Six Forces Models

SWOT Analysis

Balanced Scorecard

Marketing Mix

PESTEL Analysis

BCG Matrix

Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs

PESO Model

GE McKinsey Matrix

Kotler’s Five Product Levels

New Product Development Process

Customer Experience Map

AIDA Model

Social Selling

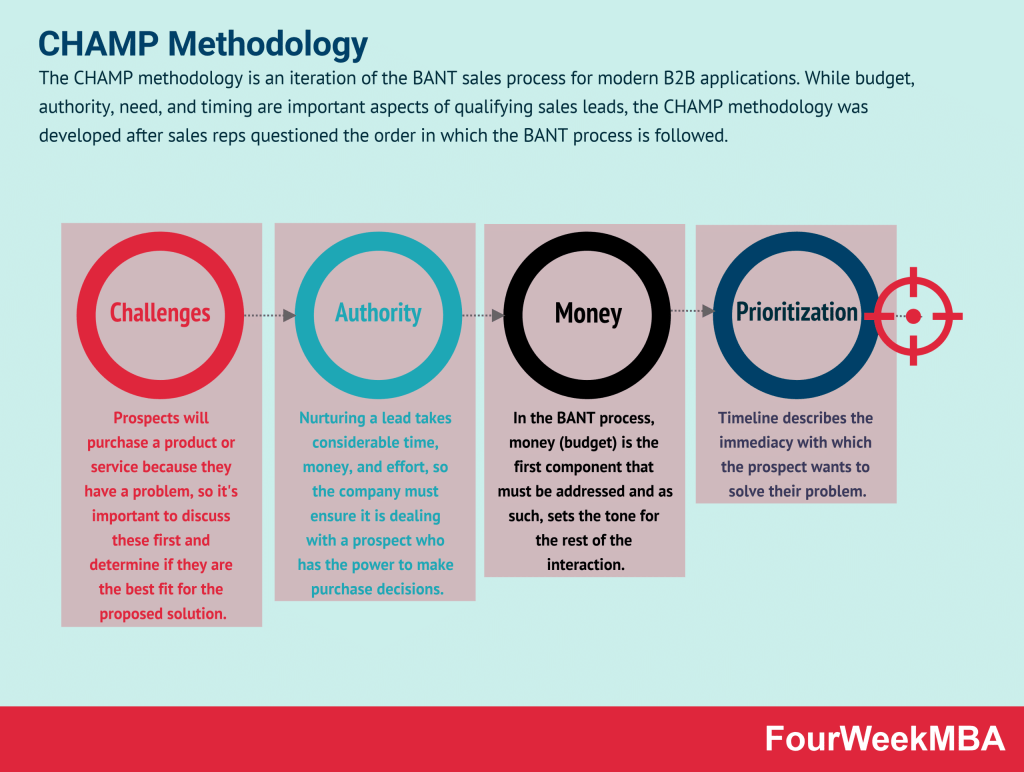
CHAMP Methodology
BANT Sales Process

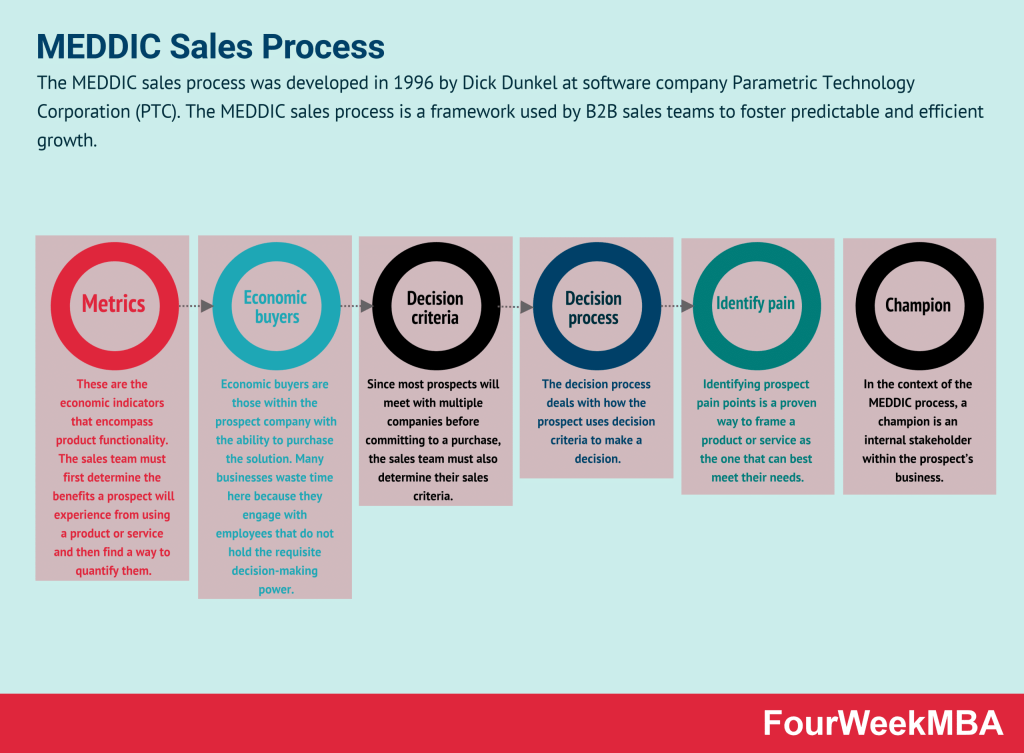
MEDDIC Sales Process
STP Marketing

Sales Funnels vs. Flywheels

Pirate Metrics

Bootstrapping

Customer Segmentation

Real-Time Marketing

Bullseye Framework

Affinity Marketing

Brand Marketing

Project Portfolio Management

Brand Storytelling

Brand Essence

Meme Marketing

Key Highlights
- Six Forces Model: The Six Forces Model is an adaptation of Porter’s Five Forces, adding the sixth force of complementary products. It is used in the tech business world to assess the impact of new market entrants and potential substitutes, especially in the context of complementary products.
- SWOT Analysis: A SWOT Analysis is a framework used to evaluate a business’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It helps identify problematic areas, maximize opportunities, and anticipate future challenges.
- Balanced Scorecard: Developed by Robert Kaplan, the balanced scorecard is a management system focusing on big-picture strategic goals. It includes four perspectives: financial, customer, business process, and organizational capacity, providing a holistic view of the business.
- Marketing Mix: The marketing mix refers to a multi-faceted approach for a complete and effective marketing plan. Traditionally, it includes the four Ps: price, product, promotion, and place, with newer additions like physical evidence, people, process, and politics.
- PESTEL Analysis: The PESTEL analysis is a framework to assess macro-economic factors affecting an organization. It helps identify potential threats and weaknesses, providing a broader understanding of the marketing environment.
- BCG Matrix: The BCG Matrix categorizes a product portfolio into cash cows, pets (dogs), question marks, and stars, based on their potential growth and market shares.
- Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: Developed by Abraham Maslow, this hierarchy explains human needs and desires. In marketing, it’s used to target specific groups based on their needs, desires, and actions.
- PESO Model: The PESO model categorizes media into paid, earned, shared, and owned media, useful for content-driven, online marketing strategies.
- GE McKinsey Matrix: This matrix guides a corporation on how to prioritize investments among business units, leading to scenarios like invest, protect, harvest, and divest.
- Kotler’s Five Product Levels: This model identifies five types of products: core product, generic product, expected product, augmented product, and potential product, based on the satisfaction of consumer needs.
- New Product Development Process: This process goes from idea generation to post-launch review, helping companies analyze aspects of launching new products.
- Customer Experience Map: Visual representations of customer interactions with a brand, including touchpoints, to enhance customer engagement.
- AIDA Model: The AIDA model describes the potential journey a customer goes through before purchasing a product: attention, interest, desire, and action.
- Social Selling: The process of developing trust and rapport with prospects through social platforms before closing sales.
- CHAMP Methodology: An iteration of the BANT sales process for modern B2B applications.
- BANT Sales Process: A process to quickly identify prospects most likely to make a purchase: budget, authority, need, and timing.
- MEDDIC Sales Process: A framework used by B2B sales teams to foster predictable and efficient growth.
- STP Marketing: A common approach in modern marketing, focusing on commercial effectiveness by selecting valuable target segments and developing a positioning strategy and marketing mix for each.
- Sales Funnels vs. Flywheels: Models representing the customer journey and structuring sales and marketing tactics.
- Pirate Metrics (AARRR): Metrics and channels to look at during the customer journey toward becoming customers and referrers.
- Bootstrapping: Financing growth from available cash flows in a viable business model.
- Customer Segmentation: Identifying different groups of people a business hopes to reach and serve.
- Real-Time Marketing: In-the-moment marketing to customers based on interactions with the brand.
- Affinity Marketing: Partnerships between businesses to sell more products, benefiting both brands.
- Brand Marketing: Building a relationship between the brand and customers, promoting the brand as a whole.
- Project Portfolio Management: A systematic approach to selecting and managing projects aligned with organizational objectives.
- Brand Storytelling: Using authentic, emotion-driven narratives to promote brand growth and customer loyalty.
- Brand Essence: Templated approach to understand the brand based on attributes, benefits, values, personality, and essence.
- Meme Marketing: Using memes to promote a brand, leveraging viral internet content.
| Marketing Concept | Description | When to Use | Advantages | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Six Forces Model | A variation of Porter’s Five Forces that adds complementary products as the sixth force, useful for assessing market context changes. | Applied in the tech industry to evaluate the impact of new market entrants and their potential roles as complementary products or long-term substitutes. | Provides a comprehensive analysis of market dynamics, including complementary products. Helps in anticipating changes and making strategic decisions. Incorporates technological considerations specific to the tech industry. | May require complex data analysis and research. Focuses primarily on the tech sector and may not be as relevant in other industries. The effectiveness depends on accurate assessments of complementary products. |
| SWOT Analysis | Framework for evaluating a business’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. | Valuable when assessing the internal and external factors influencing a business. Used for identifying areas for improvement, maximizing opportunities, and preparing for potential challenges. | Provides a structured framework for strategic analysis. Highlights internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats. Facilitates informed decision-making and planning. Can be applied to various business contexts. | Highly dependent on the quality and accuracy of the data and analysis. May oversimplify complex issues. Can be subjective, and perceptions of strengths and weaknesses may vary. Requires ongoing updates to remain relevant. |
| Balanced Scorecard | A management system focusing on strategic goals through four perspectives: financial, customer, business process, and organizational capacity. | Effective for organizations looking to align and prioritize strategic goals across different dimensions. Useful for tracking and managing overall performance and progress toward strategic objectives. | Offers a holistic view of an organization’s performance and alignment with strategic goals. Encourages a balanced approach by considering multiple perspectives. Facilitates strategic alignment and accountability throughout the organization. Can be customized to fit specific organizational needs. | Implementation may require significant organizational changes and effort. Performance measurement can be complex and time-consuming. The effectiveness depends on the clear definition and alignment of objectives and measures. |
| Marketing Mix | A comprehensive approach to marketing planning, traditionally consisting of the four Ps: price, product, promotion, and place. | Suitable for developing a complete marketing plan and strategy, addressing various aspects of product promotion. Adjusted to include additional elements like physical evidence, people, process, and politics as per modern marketing needs. | Provides a structured framework for addressing key marketing elements. Ensures a well-rounded approach to marketing planning. Adaptable to incorporate new elements and respond to evolving market dynamics. Offers flexibility in addressing various marketing challenges. | May oversimplify complex marketing strategies and interactions. Requires regular adaptation to stay current with changing market dynamics. Effectiveness depends on the accurate assessment of each marketing element’s role and importance. |
| PESTEL Analysis | A framework for assessing macro-economic factors that may impact an organization, including Political, Economic, Sociocultural, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors. | Valuable when evaluating external factors influencing an organization. Helps identify potential threats and opportunities. Can be used in conjunction with other frameworks like SWOT for a comprehensive understanding of the marketing environment. | Provides a systematic approach to understanding the external marketing environment. Highlights factors that may not be immediately apparent but can have a significant impact. Facilitates proactive planning and risk management. Supports informed decision-making and strategy development. | May require extensive data collection and analysis. Interpretation of factors can vary depending on the industry and context. The analysis may not provide specific solutions or actions but rather identifies potential influences. Requires regular updates to remain relevant. |
| BCG Matrix | A portfolio management tool categorizing products into four categories: cash cows, pets (dogs), question marks, and stars. | Useful for analyzing and managing a product portfolio based on potential growth and market share. Particularly relevant for businesses with diverse product offerings. | Helps businesses allocate resources effectively among different product categories. Offers a visual representation of product portfolio performance. Guides strategic decisions regarding product investments, divestments, or expansion. Facilitates discussions and prioritization of products. | Simplifies products into categories, potentially overlooking nuances. Assumes that high market share and growth always correlate with profitability. May not account for factors like market dynamics, competition, and external influences. The accuracy depends on the quality of data and analysis. |
| Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs | A psychological framework that identifies five levels of human needs, useful for market segmentation based on needs and desires. | Applied in marketing to understand and target specific customer segments based on their unique needs, desires, and behaviors. Helps tailor marketing messages and products to meet the specific needs of different consumer groups. | Offers a deep psychological understanding of consumer behavior and motivations. Facilitates targeted marketing and product development. Allows for segmentation based on fundamental human needs, improving product-market fit. Enables the creation of emotionally resonant marketing campaigns. | Assumes that all consumers within a segment share the same needs and motivations, potentially oversimplifying market segmentation. The hierarchy may not fully account for cultural, social, or individual variations in needs and desires. Effective application requires a nuanced understanding of consumer behavior. |
| PESO Model | Categorizes media into Paid, Earned, Shared, and Owned media, useful for optimizing marketing communications and building brand awareness. | Beneficial for content-driven, online marketing strategies. Helps organizations analyze and balance their media mix for brand awareness, customer loyalty, and market share growth. | Provides a structured approach to media categorization and analysis. Guides the allocation of resources and efforts across different media channels. Encourages a holistic view of marketing communications. Facilitates the integration of paid, earned, shared, and owned media for a comprehensive strategy. | May not cover all emerging or industry-specific media channels. Requires continuous monitoring and adaptation to changing media landscapes. Effectiveness depends on selecting the right mix of media and creating compelling content. Successful implementation may require expertise in various media types. |
| GE McKinsey Matrix | A strategy tool for prioritizing investments among business units, leading to scenarios of invest, protect, harvest, or divest. | Useful for corporations with multiple business units looking to allocate resources and prioritize investments effectively. Helps evaluate the potential of each business unit within the context of the overall corporate strategy. | Offers a structured method for prioritizing business units and making investment decisions. Facilitates discussions on resource allocation and strategic focus. Helps organizations balance their portfolio of business units and adapt to changing market dynamics. Can guide long-term strategic planning. | Requires comprehensive data and analysis to accurately assess business units. May not account for qualitative or non-financial factors affecting unit performance. The model assumes a linear relationship between market attractiveness and competitive strength, which may not always hold true. |
| Kotler’s Five Product Levels | A model that categorizes products into five levels based on the range of consumer needs they satisfy. | Valuable for marketers to understand the broader impact of their products on consumers’ lives and tailor marketing strategies accordingly. Helps position products more effectively by considering different levels of consumer value. | Offers a nuanced perspective on products beyond their physical attributes. Allows marketers to address consumers’ functional and emotional needs. Facilitates product differentiation and branding strategies. Encourages businesses to focus on providing comprehensive value to consumers. | May require a more complex marketing approach to address different levels effectively. Effective application depends on a deep understanding of consumer needs and product attributes. Not all products neatly fit into these categories, potentially leading to oversimplification. Application may vary across industries and product types. |
| New Product Development Process | A set of steps guiding the launch of new products, from idea generation to post-launch review. | Essential for organizations looking to develop and launch new products successfully. Provides a structured approach to evaluate and manage various aspects of the new product development process. Ensures that new products align with market needs and organizational objectives. | Offers a systematic approach to minimize the risks associated with new product launches. Provides clear stages for idea generation, testing, and market entry. Facilitates cross-functional collaboration and planning throughout the development process. Allows for ongoing evaluation and improvement of new products. | Requires significant time and resources to complete all stages effectively. Success depends on accurate market research and understanding customer needs. New product development can face uncertainties and challenges that may lead to delays or failures. The process may need to adapt to changing market conditions and technologies. |
| Customer Experience Map | Visual representation of customer interactions with a brand, including touchpoints from initial contact to support. | Helpful for organizations aiming to enhance the overall customer experience and improve customer relationships. Provides a visual overview of customer interactions with the brand, allowing for identification of pain points and opportunities for improvement. | Offers a comprehensive view of the customer journey and interaction points. Facilitates understanding of customer perspectives and pain points. Supports data-driven decisions to optimize customer experiences and increase satisfaction. Can be used for cross-functional collaboration and alignment. | Development and maintenance of customer experience maps require continuous data collection and updates. May not capture all possible touchpoints or customer behaviors. Effectiveness depends on the accuracy of data and alignment with customer expectations. Different customer segments may require separate experience maps. |
| AIDA Model | A model that describes the stages a customer may go through before making a purchase: Attention, Interest, Desire, Action. | Valuable for structuring marketing efforts based on the customer’s journey. Helps organizations focus on specific stages to optimize marketing activities and convert prospects into customers. | Provides a clear framework for guiding marketing strategies based on customer behavior. Helps tailor messaging and content to address different stages of the customer journey. Encourages a more systematic approach to customer acquisition and conversion. Facilitates tracking and measurement of marketing effectiveness. | Assumes a linear and simplified customer journey, which may not reflect the complexities of modern consumer behavior. Effectiveness depends on accurate segmentation and understanding of customer behavior. May not consider other factors affecting purchasing decisions, such as competitive offerings or external influences. |
| Social Selling | The process of building relationships and trust with prospects using social platforms before closing sales deals. | Ideal for sales teams looking to leverage social media platforms to engage with potential customers effectively. Particularly useful in industries where relationship-building is crucial before closing sales. | Enables salespeople to establish trust and rapport with prospects early in the sales cycle. Utilizes social platforms to reach and interact with potential customers. Enhances the effectiveness of sales efforts by building relationships and credibility. Aligns with modern buyer preferences for personalized engagement. | Requires time and effort to build and maintain a strong social presence. Effectiveness depends on the choice of appropriate social platforms and engagement strategies. May not be suitable for all industries or products with shorter sales cycles. Success hinges on the ability to provide value and foster authentic relationships. |
| CHAMP Methodology | An iteration of the BANT (Budget, Authority, Need, Timing) sales process designed for modern B2B applications. | Applicable for B2B sales teams looking to qualify and prioritize leads effectively in contemporary business environments. Helps assess the readiness of prospects and tailor sales efforts accordingly. | Offers a modern approach to lead qualification, considering factors like challenges, authority, money, and prioritization. Provides a more holistic understanding of a lead’s potential to convert into a customer. Encourages sales teams to align their efforts with the prospect’s specific needs and context. Facilitates better targeting and conversion of qualified leads. | May require training and adjustment for sales teams familiar with traditional BANT criteria. Effectiveness depends on accurate assessment and understanding of the prospect’s situation and challenges. Success hinges on the ability to engage prospects effectively and provide tailored solutions. |
| BANT Sales Process | A lead qualification process based on Budget, Authority, Need, and Timing criteria to identify prospects likely to make a purchase. | Suitable for B2B sales teams seeking to quickly identify and prioritize prospects with a higher likelihood of converting into customers. Provides a structured approach to lead qualification based on essential criteria. | Offers a straightforward method for evaluating lead readiness and potential. Helps sales teams focus their efforts on leads with the budget, authority, need, and immediate timing to make a purchase. Facilitates efficient lead qualification and allocation of resources. Can enhance the productivity and effectiveness of sales teams. | May oversimplify the complexity of B2B sales processes and relationships. Assumes that all qualified leads will progress at the same rate. Effectiveness may vary depending on industry and product/service type. Requires timely follow-up and engagement to maximize conversion rates. |
| MEDDIC Sales Process | A sales framework emphasizing Metrics, Economic buyer, Decision criteria, Decision process, Identify pain, Champion. | Relevant for B2B sales teams aiming to foster predictable and efficient growth. Helps qualify leads and opportunities thoroughly and align sales strategies with the prospect’s specific situation and needs. | Provides a comprehensive approach to lead qualification, focusing on multiple aspects of the prospect’s decision-making process. Guides sales teams to identify and address the prospect’s pain points and challenges. Enhances the understanding of the prospect’s decision criteria and economic buying factors. Facilitates effective engagement with prospects and improved conversion rates. | May require training and adoption to integrate all aspects of the MEDDIC framework effectively. Effectiveness depends on a deep understanding of the prospect’s business and decision-making processes. Success relies on identifying and engaging with the right stakeholders and champions within the prospect’s organization. |
| STP Marketing | Simplifies market segmentation and focuses on selecting valuable segments and developing tailored strategies for each. | Commonly used for commercial effectiveness, STP marketing helps marketers prioritize segments and customize marketing strategies and positioning for each segment. Ideal for organizations seeking to enhance their targeting and market positioning. | Offers a simplified approach to market segmentation and targeting. Helps allocate resources more efficiently by focusing on high-value segments. Facilitates tailored marketing messages and strategies to resonate with specific customer groups. Encourages personalization, which improves customer engagement and conversion rates. | May oversimplify market segmentation, potentially overlooking nuances in consumer behavior. Requires thorough analysis to accurately identify and prioritize valuable segments. Effectiveness depends on precise targeting and understanding of segment needs and preferences. |
Main Free Guides:









