Business Development

Marketing vs. Sales

Business Model Framework

Tech Business Model Template

Digital Transformation

Business Storytelling

3C Analysis Business Model

GE McKinsey Matrix

McKinsey 7-S Model

AIDA Model

Pirate Metrics

Freemium Business Model

Freeterprise

Go-To-Market Strategy

Customer Segmentation

Psychographic Segmentation

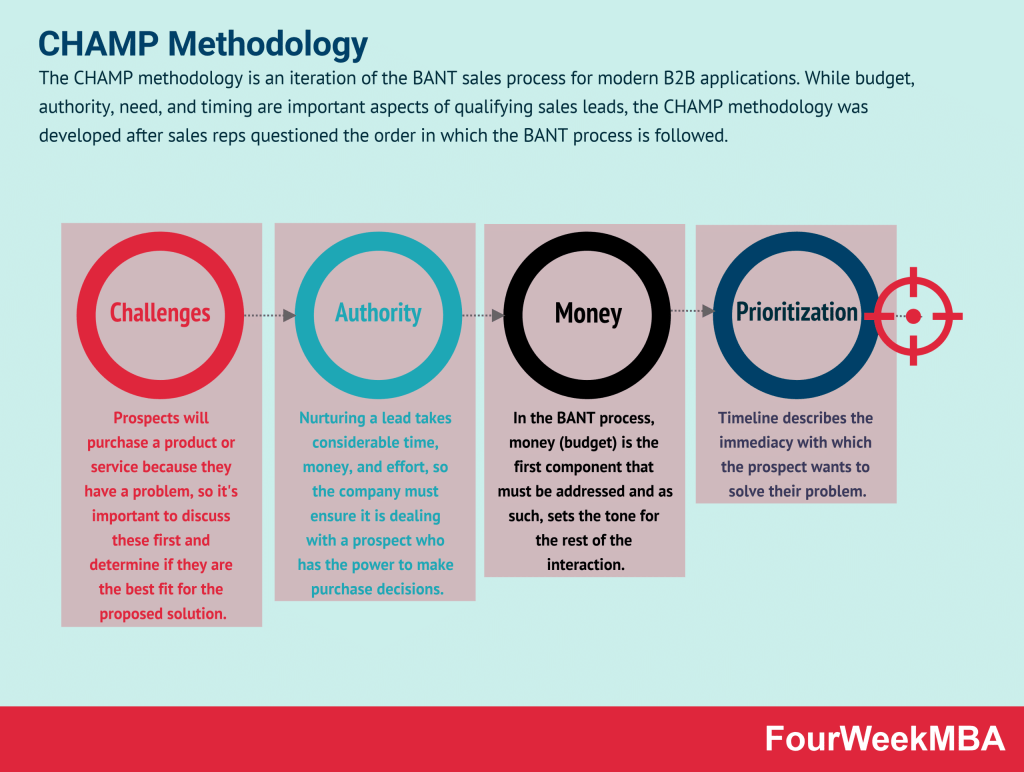
CHAMP Methodology
BANT Sales Process

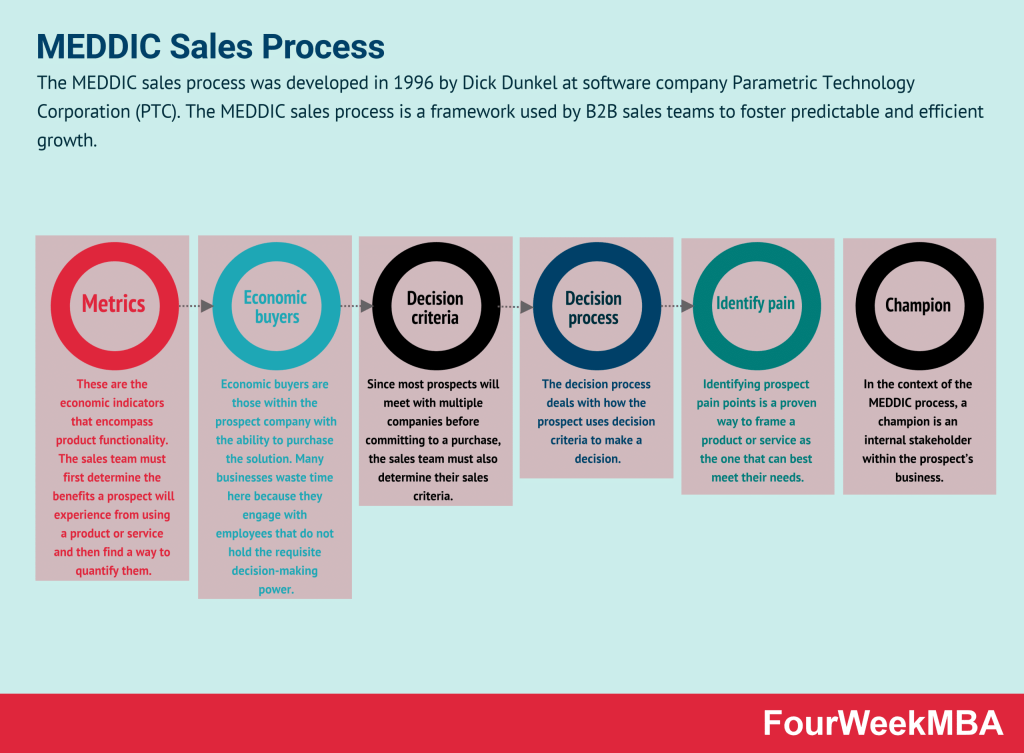
MEDDIC Sales Process
Highlights
| Concept | Description | When to Use | Advantages | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Business Development | Strategies and actions to grow a business through sales, marketing, and distribution. | When seeking growth and expansion, developing distribution channels, and entering new markets. | Facilitates business growth. | May require resource allocation and planning. |
| Marketing vs. Sales | Different approaches: marketing for wider audience reach, sales for complex B2B or high-cost products. | When deciding the appropriate approach for selling products or services based on target audience. | Matches approach to product/service type. | Oversimplifies complexities of some markets. |
| Business Model Framework | Focuses on two dimensions: people (product, brand) and financial (revenue, sustainability) aspects of a business model. | When designing or assessing a business model to ensure it aligns with customer needs and is sustainable. | Balances product and financial considerations. | Requires understanding of both dimensions. |
| Tech Business Model Template | Comprises four components: value model, technological model, distribution model, and financial model for tech businesses. | When developing a business model for a tech-oriented company and aligning technological and financial aspects. | Addresses key dimensions for tech businesses. | Requires in-depth tech and financial knowledge. |
| Digital Transformation | Leveraging digital technologies for business model innovation, focusing on better serving key customers and adapting to the digital era. | When transforming an existing business to be more digitally oriented and customer-focused. | Enhances adaptability and customer service. | May involve significant organizational change. |
| Business Storytelling | Framing the story of an organization to influence its brand identity and enable people to identify with the company. | When developing a brand narrative and communicating the values and mission of the organization. | Creates a strong brand identity. | Requires effective storytelling skills. |
| 3C Analysis Business Model | A marketing tool focusing on customers, competitors, and the company to develop effective marketing strategies. | When crafting marketing strategies to gain a competitive advantage by considering these three variables. | Informs marketing strategy effectively. | May not address external market dynamics. |
| GE McKinsey Matrix | A portfolio management tool to prioritize investments among business units, categorizing them as invest, protect, harvest, or divest. | When making investment decisions for different business units and assessing their contributions. | Guides resource allocation effectively. | Complexity in implementation and decision-making. |
| McKinsey 7-S Model | Considers seven internal elements (hard and soft) to assess an organization’s alignment with its goals and overall position. | When evaluating organizational effectiveness and alignment with strategic objectives. | Offers a comprehensive organizational view. | May require substantial data collection. |
| AIDA Model | Attention, Interest, Desire, Action model describes the customer journey stages to optimize marketing activities. | When optimizing marketing strategies and campaigns by aligning them with customers’ journey stages. | Focuses on key customer journey stages. | Simplifies complex customer behaviors. |
| Pirate Metrics | AARRR model simplifies metrics and channels at each stage of the user’s path to becoming a customer and brand referrer. | When tracking user conversion and engagement at different stages of the customer journey. | Provides a clear focus on user conversion. | May not cover all nuances of user behavior. |
| Freemium Business Model | Offers a free service to most users while converting a small percentage into paying customers, primarily a growth strategy. | When aiming to acquire users through a free product and convert them into paying customers. | Attracts a large user base for conversion. | Monetization depends on conversion success. |
| Freeterprise | Combines free and enterprise approaches, converting free users into enterprise customers through sales efforts. | When transitioning free users to enterprise-level services and aligning sales with conversion efforts. | Targets both free and enterprise customers. | Complexity in managing the transition process. |
| Go-To-Market Strategy | Defines how new products/services are developed, marketed, and delivered to target customers to gain a competitive advantage. | When launching new products or services and creating a strategic plan for reaching target customers. | Enables effective product introduction. | Requires thorough market analysis and planning. |
| Customer Segmentation | Divides customers into sub-groups with shared characteristics, enabling tailored marketing and product development strategies. | When personalizing marketing, product development, and communication strategies based on customer groups. | Enhances targeting and customization. | Requires accurate customer data and analysis. |
| Psychographic Segmentation | Focuses on psychological characteristics, such as activities and opinions, to create customer sub-groups for personalized marketing. | When seeking to personalize marketing campaigns and target customers based on psychological traits. | Tailors marketing to specific psychological traits. | Data collection and analysis can be complex. |
| CHAMP Methodology | An iteration of the BANT sales process for modern B2B applications, addressing challenges, authority, money, and prioritization. | When qualifying B2B sales leads and adapting the sales process to modern B2B sales dynamics. | Addresses key aspects of B2B sales leads. | May not cover all nuances of buyer behavior. |
| BANT Sales Process | A sales process focusing on Budget, Authority, Need, and Timing to identify prospects likely to make a purchase. | When identifying and qualifying potential customers based on specific criteria. | Simplifies lead qualification process. | May not consider all buyer readiness factors. |
| MEDDIC Sales Process | A B2B sales framework emphasizing metrics for predictable and efficient growth, used to improve lead qualification. | When aiming for predictable B2B sales growth and improving lead qualification processes. | Enhances sales predictability and efficiency. | Requires alignment with organizational goals. |
Main Free Guides:









