Flipkart is an Indian eCommerce company headquartered in Bangalore and founded by Binny Bansal and Sachin Bansal in 2007. Flipkart started as an online book retailer but soon branched out into consumer electronics, fashion, groceries, and home essentials. Today, Flipkart is the largest eCommerce site in India where it does battle with the Amazon-owned platform Snapdeal. The company and its subsidiaries secured an impressive 60% of the total market share during the Indian festive sales period in late 2021.
| Subsidiary / Division | Business Category | Key Differentiator | Integration Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flipkart | E-Commerce and Online Retail | Leading e-commerce platform in India. | Serves as the core e-commerce platform, offering a wide range of products to consumers in India and neighboring regions. |
| Myntra | Fashion E-Commerce | Online fashion and apparel marketplace. | Complements Flipkart by specializing in fashion, offering a diverse selection of clothing, footwear, and accessories. |
| PhonePe | Digital Payments and Financial Services | UPI-based payment and financial services app. | Enhances the ecosystem by providing digital payment solutions, enabling transactions and financial services for users. |
| Flipkart Wholesale | B2B E-Commerce | B2B e-commerce platform for small businesses. | Supports small businesses by providing access to a wide range of products and suppliers through digital channels. |
| Flipkart Supermart | Grocery E-Commerce | Online grocery and essentials marketplace. | Expands into the grocery market, offering a convenient platform for purchasing groceries and household essentials. |
| Flipkart Video | Streaming and Content | Video streaming service with original content. | Enhances the digital ecosystem with content streaming, complementing the shopping experience with entertainment. |
| 2GUD | Online Marketplace for Refurbished Products | Platform for certified refurbished products. | Provides a marketplace for refurbished electronics and other items, offering budget-friendly options. |
| Flipkart Ads | Advertising and Marketing | Digital advertising solutions for brands and sellers. | Supports sellers and brands in promoting their products on the Flipkart platform through targeted advertising. |
| Jeeves | After-Sales Service and Support | Home appliance repair and service solutions. | Offers after-sales services, including appliance repair and maintenance, to enhance customer satisfaction. |
| Flipkart Quick | Hyperlocal Delivery | Hyperlocal delivery service for groceries and essentials. | Provides swift delivery of daily essentials within hours, enhancing the convenience of shopping. |
Myntra
Myntra is a fashion eCommerce company founded by Mukesh Bansal, Vineet Saxena, and Ashutosh Lawania in 2007.
Myntra initially offered a personalized gift service for B2B customers selling shirts, mousepads, and mugs. Four years later, however, it transitioned to fashion and lifestyle products with more than 350 brands available by 2012.
Flipkart acquired the company in 2014 in a deal worth approximately $330 million. Myntra continues to operate as a standalone brand for fashion-conscious consumers.
PhonePe
PhonePe is a financial services and digital payments company that was founded in 2015 by Sameer Nigam, Burzin Engineer, and Rahul Chari.
The PhonePe app is one of several to utilize the United Payments Interface (UPI) system developed to facilitate P2P and P2M transactions.
The app is available in 11 Indian languages including Hindi, Bengali, and Tamil, with users able to send and receive money, recharge mobile credit, purchase insurance, and pay their utility bills, to name a few features.
Ekart
Ekart is an Indian courier delivery company that ships the majority of orders that occur on Flipkart’s eCommerce platform.
The company claims to be the largest end-to-end logistics and supply chain fulfillment business in India. It has a focus on consistency and excellence in customer service, reliability, and the ability to deliver at scale.
Upstream Commerce
Upstream Commerce is an Israeli-based analytics startup that was acquired by Flipkart in 2018 for an undisclosed amount.
The move enabled Flipkart to establish a presence in one of the world’s most innovative startup ecosystems and develop data science to help it better manage its eCommerce pursuits.
Announcing the deal, Flipkart chief executive Kalyan Krishnamurthy noted that while the company had created its own seller pricing algorithms, Upstream Commerce would strengthen its capabilities and “be able to provide them (sellers) with automated pricing and help plan better selection in the most accurate, timely, and profitable way.”
Ugenie
Ugenie is a comprehensive membership software solution for community-centric businesses such as coaches, entrepreneurs, academies, non-profits, and associations.
Features across various paid plans include branded websites and apps, community creation and management, email notifications, business analytics, GDPR compliance, and secret group functionality.
Ugenie became a Flipkart subsidiary after the company purchased the California-based social book discovery tool weRead.com. This acquisition, which occurred in 2010, was Flipkart’s first.
Inside Flipkart’s business model: the Indian Amazon!
Flipkart can be defined as the Indian Amazon, as it shares many of the features of Amazon’s business model.
Some of the distinguishing elements of the Flipkart business model are:
Platform business
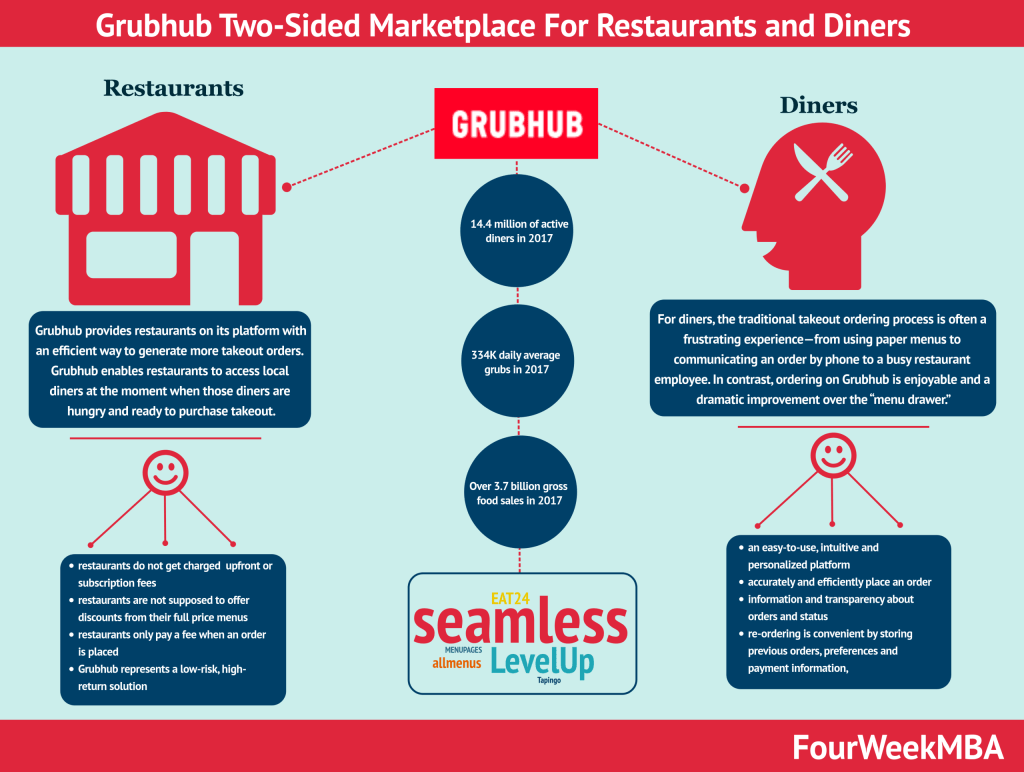
Flipkart operates a marketplace with two main parties: sellers and buyers.
As a platform, Flipkart operates as a facilitator enabling transactions between sellers and buyers and, as a result of it taking a cut on each sale (take rate).
Most items sold on Flipcart are third-party, meaning those are not owned by the company, which works primarily as a digital middleman between those two parties.
Products variety
Just like Amazon’s mission emphasizes a wide variety of products at reasonable prices.

So Flipkart offers various products in various categories (such as electronics, fashion, home, kitchen, and more).
Flipkart’s flywheel is based on enabling more and more third-party sellers to list their items on top of the e-commerce platform and facilitate those sales.
Competitive prices
Like Amazon, whose primary mission is to provide a wide selection of items in any category at a competitive price, Flipkart also emphasizes that.
The company also works with sellers to enable a promotions and discounts strategy to attract more and more customers to the platform, making the platform more interesting for sellers.
Once more sellers join the platform, more items are available at a more reasonable price; this is the essence of Amazon’s flywheel model, which Flipkart has borrowed from.

Fast Delivery
Just like Amazon’s business model, where wide selection, reasonable prices, and great customer experience (through, for instance, fast delivery).
Also, Flipkart offers fast delivery options to customers through its logistics network and partnerships with third-party delivery companies.
Flipkart, like Amazon, has built a set of fulfillment centers across India to make delivery fast and convenient.
Payment and customer service
To complete the picture of Flipkart’s business model is critical to look at easy payment solutions and great customer service as key elements to enhance its flywheel!
Indeed, Flipkart provides various payment options for customers (including cash on delivery, credit and debit card, and digital payments).
And a dedicated customer service team to handle requests from customers.
Key takeaways
- Flipkart is an Indian eCommerce company headquartered in Bangalore and founded by Binny Bansal and Sachin Bansal in 2007. Today, Flipkart is the largest eCommerce site in India where it does battle with the Amazon-owned platform Snapdeal.
- Flipkart subsidiaries include fashion eCommerce company Myntra and financial services company PhonePe. The company also acquired courier service Ekart which handles the delivery of online orders.
- Flipkart acquired Upstream Commerce in 2018 to establish a presence in the innovative Israel startup scene and develop better data-driven pricing algorithms. Community membership software platform Ugenie was part of Flipkart’s first acquisition in 2010.
Key Insights
- Platform Business: Flipkart runs a marketplace where third-party sellers list their products, and buyers can purchase them. The company acts as a facilitator in the transactions and earns a commission on each sale.
- Product Variety: Similar to Amazon, Flipkart offers a wide range of products across various categories, including electronics, fashion, home, and kitchen.
- Competitive Prices: Flipkart emphasizes competitive pricing and works with sellers to enable promotions and discounts, attracting more customers to the platform.
- Flywheel Model: Flipkart’s flywheel is based on enabling more third-party sellers to list their products on the platform, which leads to a wider selection of items at reasonable prices, attracting more customers, and thus attracting more sellers.
- Fast Delivery: Flipkart, like Amazon, offers fast delivery options through its logistics network and partnerships with third-party delivery companies. The company has fulfillment centers across India to ensure quick and convenient delivery.
- Payment and Customer Service: Flipkart provides various payment options, including cash on delivery, credit and debit cards, and digital payments, to enhance customer convenience. The company also maintains a dedicated customer service team to handle customer requests and inquiries.
Case Studies: DoorDash, Uber Eats, Postmates.
Read Next: Business Models.
Connected Visual Concepts And Case Studies










Main Free Guides:
- Innovation Theory
- Business Models
- Business Strategy
- Business Development
- Digital Business Models
- Distribution Channels
- Marketing Strategy
- Platform Business Models
- Tech Business Model
Listen Also:



![Google Subsidiaries: The List Of Companies Owned By Google [Alphabet] google-subsidiaries](https://i0.wp.com/fourweekmba.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/google-subsidiaries.png?resize=150%2C150&ssl=1)



