Entrepreneurs and business people can enhance their memory and understanding by using a few simple techniques.
| Memory/Learning Technique | Description | When to Use or Apply | Key Components and Processes | Advantages | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method of Loci | A mnemonic technique that involves associating information with points along an imaginary journey to aid memory recall. | For memorizing information with a specific order. | Imaginary journey, association with locations. | Effective for sequential recall, creative visualization. | Limited to structured information recall. |
| Feynman Technique | A method for learning and understanding complex topics by simplifying and explaining them in plain language. | In exam preparation and when tackling complex subjects. | Simplification, explanation, teaching others. | Enhances understanding, promotes active learning. | Requires time and effort for explanation. |
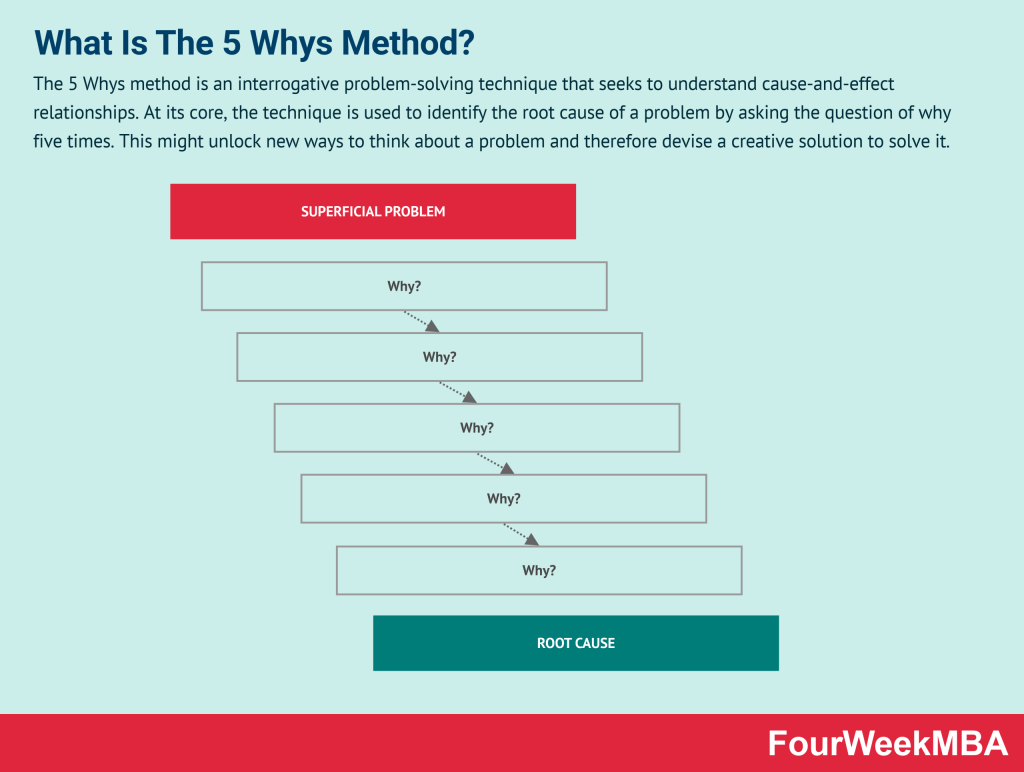
| 5 Whys Method | An interrogative problem-solving technique that uncovers the root cause of problems by repeatedly asking “why” questions. | For identifying root causes of complex problems. | Repeatedly asking “why” questions, uncovering deeper causes. | Encourages critical thinking, creative problem-solving. | May not work for all types of problems. |
| Active Recall | A technique for moving information from short-term to long-term memory through retrieval practice. | When aiming to retain information in long-term memory. | Retrieval practice, self-testing, recalling information. | Enhances long-term retention, improves learning efficiency. | Requires consistent practice and effort. |
| Forgetting Curve | A graphical representation of how information is lost over time if not actively retained or reviewed. | To understand the importance of review and repetition. | Time-based memory decay, importance of review. | Highlights the need for effective learning strategies. | May not offer specific strategies for retention. |
| Cognitive Load Theory | A theory that focuses on optimizing instructional design by considering the limits of working memory. | When designing educational materials or training programs. | Working memory limitations, cognitive load, instructional design. | Enhances learning efficiency, guides effective design. | May require adjustments to existing materials. |
| Spaced Repetition | A technique involving spaced reviews of information at increasing intervals to enhance long-term memory retention. | For efficient memorization and long-term retention. | Interval-based review schedule, repeated exposure to content. | Maximizes retention, reduces time and effort for learning. | Requires structured scheduling and discipline. |
Method of Loci

Feynman Technique

5 Whys Method
Active Recall

Forgetting Curve

Cognitive Load Theory

Spaced Repetition

Memory and Understanding Enhancement Techniques
- Method of Loci:
- How it works: Create a mental journey with specific locations or landmarks. Associate the information you want to remember with each location. When you need to recall the information, mentally walk through the journey to retrieve it.
- Benefits: Enhances memory by connecting information to spatial cues. Effective for lists, sequences, and ordered data.
- Feynman Technique:
- How it works: Choose a concept or topic you want to understand. Explain it as if you were teaching it to someone else, using simple language and examples. Identify gaps in your knowledge and revise until you can explain it clearly.
- Benefits: Deepens understanding, exposes areas of weakness, and simplifies complex ideas.
- 5 Whys Method:
- Active Recall:
- How it works: Instead of simply rereading or reviewing material, actively test your memory by recalling information from memory. This practice strengthens memory retention.
- Benefits: Improves long-term retention, reinforces learning, and enhances recall during exams or presentations.
- Forgetting Curve:
- How it works: The forgetting curve illustrates the decline in memory retention over time without active review or rehearsal. To combat this curve, schedule periodic reviews of material.
- Benefits: Maximizes memory retention and minimizes the loss of learned information over time.
- Cognitive Load Theory:
- How it works: Recognize the limits of working memory and design learning materials or presentations that minimize cognitive overload. Simplify complex content and focus on key concepts.
- Benefits: Enhances comprehension and learning efficiency by reducing cognitive strain on the brain.
- Spaced Repetition:
- How it works: Space out review sessions over increasing intervals. Start with frequent reviews and gradually extend the time between them. This technique leverages the psychological spacing effect to improve long-term retention.
- Benefits: Maximizes the transfer of information from short-term to long-term memory, leading to better recall and understanding.
- Chunking:
- How it works: Break down complex information into smaller, manageable chunks or groups. Organize related items into meaningful clusters.
- Benefits: Simplifies the processing of large amounts of information, making it easier to remember and understand.
- Mind Mapping:
- How it works: Create visual representations of information by connecting related concepts or ideas using branches and nodes. Mind maps are effective for organizing thoughts and grasping complex subjects.
- Benefits: Enhances understanding, stimulates creativity, and aids in brainstorming and problem-solving.
- Visualization:
- How it works: Create mental images or visual representations of concepts, facts, or processes you want to remember. Visualization engages the brain’s visual memory.
- Benefits: Improves memory recall by associating information with vivid mental images.
- Mnemonic Devices:
- How they work: Mnemonics are memory aids, such as acronyms, rhymes, or associations, used to remember specific information or sequences.
- Benefits: Facilitates recall by providing memorable cues or patterns.
- Dual Coding:
- How it works: Combine verbal and visual information when learning. For example, read text and create visual diagrams or drawings related to the content.
- Benefits: Enhances memory by encoding information through multiple channels (verbal and visual).
Read Next: Mnemonic Techniques
Related Strategy Concepts: Read Next: Mental Models, Biases, Bounded Rationality, Mandela Effect, Dunning-Kruger Effect, Lindy Effect, Crowding Out Effect, Bandwagon Effect, Decision-Making Matrix.







