As explained on McDonald’s website, “Dick and Mac McDonald moved to California to seek opportunities they felt unavailable in New England.” In 1948 they launched Speedee Service System featuring 15-cent hamburgers as the restaurants gained traction, leading the brothers to begin franchising their concept until they reached nine operating restaurants. The Speedee System was the foundation of the success of the first McDonald’s in San Bernardino, California.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The McDonald’s Speedee System, developed by Richard and Maurice McDonald in the 1940s, revolutionized the fast-food industry by introducing a streamlined, efficient, and consistent approach to food preparation and service. It served as the foundation for the McDonald’s brand’s success, emphasizing quick service, quality, and affordability. The primary purpose of the Speedee System was to deliver fast, reliable, and standardized food to customers, setting the stage for the global fast-food phenomenon. |
| Origin and Development | The Speedee System originated in San Bernardino, California, where the McDonald brothers operated a drive-in restaurant. Frustrated with the slow and inconsistent service typical of drive-ins at the time, they developed a systematic approach to food preparation. This system, initially called the “Speedee Service System,” aimed to provide consistently high-quality food quickly and efficiently. |
| The key innovations of the Speedee System included a simplified menu, a kitchen assembly line, and a focus on delivering food within minutes of ordering. The McDonald brothers meticulously refined and standardized their operations to ensure that every customer received a fast, tasty, and affordable meal. | |
| Mechanisms and Innovations | The Speedee System introduced several groundbreaking mechanisms and innovations: |
| – Simplified Menu: To streamline operations, the menu was simplified to include only a few items, primarily hamburgers, cheeseburgers, fries, shakes, and beverages. This reduced complexity in food preparation and order fulfillment. | |
| – Kitchen Assembly Line: The heart of the Speedee System was the kitchen assembly line. It featured a highly organized layout where each staff member had a specific role in preparing and assembling food. For example, one person would focus on grilling burgers, another on toasting buns, and another on assembling orders. | |
| – Standardized Procedures: The system emphasized consistency and quality control. Specific procedures and cooking times were established to ensure that every burger, fry, and shake met the same standards. | |
| – Speed and Efficiency: Speed and efficiency were central to the system. Orders were processed and served rapidly, with a commitment to delivering food within minutes of receiving an order. | |
| Impact on the Industry | The Speedee System had a profound impact on the fast-food industry: |
| – Birth of the Fast-Food Chain: The success of the McDonald’s Speedee System led to the creation of the first McDonald’s franchise in 1955, setting the stage for the rapid expansion of the brand and the proliferation of fast-food chains worldwide. | |
| – Standardization and Consistency: The Speedee System introduced a new level of standardization and consistency to food service. Customers could expect the same quality and taste at any McDonald’s location. | |
| – Influence on Competitors: The success of McDonald’s inspired competitors to adopt similar systems and principles, shaping the entire fast-food industry. | |
| Continual Evolution | Over the years, the McDonald’s system has continually evolved and expanded. It has incorporated technology, expanded the menu, and adapted to changing consumer preferences while still adhering to the core principles of speed, efficiency, and quality. |
| Global Reach and Brand | McDonald’s, with its Speedee System as the foundation, has become one of the most recognizable and influential global brands. It operates in over 100 countries, serving billions of customers annually. |
| Customer Experience | The Speedee System’s focus on speed and consistency has been a hallmark of the McDonald’s customer experience. It has made McDonald’s a convenient choice for millions of people seeking quick and affordable meals. |
| Challenges and Controversies | While the Speedee System brought many benefits, it also faced criticism for its role in promoting fast-food culture, potential health concerns related to fast food, and labor issues. These challenges have led to ongoing debates about the fast-food industry’s impact on society. |
| Adaptation to Modern Trends | McDonald’s has adapted to modern trends by introducing healthier menu options, incorporating sustainability initiatives, and leveraging technology to enhance customer convenience through initiatives like mobile ordering and delivery. |
| Conclusion | The McDonald’s Speedee System is a landmark in the history of the fast-food industry, representing a transformative shift in food service. Its innovative approach to standardization, efficiency, and customer experience paved the way for the global success of the McDonald’s brand and influenced the broader fast-food landscape. While it faced criticism and challenges, the Speedee System’s impact on the way people dine, its iconic golden arches, and its enduring presence make it a significant part of modern food culture. McDonald’s continues to evolve, striving to balance its commitment to speed and convenience with contemporary societal and environmental concerns. The Speedee System remains an essential chapter in the story of fast food and restaurant innovation. |
Quick History
A native Chicagoan, Ray Kroc, in 1939, was the exclusive distributor of a milkshake mixing machine called Multimixer. In short, he was a salesman.
He visited the McDonald brothers in 1954 and was impressed with their business model, which led to him becoming their franchise agent.
He opened the first restaurant for McDonald’s System, Inc., until in 1961, he acquired McDonald’s rights to the brother’s company for $2.7 million.
The McDonald brothers’ speedee system enabled the first store to operate quickly and efficiently while serving a great burger.
In fact, while the initial take from the McDonald brothers was that you could make great burgers quickly and inexpensively, those could still be done with great ingredients and maintain high quality.
McDonald’s would be able to serve them at low prices thanks to its low operational costs; since there were no servers, it was mostly a self-service experience, and the menu was minimal.
While the concept of Fast Food developed in the early 1900s, it took off later on as the McDonald brothers opened their first restaurant.
However, as Ray Kroc took over McDonald’s, the concept changed in meaning. Indeed, as the restaurants scaled their operations, the focus was more and more on speed, thus bringing the quality of food down and associating fast food with a lesser food experience.
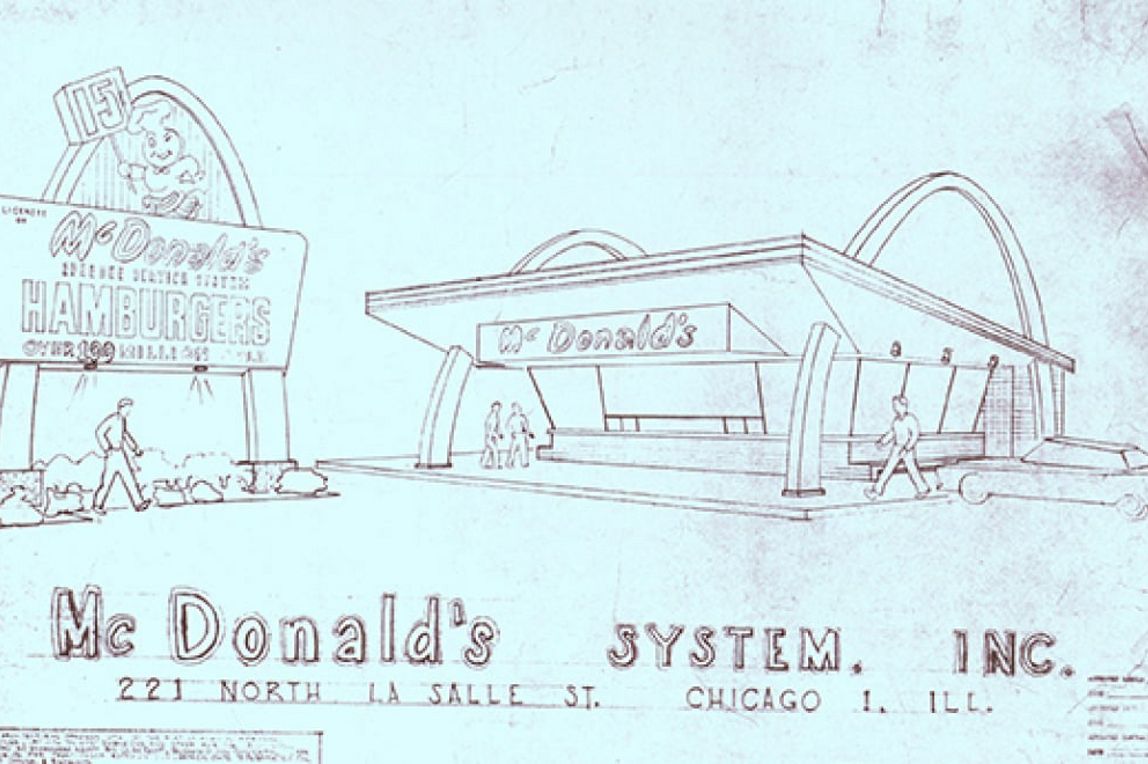
Early blueprints for signature McDonald’s Red and White restaurant with Speedee road sign (source McDonald’s).
Related Visual Stories



McDonald’s EV/Revenue Multiple





McDonald’s Operates vs. Franchised Restaurants Margins


McDonald’s Organizational Structure





Read Also: McDonald’s Business Model, Coca-Cola Business Model, Coca-Cola Distribution Strategy.









