Digital transformation enables existing businesses to leverage digital technologies for business model innovation. The process of digital transformation is not just about new distribution channels. It starts by better serving key customers, and it completes by developing a new business mindset required to succeed in the digital era.
Aspect Explanation Digital Transformation Digital Transformation is the process of using digital technologies to fundamentally change how businesses operate, deliver value to customers, and stay competitive. It involves the integration of digital technologies into all aspects of an organization, leading to significant improvements in efficiency, customer experience, and innovation. Key Components 1. Technology Integration: Incorporating digital technologies like cloud computing, AI, IoT, and data analytics into operations.
2. Cultural Shift: Fostering a digital-first mindset and promoting a culture of innovation.
3. Process Optimization: Streamlining and automating workflows to enhance efficiency.
4. Customer-Centricity: Prioritizing customer experience through digital channels.
5. Data Utilization: Leveraging data for insights and decision-making.Drivers – Competitive Pressure: The need to keep up with competitors leveraging digital technologies.
– Customer Expectations: Meeting evolving customer demands for digital interactions.
– Efficiency Gains: Achieving cost savings and operational efficiency through automation.
– Innovation: Enabling new business models and revenue streams. –
Regulatory Compliance: Meeting digital compliance requirements.Challenges – Resistance to Change: Internal resistance to adopting new technologies and ways of working.
– Legacy Systems: Dealing with outdated legacy systems that are difficult to integrate.
– Cybersecurity Risks: Protecting digital assets and data from cyber threats.
– Talent Gap: Finding and retaining skilled digital talent.
– Data Privacy: Ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations.Benefits – Improved Efficiency: Automation and digitization lead to streamlined processes and reduced costs.
– Enhanced Customer Experience: Digital channels enable personalized and convenient interactions.
– Innovation: Digital technologies open new opportunities for business models and product offerings. – Data-Driven Insights: Access to data for informed decision-making.
– Competitive Advantage: Staying ahead in a digital marketplace.Examples – Amazon: Transformed retail through e-commerce and data-driven insights.
– Netflix: Revolutionized the entertainment industry with digital streaming.
– Tesla: Redefined the automotive industry with electric vehicles and software updates.
– Uber: Disrupted the transportation sector with a digital platform.
– Microsoft: Transitioned from software sales to cloud services and AI-driven products.Industries Affected Digital Transformation has impacted nearly every industry, including retail, healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and government. It has reshaped how businesses interact with customers, deliver products and services, and compete in the global market. Future Trends – AI and Machine Learning: Further integration of AI for automation and predictive analytics.
– 5G Technology: Enhanced connectivity for IoT and real-time data processing.
– Blockchain: For secure and transparent transactions.
– Sustainability: Focus on eco-friendly digital solutions.
– Edge Computing: Processing data closer to the source for reduced latency.
Busting some myths around digital distribution
As any concept that successfully developed in the business world, digital transformation has been exaggerated and emphasized, and it has, in some contexts, lost meaning.
Digital distribution is not a digital transformation
Companies and practitioners might use the term “digital transformation” to mean that a traditional company advertises its products online. However, this is such a limited view that brings companies to talk about digital transformation when all they are doing is not even close to it.
Understanding digital distribution is the first step to digital transformation. But the process can’t be complete until the company hasn’t transformed its business model to those digital channels.
Technology does not imply digital transformation
While technology can be leveraged to have new insights about customers. Technology alone won’t help if a fundamental mindset shift won’t happen.
Therefore, technology, if properly used, it does help the process of digital transformation. Yet technology is an enhancer (which can also negatively affect your business), not the bonanza, or the primary driver of your business.
Digital transformation is not a side project
Many companies that approach the digital world are fooled to think that a little investment in time and resources will do. The problem with this approach is the lack of understanding of the core principles underlying digital business models.
Digital transformation is not digitalization alone
Imagine a successful printing publisher who starts publishing its content online. Even though the content is well adapted for physical printing and distribution, that is not thought for digital distribution.
The printing publisher comes to the conclusion that digital transformation won’t work because of that. Yet digitalization or digitizing something is not digital transformation!
Dynamic thinking and dynamic markets
Digital transformation implies a more dynamic thinking process. That’s because digital channels do add potential complexity to the mix. Thus, thinking about your business as a monolithic block might limit this process.
With digital channels and business models, it’s important to be aware of the core part of the business that needs to be controlled.
Mastering the key customers’ key behaviors

In the FourWeekMBA interview to David L. Rogers, he explained how:
Across all different industries and across, really about fifteen years or so of the digital era. And what I found was that five common behaviors kept driving when and where customers would bring their attention and their energy and their investment and spend their money:
-
Access
-
Engage
-
Customize
-
Connect
-
Collaborate
Digital business models

Digital businesses by nature have born as native digital companies. As such they took for granted the process of digitalization that instead organizations born before of the Internet era, could not understand. That doesn’t mean those companies are superior or follow better business models.
It only implies that they learned to master the digital landscape, which is highly scalable and prone to take advantage of network effects.
Platform business models

Digital distribution channels

Digital platforms business models
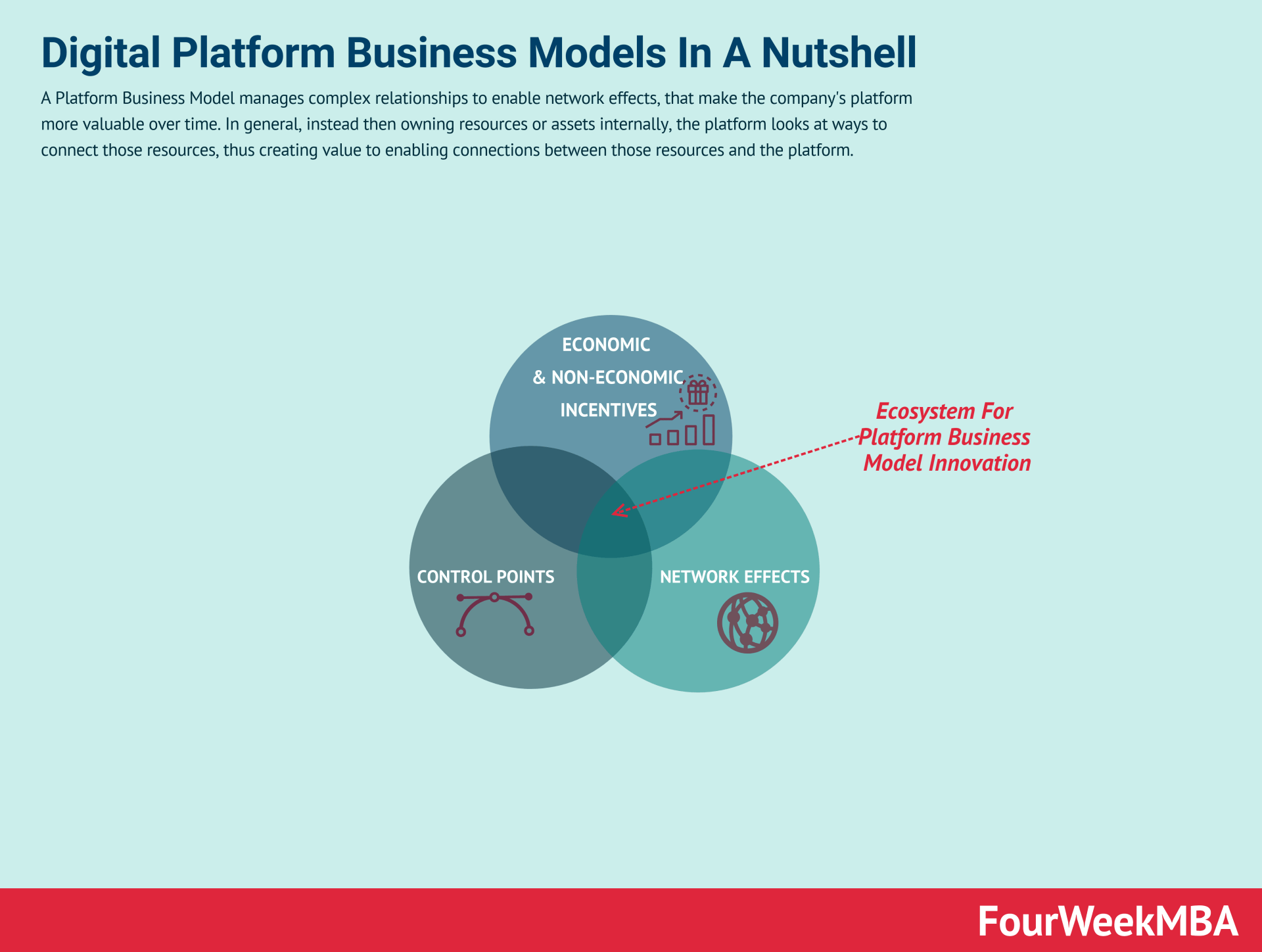
Digital platforms are focused on creating ecosystems that enable interactions among key stakeholders. When those ecosystems thrive that is when you’ve built a successful business model.
The upcoming era of Superplatforms

As the digital world enables new business playgrounds (like Blockchain-driven businesses) the whole digital trasformation playbook evolves.
In the FourWeekMBA interview to IBM’s Jerry Cuomo highlighted:
The big trick in the business playbook is to design business processes that can be worked across a team.
Business model innovation

Read Next: Business Model Innovation
In this process of business model innovation, some macro-trends and business forces have been taking place.
100 Case Studies
- Retail:
- Amazon: Amazon is a pioneer in digital transformation. They have introduced cashier-less stores like Amazon Go, where customers can shop without going through traditional checkout lines. Additionally, they’ve heavily invested in supply chain automation and drone delivery for faster shipping.
- Banking:
- Ally Bank: Ally Bank is a fully digital bank that operates exclusively online. It offers services such as online checking and savings accounts, mortgages, and auto loans, catering to customers who prefer digital banking over traditional brick-and-mortar banks.
- Healthcare:
- Philips: Philips has transitioned from being a traditional electronics company to a healthcare technology leader. They offer a range of digital health solutions, including telehealth platforms, patient monitoring devices, and AI-driven diagnostic tools.
- Automotive:
- Ford: Ford has embraced digital transformation through the development of FordPass, a mobile app that connects with their vehicles. It allows users to remotely start their cars, locate parking, and access vehicle information through their smartphones.
- Manufacturing:
- Siemens: Siemens has introduced the concept of the Digital Twin in manufacturing. This technology creates a digital replica of a physical product, allowing for real-time monitoring, simulations, and predictive maintenance.
- Hospitality:
- Hilton: Hilton’s digital transformation includes the use of the Hilton Honors mobile app, which enables guests to check-in and choose their rooms, order room service, and use their smartphones as room keys.
- Media and Entertainment:
- Disney+: Disney’s streaming service, Disney+, is a prime example of digital transformation in the media industry. It provides subscribers with on-demand access to Disney’s extensive content library, including movies and TV shows.
- Agriculture:
- John Deere: John Deere has incorporated IoT technology into its tractors and farming equipment. Farmers can collect data on soil conditions, crop health, and equipment performance to make more informed decisions and optimize yields.
- Education:
- Coursera: Coursera is an online learning platform that partners with universities and organizations to offer a wide range of courses and degrees online. It has transformed education by making high-quality learning accessible to people worldwide.
- Energy:
- Tesla: Beyond electric vehicles, Tesla is involved in energy storage and solar energy solutions. Their Powerwall product allows homeowners to store excess solar energy and use it during peak demand times.
- Telecommunications:
- AT&T: AT&T is driving digital transformation with its transition to 5G networks and the integration of software-defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV) to improve network agility and performance.
- Insurance:
- Lemonade: Lemonade is a digital insurance company that uses AI and chatbots to streamline the claims process. They provide fast and efficient service, making insurance more accessible and customer-friendly.
- Aviation:
- Boeing: Boeing utilizes digital twin technology to enhance the design and maintenance of aircraft. This enables engineers to monitor and analyze aircraft performance data in real-time, improving safety and efficiency.
- Food and Beverage:
- Domino’s: Domino’s Pizza has embraced digital transformation with an advanced online ordering system. Customers can place orders through the website or mobile app, track their delivery in real-time, and provide feedback on their experience.
- Pharmaceuticals:
- Pfizer: Pfizer utilizes data analytics and machine learning in drug discovery to accelerate the identification of potential drug candidates. This digital approach expedites the development of new medications.
- Logistics and Transportation:
- UPS: UPS employs telematics and route optimization software to enhance delivery efficiency. They also utilize sensors to monitor package conditions during transit, ensuring the safe delivery of goods.
- Real Estate:
- Zillow: Zillow has transformed the real estate industry with its online platform, allowing users to search for homes, access property information, and even buy and sell properties online.
- Fashion:
- Zara: Zara, a fashion retailer, uses data analytics and real-time inventory management to respond quickly to changing fashion trends. They’ve shortened the time between design and in-store availability.
- Government:
- Estonia: Estonia has implemented e-residency, a digital identification system that allows non-residents to access government services and conduct business online. This has streamlined bureaucracy and attracted global entrepreneurs.
- Fitness and Wellness:
- Fitbit: Fitbit’s wearable devices and mobile app enable users to track their fitness and health data, encouraging a more active and healthier lifestyle.
- Travel and Tourism:
- Airbnb: Airbnb has revolutionized the travel industry by providing a platform for people to rent accommodations from hosts worldwide. It offers a digital booking system and user reviews for transparency.
- Gaming:
- Epic Games: Epic Games, the creator of Fortnite, has embraced digital transformation by offering a digital storefront, the Epic Games Store, to compete with established gaming platforms. They also use AI for character animations.
- Consumer Electronics:
- Apple: Apple’s ecosystem of products and services, including the iPhone, iPad, Mac, and iCloud, seamlessly integrates digital technologies for a unified user experience.
- Legal Services:
- LegalZoom: LegalZoom provides online legal services, including document preparation and legal advice, making legal assistance more affordable and accessible.
- Nonprofits:
- Charity: Water: This nonprofit organization uses digital platforms to raise funds and awareness for clean water projects worldwide. They leverage social media and online campaigns for their mission.
- Human Resources:
- LinkedIn: LinkedIn is a digital platform that has transformed the way professionals network and find job opportunities. It also offers online courses and career resources.
- Advertising and Marketing:
- Google Ads: Google Ads offers businesses digital advertising solutions, including pay-per-click (PPC) advertising and targeted marketing campaigns to reach a global audience.
- Consumer Goods:
- Procter & Gamble (P&G): P&G employs digital transformation in supply chain management, using data analytics and automation to optimize inventory and distribution.
- Music:
- Spotify: Spotify has disrupted the music industry with its streaming service, giving users access to a vast library of songs and personalized playlists.
- Space Exploration:
- SpaceX: SpaceX uses digital technologies in rocket design, navigation, and autonomous landing to advance space exploration and make it more cost-effective.
- E-commerce:
- Alibaba: Alibaba, a global e-commerce giant, leverages digital technology for online marketplaces, cloud computing, and digital payments, transforming the way businesses trade internationally.
- Fashion:
- ASOS: ASOS is a digital fashion retailer known for its wide range of clothing and fashion accessories. They offer an online shopping experience with a focus on fast fashion trends.
- Travel and Hospitality:
- Expedia: Expedia is a digital travel agency that enables users to book flights, hotels, and vacation packages online, offering convenience and competitive pricing.
- Insurance:
- Aetna: Aetna uses digital health technologies to offer personalized wellness programs and virtual healthcare services to its policyholders, promoting healthier lifestyles.
- Automotive:
- General Motors (GM): GM utilizes IoT technology and OnStar services to provide vehicle connectivity, real-time diagnostics, and safety features in their vehicles.
- Fast Food:
- McDonald’s: McDonald’s has implemented digital ordering kiosks and mobile ordering apps to improve the customer experience and offer personalized menu recommendations.
- Education:
- edX: edX is an online learning platform offering courses from top universities and institutions worldwide. It promotes lifelong learning and skill development.
- Technology:
- Microsoft: Microsoft’s digital transformation includes cloud computing services (Azure), software (Office 365), and AI-driven applications to empower businesses and individuals.
- Sports:
- NBA: The NBA employs digital technologies like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) to enhance fan engagement, providing immersive experiences during games.
- Cruise Industry:
- Royal Caribbean: Royal Caribbean offers a “Smart Ship” experience with digital check-in, wearable tech, and mobile apps that allow passengers to plan activities and access services on board.
- Telecommunications:
- Verizon: Verizon’s digital transformation includes 5G network deployment, IoT solutions, and digital customer service platforms to stay at the forefront of the telecommunications industry.
- Pharmaceuticals:
- Novartis: Novartis employs data analytics and digital therapeutics to enhance drug development and patient care, aiming to improve health outcomes.
- Logistics and Delivery:
- FedEx: FedEx uses digital tracking and route optimization tools to improve package delivery efficiency and provide customers with real-time shipment updates.
- Real Estate:
- Redfin: Redfin is a digital real estate brokerage that uses technology to simplify home buying and selling, offering online property listings and virtual tours.
- Food Delivery:
- DoorDash: DoorDash is a digital food delivery platform that connects customers with local restaurants, offering a wide range of dining options with convenient delivery.
- Gaming:
- Roblox: Roblox is a digital gaming platform that allows users to create and play games developed by other users, fostering creativity and collaboration.
- Consumer Electronics:
- Sony: Sony continues to innovate in consumer electronics with products like PlayStation gaming consoles, smart TVs, and digital cameras.
- Legal Services:
- Avvo: Avvo is a digital platform that provides legal advice, ratings, and profiles of lawyers, making it easier for individuals to find legal representation.
- Nonprofits:
- Kiva: Kiva is a digital lending platform that connects lenders with borrowers in underserved communities worldwide, enabling microloans to support entrepreneurship.
- Human Resources:
- Workday: Workday offers cloud-based HR and finance software solutions for businesses, simplifying workforce management and financial operations.
- Advertising and Marketing:
- Consumer Goods:
- Unilever: Unilever utilizes digital transformation in supply chain management and sustainability efforts, focusing on reducing its environmental footprint.
- Music:
- Apple Music: Apple Music is a streaming service that offers a vast music catalog, personalized playlists, and integration with Apple devices and services.
- Space Exploration:
- NASA: NASA leverages digital technologies for space exploration, including Mars rovers, satellites, and the James Webb Space Telescope.
- E-commerce:
- eBay: eBay is a global online marketplace that enables individuals and businesses to buy and sell a wide range of products and collectibles.
- Fashion:
- H&M: H&M employs digital strategies like e-commerce, mobile shopping apps, and sustainability initiatives to adapt to changing consumer preferences.
- Travel and Hospitality:
- Booking.com: Booking.com offers digital booking services for accommodations, flights, and rental cars, providing a one-stop platform for travelers.
- Insurance:
- Progressive: Progressive uses telematics and digital claims processing to offer customers personalized auto insurance rates and efficient claims handling.
- Automotive:
- Toyota: Toyota invests in digital innovation by incorporating connected car technology and safety features in their vehicles, enhancing the driving experience.
- Fast Food:
- Starbucks: Starbucks employs digital payment options, mobile ordering, and loyalty rewards through its mobile app to enhance customer convenience.
- Education:
- Khan Academy: Khan Academy is a nonprofit educational platform offering free online lessons and resources for students and educators worldwide.
- Technology:
- IBM: IBM focuses on digital transformation through cloud computing, AI, and blockchain solutions to help businesses and industries achieve digital readiness.
- Sports:
- NFL: The NFL embraces digital transformation with streaming services, mobile apps, and digital ticketing to engage fans and deliver content.
- Cruise Industry:
- Carnival Corporation: Carnival uses digital technologies for cruise ship management, offering onboard apps and wearables for passengers and crew.
- Telecommunications:
- T-Mobile: T-Mobile leads in digital customer service and 5G network expansion, delivering faster connectivity and innovative wireless plans.
- Pharmaceuticals:
- Merck: Merck leverages digital tools for drug discovery, clinical trials, and patient engagement to advance healthcare solutions.
- Logistics and Delivery:
- DHL: DHL employs digital supply chain solutions, including IoT-enabled tracking and autonomous delivery robots, to optimize logistics operations.
- Real Estate:
- Trulia: Trulia is a digital platform that offers property listings, neighborhood insights, and real estate tools for homebuyers and renters.
- Food Delivery:
- Grubhub: Grubhub provides digital food delivery and pickup services, partnering with restaurants to offer a wide range of cuisines.
- Gaming:
- PlayStation Network: PlayStation Network offers online gaming, digital game downloads, and multiplayer experiences for PlayStation console users.
- Consumer Electronics:
- Samsung: Samsung continues to innovate in consumer electronics, including smartphones, smart home devices, and 8K TVs.
- Legal Services:
- Rocket Lawyer: Rocket Lawyer is a digital legal platform that offers legal documents, attorney services, and business compliance tools online.
- Nonprofits:
- DonorsChoose: DonorsChoose is a digital crowdfunding platform that connects donors with classroom projects, supporting educational initiatives.
- Human Resources:
- BambooHR: BambooHR provides cloud-based HR software for small and medium-sized businesses, simplifying HR management tasks.
- Advertising and Marketing:
- Adobe: Adobe offers digital marketing and creative software solutions, empowering businesses to create and optimize digital content.
- Consumer Goods:
- Coca-Cola: Coca-Cola utilizes digital marketing and data analytics to engage consumers and optimize product distribution.
- Music:
- Spotify: Spotify offers a music streaming service with personalized playlists, podcasts, and artist discovery features.
- Space Exploration:
- Blue Origin: Blue Origin focuses on commercial space travel and exploration, utilizing reusable rockets and spacecraft.
- E-commerce:
- Shopify: Shopify provides e-commerce platforms and tools for businesses to create online stores and manage digital sales.
- Fashion:
- Burberry: Burberry integrates digital technology into its fashion shows, retail stores, and customer experiences, embracing innovation.
- Travel and Hospitality:
- Airbnb Experiences: Airbnb Experiences offers unique and digital-based travel activities hosted by locals, enhancing cultural immersion.
- Insurance:
- Allstate: Allstate uses digital telematics, mobile apps, and predictive analytics to offer personalized insurance coverage and safe driving incentives.
- Automotive:
- Volkswagen: Volkswagen invests in electric and autonomous vehicles, incorporating digital cockpit technology and connectivity features.
- Fast Food:
- Subway: Subway employs digital ordering kiosks, mobile app rewards, and online catering services for customer convenience.
- Education:
- Udemy: Udemy is an online learning marketplace with a wide range of courses taught by instructors worldwide, catering to diverse learning needs.
- Technology:
- Intel: Intel advances digital transformation through semiconductor innovation, AI technology, and data center solutions for various industries.
- Sports:
- MLB Advanced Media: MLB Advanced Media provides digital content streaming, online ticketing, and fan engagement for Major League Baseball.
- Cruise Industry:
- Norwegian Cruise Line: Norwegian Cruise Line adopts digital cruise planning and onboard technology to enhance the guest experience.
- Telecommunications:
- Sprint: Sprint focuses on digital customer service and expanding its 5G network to provide high-speed connectivity for consumers and businesses.
- Pharmaceuticals:
- Johnson & Johnson: Johnson & Johnson leverages digital health solutions and remote patient monitoring for healthcare innovation.
- Logistics and Delivery:
- Amazon Logistics: Amazon Logistics offers end-to-end package delivery solutions, including delivery vans, tracking systems, and same-day delivery options.
- Real Estate:
- Redfin: Redfin utilizes digital technology to simplify the home buying and selling process, offering online listings, virtual tours, and transparent pricing.
- Food Delivery:
- Uber Eats: Uber Eats provides a digital food delivery platform with a vast selection of restaurants and contactless delivery options.
- Gaming:
- Xbox Live: Xbox Live offers an online gaming platform with multiplayer capabilities, digital game downloads, and social gaming experiences.
- Consumer Electronics:
- LG Electronics: LG Electronics develops digital home appliances, OLED displays, and smart home solutions for modern living.
- Legal Services:
- LegalMatch: LegalMatch is a digital legal marketplace that connects individuals with attorneys for legal consultations and representation.
- Nonprofits:
- Charity: Water: Charity: Water leverages digital fundraising campaigns and transparency initiatives to provide clean water access globally.
- Human Resources:
- ADP: ADP offers digital HR and payroll solutions for businesses, streamlining workforce management and compliance.
- Advertising and Marketing:
- Facebook Ads: Facebook Ads provides a digital advertising platform for businesses to reach a targeted audience on social media.
- Consumer Goods:
- Nestlé: Nestlé employs digital marketing, e-commerce platforms, and data analytics to optimize product distribution and consumer engagement.
Key Highlights
- Definition of Digital Transformation: Digital transformation involves leveraging digital technologies and capabilities to fundamentally change and improve how a business operates, interacts with customers, and delivers value. It goes beyond simple digital distribution and requires a shift in mindset and approach to adapt to dynamic markets.
- Myth: Digital Transformation Equals Digital Distribution
Many companies mistakenly equate digital transformation with merely advertising products online. True digital transformation involves a complete overhaul of the business model, not just using digital channels for distribution. - Myth: Technology Alone Drives Digital Transformation
While technology plays a crucial role in the transformation process, it is not the sole driver. A fundamental shift in the organization’s mindset and culture is equally important for successful digital transformation. - Myth: Digital Transformation is a Side Project
Treating digital transformation as a side project with minimal investment is a mistake. It requires a deep understanding of digital business models and should be approached strategically with long-term goals. - Myth: Digitalization Equals Digital Transformation
Merely digitizing existing processes or content does not equate to digital transformation. True transformation involves rethinking the entire business model to leverage digital technologies effectively. - Dynamic Thinking and Dynamic Markets
Digital transformation demands a more dynamic thinking process due to the added complexity of digital channels. Organizations must be aware of the core aspects of their business that require control while adapting to dynamic market changes. - Mastering Key Customer Behaviors
Successful digital transformation involves understanding and responding to key customer behaviors that shape the business. Five common behaviors include access, engage, customize, connect, and collaborate. - Digital Business Models
Digital business models leverage digital technology to enhance various aspects of an organization, including customer interactions, value proposition, and monetization. Native digital companies are well-positioned to take advantage of scalable and network-effect-driven landscapes. - Platform Business Models
Platform business models create value by facilitating interactions between users, leveraging network effects. These models usually have two sides: supply and demand, and success depends on kickstarting interactions between them. - Digital Distribution Channels
Digital distribution channels refer to the steps a product takes to reach customers. These can be direct or indirect, physical or digital, depending on the industry and business type. - Digital Platforms Business Models
Digital platforms focus on creating ecosystems that enable interactions among stakeholders. Successful platforms build thriving ecosystems that contribute to their success. - The Upcoming Era of Superplatforms
As new technologies like Blockchain-driven businesses emerge, the digital transformation playbook evolves. Businesses must design processes that can be executed across teams for success. - Business Model Innovation
Business model innovation involves crafting compelling value propositions and new business models to scale up customers and gain a competitive advantage. Mastering key customers is the foundation of this process.
Read Next: Business Model Innovation, Business Models.
Related Innovation Frameworks















Other resources for your business:
- Types of Business Models You Need to Know
- The Complete Guide To Business Development
- Business Strategy Examples
- What Is a Business Model Canvas? Business Model Canvas Explained
- Blitzscaling Business Model Innovation Canvas In A Nutshell
- What Is a Value Proposition? Value Proposition Canvas Explained
- What Is a Lean Startup Canvas? Lean Startup Canvas Explained
- What Is Market Segmentation? the Ultimate Guide to Market Segmentation
- Marketing Strategy: Definition, Types, And Examples
- Marketing vs. Sales: How to Use Sales Processes to Grow Your Business
- How To Write A Mission Statement
- What is Growth Hacking?









