D’Aveni’s 7S framework was created by strategy expert Richard A. D’Aveni. D’Aveni’s 7S framework is an approach to directing an organization in high velocity or hypercompetitive markets. The framework was designed to enable a business to remain competitive through a series of initiatives delivering temporary advantages. According to D’Aveni, this strategy is preferable to restructuring the business to maintain equilibrium or sustain competitive advantage.
| Element | Description | Implications | Key Characteristics | Examples | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategy | The overall plan and approach to achieve organizational goals. | – Ensures strategic alignment. – Guides decision-making. – Shapes the organization’s direction. | – Integral to the organization’s competitive positioning. – Requires adaptability in response to market changes. – Long-term focus on strategic goals. | – A technology company’s strategy emphasizes innovation and rapid product development. – A healthcare organization’s strategy focuses on patient-centered care and ethical practices. – A startup’s strategy is to disrupt an existing market with innovative solutions. | – Strategic Assessment: Use the framework to assess and understand an organization’s competitive position and adaptability. – Strategic Planning: Identify areas for improvement and formulate strategies based on the analysis. – Organizational Alignment: Ensure alignment among various internal components to support strategic goals. – Competitive Analysis: Evaluate the competitive landscape and position of the organization within it. |
| Structure | The organization’s hierarchical setup and division of responsibilities. | – Defines roles and responsibilities. – Influences communication and decision-making. – Impacts efficiency and agility. | – Reflects the organization’s hierarchy. – Can hinder or facilitate coordination. – Determines reporting relationships. | – A traditional hierarchical structure with clearly defined roles and reporting lines. – A flat organizational structure with a focus on collaboration and minimal hierarchy. – A matrix organizational structure that balances functional expertise and project-based teams. | – Strategic Assessment: Use the framework to assess and understand an organization’s competitive position and adaptability. – Strategic Planning: Identify areas for improvement and formulate strategies based on the analysis. – Organizational Alignment: Ensure alignment among various internal components to support strategic goals. – Competitive Analysis: Evaluate the competitive landscape and position of the organization within it. |
| Systems | The processes and procedures that drive operations and decision-making. | – Influences how work is done. – Impacts efficiency, quality, and consistency. – Supports or hinders innovation. | – Reflects workflow and decision flow. – Can be formal or informal. – Includes technology, workflows, and routines. | – An organization has well-defined, automated processes for order fulfillment. – An organization relies on agile methodologies and flexible workflows for software development. – An organization follows strict compliance procedures in regulatory industries. | – Strategic Assessment: Use the framework to assess and understand an organization’s competitive position and adaptability. – Strategic Planning: Identify areas for improvement and formulate strategies based on the analysis. – Organizational Alignment: Ensure alignment among various internal components to support strategic goals. – Competitive Analysis: Evaluate the competitive landscape and position of the organization within it. |
| Shared Values | The core beliefs, culture, and values that guide behavior within the organization. | – Shapes organizational culture. – Influences employee behavior and decision-making. – Drives alignment with the mission and vision. | – Reflects the organization’s culture. – Provides a sense of purpose and identity. – Guides how employees interact and make choices. | – A company values innovation, risk-taking, and creativity, fostering an entrepreneurial culture. – A healthcare organization’s shared values prioritize patient-centered care and ethical practices. – An organization values teamwork and collaboration, promoting a culture of inclusivity. | – Strategic Assessment: Use the framework to assess and understand an organization’s competitive position and adaptability. – Strategic Planning: Identify areas for improvement and formulate strategies based on the analysis. – Organizational Alignment: Ensure alignment among various internal components to support strategic goals. – Competitive Analysis: Evaluate the competitive landscape and position of the organization within it. |
| Skills | The competencies and capabilities possessed by employees within the organization. | – Influences the organization’s ability to execute strategies. – Shapes the level of expertise and innovation potential. | – Reflects the skills and expertise of the workforce. – Requires continuous development and upskilling. – Can be a source of competitive advantage. | – A technology company hires data scientists and engineers with expertise in artificial intelligence. – An educational institution invests in faculty development to enhance teaching and research capabilities. – A startup’s team possesses diverse skills in software development, design, and marketing. | – Strategic Assessment: Use the framework to assess and understand an organization’s competitive position and adaptability. – Strategic Planning: Identify areas for improvement and formulate strategies based on the analysis. – Organizational Alignment: Ensure alignment among various internal components to support strategic goals. – Competitive Analysis: Evaluate the competitive landscape and position of the organization within it. |
| Staff | The human resources, skills, and competencies within the organization. | – Determines the quality of the workforce. – Impacts recruitment and talent development strategies. | – Reflects the composition of the workforce. – Requires talent acquisition, retention, and development efforts. – Influences organizational capabilities. | – An organization hires experienced professionals in the field of artificial intelligence to advance its capabilities. – A healthcare provider invests in training and development programs to enhance clinical staff expertise. – A tech startup recruits fresh graduates to infuse new perspectives and energy into the team. | – Strategic Assessment: Use the framework to assess and understand an organization’s competitive position and adaptability. – Strategic Planning: Identify areas for improvement and formulate strategies based on the analysis. – Organizational Alignment: Ensure alignment among various internal components to support strategic goals. – Competitive Analysis: Evaluate the competitive landscape and position of the organization within it. |
| Style | The leadership and management styles employed within the organization. | – Influences organizational culture and communication. – Shapes decision-making and employee engagement. | – Reflects the leadership approach of top executives and managers. – Can be autocratic, participative, transformational, or other styles. | – An organization’s leadership style is characterized by a collaborative and participative approach, fostering open communication. – A traditional organization follows an autocratic leadership style with centralized decision-making. – A startup’s leadership style is entrepreneurial and adaptive to rapid changes. | – Strategic Assessment: Use the framework to assess and understand an organization’s competitive position and adaptability. – Strategic Planning: Identify areas for improvement and formulate strategies based on the analysis. – Organizational Alignment: Ensure alignment among various internal components to support strategic goals. – Competitive Analysis: Evaluate the competitive landscape and position of the organization within it. |
Understanding D’Aveni’s 7S framework
D’Aveni’s 7S framework was created by strategy expert Richard A. D’Aveni.
The framework was designed to enable a business to remain competitive through a series of initiatives delivering temporary advantages.
According to D’Aveni, this strategy is preferable to restructuring the business to maintain equilibrium or sustain competitive advantage.
In other words, D’Aveni believes that sustaining a competitive advantage in the modern era is impossible.
Traditionally, slow-moving and stable markets were dominated by one or two major players.
In a new era that D’Aveni calls hyper-competition, firms move quickly to disrupt the competitive advantage of market leaders.
Hyper-competition is caused by several factors, including:
- Fragmentation of customer preferences.
- Rapid technological change.
- The diminishing of geographic and industrial barriers due to globalization.
- Significant global alliances among competitors with deep pockets.
In this environment, competitive advantage is no longer sustained but continually created, eroded, destroyed, and then recreated through strategic maneuvering.
The core components of the 7S framework
D’Aveni believes that a set of seven guidelines will help businesses sustain success in the hypercompetitive era.
Let’s take a look at each in more detail.
Stakeholder satisfaction is key to winning interactions with a competitor
The most important stakeholder is the customer, but employees are also crucial to success.
They must be empowered and motivated to generate new means of delivering value to the customer.
Strategic soothsaying
It describes the process of proactively predicting what consumers will want or need in the future.
Speed is vital
Both in responding to counterattacks and taking advantage of opportunities.
Businesses should use the element of surprise to stun their competitors
While IBM was attempting to dominate the personal computer market with a strong brand and sales force, it was blindsided by Dell and its highly successful direct mail and telephone sales distribution network.
Pay attention to signals, or announcements of strategic intent to dominate
When effective, signals can be used to manipulate the future moves of competitors.
Shifting the rules of a market can greatly disrupt rival companies
For better or worse, Gillette changed the rules of the shaving market when it introduced the disposable razor.
This shifted the focus of the market from quality and price to convenience.
Here, aspects of Game theory can be used to guide strategic options.
Simultaneous or sequential thrusts describe an organization using several moves in quick succession
A classic example is a series of product announcements in different geographic markets to mislead or confuse a competitor.
Drawbacks of the 7S Framework
Over-Simplification of Complexities:
- Limited Depth: While offering a broad overview, the 7S Framework may oversimplify complex organizational dynamics and challenges.
- Lacks Quantitative Analysis: The model primarily focuses on qualitative aspects, potentially overlooking the quantitative measures crucial for organizational assessment.
Potential for Misalignment:
- Difficult to Achieve Balance: Ensuring all seven elements are aligned and mutually reinforcing can be challenging, especially in large or complex organizations.
- Static Model: The framework can be seen as static, potentially not accounting for the dynamic and evolving nature of organizations.
Implementation Challenges:
- Broad and Abstract Concepts: Some elements of the 7S (like ‘Shared Values’) are abstract, making them difficult to analyze and implement changes effectively.
- Resource Intensive: Comprehensive application of the 7S Framework requires substantial time and effort, particularly in terms of planning and employee involvement.
Lack of Focus on External Environment:
- Internal Focus: The 7S model is predominantly inward-looking and may not adequately address the impact of external environmental factors on the organization.
When to Use the 7S Framework
Suitable Scenarios:
- Organizational Realignments: Useful during mergers, acquisitions, or any major organizational restructuring that requires a holistic understanding of the organization.
- Performance Improvement Initiatives: Can be employed to diagnose and improve organizational performance issues.
- Change Management: Helpful in planning and managing significant organizational changes.
Strategic Application:
- Assessing Organizational Health: Provides a framework for evaluating the effectiveness of the internal functioning of an organization.
- Aligning Departments and Processes: Useful for ensuring various departments and processes are aligned with the overall strategy and shared values.
How to Use the 7S Framework
Applying the 7S Elements:
- Strategy: Assess and align organizational strategies with market and internal capabilities.
- Structure: Evaluate the organizational structure for efficiency and effectiveness.
- Systems: Analyze the systems and procedures in place and how they support the strategy and structure.
- Shared Values: Understand and align core values and corporate culture with strategic objectives.
- Style: Examine leadership styles and their impact on the organization and culture.
- Staff: Assess the capabilities, development, and alignment of staff with organizational goals.
- Skills: Evaluate the skills and competencies present within the organization and their alignment with strategic needs.
Implementation Considerations:
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Conduct a thorough assessment of each element and their interdependencies.
- Balanced Approach: Strive for a balance across all elements, ensuring they support and reinforce each other.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly review and adapt each element to align with evolving organizational strategies and market conditions.
What to Expect from Implementing the 7S Framework
Enhanced Organizational Alignment:
- Improved Cohesion: Promotes better alignment and cohesion across various organizational aspects.
- Holistic Perspective: Encourages a more comprehensive view of the organization’s functioning and its core elements.
Potential Implementation Challenges:
- Complex Integration: Aligning all seven elements can be complex and may require substantial organizational change.
- Change Resistance: Potential resistance from employees and management due to changes in established processes or cultural norms.
Impact on Organizational Effectiveness:
- Increased Effectiveness and Efficiency: Can lead to improvements in organizational effectiveness and operational efficiency.
- Supports Strategic Implementation: Aids in the effective implementation of new strategies and organizational changes.
Long-Term Organizational Benefits:
- Sustained Organizational Health: Aids in maintaining the long-term health and competitiveness of the organization.
- Cultural and Strategic Alignment: Enhances the alignment of organizational culture with strategy, leading to more cohesive and effective operations.
Examples and Case Studies
Technology Industry
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: Companies prioritize user experience and customer satisfaction, offering innovative products and responsive customer support.
- Strategic Soothsaying: Anticipating future technology trends, companies invest in R&D to develop cutting-edge products and services.
- Speed: Quick response to market shifts, such as the rapid development of new smartphone models in response to consumer demand.
- Surprise Factor: Apple’s introduction of the iPod disrupted the music industry by providing a convenient digital solution for music consumption.
- Signal Interpretation: Companies closely analyze competitors’ announcements and actions to predict their next moves.
- Shift Market Rules: Amazon’s introduction of the Kindle shifted the publishing industry’s focus to e-books and digital content.
- Simultaneous or Sequential Thrusts: Google’s launch of multiple interconnected products like Google Search, Android OS, and Google Maps created a complex ecosystem.
Fast Fashion Retail
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: Retailers prioritize understanding consumer preferences and delivering trendy and affordable clothing.
- Strategic Soothsaying: Predicting upcoming fashion trends to design collections that resonate with consumers.
- Speed: Rapid production and distribution of new fashion items in response to emerging trends.
- Surprise Factor: Zara’s “fast fashion” model surprised competitors by reducing time between design and store placement.
- Signal Interpretation: Monitoring competitors’ moves and adjusting pricing and inventory based on market signals.
- Shift Market Rules: Fast fashion retailers shifted the traditional seasonal fashion calendar by introducing new collections more frequently.
- Simultaneous or Sequential Thrusts: H&M’s multiple designer collaborations generated excitement and boosted sales.
Ride-Sharing Industry
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: Prioritizing both rider and driver satisfaction through features, incentives, and support.
- Strategic Soothsaying: Anticipating changing transportation trends and investing in autonomous vehicle technology.
- Speed: Quick adaptation to regulatory changes and introduction of new services like ride-sharing for food delivery.
- Surprise Factor: Uber’s innovative ride-sharing concept disrupted traditional taxi services globally.
- Signal Interpretation: Competitors closely monitor each other’s expansion plans to strategize their own growth.
- Shift Market Rules: Introduction of shared mobility options challenged the dominance of personal vehicle ownership.
- Simultaneous or Sequential Thrusts: Lyft’s launch of electric scooter and bike rentals expanded its transportation offerings.
Smartphone Industry
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: Manufacturers focus on delivering user-friendly devices and value-added features.
- Strategic Soothsaying: Predicting technological advancements and consumer needs, such as improved camera technology.
- Speed: Rapid development and release of new smartphone models to stay ahead of competitors.
- Surprise Factor: Samsung’s introduction of foldable smartphones surprised the market with a novel form factor.
- Signal Interpretation: Companies analyze competitors’ patent filings and research projects to predict future innovations.
- Shift Market Rules: Apple’s introduction of the iPhone shifted mobile phones from communication tools to personal computing devices.
- Simultaneous or Sequential Thrusts: Huawei’s expansion into various markets and segments propelled its global presence.
Streaming Entertainment
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: Platforms prioritize content quality and user experience to attract and retain subscribers.
- Strategic Soothsaying: Predicting trends in content consumption, leading to original content production and licensing.
- Speed: Quick adaptation to changing viewer preferences, such as the rise of binge-watching.
- Surprise Factor: Netflix’s transition from a DVD rental service to a streaming giant disrupted traditional entertainment distribution.
- Signal Interpretation: Competitors analyze content acquisitions and partnerships to anticipate platform strategies.
- Shift Market Rules: Streaming platforms shifted viewing habits from traditional TV schedules to on-demand streaming.
- Simultaneous or Sequential Thrusts: Disney+ launched with a vast library of content and original series to compete in the streaming market.
Key takeaways
- D’Aveni’s 7S framework helps businesses become more successful in high velocity or hypercompetitive markets.
- D’Aveni’s 7S framework argues that slow and stable markets dominated by one or two major players are a thing of the past. In this new era, every business must make rapid and concerted moves to disrupt the competitive advantage of market leaders.
- D’Aveni’s 7S framework is underpinned by seven guidelines or best practices. They suggest possible strategies for success in markets where competitive advantage is continually being destroyed and recreated.
Key Highlights
- Definition: D’Aveni’s 7S Framework, created by strategy expert Richard A. D’Aveni, is a strategic approach designed for businesses to thrive in high-velocity or hypercompetitive markets. It emphasizes a series of initiatives to achieve temporary advantages over traditional methods of sustaining equilibrium or long-term competitive advantage.
- Hypercompetition Era: D’Aveni’s framework is born out of the realization that traditional sustained competitive advantage is no longer feasible in the hypercompetitive era. Factors such as fragmented customer preferences, rapid technological change, globalization, and strategic alliances among competitors contribute to this dynamic environment.
- Core Components:
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: Prioritize customer and employee satisfaction. Empower employees to innovate and deliver value to customers.
- Strategic Soothsaying: Proactively predict future consumer needs or desires.
- Speed: Rapid response to counterattacks and seizing opportunities is crucial.
- Surprise Factor: Utilize surprise to stun competitors, as exemplified by Dell’s disruption of the PC market.
- Signal Interpretation: Pay attention to strategic signals from competitors and use them to manipulate their moves.
- Shift Market Rules: Disrupt rivals by changing the rules of the market, as Gillette did with disposable razors.
- Simultaneous or Sequential Thrusts: Employ multiple strategic moves in quick succession to mislead or confuse competitors.
- Key Characteristics:
- D’Aveni’s 7S Framework is tailored for success in hypercompetitive markets.
- The framework challenges the idea of sustained competitive advantage in favor of dynamic strategies.
- The seven guidelines provide strategic options to navigate markets where competitive advantage is continually disrupted and recreated.
| Related Frameworks | Definition | Focus | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| D’Aveni’s 7S Framework | Developed by Richard D’Aveni, it consists of seven strategic shifts (Scale, Speed, Scope, Synergy, Symbiosis, Surprise, and Simultaneity) that organizations can leverage to gain competitive advantage in dynamic and turbulent environments. | Focuses on identifying and implementing strategic shifts to navigate and thrive in rapidly changing business landscapes, helping organizations sustain competitive advantage. | Strategic Management, Competitive Strategy |
| McKinsey 7-S Framework | Developed by Tom Peters and Robert H. Waterman Jr., it identifies seven interrelated factors: Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared Values, Style, Staff, and Skills, offering a holistic approach to organizational analysis and change management. | Focuses on aligning organizational elements to achieve strategic objectives and facilitate organizational effectiveness and change. | Organizational Development, Change Management |
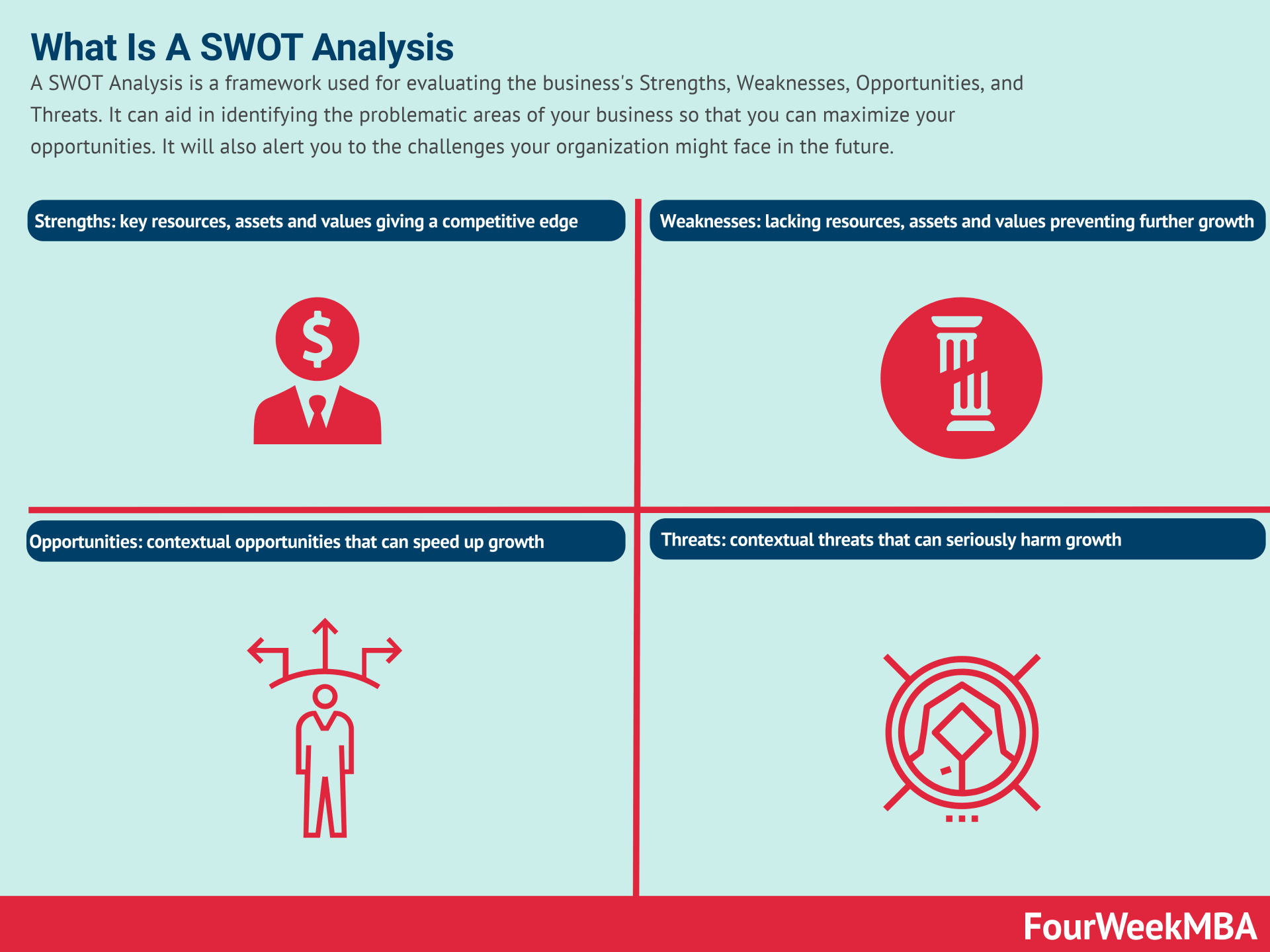
| SWOT Analysis | A strategic planning tool used to identify Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to a business venture or project. | Broad analysis covering internal and external factors impacting a business, helping in strategic decision-making and planning. | Strategic Planning, Business Analysis |
| Porter’s Five Forces | Developed by Michael Porter, it analyzes the competitive forces within an industry: Threat of New Entrants, Bargaining Power of Suppliers, Bargaining Power of Buyers, Threat of Substitutes, and Competitive Rivalry, to assess industry attractiveness and competitive intensity. | Focuses on understanding industry structure and competition to formulate strategies based on competitive forces and industry dynamics. | Competitive Strategy, Industry Analysis |
| Balanced Scorecard | A strategic planning and management system that aligns business activities to the organization’s vision and strategy, using four perspectives: Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, and Learning and Growth. | Provides a holistic view of performance by incorporating financial and non-financial metrics across different organizational dimensions. | Performance Management, Strategic Planning |
| McKinsey Growth Model | A framework for understanding and managing organizational growth, consisting of three horizons: Horizon 1 (Core Business), Horizon 2 (Adjacent Growth), and Horizon 3 (Transformational Growth), helping organizations balance short-term performance with long-term innovation. | Focuses on managing growth by allocating resources across different business horizons to sustain current operations and foster future opportunities. | Strategic Management, Growth Strategy |
| McKinsey Three Horizons Model | A strategic framework that categorizes innovation initiatives into three horizons: Horizon 1 (Core Business), Horizon 2 (Adjacent Opportunities), and Horizon 3 (Transformational Opportunities), aiming to balance short-term goals with long-term strategic vision. | Focuses on managing innovation by allocating resources across different horizons to ensure sustainable growth and competitive advantage. | Innovation Management, Strategic Planning |
| BCG Matrix | Developed by the Boston Consulting Group, it categorizes a company’s product portfolio into four quadrants: Stars, Cash Cows, Question Marks, and Dogs, helping in resource allocation and strategic decision-making regarding investment and divestment. | Focuses on managing a diversified portfolio of products by categorizing them based on market growth rate and relative market share to determine investment priorities. | Portfolio Management, Strategic Planning |
Related Strategy Tools
BCG Matrix

Benchmarking

SWOT Analysis
PESTEL Analysis

Porter’s Five Forces

Scenario Analysis

VRIO Framework

Read Next: Eisenhower Matrix, BCG Matrix, Kepner-Tregoe Matrix, Decision Matrix,RACI Matrix, SWOT Analysis, Personal SWOT Analysis, TOWS Matrix, PESTEL Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces.
Main Free Guides:









