Change Management

Operating Model

Ladder of Inference

Four-Step Innovation Process

TQM Framework

Balanced Scorecard

Sales Cycle

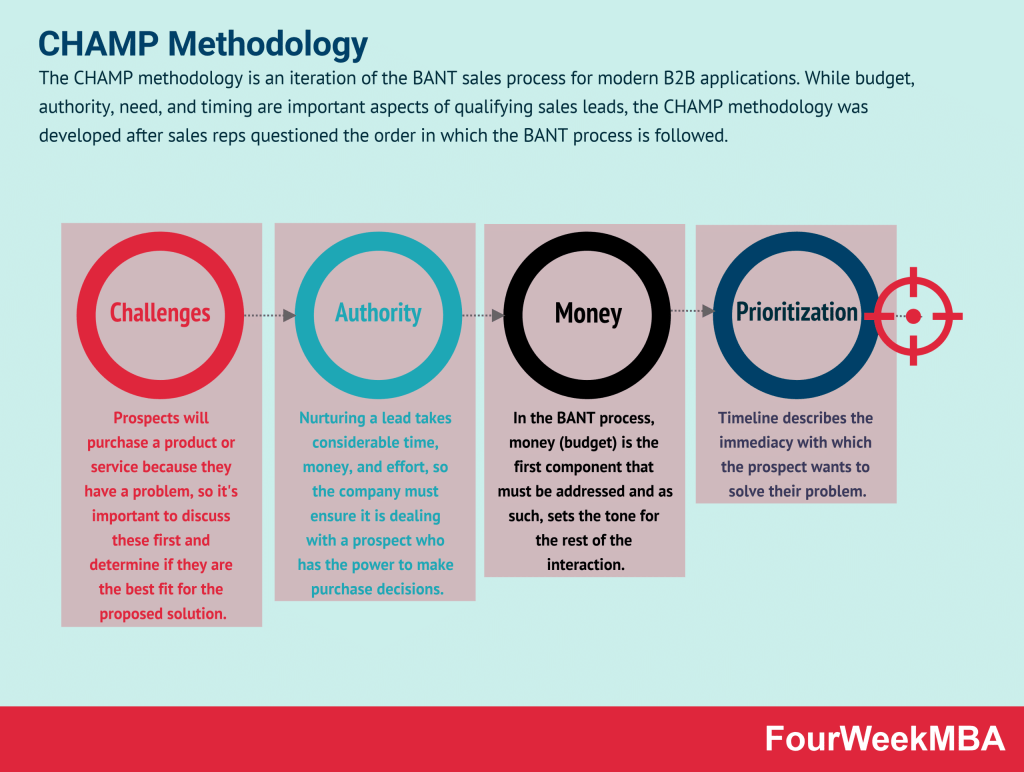
CHAMP Methodology
BANT Sales Process

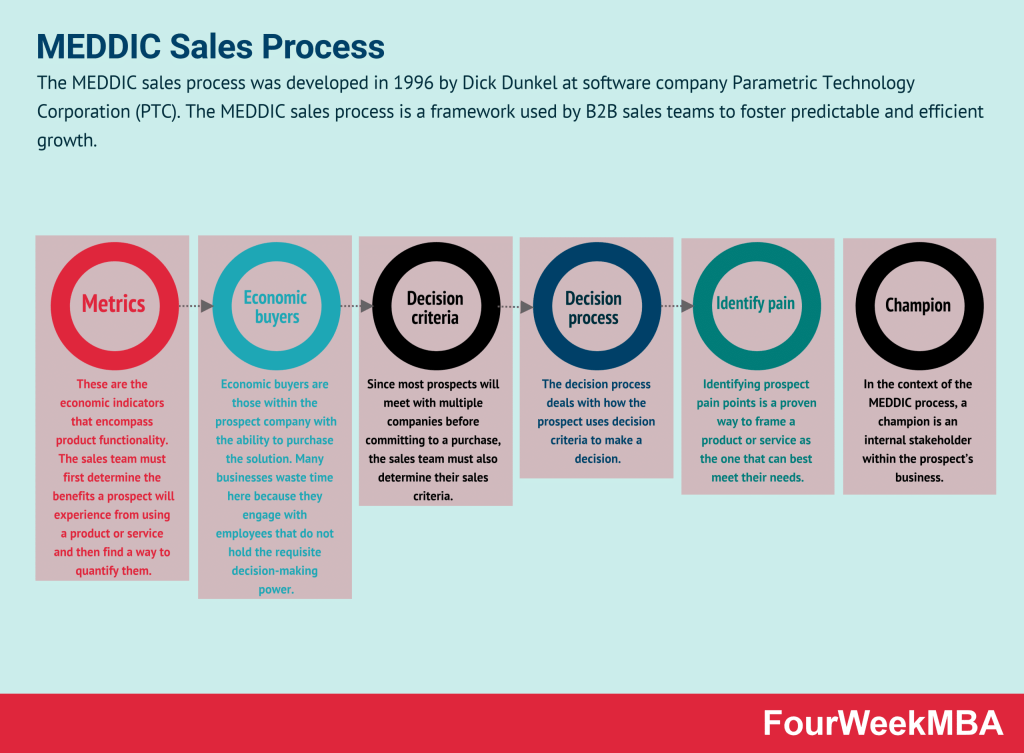
MEDDIC Sales Process
STP Marketing

Product-Process Matrix

Conceptual Modeling

Hoffman Process

Innovation Funnel

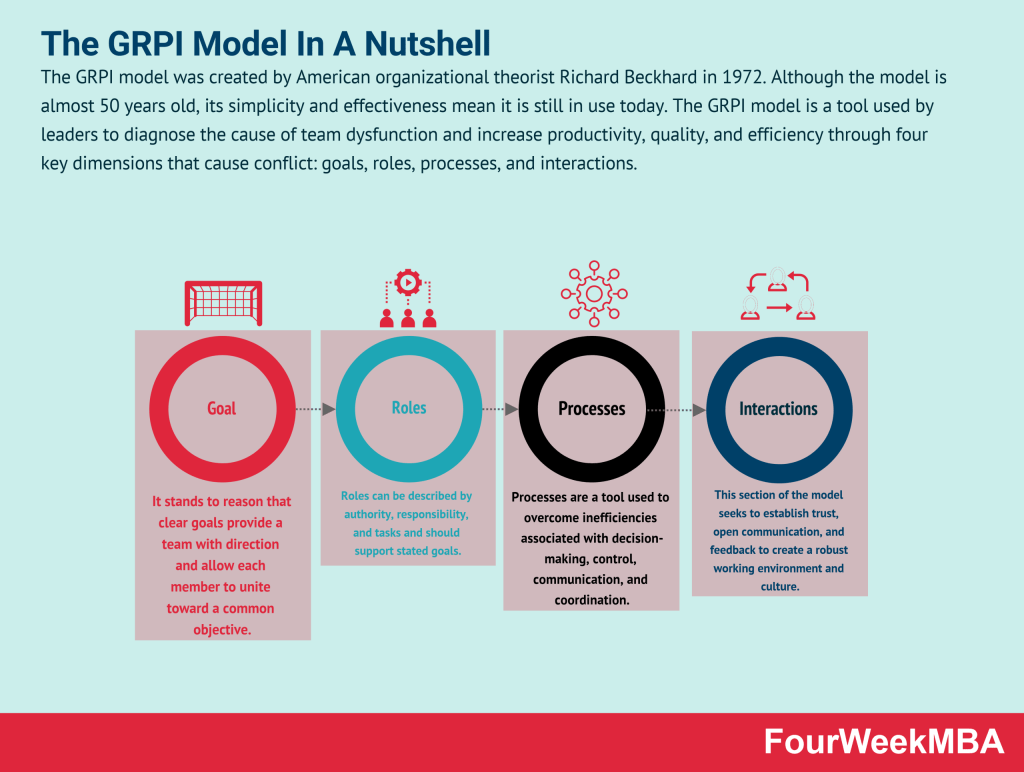
GRPI Model
ADKAR Model

SIPOC Diagram

Highlights
| Concept | Description | When to Use | Advantages | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Change Management | A systematic approach to managing organizational transformations, addressing resistance to change. | When implementing significant changes in an organization’s goals, values, technologies, or processes. | Helps navigate resistance to change. | May face challenges in employee buy-in. |
| Operating Model | A visual representation of an organization’s processes and value delivery, aligning with its business model. | When assessing and optimizing how an organization executes its business model and delivers value. | Provides clarity on organizational processes. | Requires a deep understanding of operations. |
| Ladder of Inference | A thinking process in which individuals move from facts to decisions or actions, illustrating the use of mental models. | When analyzing decision-making processes and addressing cognitive biases. | Helps identify and address cognitive biases. | May require introspection and self-awareness. |
| Four-Step Innovation Process | A tool to drive consistent innovation by encouraging sustainable problem-solving and creative solutions. | When seeking to foster innovation and solve complex problems within an organization. | Promotes creative problem-solving. | May require a cultural shift towards innovation. |
| TQM Framework | Total Quality Management emphasizes continuous improvement and employee involvement to provide value to customers. | When aiming to enhance product or service quality, customer satisfaction, and process efficiency. | Focuses on customer-centric quality. | Requires commitment to a quality-driven culture. |
| Balanced Scorecard | A management system focusing on four perspectives (financial, customer, process, organizational) to achieve strategic goals. | When aligning organizational efforts with strategic objectives and measuring performance. | Provides a holistic view of strategic goals. | Implementation may be complex and time-consuming. |
| Sales Cycle | The process that a company follows to sell its products or services, involving steps leading to a closed sale. | When managing sales processes, tracking customer interactions, and optimizing sales strategies. | Improves sales efficiency and tracking. | May vary in complexity across industries. |
| CHAMP Methodology | An iteration of the BANT sales process for B2B applications, focusing on challenges, authority, money, and prioritization. | When qualifying sales leads and improving B2B sales processes. | Emphasizes critical aspects of sales leads. | May not cover all dimensions of buyer behavior. |
| BANT Sales Process | An old but relevant process for identifying prospects most likely to make a purchase, focusing on budget, authority, need, and timing. | When identifying and qualifying potential customers based on specific criteria. | Simplifies lead qualification process. | May not consider all nuances of buyer readiness. |
| MEDDIC Sales Process | A framework used by B2B sales teams to foster predictable and efficient growth, focusing on metrics for qualification. | When pursuing growth and efficiency in B2B sales and improving lead qualification. | Enhances predictability in sales processes. | Requires alignment with organizational goals. |
| STP Marketing | A common marketing approach that simplifies market segmentation by focusing on Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning. | When developing product positioning and marketing strategies based on customer segments. | Streamlines marketing strategy development. | May require extensive market research. |
| Product-Process Matrix | An assessment tool that examines the relationship between stages of the product life cycle and process (technological) life cycle. | When aligning product development with process capabilities and understanding life cycle dynamics. | Provides insights into product-process alignment. | Complexity may vary based on industry. |
| Conceptual Modeling | The process of developing an abstract model using real-world concepts, assumptions, and relationships to understand systems. | When visualizing, understanding, or simulating complex systems or processes. | Helps conceptualize and analyze systems. | Requires a deep understanding of system dynamics. |
| Hoffman Process | A therapeutic tool to help individuals identify and address negative behaviors and moods developed during childhood. | When individuals seek to identify and overcome behavioral patterns affecting their well-being. | Focuses on self-awareness and personal growth. | Requires personal introspection and commitment. |
| Innovation Funnel | A tool or process for screening and testing innovative ideas to ensure that only the best ideas are executed. | When managing innovation pipelines, selecting promising ideas, and aligning innovation with strategy. | Improves idea selection and innovation focus. | May require clear criteria for idea evaluation. |
| GRPI Model | A model that helps diagnose team dysfunction by addressing goals, roles, processes, and interactions as key dimensions. | When addressing team conflicts, improving team productivity, and fostering effective collaboration. | Identifies key dimensions of team dysfunction. | May require team members’ openness to change. |
| ADKAR Model | A change management tool to guide individuals and organizations through transitions, focusing on Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, and Reinforcement. | When managing organizational change and ensuring employee adoption of new initiatives. | Provides a structured approach to change management. | Requires ongoing support and reinforcement. |
| SIPOC Diagram | A visual tool to illustrate high-level processes and roles in a project, ensuring common understanding and reference points. | When explaining project expectations and processes, facilitating project team alignment. | Provides clarity and alignment in project management. | May not capture detailed process steps. |
Main Free Guides:








