KFC, a popular fast food chain, operates on a business model focused on providing tasty and convenient food to fast food consumers. They offer unique flavors and recipes, emphasizing quick service and efficiency. KFC generates revenue through restaurant sales, franchise fees, and royalty/advertising fees. Their key activities include food preparation, restaurant operations, and brand marketing. Key resources include secret recipes, a robust supply chain, and brand loyalty. KFC forms partnerships with franchisees, suppliers, and delivery service providers. Their cost structure includes food/ingredient costs, restaurant operations, marketing expenses, and franchise support/training.
Customer Segments
KFC serves several key customer segments:
- General Consumers:
- Families: Offering family-sized meal options that cater to group dining.
- Individuals: Providing single-serving meals and combo options for individual customers.
- Young Adults and Students:
- Millennials and Gen Z: Attracted to KFC’s convenience, taste, and affordability.
- Students: Frequently visit for quick meals and budget-friendly options.
- Health-Conscious Consumers:
- Balanced Options: Consumers looking for healthier alternatives can choose from KFC’s range of grilled chicken and salads.
- Delivery and Takeaway Customers:
- Busy Professionals: Individuals who prefer the convenience of delivery or takeaway.
- Online Shoppers: Customers using KFC’s online ordering platforms for home delivery.
Revenue Streams
KFC generates revenue through several channels:
- Franchise Operations:
- Franchise Fees: Income from initial franchise fees and ongoing royalties based on a percentage of sales from franchisees.
- Supply Chain Services: Revenue from selling ingredients and supplies to franchisees.
- Company-Owned Stores:
- Direct Sales: Revenue from sales at company-owned restaurants, offering the full menu range.
- Product Sales:
- Menu Items: Income from a diverse menu including fried chicken, burgers, wraps, sides, and beverages.
- Promotions and Limited-Time Offers: Special promotions and seasonal items that drive additional sales.
- Delivery Services:
- Online Orders: Revenue from orders placed through KFC’s website, app, and third-party delivery services.
- Partnerships: Collaborations with delivery platforms like UberEats, DoorDash, and Grubhub, where KFC earns a share of the delivery sales.
Market Strategy
KFC’s market strategy focuses on brand recognition, menu innovation, and global expansion.
- Brand Recognition:
- Menu Innovation:
- Product Development: Continuously updating the menu with new items, flavors, and limited-time offers to keep the menu fresh and appealing.
- Healthier Options: Introducing grilled chicken and salads to attract health-conscious consumers.
- Global Expansion:
- New Markets: Entering new international markets through franchise partnerships.
- Localization: Adapting the menu to local tastes and preferences in different regions.
Distribution Strategy
KFC’s distribution strategy involves a mix of franchise and company-owned stores, along with digital platforms.
- Franchise Model:
- Company-Owned Stores:
- Direct Management: Company-owned stores allow KFC to directly manage operations, ensuring adherence to brand standards and testing new products and strategies.
- Digital and Delivery Channels:
- Online Ordering: Offering online ordering through the KFC website and mobile app for both delivery and pickup.
- Third-Party Delivery Services: Partnering with third-party delivery platforms to extend reach and convenience for customers.
Competitive Advantages
KFC’s competitive advantages lie in its strong brand equity, global presence, and continuous innovation.
- Brand Equity:
- Strong Legacy: KFC’s long history and association with Colonel Sanders provide a strong brand identity that resonates with consumers globally.
- Trust and Quality: Consistency in product quality and service builds consumer trust and loyalty.
- Global Presence:
- Widespread Locations: A vast network of restaurants in over 150 countries ensures brand visibility and accessibility.
- Adaptability: Ability to adapt menus to local tastes while maintaining core offerings ensures relevance in diverse markets.
- Continuous Innovation:
- Menu Development: Regular introduction of new and innovative menu items keeps the brand fresh and appealing.
- Technology Integration: Investment in digital platforms and delivery services enhances customer convenience and engagement.
Organizational Structure:
KFC (Kentucky Fried Chicken) operates within a hierarchical organizational structure typical of large multinational fast-food chains.
- Global Leadership:
- CEO: The Chief Executive Officer is the top executive responsible for overall strategic direction and management of the company.
- Senior Leadership Team: Comprising top executives overseeing various key functions such as operations, marketing, finance, and human resources.
- Regional Management:
- Regional Heads: KFC divides its operations into regions, each headed by a Regional President or Vice President. These regions can be based on geographic locations or specific markets.
- Country Managers: Within each region, there are Country Managers or Directors responsible for overseeing KFC’s operations in individual countries or territories.
- Corporate Functions:
- Departments: KFC has various functional departments, including Operations, Marketing, Finance, Human Resources, Legal, and Supply Chain, among others.
- Support Functions: These departments provide centralized support services, such as IT, Research and Development, and Quality Assurance.
- Franchise Relations:
- Franchise Development: Teams dedicated to recruiting new franchisees and expanding KFC’s franchise network.
- Franchisee Support: Teams that offer training, operational support, and ongoing assistance to franchisees.
- Restaurant-Level Organization:
- Restaurant Management: Each KFC restaurant has its own management team, typically including a General Manager, Assistant Managers, and Shift Supervisors.
- Staff: Restaurants employ front-line staff, including cooks, cashiers, and customer service representatives.
Leadership Style:
KFC’s leadership style is characterized by several key principles:
- Customer-Centric Focus: KFC places a strong emphasis on meeting customer expectations by delivering quality food and service.
- Operational Excellence: The company strives for operational efficiency and consistency across its global network of restaurants.
- Innovation: KFC encourages innovation in menu offerings, marketing strategies, and restaurant operations to stay competitive in the fast-food industry.
- Franchisee Collaboration: KFC maintains a collaborative relationship with its franchisees, valuing their contributions to the brand’s success.
- Brand Loyalty: The leadership fosters brand loyalty by upholding KFC’s unique flavors, recipes, and traditions while adapting to changing consumer preferences.
- Community Engagement: KFC engages with local communities through initiatives such as corporate social responsibility and philanthropy.
- Global Perspective: KFC’s leadership recognizes the importance of understanding diverse market preferences and cultural nuances in different regions.
Key Highlights
- Tasty and Convenient Food: KFC’s primary focus is on providing delicious and convenient food to fast food consumers.
- Unique Flavors and Recipes: The brand is known for its unique flavors and secret recipes that set them apart in the fast food industry.
- Quick Service and Efficiency: KFC emphasizes fast service and operational efficiency to cater to the needs of its customers.
- Revenue Generation: KFC’s revenue comes from various sources, including restaurant sales, franchise fees from new outlets, and royalty/advertising fees from existing franchises.
- Key Activities: The core activities of KFC involve food preparation, efficient restaurant operations, and strategic brand marketing.
- Secret Recipes: KFC’s closely guarded secret recipes contribute to its distinct taste and are a crucial asset for the brand.
- Supply Chain: A well-established and robust supply chain helps ensure consistent sourcing of ingredients and supplies for its outlets.
- Brand Loyalty: KFC has built a loyal customer base through its consistent quality and unique offerings.
- Partnerships: The company collaborates with franchisees, suppliers, and delivery service providers to maintain its operational network.
- Cost Structure: KFC’s cost structure includes expenses related to ingredient procurement, restaurant operations, marketing efforts, and support/training for franchisees.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Value Proposition | KFC offers the following value propositions for its customers: – Fried Chicken: Iconic and delicious fried chicken. – Variety of Flavors: Offering a range of flavors and spices. – Quick Service: Fast and convenient dining experience. – Affordability: Providing budget-friendly meal options. – Global Brand: Recognized and trusted worldwide. – Consistency: Maintaining the same taste and quality. – Innovation: Introducing new menu items and promotions. – Community Engagement: Involvement in local communities and charity. |
| Core Products/Services | Core products and services provided by KFC include: – Fried Chicken: Selling various chicken pieces and combos. – Sides and Fixings: Offering a range of sides like mashed potatoes and coleslaw. – Beverages: Providing soft drinks and other beverages. – Desserts: Offering desserts like cakes and pies. – Family Meals: Combo meals for families and groups. – Value Menus: Budget-friendly menu options. – Online Ordering: Online and mobile app ordering. – Delivery and Takeout: Delivery and takeout services. |
| Customer Segments | KFC targets various customer segments: – Individuals: Individuals seeking quick and tasty meals. – Families: Families looking for convenient dining options. – Students: Students on a budget. – Working Professionals: Busy professionals seeking quick lunches. – Food Enthusiasts: Customers who enjoy fried chicken. – Party Planners: Those ordering for events and gatherings. – Online Customers: Users of online ordering and delivery. – Community Supporters: Individuals who value community engagement. |
| Revenue Streams | KFC generates revenue through several revenue streams: – Menu Sales: Earnings from sales of menu items. – Combo Sales: Revenue from combo meal sales. – Beverage Sales: Income from beverage sales. – Dessert Sales: Earnings from dessert sales. – Delivery and Takeout Fees: Fees from delivery and takeout services. – Franchise Fees: Income from franchise operations. – Online Ordering Fees: Charges for online orders and delivery. – Marketing Partnerships: Income from marketing collaborations. |
| Distribution Strategy | The distribution strategy for KFC includes various channels: – Physical Locations: Operating a network of physical restaurant locations. – Drive-Thru Services: Offering drive-thru services for quick orders. – Delivery Services: Providing delivery options through own or third-party services. – Online and Mobile Apps: Offering online and mobile app ordering. – Marketing Campaigns: Promoting products through marketing channels. – Franchise Model: Partnering with franchisees for expansion. – Community Engagement: Involvement in local communities and charity efforts. – Global Presence: International restaurant presence. |
Related Visual Stories



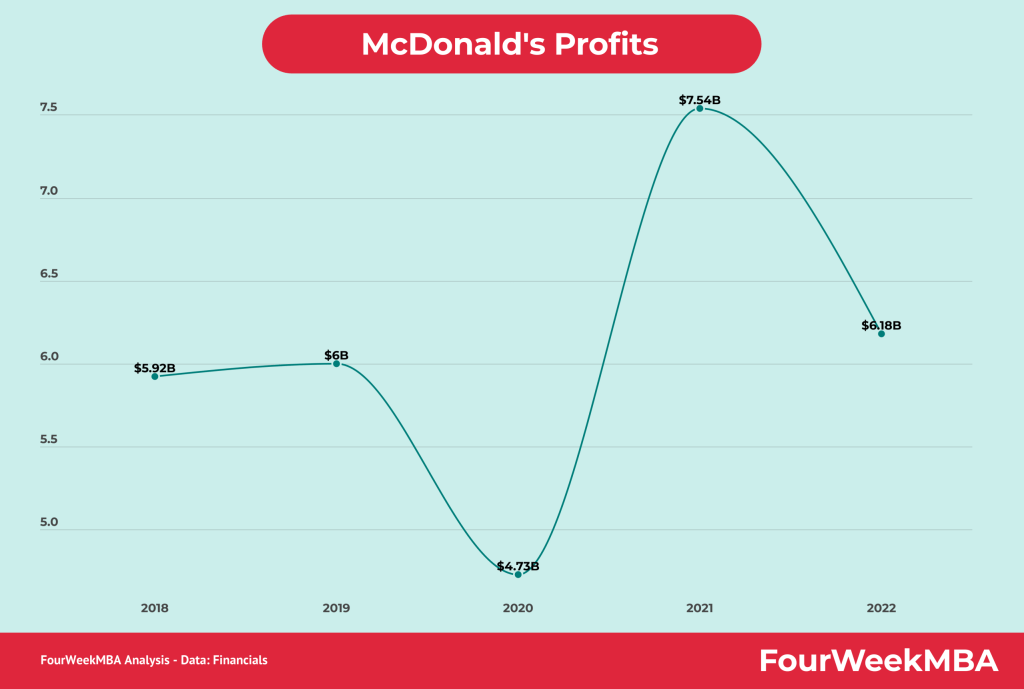
McDonald’s EV/Revenue Multiple





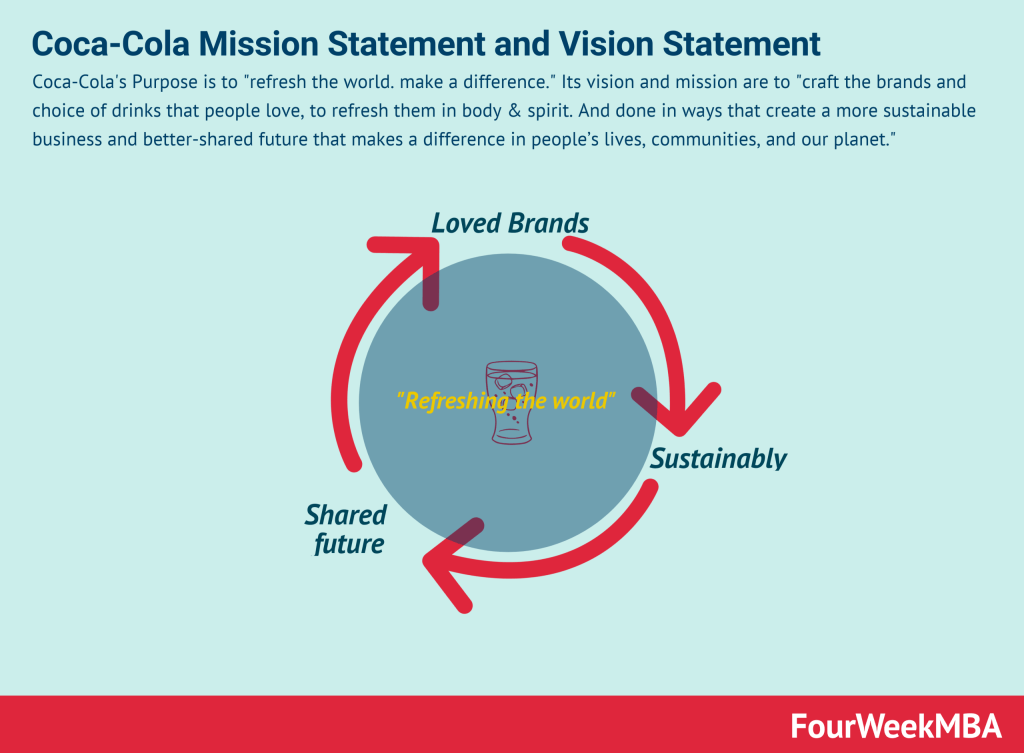
McDonald’s Organizational Structure





Read Also: McDonald’s Business Model, Coca-Cola Business Model, Coca-Cola Distribution Strategy.
Read More:







