads. – Real-Time Tracking: Enabling real-time tracking and visibility of shipments. – Pricing and Quotes: Providing transparent pricing and quoting tools. – Payment Solutions: Facilitating quick and guaranteed payments to carriers. – Driver App: Offering a mobile app for drivers to manage loads and tasks. – Analytics and Insights: Providing data and analytics for informed decisions. – Support and Resources: Offering support and resources for carriers and drivers. – Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating with shippers’ existing systems. – Safety and Compliance Tools: Promoting safety and compliance in logistics operations. |
| Customer Segments | Uber Freight serves a diverse range of customer segments, including: – Shippers: Attracting businesses that need to transport goods and materials. – Carriers: Engaging with trucking companies and independent owner-operators. – Drivers: Providing tools and resources for truck drivers on the road. – Logistics Managers: Serving professionals responsible for supply chain and logistics. – Manufacturers: Targeting manufacturers seeking transportation solutions. – Distributors: Providing distribution companies with efficient freight options. – Retailers: Serving retailers in need of reliable transportation. – Freight Brokers: Engaging with freight brokerage firms. – 3PLs (Third-Party Logistics): Partnering with third-party logistics providers. – Small Businesses: Offering transportation solutions to small businesses. |
| Revenue Streams | Uber Freight generates revenue through various revenue streams: – Booking Fees: Earnings from fees charged to shippers for booking loads. – Service Fees: Income from fees charged to shippers and carriers for platform use. – Surge Pricing: Potential revenue from surge pricing during peak demand. – Subscription Plans: Earnings from premium subscription offerings. – Payment Processing Fees: Income from payment processing services. – Data Analytics: Revenue from selling data and analytics to industry partners. – Premium Features: Earnings from premium features for shippers and carriers. – Load Optimization: Income from load optimization services. – Integration Services: Potential earnings from integrating with shippers’ systems. – Safety and Compliance Tools: Revenue from safety and compliance solutions. |
| Distribution Strategy | Uber Freight employs a strategic distribution strategy to reach users: – Digital Platform: Operating a digital platform accessible via web and mobile app. – Mobile App: Providing a user-friendly mobile app for drivers and carriers. – National Coverage: Expanding services to cover transportation needs across the U.S. – Integration Partnerships: Collaborating with logistics software providers for integration. – Industry Partnerships: Partnering with shippers, carriers, and industry stakeholders. – APIs and Data Integration: Offering APIs for seamless data exchange. – Driver Network: Building a network of drivers and carriers for capacity. – Customer Support: Providing assistance and support to shippers and carriers. – Feedback Loop: Incorporating user feedback for continuous improvement. – Safety Initiatives: Promoting safety and compliance in the trucking industry. |
Visual Stories Related To the Uber Business Model





In 2022, Uber mobility took 27% of each booking on the platform. At the same time, Uber Eats took 20% of each booking on the delivery platform. The take rate varies according to demand and supply but also market dynamics. In short, in periods of increased competition, the service might charge lower take rates to keep up with it. In 2022, Uber pushed on efficiency, thus raising its take rates, to move toward profitability.
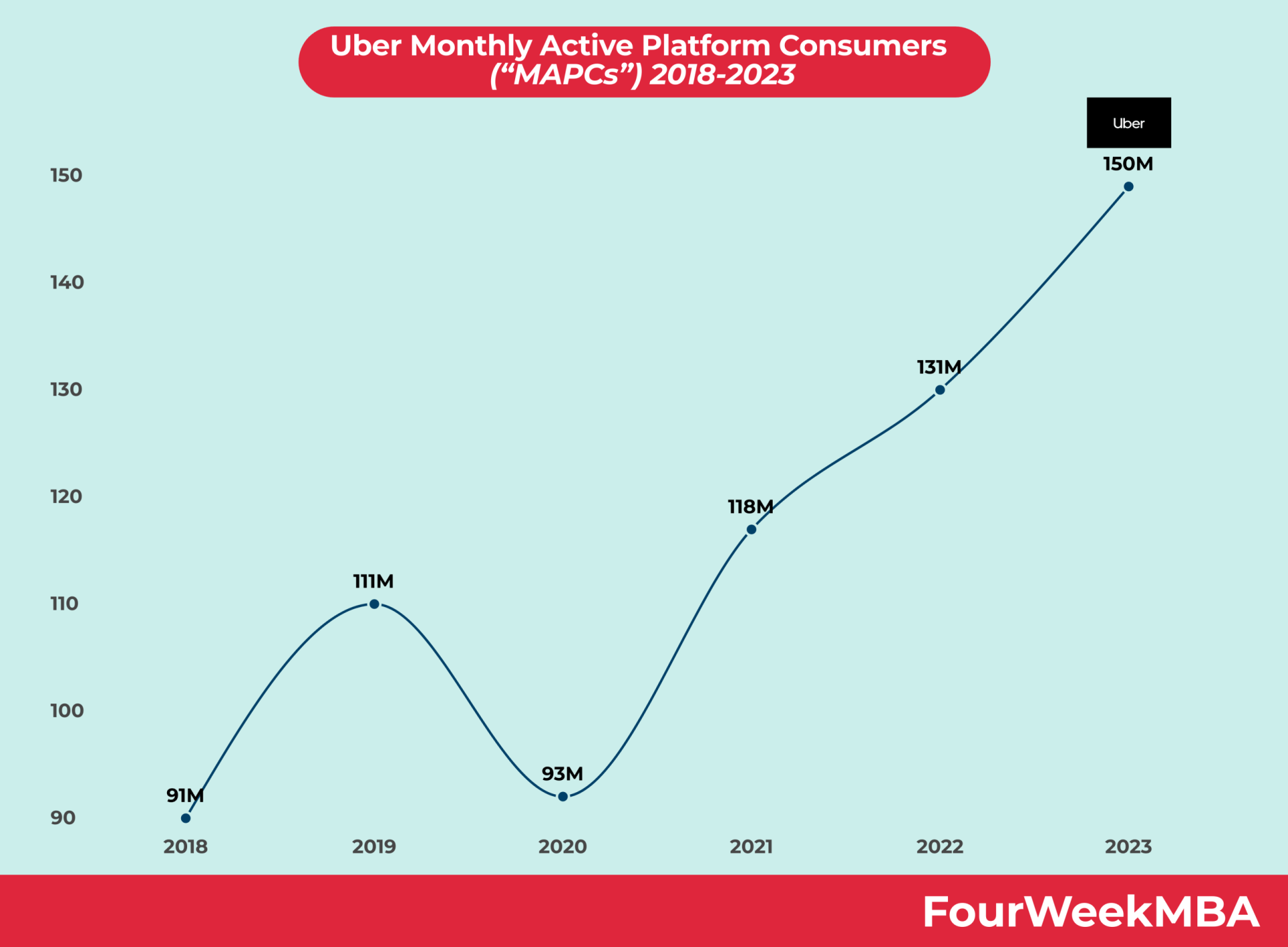
Uber Platform Users