Uber Eats and DoorDash are delivery apps and marketplaces that make money by charging a fee for each transaction/booking happening through the platform. In 2023, Uber Eats generated more than $12.2 billion in revenue, compared to DoorDash’s almost $8.63 billion in revenue.
| Elements | Uber Eats | DoorDash | Similarities | Differences | Competitive Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Segments | Individual consumers, restaurants | Individual consumers, restaurants, businesses | Both serve individual consumers, restaurants, and businesses by offering food delivery services. | Uber Eats focuses primarily on individual consumers and restaurants, while DoorDash also targets businesses as customers. | Broader customer base (DoorDash). |
| Value Proposition | Convenience, food delivery, wide restaurant network | Food delivery, restaurant selection, convenience | Both provide the convenience of food delivery and access to a variety of restaurants. Uber Eats emphasizes its wide restaurant network, while DoorDash highlights restaurant selection and convenience. | Uber Eats boasts a broad restaurant network and convenience for customers. DoorDash emphasizes restaurant selection and offers a strong focus on convenience in its value proposition. | Restaurant selection and convenience (DoorDash). |
| Channels | Mobile app, website, partnerships | Mobile app, website, partnerships | Both operate through mobile apps and websites, and they establish partnerships with restaurants and businesses to expand their reach. | Uber Eats’ primary focus is on connecting consumers with restaurants through its platform. DoorDash extends its services to include a broader range of partnerships and businesses. | Diversified partnerships (DoorDash). |
| Customer Relationships | Mobile app, customer support, user ratings | Mobile app, customer support, user ratings | Both maintain customer relationships through their mobile apps and offer customer support. Users can rate and provide feedback on their experiences. | Uber Eats and DoorDash both rely on mobile apps and customer support to manage customer relationships. User ratings and feedback mechanisms are common to both platforms. | User ratings and feedback mechanisms (Both). |
| Key Activities | Food delivery, platform maintenance | Food delivery, platform maintenance | Both engage in food delivery and platform maintenance activities. | Uber Eats’ key activities revolve around food delivery and maintaining its platform. DoorDash also focuses on food delivery and platform maintenance. | Similar key activities (Both). |
| Key Resources | Mobile app, restaurant partnerships | Mobile app, restaurant partnerships | Both rely on key resources such as their mobile apps and partnerships with restaurants to deliver their services. | Key resources for Uber Eats include its mobile app and partnerships with restaurants. DoorDash similarly relies on its mobile app and restaurant partnerships. | Leveraging partnerships with restaurants (Both). |
| Key Partnerships | Restaurants, delivery drivers | Restaurants, delivery drivers, businesses | Both collaborate with restaurants and delivery drivers to facilitate food delivery. DoorDash also partners with businesses to expand its services. | Uber Eats’ primary partnerships are with restaurants and delivery drivers. DoorDash extends its services to include partnerships with businesses, in addition to restaurants and delivery drivers. | Diversified partnership network (DoorDash). |
| Revenue Streams | Delivery fees, restaurant fees | Delivery fees, restaurant fees | Both generate revenue from delivery fees charged to customers and fees paid by restaurants. | Uber Eats primarily earns revenue from delivery fees and fees charged to restaurants. DoorDash follows a similar revenue model, relying on delivery fees and fees from restaurants. | Similar revenue streams (Both). |
| Cost Structure | Delivery costs, platform maintenance | Delivery costs, platform maintenance | Both incur costs related to food delivery and platform maintenance. | Both Uber Eats and DoorDash have cost structures that include expenses related to food delivery and maintaining their platforms. | Comparable cost structures (Both). |


Related Visual Stories






Visual Stories Related To the Uber Business Model





In 2022, Uber mobility took 27% of each booking on the platform. At the same time, Uber Eats took 20% of each booking on the delivery platform. The take rate varies according to demand and supply but also market dynamics. In short, in periods of increased competition, the service might charge lower take rates to keep up with it. In 2022, Uber pushed on efficiency, thus raising its take rates, to move toward profitability.
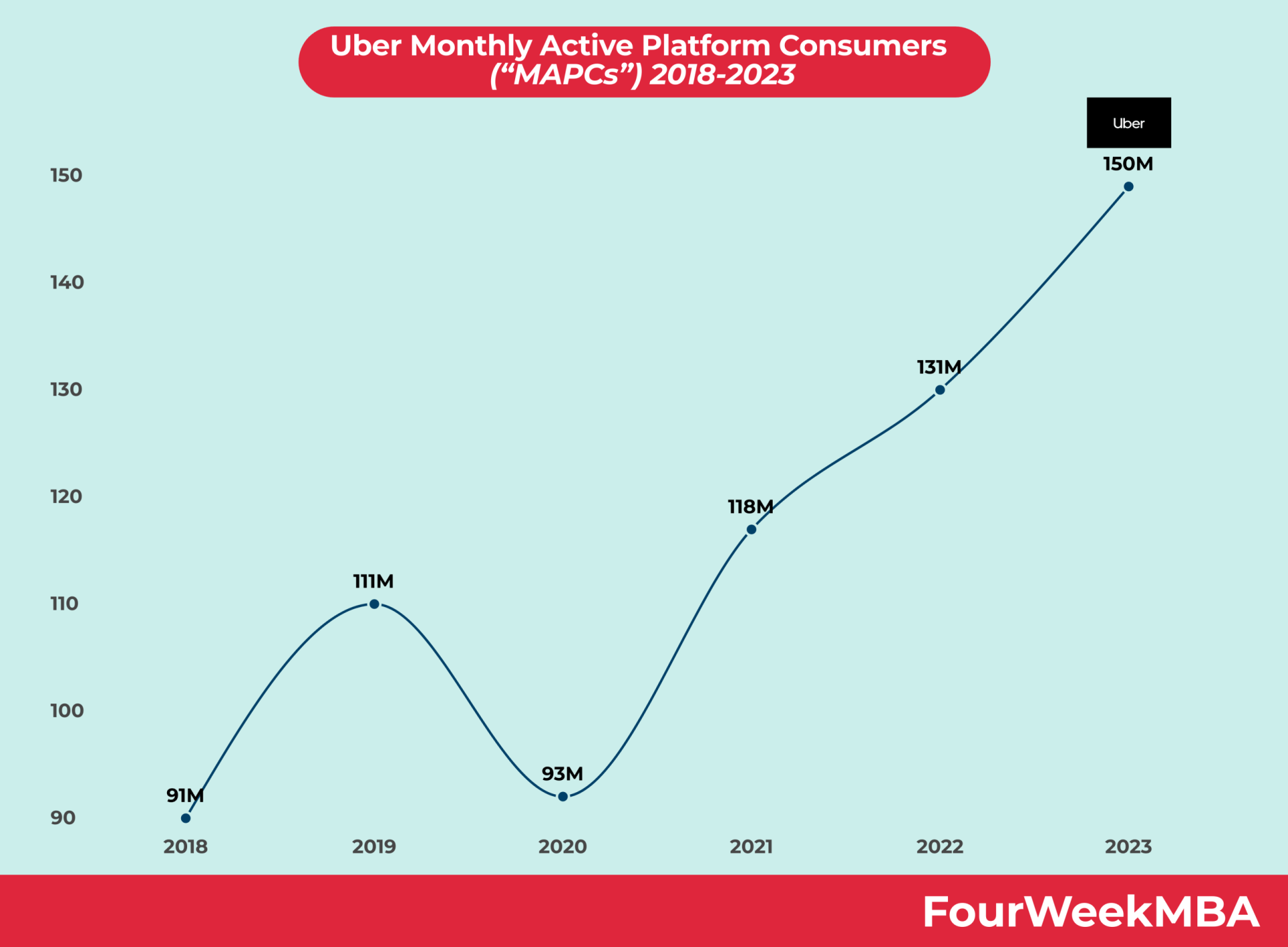
Uber Platform Users