In a Business Model Canvas, the building block associated with Key Resources describes the resources necessary to carry out business activities. Key resources describe any resource the organization requires for its business model to work.
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Key Resources | – Key Resources is one of the nine building blocks in the Business Model Canvas, a strategic management tool used to describe, design, and analyze a business model. It refers to the essential assets and capabilities a business needs to operate successfully. |
| Importance | – Identifying and acquiring the right key resources is crucial for a business’s sustainability and competitive advantage. These resources underpin the business’s operations, value delivery, and overall ability to create value for customers. |
| Types of Resources | – Key resources can be categorized into various types, including physical assets (e.g., manufacturing facilities), intellectual property (e.g., patents), human resources (e.g., skilled workforce), and financial resources (e.g., capital). |
| Scalability | – Key resources must be scalable to accommodate business growth. Scalability ensures that the business can expand its operations, serve more customers, and adapt to changing market demands without resource constraints becoming a barrier. |
| Value Proposition | – The choice of key resources should align with the Value Proposition offered by the business. These resources are the foundation for delivering the promised value to customers, and their adequacy influences customer satisfaction. |
| Cost Structure | – Key resources significantly influence the Cost Structure of a business. Managing these resources efficiently is essential for controlling costs and maximizing profitability. Businesses should optimize their resource allocation. |
| Strategic Partnerships | – In some cases, businesses may access key resources through strategic partnerships rather than owning them outright. Collaborations with suppliers, distributors, or other organizations can provide access to critical resources. |
| Ownership vs. Access | – Businesses must consider whether owning certain resources is necessary or if access to them through rentals, leases, or partnerships is more cost-effective. The decision can impact capital allocation and long-term sustainability. |
| Intellectual Property | – Intellectual property, such as patents, copyrights, and trademarks, can be a valuable type of key resource. It provides legal protection and competitive advantage, preventing others from replicating the business’s innovations. |
| Maintenance and Upkeep | – Regular maintenance and upkeep of key resources are essential to ensure their continued functionality and longevity. Neglecting resource maintenance can lead to disruptions and increased costs. |
| Resource Dependency | – Businesses should be aware of dependencies on specific key resources. Over-reliance on a single supplier or a critical resource can pose risks if disruptions occur, highlighting the need for contingency plans. |
| Innovation | – Innovation in key resources can drive competitive advantage. Businesses should continuously explore ways to improve or acquire new resources that enhance their products, services, or operations. |
| Conclusion | – Key Resources are the backbone of a business’s operations and value creation. Strategic resource management, scalability, and alignment with the value proposition are essential for long-term success and competitiveness. |
Understanding key resources in the Business Model Canvas
These resources allow the organization to create a value proposition for consumers, release products to the market, maintain customer segment relationships, and earn revenue.
Before developing its key resources, the business must consider these other blocks first. In other words, can the available resources meet key operational needs? If there aren’t the means to provide value, then no value exists.
Key resources may be tangible or intangible and represent assets that differ from company to company. In most cases, however, key resources will be defined by materials, equipment, and people. The business may own these resources, lease them out, or acquire them by other means.
Types of key resources
Broadly speaking, key resources can be categorized into four types:
- Physical – or tangible assets such as equipment, manufacturing facilities, distribution networks, inventory, and other buildings. Chip manufacturer Intel relies on semiconductor plants as a key resource.
- Intellectual – or intangible assets such as intellectual property, patents, and partnerships. Knowledge about customers is also a key intellectual resource. While these resources take time and money to develop, they are a major driver of innovation and growth. For example, the brand equity of Microsoft and Adobe has been crafted by years of research and development in software.
- Human – employee-related resources are utilized by organizations in the service, software, finance, science, and technology industries. These resources are important to any organization where creativity and a diverse knowledge pool drives growth. Pharmaceutical giant Novartis is dependent on a team of highly qualified scientists and sales representatives to sell its products to doctors.
- Financial – this includes cash, credit, and stock options for publicly listed companies. While all organizations rely on financial resources to some degree, they are particularly important in the banking and insurance industries. For example, an insurance company with insufficient capital to pay out insurance claims is unlikely to be viable.
How to determine key resources
Businesses requiring assistance with identifying key resources must consider the following questions:
- What key resources does the value proposition require? For example, a company selling sustainable and reliable electric vehicles must have access to the necessary raw materials, patents, and intellectual property concerning battery technology.
- What key activities does the value proposition require? Some businesses choose to work backward from the key activities of their business model. This can be achieved by evaluating the actions of other companies in the same industry.
- What key resources do the marketing and distribution channels require?
- How do key resources support existing revenue streams?
Key takeaways:
- In a Business Model Canvas, the building block associated with Key Resources describes the resources necessary to carry out business activities. The business may own these resources, lease them out, or acquire them by other means.
- Key resources are broadly categorized into four types: physical, intellectual, human, and financial. Resources may be tangible or intangible.
- Key resources can be determined by the business evaluating its value proposition. Some businesses also choose to work backward and determine the activities that will support the value proposition. This can be done by analyzing the actions of companies in the same industry.
Key Highlights
- Key Resources Definition: In the Business Model Canvas, the “Key Resources” building block outlines the resources required for a business to carry out its activities and deliver value to customers. These resources are essential for creating a value proposition, producing and releasing products, maintaining customer relationships, and generating revenue.
- Resource Importance: Key resources are crucial for the business model’s viability. Without adequate resources to provide value, the entire business model could be compromised.
- Resource Types: Key resources can be categorized into four main types:
- Physical Resources: Tangible assets such as equipment, manufacturing facilities, inventory, and distribution networks. For instance, chip manufacturer Intel relies on semiconductor plants as a key physical resource.
- Intellectual Resources: Intangible assets like patents, intellectual property, and partnerships. These resources require investment but drive innovation and growth. Companies like Microsoft and Adobe have built brand equity through years of software research and development.
- Human Resources: Employee-related assets, especially in industries driven by creativity and diverse knowledge, such as technology and science. Companies like Novartis depend on highly qualified scientists and sales representatives.
- Financial Resources: Financial assets like cash, credit, and stock options. These are crucial for viability, especially in industries like banking and insurance where capital adequacy is vital.
- Determining Key Resources: Businesses can identify key resources by asking several critical questions:
- What resources does the value proposition necessitate? For example, an electric vehicle company needs access to raw materials, patents, and battery technology IP.
- What activities support the value proposition? Some companies work backward by evaluating industry peers’ actions to determine their key resources.
- What resources do marketing and distribution channels require?
- How do key resources support existing revenue streams?
- Takeaways:
- Key Resources in the Business Model Canvas are essential for executing business activities and delivering value.
- Four main types of key resources: physical, intellectual, human, and financial.
- Identification of key resources can be based on value proposition requirements or by analyzing industry peers’ activities.
| Related Frameworks, Models, or Concepts | Description | When to Apply |
|---|---|---|
| Lean Startup Methodology | The Lean Startup Methodology is an approach to developing and managing startups that focuses on rapid iteration, customer feedback, and validated learning. It involves creating a minimum viable product (MVP), testing hypotheses through experimentation, and iterating based on customer feedback. By applying lean startup principles, entrepreneurs can minimize waste, mitigate risks, and increase the chances of building successful and sustainable businesses. | Consider Lean Startup Methodology when launching a new venture or developing innovative products or services. Use it to validate assumptions, identify customer needs, and iterate on your business model based on real-world feedback. Implement Lean Startup Methodology as a framework for achieving product-market fit, accelerating growth, and maximizing the chances of startup success within your organization. |
| Value Proposition Canvas | The Value Proposition Canvas is a tool for designing and refining value propositions that resonate with customer needs and preferences. It involves mapping customer profiles (jobs, pains, gains) and corresponding value propositions (products, services, solutions) to identify areas of alignment and opportunities for differentiation. By using the Value Proposition Canvas, organizations can develop compelling value propositions that address customer needs and create competitive advantage. | Consider the Value Proposition Canvas when designing or refining your organization’s value propositions. Use it to understand customer needs, pain points, and aspirations, and align your offerings to deliver unique value and differentiation. Implement the Value Proposition Canvas as a framework for developing customer-centric products, services, and solutions that drive customer satisfaction and loyalty within your organization. |
| Business Model Innovation | Business Model Innovation involves creating, adapting, or reinventing the fundamental structure and logic of how a business creates, delivers, and captures value. It encompasses changes to key elements of the business model, such as revenue streams, cost structure, value proposition, and customer segments, to drive growth and competitiveness. By innovating their business models, organizations can seize new opportunities, respond to market disruptions, and outperform competitors. | Consider Business Model Innovation when seeking to transform or disrupt traditional business models within your industry. Use it to explore new revenue streams, business models, and value creation opportunities that capitalize on emerging trends and technologies. Implement Business Model Innovation as a framework for driving organizational change, fostering innovation, and creating sustainable competitive advantage within your organization. |
| Blue Ocean Strategy | Blue Ocean Strategy is a strategic approach that focuses on creating uncontested market space and making competition irrelevant. It involves identifying and capturing new market opportunities by offering innovative value propositions that differentiate from existing competitors. By pursuing Blue Ocean Strategy, organizations can unlock new growth opportunities, differentiate themselves from competitors, and capture untapped market demand. | Consider Blue Ocean Strategy when seeking to develop innovative value propositions and new market opportunities. Use it to identify unmet customer needs, challenge industry assumptions, and create new market spaces where competition is irrelevant. Implement Blue Ocean Strategy as a framework for driving innovation, differentiation, and growth within your organization by offering compelling value propositions that resonate with customers. |
| Design Thinking | Design Thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation and problem-solving that emphasizes empathy, creativity, and iterative prototyping. It involves understanding user needs, ideating potential solutions, prototyping and testing concepts, and iterating based on feedback. By applying design thinking principles, organizations can develop customer-centric products, services, and experiences that meet user needs and preferences effectively. | Consider Design Thinking when developing new products, services, or processes within your organization. Use it to gain deep insights into user needs, generate creative solutions, and iterate rapidly to develop prototypes that address customer pain points and aspirations. Implement Design Thinking as a framework for fostering innovation, collaboration, and customer-centricity within your organization to drive business growth and success. |
| Platform Business Model | The Platform Business Model is a business model that creates value by facilitating interactions between two or more distinct groups of users. Platforms provide a marketplace or infrastructure that enables users to connect, interact, and exchange goods, services, or information. By leveraging network effects and economies of scale, platform businesses can create value for both users and stakeholders and achieve rapid growth and scalability. | Consider the Platform Business Model when building digital platforms or ecosystems that connect multiple users or stakeholders. Use it to create network effects, drive user engagement, and unlock new value creation opportunities through platform interactions and transactions. Implement the Platform Business Model as a framework for building scalable and sustainable businesses that leverage network effects and ecosystem dynamics to create value within your organization. |
| Business Ecosystem | A Business Ecosystem is a network of interconnected organizations, stakeholders, and resources that collaborate and compete to create and capture value. Business ecosystems involve complex relationships and interdependencies between participants, such as suppliers, partners, customers, and competitors, that influence industry dynamics and market outcomes. By understanding and leveraging business ecosystems, organizations can identify strategic partners, seize new opportunities, and navigate competitive landscapes effectively. | Consider Business Ecosystems when analyzing industry dynamics and market opportunities within your organization. Use it to identify key stakeholders, ecosystem partners, and value chain relationships that influence your organization’s competitiveness and growth prospects. Implement Business Ecosystems as a framework for building strategic alliances, fostering collaboration, and creating value within interconnected business networks within your organization. |
| Frugal Innovation | Frugal Innovation is an approach to innovation that focuses on creating affordable and accessible solutions to address the needs of resource-constrained consumers and markets. It involves simplifying products, processes, or business models to reduce costs while maintaining quality and functionality. By adopting frugal innovation principles, organizations can reach new customer segments, penetrate emerging markets, and drive inclusive growth and sustainability. | Consider Frugal Innovation when developing products or services for price-sensitive or underserved markets. Use it to design simple, affordable solutions that address basic needs and preferences of target consumers while optimizing resource utilization. Implement Frugal Innovation as a framework for expanding market reach, driving affordability, and fostering sustainable growth within your organization. |
| Open Innovation | Open Innovation is a collaborative approach to innovation that involves sourcing ideas, technologies, and expertise from external partners, such as customers, suppliers, universities, and competitors. It involves leveraging external knowledge and resources to complement internal capabilities and accelerate innovation processes. By embracing open innovation principles, organizations can access diverse perspectives, stimulate creativity, and drive breakthrough innovations more effectively. | Consider Open Innovation when seeking to access external expertise, insights, and resources to drive innovation within your organization. Use it to establish partnerships, collaborations, and ecosystems that facilitate knowledge exchange, idea generation, and technology transfer. Implement Open Innovation as a framework for leveraging external networks, crowdsourcing, and collaborative platforms to accelerate innovation and enhance competitiveness within your organization. |
| Agile Business Model Canvas | The Agile Business Model Canvas is an adaptation of the traditional Business Model Canvas that incorporates agile principles and practices into the strategic planning process. It involves iterative development, continuous feedback, and flexible adaptation to changing market conditions and customer needs. By adopting the Agile Business Model Canvas, organizations can respond quickly to market dynamics, experiment with new ideas, and iterate on business models effectively. | Consider the Agile Business Model Canvas when operating in fast-paced and uncertain environments. Use it to visualize and iterate on your business model, test assumptions, and adapt strategies based on real-time feedback and market insights. Implement the Agile Business Model Canvas as a framework for fostering agility, responsiveness, and innovation within your organization to drive sustainable growth and competitiveness. |
Alternatives to the Business Model Canvas
FourWeekMBA Squared Triangle Business Model
This framework has been thought for any type of business model, be it digital or not. It’s a framework to start mind mapping the key components of your business or how it might look as it grows. Here, as usual, what matters is not the framework itself (let’s prevent to fall trap of the Maslow’s Hammer), what matters is to have a framework that enables you to hold the key components of your business in your mind, and execute fast to prevent running the business on too many untested assumptions, especially about what customers really want. Any framework that helps us test fast, it’s welcomed in our business strategy.

FourWeekMBA VTDF Framework For Tech Business Models
This framework is well suited for all these cases where technology plays a key role in enhancing the value proposition for the users and customers. In short, when the company you’re building, analyzing, or looking at is a tech or platform business model, the template below is perfect for the job.


Download The VTDF Framework Template Here
FourWeekMBA VBDE Framework For Blockchain Business Models
This framework is well suited to analyze and understand blockchain-based business models. Here, the underlying blockchain protocol, and the token economics behind it play a key role in aligning incentives and also in creating disincentives for the community of developers, individual contributors, entrepreneurs, and investors that enable the whole business model. The blockchain-based model is similar to a platform-based business model, but with an important twist, decentralization should be the key element enabling both decision-making and how incentives are distributed across the network.

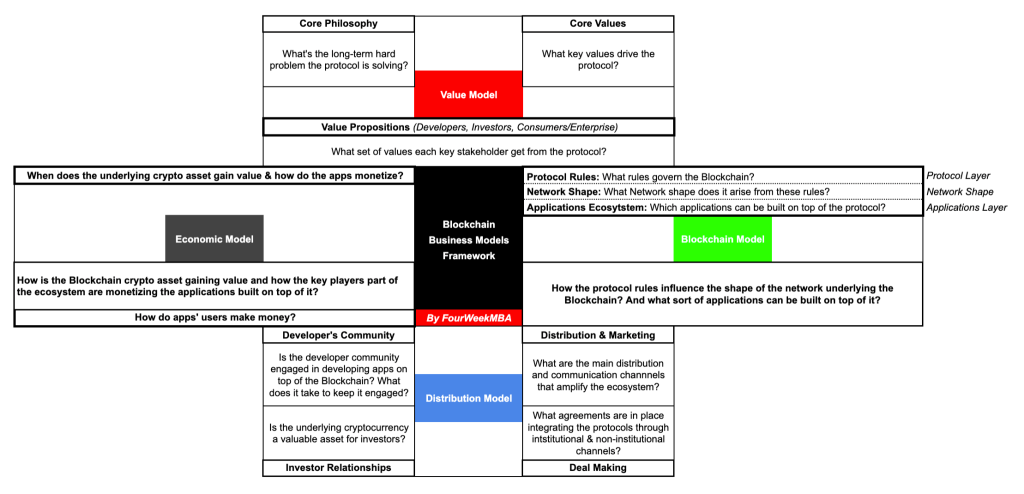
Download The VBDE Framework Template Here
Main Free Guides:
- Business Models
- Business Strategy
- Business Development
- Digital Business Models
- Distribution Channels
- Marketing Strategy
- Platform Business Models
- Revenue Models
- Tech Business Models
- Blockchain Business Models Framework
FourWeekMBA Business Toolbox











Asymmetric Betting





Read Also:






