In the Business Model Canvas, the Customer Relationships building block describes the type of relationships a business creates with different customer segments. In short, these represent the set of actions a company needs to take in order to grow and maintain its customer base.
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Customer Relationships | – Customer Relationships is one of the nine building blocks in the Business Model Canvas, a strategic management tool used to describe, design, and analyze a business model. It outlines how a company interacts with and engages its customers. |
| Importance | – Building and maintaining strong customer relationships are vital for customer retention, loyalty, and long-term revenue generation. It directly impacts a business’s ability to satisfy customers and sustain growth. |
| Types of Relationships | – Customer relationships can take various forms, including personal assistance, self-service, automated services, communities, and more. The choice of relationship type depends on the nature of the business and customer preferences. |
| Customer Segments | – The type of customer relationships a business establishes should align with the needs and preferences of its Customer Segments. Different segments may require different levels of engagement and support. |
| Channels | – Customer relationships are closely linked to Channels, as they often determine how businesses interact with customers. For example, a company might use in-person sales for personalized assistance or online platforms for self-service. |
| Value Proposition | – The nature of customer relationships should align with the Value Proposition offered by the business. If the value proposition emphasizes personalized support, the customer relationship strategy should reflect that. |
| Feedback Loop | – Establishing a feedback loop is essential for understanding customer needs and preferences. It allows businesses to continuously improve their products, services, and the customer experience, fostering stronger relationships. |
| Customer Support | – Providing excellent customer support is a critical aspect of building positive relationships. It involves addressing inquiries, resolving issues promptly, and ensuring customers feel valued and heard. |
| Data and Analytics | – Utilizing data and analytics can help businesses gain insights into customer behavior and preferences, enabling them to tailor their interactions and offerings for more meaningful and relevant relationships. |
| Retention Strategies | – Building lasting relationships often requires the implementation of customer retention strategies. These strategies may include loyalty programs, exclusive offers, or personalized recommendations based on customer history. |
| Crisis Management | – Businesses should also be prepared for managing customer relationships during challenging times or crises. Effective communication and support can play a crucial role in maintaining trust and goodwill. |
| Conclusion | – Customer Relationships define how a business interacts with and serves its customers. Understanding and nurturing these relationships are key to customer satisfaction, loyalty, and long-term success. |
Understanding customer relationships in the Business Model Canvas
In defining the ideal customer relationships, businesses should put themselves in their customers’ shoes. That is, what would they consider to be the ideal relationship? Would it be automated, personal, or somewhere in between? It is important to remember that consumers have certain expectations regarding the sort of relationship a business establishes with them.
Indeed, the quality of customer relationships has direct consequences for the customer experience. Organizations with consistently high-quality customer interactions across multiple touchpoints will be rewarded with devoted and brand loyal followers. These relationships can also be used to acquire new customers or upsell existing customers to boost sales volume.
Under this section of the Business Model Canvas, the business should consider the following questions:
- What type of customer relationship does each of our customer segments expect?
- Which relationships are already established?
- How much do they cost?
- To what extent are they integrated with our business model?
Six types of customer relationships
There are many different customer relationships types, with many co-existing within a single customer segment.
Here is a brief look at six of them:
- Dedicated personal assistance – in the first type, the business may assign a dedicated customer care representative who takes the time to understand the customer’s unique and specific needs. Banks and casinos employ this strategy to look after wealthy individuals.
- Personal assistance – perhaps one of the most common relationship types, where customers can interact with a single sales representative before making a purchase. Personal assistance also encompasses after-sales support.
- Self-service – where the business gives the customer everything they need to provide a service to themselves. Furniture maker IKEA is one example, selling flatpack furniture that must be assembled by the purchaser. Supermarkets and retailers that offer self-serve checkouts are another example.
- Automated services – essentially, this is a self-service relationship with automated processes that can identify specific customers and make tailored recommendations. Though automation will never replace a human touch, it can nevertheless provide excellent and efficient customer service.
- Communities – customer communities which the business owns and manages are also used to build relationships. Customers assemble to solve common problems and exchange knowledge, with this information used by the business to deepen its understanding of each segment. GlaxoSmithKline launched an online community for a prescription-free weight loss product. The pharmaceutical company wanted to understand the challenges overweight adults faced to better manage their expectations during treatment.
- Co-creation – where the business asks its customers to help them design a new product or service. This is a customer relationship that is highly beneficial for both parties. For the business, the inclusivity of the approach builds brand loyalty and trust. For the user, they get more say in a product designed around their needs.
Key takeaways:
- In the Business Model Canvas, the Customer Relationships building block describes the type of relationships a business creates with different customer segments. For best results, the business needs to maintain high-quality interactions with customers across multiple touchpoints.
- Customer relationships are designed around three major goals: customer acquisition, customer retention, and upselling.
- The six most common types of customer relationships include dedicated personal assistance, personal assistance, self-service, automated services, communities, and co-creation. One or several may exist in a single customer segment.
Key Highlights
- Customer Relationships Definition: In the Business Model Canvas, the Customer Relationships building block refers to the types of relationships a business establishes with various customer segments. These relationships represent the actions necessary to attract and retain customers.
- Customer-Centric Approach: To define ideal customer relationships, businesses should empathize with their customers and consider what kind of relationship would best suit their needs and expectations.
- Impact on Customer Experience: Quality customer relationships directly influence the overall customer experience. Consistently positive interactions across various touchpoints lead to loyal and devoted customers, which can further drive sales and customer growth.
- Key Considerations for Customer Relationships:
- Six Types of Customer Relationships:
- Dedicated Personal Assistance: Assigning a dedicated representative to cater to the unique needs of individual customers, often seen in businesses serving wealthy clients.
- Personal Assistance: Interaction with a single sales representative for pre-purchase and after-sales support.
- Self-Service: Empowering customers to serve themselves, as seen in businesses like IKEA and supermarkets with self-checkouts.
- Automated Services: Combining self-service with automated processes to offer personalized recommendations and efficient customer service.
- Communities: Building customer communities where customers share knowledge and solve problems, benefiting both customers and the business.
- Co-Creation: Involving customers in product or service design, fostering brand loyalty and trust while meeting customer needs.
- Key Takeaways:
- Customer Relationships in the Business Model Canvas focus on the types of relationships a business establishes with different customer segments.
- Successful customer relationships contribute to customer acquisition, retention, and upselling.
- Six common types of customer relationships include dedicated personal assistance, personal assistance, self-service, automated services, communities, and co-creation. These types can coexist within a single customer segment.
| Related Frameworks, Models, or Concepts | Description | When to Apply |
|---|---|---|
| Lean Startup Methodology | The Lean Startup Methodology is an approach to developing and managing startups that focuses on rapid iteration, customer feedback, and validated learning. It involves creating a minimum viable product (MVP), testing hypotheses through experimentation, and iterating based on customer feedback. By applying lean startup principles, entrepreneurs can minimize waste, mitigate risks, and increase the chances of building successful and sustainable businesses. | Consider Lean Startup Methodology when launching a new venture or developing innovative products or services. Use it to validate assumptions, identify customer needs, and iterate on your business model based on real-world feedback. Implement Lean Startup Methodology as a framework for achieving product-market fit, accelerating growth, and maximizing the chances of startup success within your organization. |
| Value Proposition Canvas | The Value Proposition Canvas is a tool for designing and refining value propositions that resonate with customer needs and preferences. It involves mapping customer profiles (jobs, pains, gains) and corresponding value propositions (products, services, solutions) to identify areas of alignment and opportunities for differentiation. By using the Value Proposition Canvas, organizations can develop compelling value propositions that address customer needs and create competitive advantage. | Consider the Value Proposition Canvas when designing or refining your organization’s value propositions. Use it to understand customer needs, pain points, and aspirations, and align your offerings to deliver unique value and differentiation. Implement the Value Proposition Canvas as a framework for developing customer-centric products, services, and solutions that drive customer satisfaction and loyalty within your organization. |
| Business Model Innovation | Business Model Innovation involves creating, adapting, or reinventing the fundamental structure and logic of how a business creates, delivers, and captures value. It encompasses changes to key elements of the business model, such as revenue streams, cost structure, value proposition, and customer segments, to drive growth and competitiveness. By innovating their business models, organizations can seize new opportunities, respond to market disruptions, and outperform competitors. | Consider Business Model Innovation when seeking to transform or disrupt traditional business models within your industry. Use it to explore new revenue streams, business models, and value creation opportunities that capitalize on emerging trends and technologies. Implement Business Model Innovation as a framework for driving organizational change, fostering innovation, and creating sustainable competitive advantage within your organization. |
| Blue Ocean Strategy | Blue Ocean Strategy is a strategic approach that focuses on creating uncontested market space and making competition irrelevant. It involves identifying and capturing new market opportunities by offering innovative value propositions that differentiate from existing competitors. By pursuing Blue Ocean Strategy, organizations can unlock new growth opportunities, differentiate themselves from competitors, and capture untapped market demand. | Consider Blue Ocean Strategy when seeking to develop innovative value propositions and new market opportunities. Use it to identify unmet customer needs, challenge industry assumptions, and create new market spaces where competition is irrelevant. Implement Blue Ocean Strategy as a framework for driving innovation, differentiation, and growth within your organization by offering compelling value propositions that resonate with customers. |
| Design Thinking | Design Thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation and problem-solving that emphasizes empathy, creativity, and iterative prototyping. It involves understanding user needs, ideating potential solutions, prototyping and testing concepts, and iterating based on feedback. By applying design thinking principles, organizations can develop customer-centric products, services, and experiences that meet user needs and preferences effectively. | Consider Design Thinking when developing new products, services, or processes within your organization. Use it to gain deep insights into user needs, generate creative solutions, and iterate rapidly to develop prototypes that address customer pain points and aspirations. Implement Design Thinking as a framework for fostering innovation, collaboration, and customer-centricity within your organization to drive business growth and success. |
| Platform Business Model | The Platform Business Model is a business model that creates value by facilitating interactions between two or more distinct groups of users. Platforms provide a marketplace or infrastructure that enables users to connect, interact, and exchange goods, services, or information. By leveraging network effects and economies of scale, platform businesses can create value for both users and stakeholders and achieve rapid growth and scalability. | Consider the Platform Business Model when building digital platforms or ecosystems that connect multiple users or stakeholders. Use it to create network effects, drive user engagement, and unlock new value creation opportunities through platform interactions and transactions. Implement the Platform Business Model as a framework for building scalable and sustainable businesses that leverage network effects and ecosystem dynamics to create value within your organization. |
| Business Ecosystem | A Business Ecosystem is a network of interconnected organizations, stakeholders, and resources that collaborate and compete to create and capture value. Business ecosystems involve complex relationships and interdependencies between participants, such as suppliers, partners, customers, and competitors, that influence industry dynamics and market outcomes. By understanding and leveraging business ecosystems, organizations can identify strategic partners, seize new opportunities, and navigate competitive landscapes effectively. | Consider Business Ecosystems when analyzing industry dynamics and market opportunities within your organization. Use it to identify key stakeholders, ecosystem partners, and value chain relationships that influence your organization’s competitiveness and growth prospects. Implement Business Ecosystems as a framework for building strategic alliances, fostering collaboration, and creating value within interconnected business networks within your organization. |
| Frugal Innovation | Frugal Innovation is an approach to innovation that focuses on creating affordable and accessible solutions to address the needs of resource-constrained consumers and markets. It involves simplifying products, processes, or business models to reduce costs while maintaining quality and functionality. By adopting frugal innovation principles, organizations can reach new customer segments, penetrate emerging markets, and drive inclusive growth and sustainability. | Consider Frugal Innovation when developing products or services for price-sensitive or underserved markets. Use it to design simple, affordable solutions that address basic needs and preferences of target consumers while optimizing resource utilization. Implement Frugal Innovation as a framework for expanding market reach, driving affordability, and fostering sustainable growth within your organization. |
| Open Innovation | Open Innovation is a collaborative approach to innovation that involves sourcing ideas, technologies, and expertise from external partners, such as customers, suppliers, universities, and competitors. It involves leveraging external knowledge and resources to complement internal capabilities and accelerate innovation processes. By embracing open innovation principles, organizations can access diverse perspectives, stimulate creativity, and drive breakthrough innovations more effectively. | Consider Open Innovation when seeking to access external expertise, insights, and resources to drive innovation within your organization. Use it to establish partnerships, collaborations, and ecosystems that facilitate knowledge exchange, idea generation, and technology transfer. Implement Open Innovation as a framework for leveraging external networks, crowdsourcing, and collaborative platforms to accelerate innovation and enhance competitiveness within your organization. |
| Agile Business Model Canvas | The Agile Business Model Canvas is an adaptation of the traditional Business Model Canvas that incorporates agile principles and practices into the strategic planning process. It involves iterative development, continuous feedback, and flexible adaptation to changing market conditions and customer needs. By adopting the Agile Business Model Canvas, organizations can respond quickly to market dynamics, experiment with new ideas, and iterate on business models effectively. | Consider the Agile Business Model Canvas when operating in fast-paced and uncertain environments. Use it to visualize and iterate on your business model, test assumptions, and adapt strategies based on real-time feedback and market insights. Implement the Agile Business Model Canvas as a framework for fostering agility, responsiveness, and innovation within your organization to drive sustainable growth and competitiveness. |
Alternatives to the Business Model Canvas
FourWeekMBA Squared Triangle Business Model
This framework has been thought for any type of business model, be it digital or not. It’s a framework to start mind mapping the key components of your business or how it might look as it grows. Here, as usual, what matters is not the framework itself (let’s prevent to fall trap of the Maslow’s Hammer), what matters is to have a framework that enables you to hold the key components of your business in your mind, and execute fast to prevent running the business on too many untested assumptions, especially about what customers really want. Any framework that helps us test fast, it’s welcomed in our business strategy.

FourWeekMBA VTDF Framework For Tech Business Models
This framework is well suited for all these cases where technology plays a key role in enhancing the value proposition for the users and customers. In short, when the company you’re building, analyzing, or looking at is a tech or platform business model, the template below is perfect for the job.


Download The VTDF Framework Template Here
FourWeekMBA VBDE Framework For Blockchain Business Models
This framework is well suited to analyze and understand blockchain-based business models. Here, the underlying blockchain protocol, and the token economics behind it play a key role in aligning incentives and also in creating disincentives for the community of developers, individual contributors, entrepreneurs, and investors that enable the whole business model. The blockchain-based model is similar to a platform-based business model, but with an important twist, decentralization should be the key element enabling both decision-making and how incentives are distributed across the network.

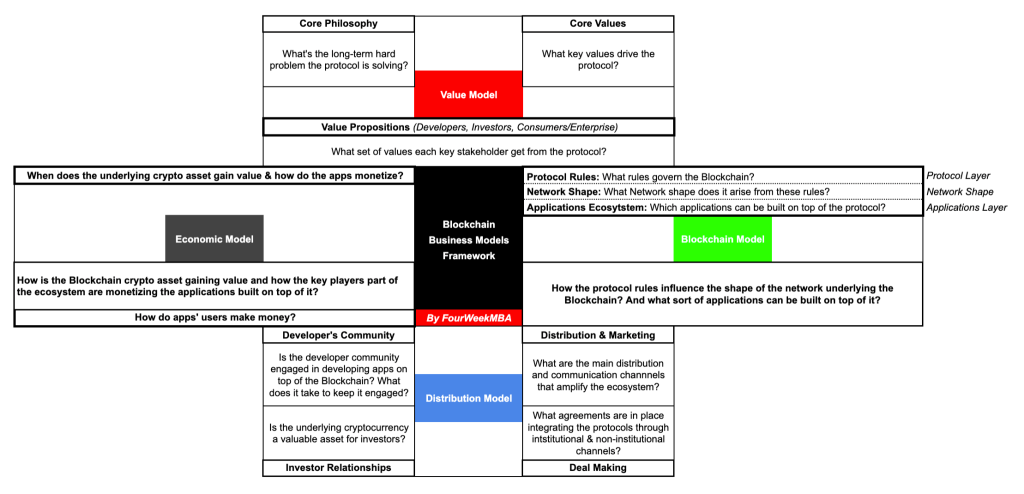
Download The VBDE Framework Template Here
More Resources:
Main Free Guides:
- Business Models
- Business Strategy
- Business Development
- Digital Business Models
- Distribution Channels
- Marketing Strategy
- Platform Business Models
- Revenue Models
- Tech Business Models
- Blockchain Business Models Framework
FourWeekMBA Business Toolbox











Asymmetric Betting





Read Also:






