Uber Eats faces competition from various players in the food delivery market. Key competitors include DoorDash, Grubhub, Postmates, Deliveroo, Just Eat, Zomato, Swiggy, Glovo, Caviar, and Seamless. These platforms connect customers with local restaurants and provide on-demand food delivery services, offering a wide range of options for consumers.
| Competitor | Description | Key Insights | Competitive Overlap | Differentiation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DoorDash | A food delivery platform offering delivery from various restaurants. DoorDash competes directly with Uber Eats in the on-demand food delivery market. | DoorDash provides food delivery services from a wide range of restaurants, directly competing with Uber Eats in segments like on-demand delivery, targeting consumers looking for convenient meal options. | Both compete in the on-demand food delivery market, offering delivery from local restaurants, with DoorDash’s focus on restaurant partnerships and a strong presence in North America. | DoorDash’s extensive restaurant partnerships and North American market dominance. |
| Grubhub | An online food ordering and delivery platform that connects users to local restaurants. Grubhub competes with Uber Eats in the online food delivery and ordering sector. | Grubhub offers online food ordering and delivery services, directly competing with Uber Eats in segments like online restaurant partnerships and meal delivery, targeting users looking for a variety of dining options. | Both compete in the online food delivery and ordering market, connecting users with local restaurants, with Grubhub’s focus on an extensive restaurant network and order-ahead capabilities. | Grubhub’s extensive restaurant network and order-ahead options. |
| Postmates | A delivery platform that offers on-demand delivery from local restaurants and stores. Postmates competes with Uber Eats in the on-demand delivery market. | Postmates provides on-demand delivery services for food, groceries, and more, directly competing with Uber Eats in segments like local restaurant delivery and convenience items, targeting users seeking quick and flexible delivery options. | Both compete in the on-demand delivery market, offering delivery from restaurants and stores, with Postmates’ focus on a wide range of delivery categories and flexibility. | Postmates’ diverse delivery offerings and flexibility. |
| GrubMarket | An online marketplace for farm-fresh and locally-sourced food products, including meal kits and groceries. GrubMarket competes with Uber Eats in the food delivery and grocery delivery sector. | GrubMarket offers online access to fresh food products and meal kits, directly competing with Uber Eats in segments like meal kit delivery and grocery delivery, targeting consumers interested in cooking at home with high-quality ingredients. | Both compete in the food delivery and grocery delivery market, offering access to fresh food products, with GrubMarket’s focus on sourcing locally and supporting small farms. | GrubMarket’s emphasis on fresh and locally-sourced ingredients. |
| Instacart | An online grocery delivery and pickup service that partners with various grocery stores. Instacart competes with Uber Eats in the grocery delivery and convenience sector. | Instacart offers online grocery ordering and delivery from multiple grocery stores, directly competing with Uber Eats in segments like grocery and convenience item delivery, targeting users looking for a convenient way to shop for groceries online. | Both compete in the grocery delivery and convenience market, offering access to grocery store products, with Instacart’s focus on partnerships with major grocery chains and diverse product offerings. | Instacart’s partnerships with major grocery chains and wide product selection. |
| Just Eat Takeaway | A global food ordering and delivery company that connects users to local restaurants. Just Eat Takeaway competes with Uber Eats in the global online food delivery market. | Just Eat Takeaway provides online food ordering and delivery services in various countries, directly competing with Uber Eats in segments like global restaurant partnerships and international delivery, targeting users looking for diverse cuisine options. | Both compete in the global online food delivery market, connecting users with local restaurants worldwide, with Just Eat Takeaway’s focus on international expansion and diverse restaurant offerings. | Just Eat Takeaway’s international presence and diverse cuisine options. |
| Deliveroo | A food delivery platform offering restaurant delivery and food pickup services. Deliveroo competes with Uber Eats in the restaurant food delivery market. | Deliveroo provides restaurant food delivery and pickup services, directly competing with Uber Eats in segments like restaurant partnerships and quick delivery, targeting users seeking restaurant-quality meals at home. | Both compete in the restaurant food delivery market, offering delivery from local restaurants, with Deliveroo’s focus on partnerships with premium restaurants and fast delivery. | Deliveroo’s partnerships with premium restaurants and focus on quality. |
| Caviar | A premium food delivery service offering delivery from upscale restaurants. Caviar competes with Uber Eats in the premium restaurant delivery and gourmet food sector. | Caviar provides premium food delivery from upscale restaurants, directly competing with Uber Eats in segments like gourmet cuisine and high-end restaurant delivery, targeting users looking for upscale dining experiences at home. | Both compete in the premium restaurant delivery and gourmet food market, offering delivery from high-end restaurants, with Caviar’s focus on upscale dining options and curated menus. | Caviar’s emphasis on upscale dining experiences and curated menus. |
| Seamless | An online food ordering and delivery platform that connects users to local restaurants. Seamless competes with Uber Eats in the online food delivery and ordering sector. | Seamless offers online food ordering and delivery services, directly competing with Uber Eats in segments like online restaurant partnerships and meal delivery, targeting users looking for a variety of dining options. | Both compete in the online food delivery and ordering market, connecting users with local restaurants, with Seamless’ focus on a user-friendly ordering experience and wide restaurant selection. | Seamless’ user-friendly interface and restaurant variety. |
| Zomato | An online restaurant discovery and food delivery platform operating in multiple countries. Zomato competes with Uber Eats in the global online food delivery and restaurant discovery market. | Zomato offers restaurant discovery and food delivery services in various countries, directly competing with Uber Eats in segments like global restaurant partnerships and international food delivery, targeting users seeking diverse cuisine options and restaurant recommendations. | Both compete in the global online food delivery and restaurant discovery market, connecting users with local restaurants worldwide, with Zomato’s focus on restaurant reviews and recommendations. | Zomato’s emphasis on restaurant discovery and recommendations. |
- DoorDash: An on-demand food delivery platform that partners with restaurants to offer delivery services.
- Grubhub: A leading food delivery platform connecting restaurants with customers through its website and app.
- Postmates: A versatile delivery platform that delivers food, groceries, and other goods.
- Deliveroo: A food delivery company operating in multiple countries, connecting customers with local restaurants.
- Just Eat: An online food delivery service facilitating orders from a wide range of restaurants.
- Zomato: A popular restaurant search and discovery platform that also offers food delivery services.
- Swiggy: An India-based online food ordering and delivery platform with a large network of restaurant partners.
- Glovo: A delivery platform providing on-demand services for food, groceries, and other products.
- Caviar: A premium food delivery service specializing in high-quality cuisine and partnering with select restaurants.
- Seamless: An online food ordering platform serving numerous cities across the United States, known for its extensive restaurant selection.
Visual Stories Related To Uber Business Model





In 2022, Uber mobility took 27% of each booking on the platform. At the same time, Uber Eats took 20% of each booking on the delivery platform. The take rate varies according to demand and supply but also market dynamics. In short, in periods of increased competition, the service might charge lower take rates to keep up with it. In 2022, Uber pushed on efficiency, thus raising its take rates, to move toward profitability.
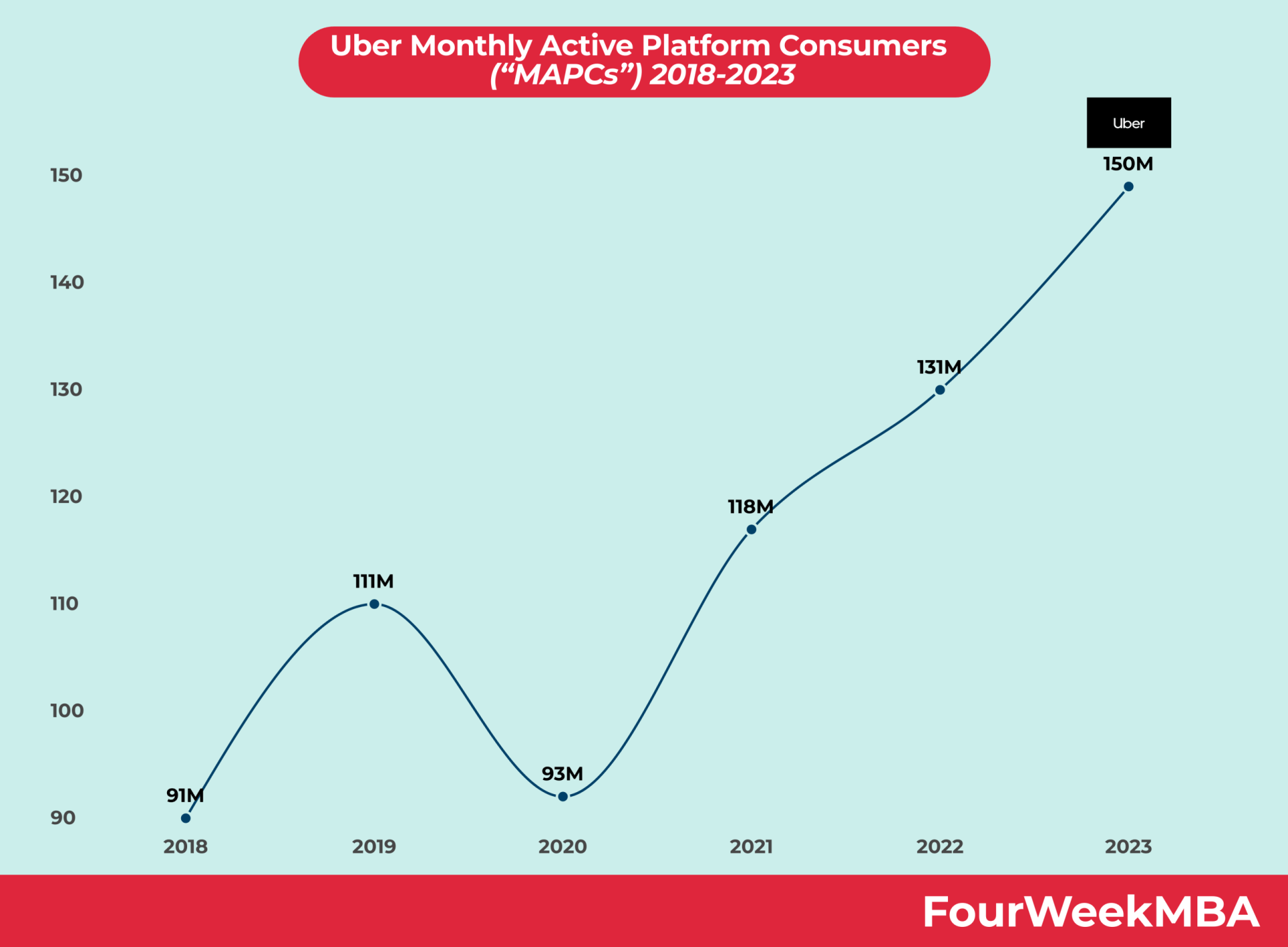
Uber Platform Users